
atlas-mcp-server
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for ATLAS, a Neo4j-powered task management system for LLM Agents - implementing a three-tier architecture (Projects, Tasks, Knowledge) to manage complex workflows.
Stars: 112
ATLAS (Adaptive Task & Logic Automation System) is a high-performance Model Context Protocol server designed for LLMs to manage complex task hierarchies. Built with TypeScript, it features ACID-compliant storage, efficient task tracking, and intelligent template management. ATLAS provides LLM Agents task management through a clean, flexible tool interface. The server implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for standardized communication between LLMs and external systems, offering hierarchical task organization, task state management, smart templates, enterprise features, and performance optimization.
README:
ATLAS (Adaptive Task & Logic Automation System) is a task management system for LLM Agents.
Built on a three-tier architecture:
+------------------------------------------+
| PROJECT |
|------------------------------------------|
| id: string |
| name: string |
| description: string |
| status: string |
| urls?: Array<{title: string, url: string}>|
| completionRequirements: string |
| outputFormat: string |
| taskType: string |
| createdAt: string |
| updatedAt: string |
+----------------+-------------------------+
| |
| |
v v
+----------------------------------+ +----------------------------------+
| TASK | | KNOWLEDGE |
|----------------------------------| |----------------------------------|
| id: string | | id: string |
| projectId: string | | projectId: string |
| title: string | | text: string |
| description: string | | tags?: string[] |
| priority: string | | domain: string |
| status: string | | citations?: string[] |
| assignedTo?: string | | createdAt: string |
| urls?: Array<{title: string, | | |
| url: string}> | | updatedAt: string |
| tags?: string[] | | |
| completionRequirements: string | | |
| outputFormat: string | | |
| taskType: string | | |
| createdAt: string | | |
| updatedAt: string | | |
+----------------------------------+ +----------------------------------+
Implemented as a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, ATLAS allows LLM agents to interact with project management database, enabling managing projects, tasks, and knowledge items.
Important Version Note: Version 1.5.4 is the last version that uses SQLite as the database. Version 2.0 and onwards has been completely rewritten to use Neo4j, which requires either:
- Self-hosting using Docker (docker-compose included in repository)
- Using Neo4j AuraDB cloud service: https://neo4j.com/product/auradb/
Version 2.5.0 introduces a new 3-node system (Projects, Tasks, Knowledge) that replaces the previous structure.
- Overview
- Features
- Installation
- Configuration
- Project Structure
- Tools
- Resources
- Database Backup and Restore
- Examples
- Contributing
- License
ATLAS implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling standardized communication between LLMs and external systems through:
- Clients: Claude Desktop, IDEs, and other MCP-compatible clients
- Servers: Tools and resources for project, task, and knowledge management
- LLM Agents: AI models that leverage the server's management capabilities
The Atlas Platform integrates these components into a cohesive system:
- Project-Task Relationship: Projects contain tasks that represent actionable steps needed to achieve project goals. Tasks inherit context from their parent project while providing granular tracking of individual work items.
- Knowledge Integration: Both projects and tasks can be enriched with knowledge items, providing team members with necessary information and context.
- Dependency Management: Both projects and tasks support dependency relationships, allowing for complex workflows with prerequisites and sequential execution requirements.
- Unified Search: The platform provides cross-entity search capabilities, allowing users to find relevant projects, tasks, or knowledge based on various criteria.
- Comprehensive Tracking: Manage project metadata, statuses, and rich content (notes, links, etc.) with built-in support for bulk operations.
- Dependency & Relationship Handling: Automatically validate and track inter-project dependencies.
- Task Lifecycle Management: Create, track, and update tasks through their entire lifecycle.
- Prioritization & Categorization: Assign priority levels and categorize tasks with tags for better organization.
- Dependency Tracking: Establish task dependencies to create structured workflows.
- Structured Knowledge Repository: Maintain a searchable repository of project-related information.
- Domain Categorization: Organize knowledge by domain and tags for easy retrieval.
- Citation Support: Track sources and references for knowledge items.
- Native Relationship Management: Leverage Neo4j's ACID-compliant transactions and optimized queries for robust data integrity.
- Advanced Search & Scalability: Perform property-based searches with fuzzy matching and wildcards while maintaining high performance.
- Cross-Entity Search: Find relevant projects, tasks, or knowledge based on content, metadata, or relationships.
- Flexible Query Options: Support for case-insensitive, fuzzy, and advanced filtering options.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/cyanheads/atlas-mcp-server.git
cd atlas-mcp-server- Install dependencies:
npm install- Configure Neo4j:
# Start Neo4j using Docker
docker-compose up -d- Build the project:
npm run buildCreate a .env file based on .env.example:
# Neo4j Configuration
NEO4J_URI=bolt://localhost:7687
NEO4J_USER=neo4j
NEO4J_PASSWORD=password2
# Application Configuration
LOG_LEVEL=info # debug, info, warn, error
NODE_ENV=development # development, productionAdd to your MCP client settings:
{
"mcpServers": {
"atlas": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/path/to/atlas-mcp-server/dist/index.js"],
"env": {
"NEO4J_URI": "bolt://localhost:7687",
"NEO4J_USER": "neo4j",
"NEO4J_PASSWORD": "password2",
"LOG_LEVEL": "info",
"NODE_ENV": "production"
}
}
}
}The codebase follows a modular structure:
src/
├── config/ # Configuration management (index.ts)
├── index.ts # Main server entry point
├── mcp/ # MCP server implementation (server.ts)
│ ├── resources/ # MCP resource handlers (index.ts, types.ts, knowledge/, projects/, tasks/)
│ └── tools/ # MCP tool handlers (individual tool directories)
├── services/ # Core application services
│ └── neo4j/ # Neo4j database services (index.ts, driver.ts, backupRestoreService.ts, etc.)
├── types/ # Shared TypeScript type definitions (errors.ts, mcp.ts, tool.ts)
└── utils/ # Utility functions (logger.ts, errorHandler.ts, etc.)
Note: ID generation logic is implemented within the specific service files (e.g., projectService.ts, taskService.ts, knowledgeService.ts) rather than in a separate utility file.
ATLAS provides a comprehensive suite of tools for project, task, and knowledge management, callable via the Model Context Protocol.
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_project_create |
Creates new projects (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), project details (name, description, status, urls, completionRequirements, dependencies, outputFormat, taskType), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
atlas_project_list |
Lists projects (all/details). |
mode ('all'/'details'), id (for details), filters (status, taskType), pagination (page, limit), includes (includeKnowledge, includeTasks), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
atlas_project_update |
Updates existing projects (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), id, updates object, responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). Bulk mode uses projects array. |
atlas_project_delete |
Deletes projects (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), id (single) or projectIds array (bulk), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_task_create |
Creates new tasks (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), projectId, task details (title, description, priority, status, assignedTo, tags, completionRequirements, dependencies, outputFormat, taskType), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
atlas_task_update |
Updates existing tasks (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), id, updates object, responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). Bulk mode uses tasks array. |
atlas_task_delete |
Deletes tasks (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), id (single) or taskIds array (bulk), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
atlas_task_list |
Lists tasks for a specific project. |
projectId (required), filters (status, assignedTo, priority, tags, taskType), sorting (sortBy, sortDirection), pagination (page, limit), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_knowledge_add |
Adds new knowledge items (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), projectId, knowledge details (text, tags, domain, citations), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). Bulk mode uses knowledge array. |
atlas_knowledge_delete |
Deletes knowledge items (single/bulk). |
mode ('single'/'bulk'), id (single) or knowledgeIds array (bulk), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
atlas_knowledge_list |
Lists knowledge items for a specific project. |
projectId (required), filters (tags, domain, search), pagination (page, limit), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_unified_search |
Performs unified search across entities. |
value (search term), property (optional), filters (entityTypes, taskType), options (caseInsensitive, fuzzy), pagination (page, limit), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_deep_research |
Initiates a structured deep research process by creating a hierarchical plan within the Atlas knowledge base. |
projectId (required), researchTopic (required), researchGoal (required), scopeDefinition (optional), subTopics (required array with questions and search queries), researchDomain (optional), initialTags (optional), planNodeId (optional), responseFormat (optional). |
| Tool Name | Description | Key Arguments |
|---|---|---|
atlas_database_clean |
Destructive: Completely resets the database, removing all projects, tasks, and knowledge. |
acknowledgement (must be set to true to confirm), responseFormat ('formatted'/'json', optional). |
ATLAS exposes project, task, and knowledge data through standard MCP resource endpoints.
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
atlas://projects |
List of all projects in the Atlas platform with pagination support. |
atlas://tasks |
List of all tasks in the Atlas platform with pagination and filtering support. |
atlas://knowledge |
List of all knowledge items in the Atlas platform with pagination and filtering support. |
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
atlas://projects/{projectId} |
Retrieves a single project by its unique identifier (projectId). |
atlas://tasks/{taskId} |
Retrieves a single task by its unique identifier (taskId). |
atlas://projects/{projectId}/tasks |
Retrieves all tasks belonging to a specific project (projectId). |
atlas://knowledge/{knowledgeId} |
Retrieves a single knowledge item by its unique identifier (knowledgeId). |
atlas://projects/{projectId}/knowledge |
Retrieves all knowledge items belonging to a specific project (projectId). |
ATLAS provides functionality to back up and restore the Neo4j database content. The core logic resides in src/services/neo4j/backupRestoreService.ts.
Important: The automatic backup functionality has been removed due to inefficiency. The call to triggerBackgroundBackup in src/services/neo4j/driver.ts is commented out with a note indicating it was removed. Please use the manual backup process described below to protect your data.
-
Mechanism: The backup process exports all
Project,Task, andKnowledgenodes, along with their relationships, into separate JSON files. -
Output: Each backup creates a timestamped directory (e.g.,
atlas-backup-YYYYMMDDHHMMSS) within the configured backup path (default:./atlas-backups/). This directory containsprojects.json,tasks.json,knowledge.json, andrelationships.json. -
Manual Backup: You can trigger a manual backup using the provided script:
This command executes
npm run db:backup
scripts/db-backup.ts, which calls theexportDatabasefunction.
- Mechanism: The restore process first completely clears the existing Neo4j database. Then, it imports nodes and relationships from the JSON files located in the specified backup directory.
- Warning: Restoring from a backup is a destructive operation. It will overwrite all current data in your Neo4j database.
-
Manual Restore: To restore the database from a backup directory, use the import script:
Replace
npm run db:import <path_to_backup_directory>
<path_to_backup_directory>with the actual path to the backup folder (e.g.,./atlas-backups/atlas-backup-20250326120000). This command executesscripts/db-import.ts, which calls theimportDatabasefunction. -
Relationship Handling: The import process attempts to recreate relationships based on the
idproperties stored within the nodes during export. Ensure your nodes have consistentidproperties for relationships to be restored correctly.
The examples/ directory contains practical examples demonstrating various features of the ATLAS MCP Server.
-
Backup Example: Located in
examples/backup-example/, this shows the structure and format of the JSON files generated by thenpm run db:backupcommand. See the Examples README for more details.
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Commit your changes with a descriptive message
- Push to the branch
- Create a Pull Request
For bugs and feature requests, please create an issue.
Apache License 2.0
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for atlas-mcp-server
Similar Open Source Tools

atlas-mcp-server
ATLAS (Adaptive Task & Logic Automation System) is a high-performance Model Context Protocol server designed for LLMs to manage complex task hierarchies. Built with TypeScript, it features ACID-compliant storage, efficient task tracking, and intelligent template management. ATLAS provides LLM Agents task management through a clean, flexible tool interface. The server implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for standardized communication between LLMs and external systems, offering hierarchical task organization, task state management, smart templates, enterprise features, and performance optimization.
paperbanana
PaperBanana is an automated academic illustration tool designed for AI scientists. It implements an agentic framework for generating publication-quality academic diagrams and statistical plots from text descriptions. The tool utilizes a two-phase multi-agent pipeline with iterative refinement, Gemini-based VLM planning, and image generation. It offers a CLI, Python API, and MCP server for IDE integration, along with Claude Code skills for generating diagrams, plots, and evaluating diagrams. PaperBanana is not affiliated with or endorsed by the original authors or Google Research, and it may differ from the original system described in the paper.
code-cli
Autohand Code CLI is an autonomous coding agent in CLI form that uses the ReAct pattern to understand, plan, and execute code changes. It is designed for seamless coding experience without context switching or copy-pasting. The tool is fast, intuitive, and extensible with modular skills. It can be used to automate coding tasks, enforce code quality, and speed up development. Autohand can be integrated into team workflows and CI/CD pipelines to enhance productivity and efficiency.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
augustus
Augustus is a Go-based LLM vulnerability scanner designed for security professionals to test large language models against a wide range of adversarial attacks. It integrates with 28 LLM providers, covers 210+ adversarial attacks including prompt injection, jailbreaks, encoding exploits, and data extraction, and produces actionable vulnerability reports. The tool is built for production security testing with features like concurrent scanning, rate limiting, retry logic, and timeout handling out of the box.
FDAbench
FDABench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating data agents' reasoning ability over heterogeneous data in analytical scenarios. It offers 2,007 tasks across various data sources, domains, difficulty levels, and task types. The tool provides ready-to-use data agent implementations, a DAG-based evaluation system, and a framework for agent-expert collaboration in dataset generation. Key features include data agent implementations, comprehensive evaluation metrics, multi-database support, different task types, extensible framework for custom agent integration, and cost tracking. Users can set up the environment using Python 3.10+ on Linux, macOS, or Windows. FDABench can be installed with a one-command setup or manually. The tool supports API configuration for LLM access and offers quick start guides for database download, dataset loading, and running examples. It also includes features like dataset generation using the PUDDING framework, custom agent integration, evaluation metrics like accuracy and rubric score, and a directory structure for easy navigation.
gpt-load
GPT-Load is a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI API transparent proxy service designed for enterprises and developers needing to integrate multiple AI services. Built with Go, it features intelligent key management, load balancing, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities for high-concurrency production environments. The tool serves as a transparent proxy service, preserving native API formats of various AI service providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude. It supports dynamic configuration, distributed leader-follower deployment, and a Vue 3-based web management interface. GPT-Load is production-ready with features like dual authentication, graceful shutdown, and error recovery.
docutranslate
Docutranslate is a versatile tool for translating documents efficiently. It supports multiple file formats and languages, making it ideal for businesses and individuals needing quick and accurate translations. The tool uses advanced algorithms to ensure high-quality translations while maintaining the original document's formatting. With its user-friendly interface, Docutranslate simplifies the translation process and saves time for users. Whether you need to translate legal documents, technical manuals, or personal letters, Docutranslate is the go-to solution for all your document translation needs.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
mcp-devtools
MCP DevTools is a high-performance server written in Go that replaces multiple Node.js and Python-based servers. It provides access to essential developer tools through a unified, modular interface. The server is efficient, with minimal memory footprint and fast response times. It offers a comprehensive tool suite for agentic coding, including 20+ essential developer agent tools. The tool registry allows for easy addition of new tools. The server supports multiple transport modes, including STDIO, HTTP, and SSE. It includes a security framework for multi-layered protection and a plugin system for adding new tools.
ruler
Ruler is a tool designed to centralize AI coding assistant instructions, providing a single source of truth for managing instructions across multiple AI coding tools. It helps in avoiding inconsistent guidance, duplicated effort, context drift, onboarding friction, and complex project structures by automatically distributing instructions to the right configuration files. With support for nested rule loading, Ruler can handle complex project structures with context-specific instructions for different components. It offers features like centralised rule management, nested rule loading, automatic distribution, targeted agent configuration, MCP server propagation, .gitignore automation, and a simple CLI for easy configuration management.

dingo
Dingo is a data quality evaluation tool that automatically detects data quality issues in datasets. It provides built-in rules and model evaluation methods, supports text and multimodal datasets, and offers local CLI and SDK usage. Dingo is designed for easy integration into evaluation platforms like OpenCompass.
agentops
AgentOps is a toolkit for evaluating and developing robust and reliable AI agents. It provides benchmarks, observability, and replay analytics to help developers build better agents. AgentOps is open beta and can be signed up for here. Key features of AgentOps include: - Session replays in 3 lines of code: Initialize the AgentOps client and automatically get analytics on every LLM call. - Time travel debugging: (coming soon!) - Agent Arena: (coming soon!) - Callback handlers: AgentOps works seamlessly with applications built using Langchain and LlamaIndex.
PDFMathTranslate
PDFMathTranslate is a tool designed for translating scientific papers and conducting bilingual comparisons. It preserves formulas, charts, table of contents, and annotations. The tool supports multiple languages and diverse translation services. It provides a command-line tool, interactive user interface, and Docker deployment. Users can try the application through online demos. The tool offers various installation methods including command-line, portable, graphic user interface, and Docker. Advanced options allow users to customize translation settings. Additionally, the tool supports secondary development through APIs for Python and HTTP. Future plans include parsing layout with DocLayNet based models, fixing page rotation and format issues, supporting non-PDF/A files, and integrating plugins for Zotero and Obsidian.
shodh-memory
Shodh-Memory is a cognitive memory system designed for AI agents to persist memory across sessions, learn from experience, and run entirely offline. It features Hebbian learning, activation decay, and semantic consolidation, packed into a single ~17MB binary. Users can deploy it on cloud, edge devices, or air-gapped systems to enhance the memory capabilities of AI agents.
ai
A TypeScript toolkit for building AI-driven video workflows on the server, powered by Mux! @mux/ai provides purpose-driven workflow functions and primitive functions that integrate with popular AI/LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. It offers pre-built workflows for tasks like generating summaries and tags, content moderation, chapter generation, and more. The toolkit is cost-effective, supports multi-modal analysis, tone control, and configurable thresholds, and provides full TypeScript support. Users can easily configure credentials for Mux and AI providers, as well as cloud infrastructure like AWS S3 for certain workflows. @mux/ai is production-ready, offers composable building blocks, and supports universal language detection.
For similar tasks

atlas-mcp-server
ATLAS (Adaptive Task & Logic Automation System) is a high-performance Model Context Protocol server designed for LLMs to manage complex task hierarchies. Built with TypeScript, it features ACID-compliant storage, efficient task tracking, and intelligent template management. ATLAS provides LLM Agents task management through a clean, flexible tool interface. The server implements the Model Context Protocol (MCP) for standardized communication between LLMs and external systems, offering hierarchical task organization, task state management, smart templates, enterprise features, and performance optimization.
scaleapi-python-client
The Scale AI Python SDK is a tool that provides a Python interface for interacting with the Scale API. It allows users to easily create tasks, manage projects, upload files, and work with evaluation tasks, training tasks, and Studio assignments. The SDK handles error handling and provides detailed documentation for each method. Users can also manage teammates, project groups, and batches within the Scale Studio environment. The SDK supports various functionalities such as creating tasks, retrieving tasks, canceling tasks, auditing tasks, updating task attributes, managing files, managing team members, and working with evaluation and training tasks.
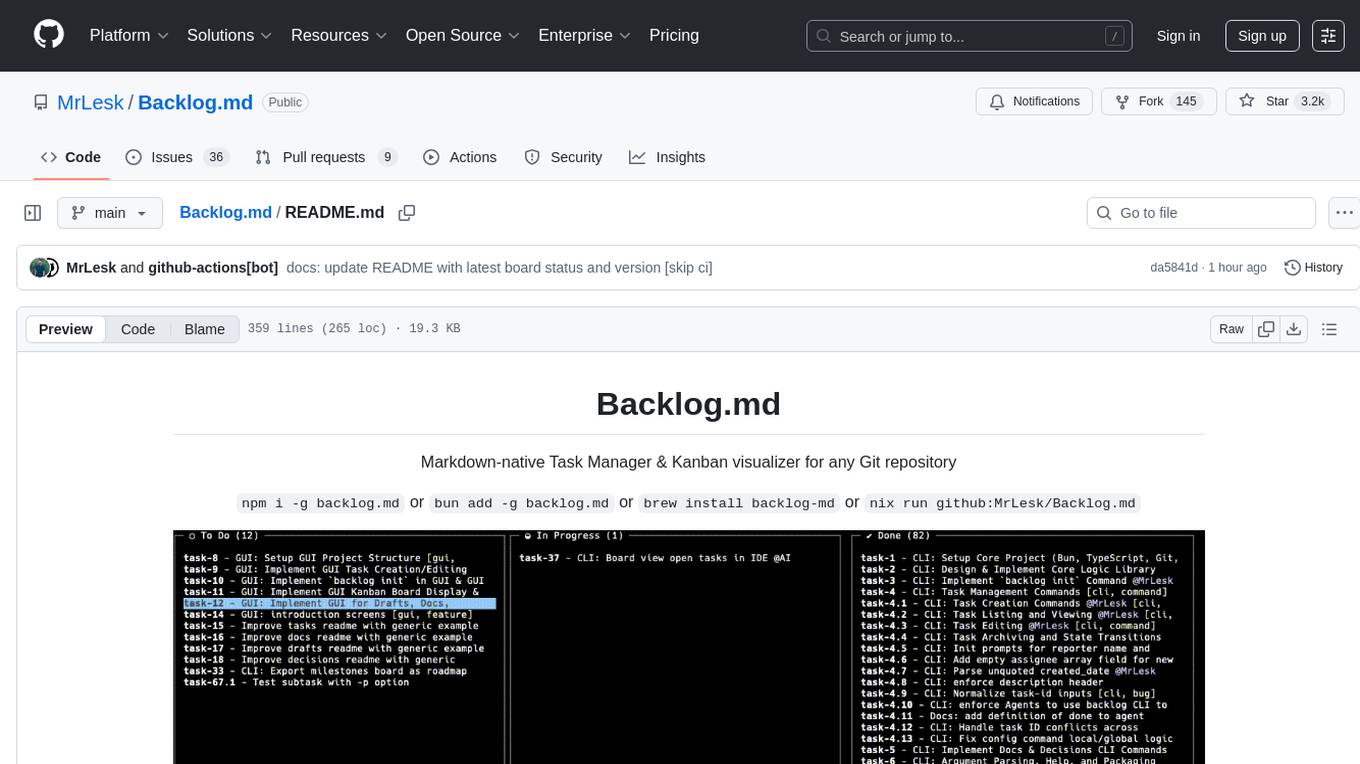
Backlog.md
Backlog.md is a Markdown-native Task Manager & Kanban visualizer for any Git repository. It turns any folder with a Git repo into a self-contained project board powered by plain Markdown files and a zero-config CLI. Features include managing tasks as plain .md files, private & offline usage, instant terminal Kanban visualization, board export, modern web interface, AI-ready CLI, rich query commands, cross-platform support, and MIT-licensed open-source. Users can create tasks, view board, assign tasks to AI, manage documentation, make decisions, and configure settings easily.
For similar jobs

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.
nvidia_gpu_exporter
Nvidia GPU exporter for prometheus, using `nvidia-smi` binary to gather metrics.

tracecat
Tracecat is an open-source automation platform for security teams. It's designed to be simple but powerful, with a focus on AI features and a practitioner-obsessed UI/UX. Tracecat can be used to automate a variety of tasks, including phishing email investigation, evidence collection, and remediation plan generation.

openinference
OpenInference is a set of conventions and plugins that complement OpenTelemetry to enable tracing of AI applications. It provides a way to capture and analyze the performance and behavior of AI models, including their interactions with other components of the application. OpenInference is designed to be language-agnostic and can be used with any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend. It includes a set of instrumentations for popular machine learning SDKs and frameworks, making it easy to add tracing to your AI applications.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

kong
Kong, or Kong API Gateway, is a cloud-native, platform-agnostic, scalable API Gateway distinguished for its high performance and extensibility via plugins. It also provides advanced AI capabilities with multi-LLM support. By providing functionality for proxying, routing, load balancing, health checking, authentication (and more), Kong serves as the central layer for orchestrating microservices or conventional API traffic with ease. Kong runs natively on Kubernetes thanks to its official Kubernetes Ingress Controller.





