
LightMem
[ICLR 2026] LightMem: Lightweight and Efficient Memory-Augmented Generation
Stars: 564
LightMem is a lightweight and efficient memory management framework designed for Large Language Models and AI Agents. It provides a simple yet powerful memory storage, retrieval, and update mechanism to help you quickly build intelligent applications with long-term memory capabilities. The framework is minimalist in design, ensuring minimal resource consumption and fast response times. It offers a simple API for easy integration into applications with just a few lines of code. LightMem's modular architecture supports custom storage engines and retrieval strategies, making it flexible and extensible. It is compatible with various cloud APIs like OpenAI and DeepSeek, as well as local models such as Ollama and vLLM.
README:
LightMem is a lightweight and efficient memory management framework designed for Large Language Models and AI Agents. It provides a simple yet powerful memory storage, retrieval, and update mechanism to help you quickly build intelligent applications with long-term memory capabilities.
-
🚀 Lightweight & Efficient
Minimalist design with minimal resource consumption and fast response times -
🎯 Easy to Use
Simple API design - integrate into your application with just a few lines of code -
🔌 Flexible & Extensible
Modular architecture supporting custom storage engines and retrieval strategies -
🌐 Broad Compatibility
Support for cloud APIs (OpenAI, DeepSeek) and local models (Ollama, vLLM, etc.)
- [2026-01-26]: 🎉🎉🎉 LightMem: Lightweight and Efficient Memory-Augmented Generation has been accepted by ICLR 2026!
- [2026-01-17]: 🚀 We provide a comprehensive baseline evaluation framework, supporting the benchmarking of memory layers such as Mem0, A-MEM, and LangMem on multiple datasets like LoCoMo and LongMemEval.
- [2025-12-09]: 🎬 Released a Demo Video showcasing long-context handling, along with comprehensive Tutorial Notebooks for various scenarios!
- [2025-11-30]: 🚌 LightMem now supports calling multiple tools provided by its MCP Server.
- [2025-11-26]: 🚀 Added full LoCoMo dataset support, delivering strong results with leading performance and efficiency! Here is the reproduction script!
- [2025-11-09]: ✨ LightMem now supports local deployment via Ollama, vLLM, and Transformers auto-loading!
- [2025-10-12]: 🎉 LightMem project is officially Open-Sourced!
We provide lightweight, ready-to-run scripts for reproducing results on LoCoMo, LongMemEval, and their combined baselines.
| Dataset | Description | Script | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| LongMemEval | Run LightMem on LongMemEval, including evaluation and offline memory update. | run_lightmem_longmemeval.md | LongMemEval Results |
| LoCoMo | Scripts for reproducing LightMem results on LoCoMo. | run_lightmem_locomo.md | LoCoMo Results |
| LongMemEval & LoCoMo | Unified baseline scripts for running both datasets. | run_baselines.md | Baseline Results |
We provide a comprehensive baseline evaluation framework, supporting the benchmarking of memory layers such as Mem0, A-MEM, and LangMem on multiple datasets like LoCoMo and LongMemEval.
Watch Demo: YouTube | Bilibili
We provide ready-to-use Jupyter notebooks corresponding to the demo and other use cases. You can find them in the tutorial-notebooks directory.
| Scenario | Description | Notebook Link |
|---|---|---|
| Travel Planning | A complete guide to building a travel agent with memory. | LightMem_Example_travel.ipynb |
| Code Assistant | A complete guide to building a code agent with memory. | LightMem_Example_code.ipynb |
| LongMemEval | A tutorial on how to run evaluations on LongMemEval benchmarks using LightMem. | LightMem_Example_longmemeval.ipynb |
LightMem is continuously evolving! Here's what's coming:
- Offline Pre-computation of KV Cache for Update (Lossless)
- Online Pre-computation of KV Cache Before Q&A (Lossy)
- Integration More Models and Feature Enhancement
- Coordinated Use of Context and Long-Term Memory Storage
- Multi Modal Memory
- 📢 News
- 🧪 Reproduction Scripts
- 🧪 Baseline Evaluation
- 🎥 Demo & Tutorials
- ☑️ Todo List
- 🔧 Installation
- ⚡ Quick Start
- 🏗️ Architecture
- 💡 Examples
- 📁 Experimental Results
- ⚙️ Configuration
- 👥 Contributors
- 🔗 Related Projects
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/zjunlp/LightMem.git
cd LightMem
# Create virtual environment
conda create -n lightmem python=3.11 -y
conda activate lightmem
# Install dependencies
unset ALL_PROXY
pip install -e .pip install lightmem # Coming soon-
Modify the
JUDGE_MODEL,LLM_MODEL, and their respectiveAPI_KEYandBASE_URLinAPI Configuration. -
Download
LLMLINGUA_MODELfrom microsoft/llmlingua-2-bert-base-multilingual-cased-meetingbank andEMBEDDING_MODELfrom sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 and modify their paths inModel Paths. -
Download the dataset from longmemeval-cleaned, and modidy the path in
Data Configuration.
cd experiments
python run_lightmem_qwen.pyLightMem adopts a modular design, breaking down the memory management process into several pluggable components. The core directory structure exposed to users is outlined below, allowing for easy customization and extension:
LightMem/
├── src/lightmem/ # Main package
│ ├── __init__.py # Package initialization
│ ├── configs/ # Configuration files
│ ├── factory/ # Factory methods
│ ├── memory/ # Core memory management
│ └── memory_toolkits/ # Memory toolkits
├── mcp/ # LightMem MCP server
├── experiments/ # Experiment scripts
├── datasets/ # Datasets files
└── examples/ # ExamplesThe following table lists the backends values currently recognized by each configuration module. Use the model_name field (or the corresponding config object) to select one of these backends.
| Module (config) | Supported backends |
|---|---|
PreCompressorConfig |
llmlingua-2, entropy_compress
|
TopicSegmenterConfig |
llmlingua-2 |
MemoryManagerConfig |
openai, deepseek, ollama, vllm, etc. |
TextEmbedderConfig |
huggingface |
MMEmbedderConfig |
huggingface |
EmbeddingRetrieverConfig |
qdrant |
import os
from datetime import datetime
from lightmem.memory.lightmem import LightMemory
LOGS_ROOT = "./logs"
RUN_TIMESTAMP = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
RUN_LOG_DIR = os.path.join(LOGS_ROOT, RUN_TIMESTAMP)
os.makedirs(RUN_LOG_DIR, exist_ok=True)
API_KEY='your_api_key'
API_BASE_URL='your_api_base_url'
LLM_MODEL='your_model_name' # such as 'gpt-4o-mini' (API) or 'gemma3:latest' (Local Ollama) ...
EMBEDDING_MODEL_PATH='/your/path/to/models/all-MiniLM-L6-v2'
LLMLINGUA_MODEL_PATH='/your/path/to/models/llmlingua-2-bert-base-multilingual-cased-meetingbank'
config_dict = {
"pre_compress": True,
"pre_compressor": {
"model_name": "llmlingua-2",
"configs": {
"llmlingua_config": {
"model_name": LLMLINGUA_MODEL_PATH,
"device_map": "cuda",
"use_llmlingua2": True,
},
}
},
"topic_segment": True,
"precomp_topic_shared": True,
"topic_segmenter": {
"model_name": "llmlingua-2",
},
"messages_use": "user_only",
"metadata_generate": True,
"text_summary": True,
"memory_manager": {
"model_name": 'xxx', # such as 'openai' or 'ollama' ...
"configs": {
"model": LLM_MODEL,
"api_key": API_KEY,
"max_tokens": 16000,
"xxx_base_url": API_BASE_URL # API model specific, such as 'openai_base_url' or 'deepseek_base_url' ...
}
},
"extract_threshold": 0.1,
"index_strategy": "embedding",
"text_embedder": {
"model_name": "huggingface",
"configs": {
"model": EMBEDDING_MODEL_PATH,
"embedding_dims": 384,
"model_kwargs": {"device": "cuda"},
},
},
"retrieve_strategy": "embedding",
"embedding_retriever": {
"model_name": "qdrant",
"configs": {
"collection_name": "my_long_term_chat",
"embedding_model_dims": 384,
"path": "./my_long_term_chat",
}
},
"update": "offline",
"logging": {
"level": "DEBUG",
"file_enabled": True,
"log_dir": RUN_LOG_DIR,
}
}
lightmem = LightMemory.from_config(config_dict)session = {
"timestamp": "2025-01-10",
"turns": [
[
{"role": "user", "content": "My favorite ice cream flavor is pistachio, and my dog's name is Rex."},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Got it. Pistachio is a great choice."}],
]
}
for turn_messages in session["turns"]:
timestamp = session["timestamp"]
for msg in turn_messages:
msg["time_stamp"] = timestamp
store_result = lightmem.add_memory(
messages=turn_messages,
force_segment=True,
force_extract=True
)lightmem.construct_update_queue_all_entries()
lightmem.offline_update_all_entries(score_threshold=0.8)question = "What is the name of my dog?"
related_memories = lightmem.retrieve(question, limit=5)
print(related_memories)LightMem also supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP) server:
# Running at Root Directory
cd LightMem
# Environment
pip install '.[mcp]'
# MCP Inspector [Optional]
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector python mcp/server.py
# Start API by HTTP (http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp)
fastmcp run mcp/server.py:mcp --transport http --port 8000The MCP config json file of your local client may looks like:
{
"yourMcpServers": {
"LightMem": {
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp",
"otherParameters": "..."
}
}
}For transparency and reproducibility, we have shared the results of our experiments on Google Drive. This includes model outputs, evaluation logs, and predictions used in our study.
🔗 Access the data here: Google Drive - Experimental Results
Please feel free to download, explore, and use these resources for research or reference purposes.
backbone: gpt-4o-mini, judge model: gpt-4o-mini & qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | ACC(%) gpt-4o-mini | ACC(%) qwen2.5-32b-instruct | Memory-Con Tokens(k) Total | QA Tokens(k) total | Total(k) | Calls | Runtime(s) total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 73.83 | 73.18 | – | 54,884.479 | 54,884.479 | – | 6,971 |
| NaiveRAG | 63.64 | 63.12 | – | 3,870.187 | 3,870.187 | – | 1,884 |
| A-MEM | 64.16 | 60.71 | 11,494.344 | 10,170.567 | 21,664.907 | 11,754 | 67,084 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 58.25 | 61.04 | 2,870.036 | 7,649.343 | 10,519.379 | 5,534 | 26,129 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 54.87 | 55.91 | 5,264.801 | 6,126.111 | 11,390.004 | 10,160 | 37,912 |
| Mem0 | 36.49 | 37.01 | 24,304.872 | 1,488.618 | 25,793.490 | 19,070 | 120,175 |
| Mem0(api) | 61.69 | 61.69 | 68,347.720 | 4,169.909 | 72,517.629 | 6,022 | 10,445 |
| Mem0-g(api) | 60.32 | 59.48 | 69,684.818 | 4,389.147 | 74,073.965 | 6,022 | 10,926 |
backbone: qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, judge model: gpt-4o-mini & qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | ACC(%) gpt-4o-mini | ACC(%) qwen2.5-32b-instruct | Memory-Con Tokens(k) Total | QA Tokens(k) total | Total(k) | Calls | Runtime(s) total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 74.87 | 74.35 | – | 60,873.076 | 60,873.076 | – | 10,555 |
| NaiveRAG | 66.95 | 64.68 | – | 4,271.052 | 4,271.052 | – | 1,252 |
| A-MEM | 56.10 | 54.81 | 16,267.997 | 17,340.881 | 33,608.878 | 11,754 | 69,339 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 61.04 | 59.81 | 3,615.087 | 9,703.169 | 11,946.442 | 4,147 | 13,710 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 51.30 | 51.95 | 6,663.527 | 7,764.991 | 14,428.518 | 10,046 | 20,830 |
| Mem0 | 43.31 | 43.25 | 17,994.035 | 1,765.570 | 19,759.605 | 16,145 | 46,500 |
backbone: gpt-4o-mini, judge model: gpt-4o-mini & qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | Summary Tokens(k) In | Summary Tokens(k) Out | Update Tokens(k) In | Update Tokens(k) Out | QA Tokens(k) In | QA Tokens(k) Out | Runtime(s) mem-con | Runtime(s) qa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | – | – | – | – | 54,858.770 | 25.709 | – | 6,971 |
| NaiveRAG | – | – | – | – | 3,851.029 | 19.158 | – | 1,884 |
| A-MEM | 1,827.373 | 492.883 | 7,298.878 | 1,875.210 | 10,113.252 | 57.315 | 60,607 | 6,477 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 1,109.849 | 333.970 | 780.807 | 645.410 | 7,638.539 | 10.804 | 24,220 | 1,909 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 1,007.729 | 294.601 | 3,037.509 | 924.962 | 6,116.239 | 9.872 | 33,325 | 4,587 |
| Mem0 | 8,127.398 | 253.187 | 12,722.011 | 3,202.276 | 1,478.830 | 9.788 | 118,268 | 1,907 |
| Mem0(api) | \ | \ | \ | \ | 4,156.850 | 13.059 | 4,328 | 6,117 |
| Mem0-g(api) | \ | \ | \ | \ | 4,375.900 | 13.247 | 5,381 | 5,545 |
backbone: qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, judge model: gpt-4o-mini & qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | Summary Tokens(k) In | Summary Tokens(k) Out | Update Tokens(k) In | Update Tokens(k) Out | QA Tokens(k) In | QA Tokens(k) Out | Runtime(s) mem-con | Runtime(s) qa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | – | – | – | – | 60,838.694 | 34.382 | – | 10,555 |
| NaiveRAG | – | – | – | – | 4,239.030 | 32.022 | – | 1,252 |
| A-MEM | 1,582.942 | 608.507 | 9,241.928 | 4,835.070 | 17,528.876 | 82.005 | 55,439 | 13,900 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 1,222.139 | 531.157 | 1,044.307 | 817.484 | 9,679.996 | 23.173 | 12,697 | 1,012 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 2,288.533 | 516.024 | 2,422.693 | 1,436.277 | 7,743.391 | 21.600 | 19,822 | 1,007 |
| Mem0 | 8,270.874 | 186.354 | 7,638.827 | 1,897.980 | 1,739.246 | 26.324 | 45,407 | 1,093 |
backbone: gpt-4o-mini, judge model: gpt-4o-mini
| Method | Overall ↑ | Multi | Open | Single | Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 73.83 | 68.79 | 56.25 | 86.56 | 50.16 |
| NaiveRAG | 63.64 | 55.32 | 47.92 | 70.99 | 56.39 |
| A-MEM | 64.16 | 56.03 | 31.25 | 72.06 | 60.44 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 58.25 | 56.74 | 45.83 | 67.06 | 40.19 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 54.87 | 52.13 | 43.75 | 63.97 | 36.76 |
| Mem0 | 36.49 | 30.85 | 34.38 | 38.41 | 37.07 |
| Mem0(api) | 61.69 | 56.38 | 43.75 | 66.47 | 59.19 |
| Mem0-g(api) | 60.32 | 54.26 | 39.58 | 65.99 | 57.01 |
backbone: gpt-4o-mini, judge model: qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | Overall ↑ | Multi | Open | Single | Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 73.18 | 68.09 | 54.17 | 86.21 | 49.22 |
| NaiveRAG | 63.12 | 53.55 | 50.00 | 71.34 | 53.89 |
| A-MEM | 60.71 | 53.55 | 32.29 | 69.08 | 53.58 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 61.04 | 64.18 | 40.62 | 70.15 | 40.50 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 55.91 | 52.48 | 41.67 | 66.35 | 35.83 |
| Mem0 | 37.01 | 31.91 | 37.50 | 38.53 | 37.38 |
| Mem0(api) | 61.69 | 54.26 | 46.88 | 67.66 | 57.01 |
| Mem0-g(api) | 59.48 | 55.32 | 42.71 | 65.04 | 53.58 |
backbone: qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, judge model: gpt-4o-mini
| Method | Overall ↑ | Multi | Open | Single | Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 74.87 | 69.86 | 57.29 | 87.40 | 51.71 |
| NaiveRAG | 66.95 | 62.41 | 57.29 | 76.81 | 47.98 |
| A-MEM | 56.10 | 57.45 | 43.75 | 67.90 | 27.73 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 61.04 | 62.77 | 51.04 | 72.29 | 33.02 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 51.30 | 52.48 | 40.62 | 61.59 | 26.48 |
| Mem0 | 43.31 | 42.91 | 46.88 | 46.37 | 34.58 |
| Mem0(api) | 61.69 | 54.26 | 46.88 | 67.66 | 57.01 |
| Mem0-g(api) | 59.48 | 55.32 | 42.71 | 65.04 | 53.58 |
backbone: qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, judge model: qwen2.5-32b-instruct
| Method | Overall ↑ | Multi | Open | Single | Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FullText | 74.35 | 68.09 | 63.54 | 86.33 | 51.71 |
| NaiveRAG | 64.68 | 60.28 | 52.08 | 75.62 | 43.61 |
| A-MEM | 54.81 | 56.74 | 39.58 | 67.42 | 24.61 |
| MemoryOS(eval) | 59.81 | 63.12 | 48.96 | 70.51 | 32.09 |
| MemoryOS(pypi) | 51.95 | 55.67 | 39.58 | 61.47 | 27.41 |
| Mem0 | 43.25 | 45.04 | 46.88 | 45.78 | 33.96 |
| Mem0(api) | 61.69 | 54.26 | 46.88 | 67.66 | 57.01 |
| Mem0-g(api) | 59.48 | 55.32 | 42.71 | 65.04 | 53.58 |
All behaviors of LightMem are controlled via the BaseMemoryConfigs configuration class. Users can customize aspects like pre-processing, memory extraction, retrieval strategy, and update mechanisms by providing a custom configuration.
| Option | Default | Usage (allowed values and behavior) |
|---|---|---|
pre_compress |
False |
True / False. If True, input messages are pre-compressed using the pre_compressor configuration before being stored. This reduces storage and indexing cost but may remove fine-grained details. If False, messages are stored without pre-compression. |
pre_compressor |
None |
dict / object. Configuration for the pre-compression component (PreCompressorConfig) with fields like model_name (e.g., llmlingua-2, entropy_compress) and configs (model-specific parameters). Effective only when pre_compress=True. |
topic_segment |
False |
True / False. Enables topic-based segmentation of long conversations. When True, long conversations are split into topic segments and each segment can be indexed/stored independently (requires topic_segmenter). When False, messages are stored sequentially. |
precomp_topic_shared |
False |
True / False. If True, pre-compression and topic segmentation can share intermediate results to avoid redundant processing. May improve performance but requires careful configuration to avoid cross-topic leakage. |
topic_segmenter |
None |
dict / object. Configuration for topic segmentation (TopicSegmenterConfig), including model_name and configs (segment length, overlap, etc.). Used when topic_segment=True. |
messages_use |
'user_only' |
'user_only' / 'assistant_only' / 'hybrid'. Controls which messages are used to generate metadata and summaries: user_only uses user inputs, assistant_only uses assistant responses, hybrid uses both. Choosing hybrid increases processing but yields richer context. |
metadata_generate |
True |
True / False. If True, metadata such as keywords and entities are extracted and stored to support attribute-based and filtered retrieval. If False, no metadata extraction occurs. |
text_summary |
True |
True / False. If True, a text summary is generated and stored alongside the original text (reduces retrieval cost and speeds review). If False, only the original text is stored. Summary quality depends on memory_manager. |
memory_manager |
MemoryManagerConfig() |
dict / object. Controls the model used to generate summaries and metadata (MemoryManagerConfig), e.g., model_name (openai, ollama, etc.) and configs. Changing this affects summary style, length, and cost. |
extract_threshold |
0.5 |
float (0.0 - 1.0). Threshold used to decide whether content is important enough to be extracted as metadata or highlight. Higher values (e.g., 0.8) mean more conservative extraction; lower values (e.g., 0.2) extract more items (may increase noise). |
index_strategy |
None |
'embedding' / 'context' / 'hybrid' / None. Determines how memories are indexed: 'embedding' uses vector-based indexing (requires embedders/retriever) for semantic search; 'context' uses text-based/contextual retrieval (requires context_retriever) for keyword/document similarity; and 'hybrid' combines context filtering and vector reranking for robustness and higher accuracy. |
text_embedder |
None |
dict / object. Configuration for text embedding model (TextEmbedderConfig) with model_name (e.g., huggingface) and configs (batch size, device, embedding dim). Required when index_strategy or retrieve_strategy includes 'embedding'. |
multimodal_embedder |
None |
dict / object. Configuration for multimodal/image embedder (MMEmbedderConfig). Used for non-text modalities. |
history_db_path |
os.path.join(lightmem_dir, "history.db") |
str. Path to persist conversation history and lightweight state. Useful to restore state across restarts. |
retrieve_strategy |
'embedding' |
'embedding' / 'context' / 'hybrid'. Strategy used at query time to fetch relevant memories. Pick based on data and query type: semantic queries -> 'embedding'; keyword/structured queries -> 'context'; mixed -> 'hybrid'. |
context_retriever |
None |
dict / object. Configuration for context-based retriever (ContextRetrieverConfig), e.g., model_name='BM25' and configs like top_k. Used when retrieve_strategy includes 'context'. |
embedding_retriever |
None |
dict / object. Vector store configuration (EmbeddingRetrieverConfig), e.g., model_name='qdrant' and connection/index params. Used when retrieve_strategy includes 'embedding'. |
update |
'offline' |
'online' / 'offline'. 'online': update memories immediately after each interaction (low latency for fresh memories but higher operational cost). 'offline': batch or scheduled updates to save cost and aggregate changes. |
kv_cache |
False |
True / False. If True, attempt to precompute and persist model KV caches to accelerate repeated LLM calls (requires support from the LLM runtime and may increase storage). Uses kv_cache_path to store cache. |
kv_cache_path |
os.path.join(lightmem_dir, "kv_cache.db") |
str. File path for KV cache storage when kv_cache=True. |
graph_mem |
False |
True / False. When True, some memories will be organized as a graph (nodes and relationships) to support complex relation queries and reasoning. Requires additional graph processing/storage. |
version |
'v1.1' |
str. Configuration/API version. Only change if you know compatibility implications. |
logging |
'None' |
dict / object. Configuration for logging enabled. |
|
JizhanFang |
Xinle-Deng |
Xubqpanda |
HaomingX |
453251 |
James-TYQ |
evy568 |
Norah-Feathertail |
TongjiCst |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LightMem
Similar Open Source Tools

LightMem
LightMem is a lightweight and efficient memory management framework designed for Large Language Models and AI Agents. It provides a simple yet powerful memory storage, retrieval, and update mechanism to help you quickly build intelligent applications with long-term memory capabilities. The framework is minimalist in design, ensuring minimal resource consumption and fast response times. It offers a simple API for easy integration into applications with just a few lines of code. LightMem's modular architecture supports custom storage engines and retrieval strategies, making it flexible and extensible. It is compatible with various cloud APIs like OpenAI and DeepSeek, as well as local models such as Ollama and vLLM.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
react-native-nitro-mlx
The react-native-nitro-mlx repository allows users to run LLMs, Text-to-Speech, and Speech-to-Text on-device in React Native using MLX Swift. It provides functionalities for downloading models, loading and generating responses, streaming audio, text-to-speech, and speech-to-text capabilities. Users can interact with various MLX-compatible models from Hugging Face, with pre-defined models available for convenience. The repository supports iOS 26.0+ and offers detailed API documentation for each feature.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.
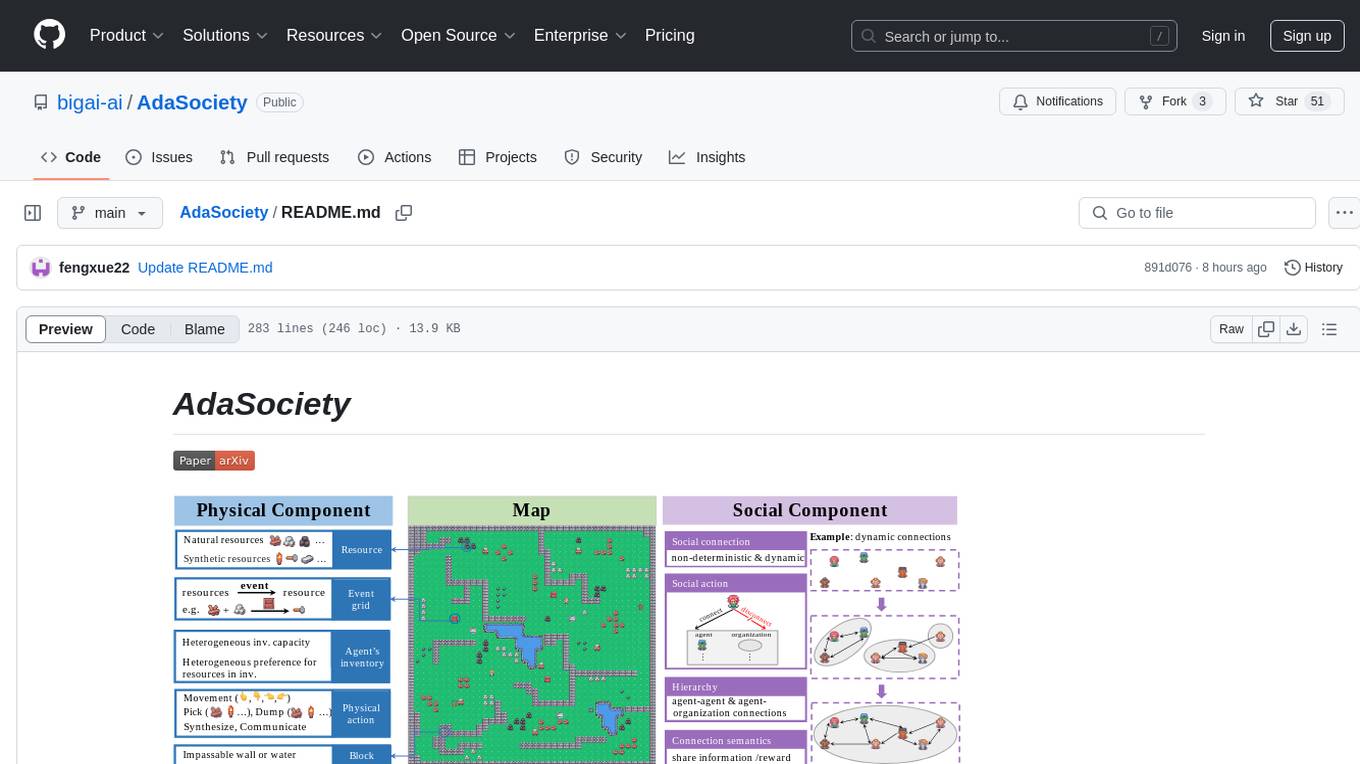
AdaSociety
AdaSociety is a multi-agent environment designed for simulating social structures and decision-making processes. It offers built-in resources, events, and player interactions. Users can customize the environment through JSON configuration or custom Python code. The environment supports training agents using RLlib and LLM frameworks. It provides a platform for studying multi-agent systems and social dynamics.
agentkit-samples
AgentKit Samples is a repository containing a series of examples and tutorials to help users understand, implement, and integrate various functionalities of AgentKit into their applications. The platform offers a complete solution for building, deploying, and maintaining AI agents, significantly reducing the complexity of developing intelligent applications. The repository provides different levels of examples and tutorials, including basic tutorials for understanding AgentKit's concepts and use cases, as well as more complex examples for experienced developers.
OneClickLLAMA
OneClickLLAMA is a tool designed to run local LLM models such as Qwen2.5 and SakuraLLM with ease. It can be used in conjunction with various OpenAI format translators and analyzers, including LinguaGacha and KeywordGacha. By following the setup guides provided on the page, users can optimize performance and achieve a 3-5 times speed improvement compared to default settings. The tool requires a minimum of 8GB dedicated graphics memory, preferably NVIDIA, and the latest version of graphics drivers installed. Users can download the tool from the release page, choose the appropriate model based on usage and memory size, and start the tool by selecting the corresponding launch script.
beet
Beet is a collection of crates for authoring and running web pages, games and AI behaviors. It includes crates like `beet_flow` for scenes-as-control-flow bevy library, `beet_spatial` for spatial behaviors, `beet_ml` for machine learning, `beet_sim` for simulation tooling, `beet_rsx` for authoring tools for html and bevy, and `beet_router` for file-based router for web docs. The `beet` crate acts as a base crate that re-exports sub-crates based on feature flags, similar to the `bevy` crate structure.
go-cyber
Cyber is a superintelligence protocol that aims to create a decentralized and censorship-resistant internet. It uses a novel consensus mechanism called CometBFT and a knowledge graph to store and process information. Cyber is designed to be scalable, secure, and efficient, and it has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with the internet.

MOSS-TTS
MOSS-TTS Family is an open-source speech and sound generation model family designed for high-fidelity, high-expressiveness, and complex real-world scenarios. It includes five production-ready models: MOSS-TTS, MOSS-TTSD, MOSS-VoiceGenerator, MOSS-TTS-Realtime, and MOSS-SoundEffect, each serving specific purposes in speech generation, dialogue, voice design, real-time interactions, and sound effect generation. The models offer features like long-speech generation, fine-grained control over phonemes and duration, multilingual synthesis, voice cloning, and real-time voice agents.
search2ai
S2A allows your large model API to support networking, searching, news, and web page summarization. It currently supports OpenAI, Gemini, and Moonshot (non-streaming). The large model will determine whether to connect to the network based on your input, and it will not connect to the network for searching every time. You don't need to install any plugins or replace keys. You can directly replace the custom address in your commonly used third-party client. You can also deploy it yourself, which will not affect other functions you use, such as drawing and voice.
VoiceBench
VoiceBench is a repository containing code and data for benchmarking LLM-Based Voice Assistants. It includes a leaderboard with rankings of various voice assistant models based on different evaluation metrics. The repository provides setup instructions, datasets, evaluation procedures, and a curated list of awesome voice assistants. Users can submit new voice assistant results through the issue tracker for updates on the ranking list.
no-cost-ai
No-cost-ai is a repository dedicated to providing a comprehensive list of free AI models and tools for developers, researchers, and curious builders. It serves as a living index for accessing state-of-the-art AI models without any cost. The repository includes information on various AI applications such as chat interfaces, media generation, voice and music tools, AI IDEs, and developer APIs and platforms. Users can find links to free models, their limits, and usage instructions. Contributions to the repository are welcome, and users are advised to use the listed services at their own risk due to potential changes in models, limitations, and reliability of free services.
apidash
API Dash is an open-source cross-platform API Client that allows users to easily create and customize API requests, visually inspect responses, and generate API integration code. It supports various HTTP methods, GraphQL requests, and multimedia API responses. Users can organize requests in collections, preview data in different formats, and generate code for multiple languages. The tool also offers dark mode support, data persistence, and various customization options.
Free-LLM-Collection
Free-LLM-Collection is a curated list of free resources for mastering the Legal Language Model (LLM) technology. It includes datasets, research papers, tutorials, and tools to help individuals learn and work with LLM models. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of materials to support researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in exploring and leveraging LLM technology for various applications in the legal domain.
EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
For similar tasks
wanwu
Wanwu AI Agent Platform is an enterprise-grade one-stop commercially friendly AI agent development platform designed for business scenarios. It provides enterprises with a safe, efficient, and compliant one-stop AI solution. The platform integrates cutting-edge technologies such as large language models and business process automation to build an AI engineering platform covering model full life-cycle management, MCP, web search, AI agent rapid development, enterprise knowledge base construction, and complex workflow orchestration. It supports modular architecture design, flexible functional expansion, and secondary development, reducing the application threshold of AI technology while ensuring security and privacy protection of enterprise data. It accelerates digital transformation, cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and business innovation for enterprises of all sizes.

LightMem
LightMem is a lightweight and efficient memory management framework designed for Large Language Models and AI Agents. It provides a simple yet powerful memory storage, retrieval, and update mechanism to help you quickly build intelligent applications with long-term memory capabilities. The framework is minimalist in design, ensuring minimal resource consumption and fast response times. It offers a simple API for easy integration into applications with just a few lines of code. LightMem's modular architecture supports custom storage engines and retrieval strategies, making it flexible and extensible. It is compatible with various cloud APIs like OpenAI and DeepSeek, as well as local models such as Ollama and vLLM.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.






