
nodetool
Visual Builder for AI Workflows and Agents
Stars: 268
NodeTool is a platform designed for AI enthusiasts, developers, and creators, providing a visual interface to access a variety of AI tools and models. It simplifies access to advanced AI technologies, offering resources for content creation, data analysis, automation, and more. With features like a visual editor, seamless integration with leading AI platforms, model manager, and API integration, NodeTool caters to both newcomers and experienced users in the AI field.
README:
NodeTool is an open-source visual programming tool for building AI workflows. Connect LLMs, real-time systems, build AI agents and generate media through a drag-and-drop node interface.
- Node-based visual interface: Connect nodes by dragging lines between them for AI workflow orchestration
- Run anywhere: Your laptop, a server, or the cloud - local execution engine for macOS, Windows, and Linux
- Local-first AI: Run models entirely on your machine with support for local LLMs via Ollama, MLX, and GGML/GGUF formats
- Streaming: Real-time workflow execution with async data streams
- Build AI agents: Create LLM agents with tool use and secure code execution
- Type-safe connections: Ensure compatibility between node inputs and outputs
- Multimodal AI: Process text, images, video, and audio
- Run locally: Apple Silicon (M1+), NVIDIA GPUs, or CPU (works offline)
- Access models: 500,000+ models from HuggingFace
- Cloud APIs: OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, OpenRouter, Kie, Fal, MiniMax, Replicate
- Secure Code execution: Execute code in secure containers
- Build RAG systems: Vector database integration for semantic search
- Deploy anywhere: Docker, RunPod, Google Cloud Run
- Extend with Python: Build custom nodes
Common applications: LLM agents with tool use, creative pipelines, RAG systems, generative media, document processing, and data transformation.
vs ComfyUI: While ComfyUI focuses on media generation workflows, NodeTool extends the node-based concept to general AI workflows including LLM agents, real-time streaming and RAG systems.
vs n8n: While n8n is a general workflow automation tool for business processes and API integrations, NodeTool is specialized for AI workloads with native support for model management, local LLMs, multimodal, RAG and secure code execution.
Access the latest AI models through simple nodes:
Video: OpenAI Sora 2 Pro, Google Veo 3.1, xAI Grok Imagine, Alibaba Wan 2.6, MiniMax Hailuo 2.3, Kling 2.6
Image & Audio: Black Forest Labs FLUX.2, Google Nano Banana Pro
Use TextToVideo, ImageToVideo, or TextToImage nodes and select your provider and model.
Some models need direct API keys. Others work through kie.ai, which combines multiple providers and often has better prices.
| Platform | Get It | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | Download | NVIDIA GPU recommended, 4GB+ VRAM (local AI), 20GB space |
| macOS | Download | M1+ Apple Silicon, 16GB+ RAM (local AI) |
| Linux | Download • Flatpak CI Builds | NVIDIA GPU recommended, 4GB+ VRAM (local AI) |
Cloud-only usage requires no GPU—just use API services.
- Getting Started - Build your first workflow
- Node Packs - Available operations and integrations
- Custom Nodes - Extend NodeTool
- Deployment - Share your work
- API Reference - Programmatic access
For core library work, see nodetool-core.
Prerequisites: Python 3.11, Conda, Node.js LTS
Quick start:
# Setup
conda env update -f environment.yml --prune
conda activate nodetool
# Install
uv pip install git+https://github.com/nodetool-ai/nodetool-core git+https://github.com/nodetool-ai/nodetool-base
# Run (backend on port 7777, frontend on port 3000)
nodetool serve --reload &
cd web && npm install && npm startRequires CUDA driver ≥525.60.13 (Linux) or ≥527.41 (Windows):
uv pip install git+https://github.com/nodetool-ai/nodetool-huggingface --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu128uv pip install git+https://github.com/nodetool-ai/nodetool-mlxSet your Conda path in settings.yaml and run make electron.
Run Mini Apps on iOS and Android:
cd mobile && npm install && npm startSee mobile/README.md for setup.
# Unit tests
cd electron && npm test && npm run lint
cd web && npm test && npm run lint
# End-to-end tests
# Web e2e (needs backend server running on port 7777)
cd web && npm run test:e2e
# Electron e2e (requires xvfb on Linux headless)
cd electron && npm run test:e2ePrerequisites for E2E tests:
- Web tests require Playwright browsers:
cd web && npx playwright install chromium - Electron tests require:
- Built Electron app:
cd electron && npm run vite:build && npx tsc - Playwright browsers:
cd electron && npx playwright install chromium - On Linux headless: xvfb (test scripts handle this automatically)
- Built Electron app:
For detailed testing documentation, see web/TESTING.md.
We welcome:
- Bug reports and feature requests
- Code contributions
- New node creation
Open an issue before starting major work.
- General: [email protected]
- Team: [email protected], [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nodetool
Similar Open Source Tools

nodetool
NodeTool is a platform designed for AI enthusiasts, developers, and creators, providing a visual interface to access a variety of AI tools and models. It simplifies access to advanced AI technologies, offering resources for content creation, data analysis, automation, and more. With features like a visual editor, seamless integration with leading AI platforms, model manager, and API integration, NodeTool caters to both newcomers and experienced users in the AI field.
sandboxed.sh
sandboxed.sh is a self-hosted cloud orchestrator for AI coding agents that provides isolated Linux workspaces with Claude Code, OpenCode & Amp runtimes. It allows users to hand off entire development cycles, run multi-day operations unattended, and keep sensitive data local by analyzing data against scientific literature. The tool features dual runtime support, mission control for remote agent management, isolated workspaces, a git-backed library, MCP registry, and multi-platform support with a web dashboard and iOS app.

AionUi
AionUi is a user interface library for building modern and responsive web applications. It provides a set of customizable components and styles to create visually appealing user interfaces. With AionUi, developers can easily design and implement interactive web interfaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. The library is built using the latest web technologies and follows best practices for performance and accessibility. Whether you are working on a personal project or a professional application, AionUi can help you streamline the UI development process and deliver a seamless user experience.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.

OpenChat
OS Chat is a free, open-source AI personal assistant that combines 40+ language models with powerful automation capabilities. It allows users to deploy background agents, connect services like Gmail, Calendar, Notion, GitHub, and Slack, and get things done through natural conversation. With features like smart automation, service connectors, AI models, chat management, interface customization, and premium features, OS Chat offers a comprehensive solution for managing digital life and workflows. It prioritizes privacy by being open source and self-hostable, with encrypted API key storage.
local-cocoa
Local Cocoa is a privacy-focused tool that runs entirely on your device, turning files into memory to spark insights and power actions. It offers features like fully local privacy, multimodal memory, vector-powered retrieval, intelligent indexing, vision understanding, hardware acceleration, focused user experience, integrated notes, and auto-sync. The tool combines file ingestion, intelligent chunking, and local retrieval to build a private on-device knowledge system. The ultimate goal includes more connectors like Google Drive integration, voice mode for local speech-to-text interaction, and a plugin ecosystem for community tools and agents. Local Cocoa is built using Electron, React, TypeScript, FastAPI, llama.cpp, and Qdrant.
neuropilot
NeuroPilot is an open-source AI-powered education platform that transforms study materials into interactive learning resources. It provides tools like contextual chat, smart notes, flashcards, quizzes, and AI podcasts. Supported by various AI models and embedding providers, it offers features like WebSocket streaming, JSON or vector database support, file-based storage, and configurable multi-provider setup for LLMs and TTS engines. The technology stack includes Node.js, TypeScript, Vite, React, TailwindCSS, JSON database, multiple LLM providers, and Docker for deployment. Users can contribute to the project by integrating AI models, adding mobile app support, improving performance, enhancing accessibility features, and creating documentation and tutorials.
tingly-box
Tingly Box is a tool that helps in deciding which model to call, compressing context, and routing requests efficiently. It offers secure, reliable, and customizable functional extensions. With features like unified API, smart routing, context compression, auto API translation, blazing fast performance, flexible authentication, visual control panel, and client-side usage stats, Tingly Box provides a comprehensive solution for managing AI models and tokens. It supports integration with various IDEs, CLI tools, SDKs, and AI applications, making it versatile and easy to use. The tool also allows seamless integration with OAuth providers like Claude Code, enabling users to utilize existing quotas in OpenAI-compatible tools. Tingly Box aims to simplify AI model management and usage by providing a single endpoint for multiple providers with minimal configuration, promoting seamless integration with SDKs and CLI tools.
yournextstore
Your Next Store is an open-source Next.js e-commerce platform designed for AI development. It offers a Stripe-native integration, ultra-fast page loads, and typed APIs. The codebase follows consistent patterns, provides blazing fast performance with Next.js 16 and edge caching, and allows direct API integration without the need for plugins. With a focus on AI coding tools, Your Next Store offers familiar patterns, typed APIs for Commerce Kit SDK methods, and a well-defined domain for commerce data models, making it easier for AI models to generate accurate suggestions and write correct code.
astron-rpa
AstronRPA is an enterprise-grade Robotic Process Automation (RPA) desktop application that supports low-code/no-code development. It enables users to rapidly build workflows and automate desktop software and web pages. The tool offers comprehensive automation support for various applications, highly component-based design, enterprise-grade security and collaboration features, developer-friendly experience, native agent empowerment, and multi-channel trigger integration. It follows a frontend-backend separation architecture with components for system operations, browser automation, GUI automation, AI integration, and more. The tool is deployed via Docker and designed for complex RPA scenarios.
lean-spec
LeanSpec is a tool for Spec-Driven Development that aims to help users ship faster with higher quality by creating small, focused documents that both humans and AI can understand. It provides features like Kanban board, smart search, dependency tracking, web UI, project stats, and AI integration. The tool is designed to work with various AI coding assistants and offers agent skills to teach AI the Spec-Driven Development methodology. LeanSpec is compatible with tools like VS Code Copilot, Claude Code, GitHub Copilot, and more, and it requires Node.js, pnpm, and Rust for development. The desktop app has a separate repository for development, and the tool supports common development tasks like testing, building, and documentation.
seline
Seline is a local-first AI desktop application that integrates conversational AI, visual generation tools, vector search, and multi-channel connectivity. It allows users to connect WhatsApp, Telegram, or Slack to create always-on bots with full context and background task delivery. The application supports multi-channel connectivity, deep research mode, local web browsing with Puppeteer, local knowledge and privacy features, visual and creative tools, automation and agents, developer experience enhancements, and more. Seline is actively developed with a focus on improving user experience and functionality.

orbit
ORBIT (Open Retrieval-Based Inference Toolkit) is a middleware platform that provides a unified API for AI inference. It acts as a central gateway, allowing you to connect various local and remote AI models with your private data sources like SQL databases, vector stores, and local files. ORBIT uses a flexible adapter architecture to connect your data to AI models, creating specialized 'agents' for specific tasks. It supports scenarios like Knowledge Base Q&A and Chat with Your SQL Database, enabling users to interact with AI models seamlessly. The tool offers a RESTful API for programmatic access and includes features like authentication, API key management, system prompts, health monitoring, and file management. ORBIT is designed to streamline AI inference tasks and facilitate interactions between users and AI models.

InsForge
InsForge is a backend development platform designed for AI coding agents and AI code editors. It serves as a semantic layer that enables agents to interact with backend primitives such as databases, authentication, storage, and functions in a meaningful way. The platform allows agents to fetch backend context, configure primitives, and inspect backend state through structured schemas. InsForge facilitates backend context engineering for AI coding agents to understand, operate, and monitor backend systems effectively.
steedos-platform
Steedos Platform is an enterprise-grade implementation of the ObjectStack architecture, combining Metadata Driven Architecture with Generative AI. It provides a Universal Metadata Standard (ObjectQL) for AI to generate complex applications instantly. The platform consists of ObjectQL (Protocol), ObjectOS (Engine), and Object UI (Renderer), offering AI data modeling, generative UI, and logic & automation capabilities. Users can transition from a monolithic structure to a monorepo workspace with core type definitions, ORM, frontend rendering engine, and modular business application packages. Steedos Platform aims to redefine software development by leveraging AI and metadata to build applications faster and more efficiently.
LingEcho-App
LingEcho is an enterprise-grade intelligent voice interaction platform that integrates advanced speech recognition, text-to-speech, large language models, and real-time communication technologies. It provides features such as AI character real-time calls, voice cloning, workflow automation, knowledge base management, application integration, device management, alert system, billing system, organization management, key management, VAD voice activity detection, voiceprint recognition service, ASR-TTS service, MCP service, and hardware device support.
For similar tasks
Awesome-AITools
This repo collects AI-related utilities. ## All Categories * All Categories * ChatGPT and other closed-source LLMs * AI Search engine * Open Source LLMs * GPT/LLMs Applications * LLM training platform * Applications that integrate multiple LLMs * AI Agent * Writing * Programming Development * Translation * AI Conversation or AI Voice Conversation * Image Creation * Speech Recognition * Text To Speech * Voice Processing * AI generated music or sound effects * Speech translation * Video Creation * Video Content Summary * OCR(Optical Character Recognition)
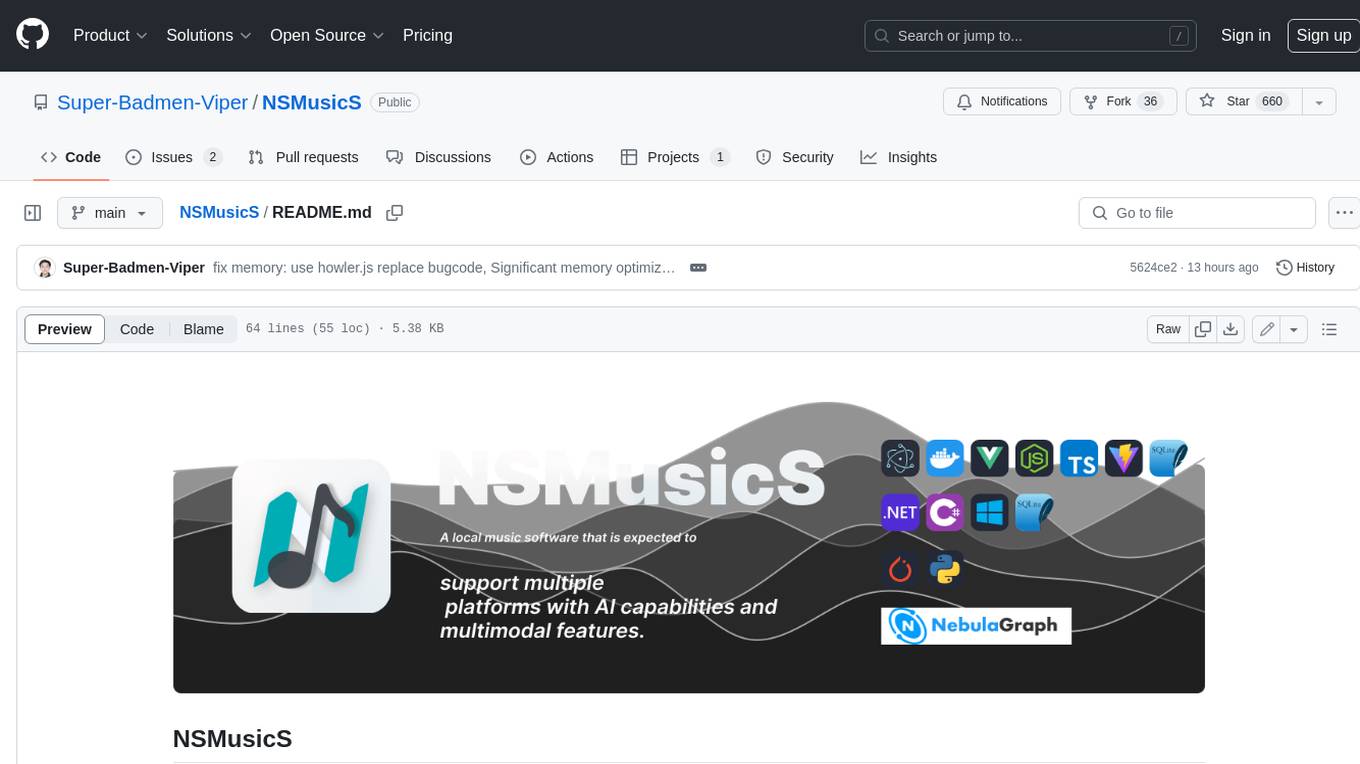
NSMusicS
NSMusicS is a local music software that is expected to support multiple platforms with AI capabilities and multimodal features. The goal of NSMusicS is to integrate various functions (such as artificial intelligence, streaming, music library management, cross platform, etc.), which can be understood as similar to Navidrome but with more features than Navidrome. It wants to become a plugin integrated application that can almost have all music functions.
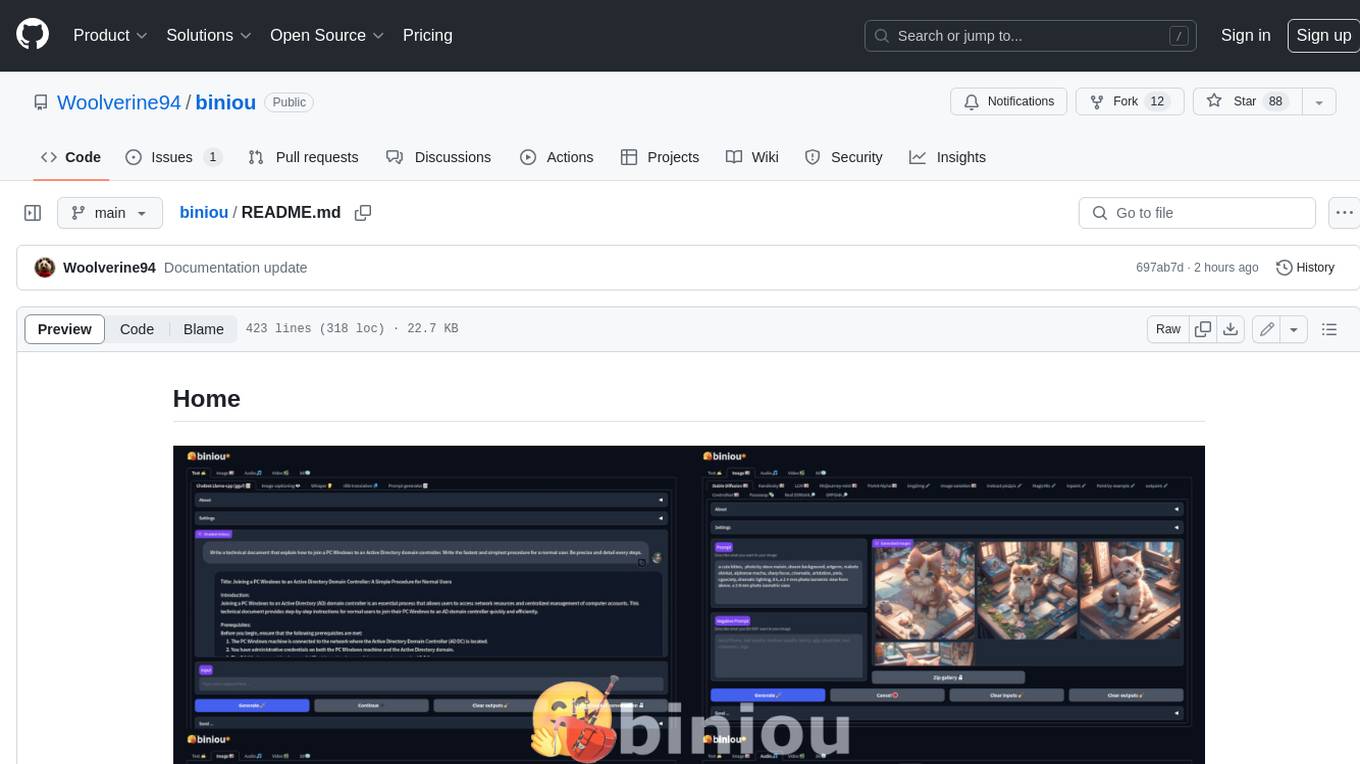
biniou
biniou is a self-hosted webui for various GenAI (generative artificial intelligence) tasks. It allows users to generate multimedia content using AI models and chatbots on their own computer, even without a dedicated GPU. The tool can work offline once deployed and required models are downloaded. It offers a wide range of features for text, image, audio, video, and 3D object generation and modification. Users can easily manage the tool through a control panel within the webui, with support for various operating systems and CUDA optimization. biniou is powered by Huggingface and Gradio, providing a cross-platform solution for AI content generation.
generative-ai-js
Generative AI JS is a JavaScript library that provides tools for creating generative art and music using artificial intelligence techniques. It allows users to generate unique and creative content by leveraging machine learning models. The library includes functions for generating images, music, and text based on user input and preferences. With Generative AI JS, users can explore the intersection of art and technology, experiment with different creative processes, and create dynamic and interactive content for various applications.
pictureChange
The 'pictureChange' repository is a plugin that supports image processing using Baidu AI, stable diffusion webui, and suno music composition AI. It also allows for file summarization and image summarization using AI. The plugin supports various stable diffusion models, administrator control over group chat features, concurrent control, and custom templates for image and text generation. It can be deployed on WeChat enterprise accounts, personal accounts, and public accounts.
Generative-AI-Indepth-Basic-to-Advance
Generative AI Indepth Basic to Advance is a repository focused on providing tutorials and resources related to generative artificial intelligence. The repository covers a wide range of topics from basic concepts to advanced techniques in the field of generative AI. Users can find detailed explanations, code examples, and practical demonstrations to help them understand and implement generative AI algorithms. The goal of this repository is to help beginners get started with generative AI and to provide valuable insights for more experienced practitioners.

nodetool
NodeTool is a platform designed for AI enthusiasts, developers, and creators, providing a visual interface to access a variety of AI tools and models. It simplifies access to advanced AI technologies, offering resources for content creation, data analysis, automation, and more. With features like a visual editor, seamless integration with leading AI platforms, model manager, and API integration, NodeTool caters to both newcomers and experienced users in the AI field.
ai-enhanced-audio-book
The ai-enhanced-audio-book repository contains AI-enhanced audio plugins developed using C++, JUCE, libtorch, RTNeural, and other libraries. It showcases neural networks learning to emulate guitar amplifiers through waveforms. Users can visit the official website for more information and obtain a copy of the book from the publisher Taylor and Francis/ Routledge/ Focal.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.








