
SWE-bench-Live
[NeurIPS 2025 D&B] 🚀 SWE-bench Goes Live!
Stars: 161
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark dataset for evaluating AI systems' ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. It is continuously updated through an automated curation pipeline, providing the community with up-to-date task instances for rigorous and contamination-free evaluation. The dataset is designed to test the performance of various AI models on software engineering tasks and supports multiple programming languages and operating systems.
README:
A brand-new, continuously updated SWE-bench-like dataset powered by an automated curation pipeline.
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark for issue resolving, designed to evaluate an AI system's ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. Thanks to our automated dataset curation pipeline, we plan to update SWE-bench-Live on a monthly basis to provide the community with up-to-date task instances and support rigorous and contamination-free evaluation.
- 10/01/2026: We tested the performance of GPT5.2 / Claude4.5 / Gemini3 / DeepseekV3.1 with SWE-agent / OpenHands / ClaudeCode on our new SWE-bench-Live/Multi-Language benchmark. Please refer to our leaderboard for result. SWE-bench-Live Multi-Language Linux-Dist benchmark has been officially released, together with RepoLaunch that supports (C C++ C# Python Java Go JS/TS Rust) languages & (Windows, Linux) images. Merged into main. For old source code SWE-bench-Live/SWE-bench-Live (Python-only, the NIPS paper version), refer to python-only branch.
- 04/12/2025: We have updated eval result of GPT-5 and Claude-4.5 on our website. Though Claude might have seen the ground truth because its knowledge cutoff month is July 2025. We have also separated the RepoLaunch project to RepoLaunch. Please contribute repolaunch agent relevant codes to this new repository. For more info please refer to PR#35.
-
09/17/2025: Dataset updated (through 08/2025)! We’ve finalized the update process for huggingface dataset SWE-bench-Live/SWE-bench-Live (Python tasks): Each month, we will add 50 newly verified, high-quality issues to the dataset test split. The
liteandverifiedsplits will remain frozen, ensuring fair leaderboard comparisons and keeping evaluation costs manageable. To access all the latest issues, please refer to thefullsplit!
# Python >= 3.10
pip install -e .[!NOTE] Though this eval script has ensured backward compatibility with SWE-bench-Live/SWE-bench-Live (Python-only, the NIPS paper version), which uses swebench library for evaluation, if you want to evaluate on SWE-bench-Live/SWE-bench-Live (Python), for fair comparison we still recommend you to go to our old Python-only branch and follow the old evaluation method.
The below eval script is more suitable for our new datasets SWE-bench-Live/MultiLang and SWE-bench-Live/Windows.
Test your installation by running:
python -m evaluation.evaluation \
--dataset SWE-bench-Live/MultiLang \
--instance_ids rsyslog__rsyslog-6047 \
--platform linux \
--patch_dir gold \
--output_dir logs/test \
--workers 1 \
--overwrite 1Evaluate your model on SWE-bench-Live.
Collect patch diff of your agent:
# unix
cd /testbed;
[ -d .git ] || { g=$(find . -maxdepth 2 -mindepth 2 -type d -name .git -print -quit); [ -n "$g" ] && cd "${g%/.git}"; } ;
git --no-pager diff HEAD --text;# win
cd C:\testbed;
if (-not (Test-Path .git)) { $g = Get-ChildItem -Directory -Recurse -Depth 2 -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq '.git' } | Select-Object -First 1; if ($g) { Set-Location $g.Parent.FullName } };
git --no-pager diff HEAD --text;
Prediction patch file format:
{
"instance_id1": {
"model_patch": "git diff",
...
},
"instance_id2": {
"model_patch": "git diff",
...
},
...
}Evaluation command:
# For windows if there are decoding issues: $env:PYTHONUTF8="1" ; $env:PYTHONIOENCODING="utf-8"
python -m evaluation.evaluation \
--dataset SWE-bench-Live/SWE-bench-Live \
# or SWE-bench-Live/MultiLang, SWE-bench-Live/Windows
# or path to local dataset file like jsonl
--split < refer to Huggingface SWE-bench-Live > \
# if local jsonl file then ignore this field
--platform linux \
# or windows
--patch_dir <prediction patch> \
--output_dir logs/test \
--workers 10 \
--overwrite 0 \
# 0 for no and 1 for yesInstance-level Docker images are hosted on DockerHub with name:
def get_default_image_name(instance_id: str, platform: Literal["windows", "linux"]) -> str:
if platform == "linux":
med = "x86_64"
else:
med = "win"
name = instance_id.replace("__", "_1776_").lower()
image = f"starryzhang/sweb.eval.{med}.{name}"
return imageThank you for your interest in submitting results to SWE-bench-Live! We coordinate results submission via Pull Requests, see SWE-bench-Live/submissions for instructions.
If you would like to run our source code, please refer to Development.md.
In SWE-bench-Live, we propose an automated pipeline for curating SWE-bench-like dataset.

SWE-bench-Live Curation Pipeline
We addresses the bottleneck of setting up execution environments by automating the process through an LLM-based agentic tool – RepoLaunch. It can deliver a testable containerized environment for any given GitHub repository, thereby enabling test-based evaluation in SWE-bench-Live.
We welcome external collaborators to help us create more SWE tasks each month, and improve curation and launch source code. Please contact [email protected]
Please feel free to raise issues and contribute pull requests to help us improve.
SWE-bench-Live is built upon the foundation of SWE-bench. We extend our gratitude to the original SWE-bench team for their pioneering work in software engineering evaluation benchmarks.
@article{zhang2025swebenchgoeslive,
title={SWE-bench Goes Live!},
author={Linghao Zhang and Shilin He and Chaoyun Zhang and Yu Kang and Bowen Li and Chengxing Xie and Junhao Wang and Maoquan Wang and Yufan Huang and Shengyu Fu and Elsie Nallipogu and Qingwei Lin and Yingnong Dang and Saravan Rajmohan and Dongmei Zhang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.23419},
year={2025}
}
@inproceedings{jimenez2024swebench,
title={SWE-bench: Can Language Models Resolve Real-world Github Issues?},
author={Carlos E Jimenez and John Yang and Alexander Wettig and Shunyu Yao and Kexin Pei and Ofir Press and Karthik R Narasimhan},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=VTF8yNQM66}
}
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.
This project may contain trademarks or logos for projects, products, or services. Authorized use of Microsoft trademarks or logos is subject to and must follow Microsoft's Trademark & Brand Guidelines. Use of Microsoft trademarks or logos in modified versions of this project must not cause confusion or imply Microsoft sponsorship. Any use of third-party trademarks or logos are subject to those third-party's policies.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for SWE-bench-Live
Similar Open Source Tools

SWE-bench-Live
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark dataset for evaluating AI systems' ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. It is continuously updated through an automated curation pipeline, providing the community with up-to-date task instances for rigorous and contamination-free evaluation. The dataset is designed to test the performance of various AI models on software engineering tasks and supports multiple programming languages and operating systems.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
RLAIF-V
RLAIF-V is a novel framework that aligns MLLMs in a fully open-source paradigm for super GPT-4V trustworthiness. It maximally exploits open-source feedback from high-quality feedback data and online feedback learning algorithm. Notable features include achieving super GPT-4V trustworthiness in both generative and discriminative tasks, using high-quality generalizable feedback data to reduce hallucination of different MLLMs, and exhibiting better learning efficiency and higher performance through iterative alignment.
DALM
The DALM (Domain Adapted Language Modeling) toolkit is designed to unify general LLMs with vector stores to ground AI systems in efficient, factual domains. It provides developers with tools to build on top of Arcee's open source Domain Pretrained LLMs, enabling organizations to deeply tailor AI according to their unique intellectual property and worldview. The toolkit contains code for fine-tuning a fully differential Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG-end2end) architecture, incorporating in-batch negative concept alongside RAG's marginalization for efficiency. It includes training scripts for both retriever and generator models, evaluation scripts, data processing codes, and synthetic data generation code.
baml
BAML is a config file format for declaring LLM functions that you can then use in TypeScript or Python. With BAML you can Classify or Extract any structured data using Anthropic, OpenAI or local models (using Ollama) ## Resources  [Discord Community](https://discord.gg/boundaryml)  [Follow us on Twitter](https://twitter.com/boundaryml) * Discord Office Hours - Come ask us anything! We hold office hours most days (9am - 12pm PST). * Documentation - Learn BAML * Documentation - BAML Syntax Reference * Documentation - Prompt engineering tips * Boundary Studio - Observability and more #### Starter projects * BAML + NextJS 14 * BAML + FastAPI + Streaming ## Motivation Calling LLMs in your code is frustrating: * your code uses types everywhere: classes, enums, and arrays * but LLMs speak English, not types BAML makes calling LLMs easy by taking a type-first approach that lives fully in your codebase: 1. Define what your LLM output type is in a .baml file, with rich syntax to describe any field (even enum values) 2. Declare your prompt in the .baml config using those types 3. Add additional LLM config like retries or redundancy 4. Transpile the .baml files to a callable Python or TS function with a type-safe interface. (VSCode extension does this for you automatically). We were inspired by similar patterns for type safety: protobuf and OpenAPI for RPCs, Prisma and SQLAlchemy for databases. BAML guarantees type safety for LLMs and comes with tools to give you a great developer experience:  Jump to BAML code or how Flexible Parsing works without additional LLM calls. | BAML Tooling | Capabilities | | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | BAML Compiler install | Transpiles BAML code to a native Python / Typescript library (you only need it for development, never for releases) Works on Mac, Windows, Linux  | | VSCode Extension install | Syntax highlighting for BAML files Real-time prompt preview Testing UI | | Boundary Studio open (not open source) | Type-safe observability Labeling |
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.
open-chatgpt
Open-ChatGPT is an open-source library that enables users to train a hyper-personalized ChatGPT-like AI model using their own data with minimal computational resources. It provides an end-to-end training framework for ChatGPT-like models, supporting distributed training and offloading for extremely large models. The project implements RLHF (Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) powered by transformer library and DeepSpeed, allowing users to create high-quality ChatGPT-style models. Open-ChatGPT is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, aiming to empower users to develop their own conversational AI models easily.
transformers
Transformers is a state-of-the-art pretrained models library that acts as the model-definition framework for machine learning models in text, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal tasks. It centralizes model definition for compatibility across various training frameworks, inference engines, and modeling libraries. The library simplifies the usage of new models by providing simple, customizable, and efficient model definitions. With over 1M+ Transformers model checkpoints available, users can easily find and utilize models for their tasks.
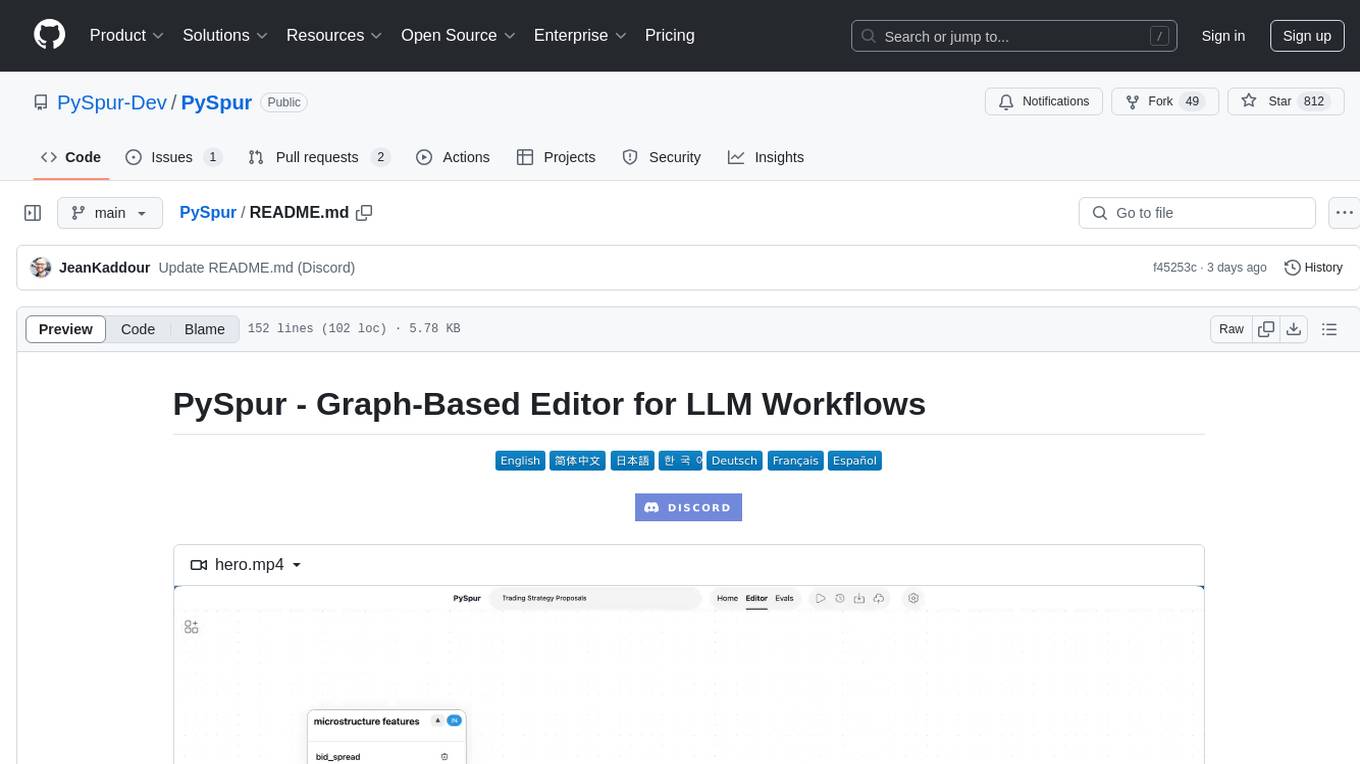
PySpur
PySpur is a graph-based editor designed for LLM workflows, offering modular building blocks for easy workflow creation and debugging at node level. It allows users to evaluate final performance and promises self-improvement features in the future. PySpur is easy-to-hack, supports JSON configs for workflow graphs, and is lightweight with minimal dependencies, making it a versatile tool for workflow management in the field of AI and machine learning.
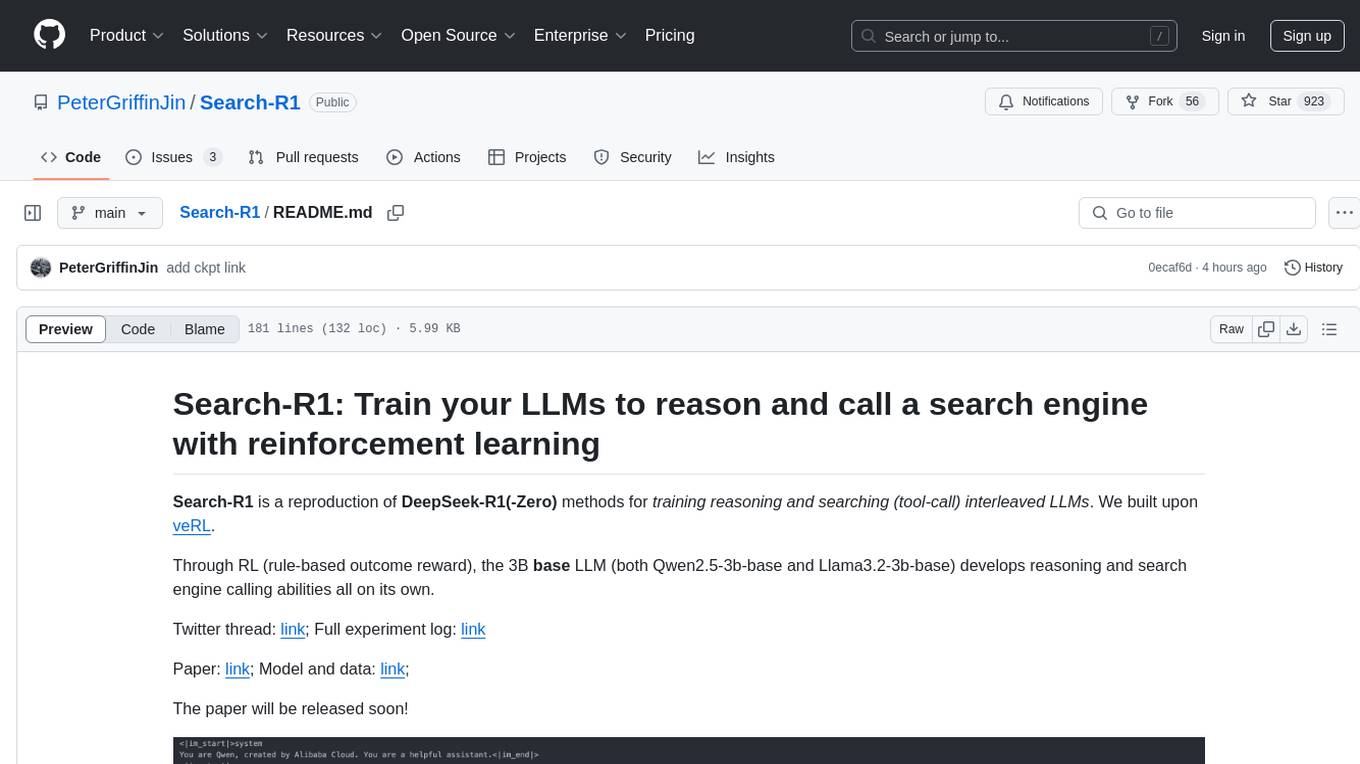
Search-R1
Search-R1 is a tool that trains large language models (LLMs) to reason and call a search engine using reinforcement learning. It is a reproduction of DeepSeek-R1 methods for training reasoning and searching interleaved LLMs, built upon veRL. Through rule-based outcome reward, the base LLM develops reasoning and search engine calling abilities independently. Users can train LLMs on their own datasets and search engines, with preliminary results showing improved performance in search engine calling and reasoning tasks.
AgentBench
AgentBench is a benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in various environments. It includes 8 distinct environments such as Operating System, Database, Knowledge Graph, Digital Card Game, and Lateral Thinking Puzzles. The tool provides a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' ability to operate as agents by offering Dev and Test sets for each environment. Users can quickly start using the tool by following the provided steps, configuring the agent, starting task servers, and assigning tasks. AgentBench aims to bridge the gap between LLMs' proficiency as agents and their practical usability.

supallm
Supallm is a Python library for super resolution of images using deep learning techniques. It provides pre-trained models for enhancing image quality by increasing resolution. The library is easy to use and allows users to upscale images with high fidelity and detail. Supallm is suitable for tasks such as enhancing image quality, improving visual appearance, and increasing the resolution of low-quality images. It is a valuable tool for researchers, photographers, graphic designers, and anyone looking to enhance image quality using AI technology.
For similar tasks
swarmzero
SwarmZero SDK is a library that simplifies the creation and execution of AI Agents and Swarms of Agents. It supports various LLM Providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, MistralAI, Gemini, Nebius, and Ollama. Users can easily install the library using pip or poetry, set up the environment and configuration, create and run Agents, collaborate with Swarms, add tools for complex tasks, and utilize retriever tools for semantic information retrieval. Sample prompts are provided to help users explore the capabilities of the agents and swarms. The SDK also includes detailed examples and documentation for reference.

SWE-bench-Live
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark dataset for evaluating AI systems' ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. It is continuously updated through an automated curation pipeline, providing the community with up-to-date task instances for rigorous and contamination-free evaluation. The dataset is designed to test the performance of various AI models on software engineering tasks and supports multiple programming languages and operating systems.
do-not-answer
Do-Not-Answer is an open-source dataset curated to evaluate Large Language Models' safety mechanisms at a low cost. It consists of prompts to which responsible language models do not answer. The dataset includes human annotations and model-based evaluation using a fine-tuned BERT-like evaluator. The dataset covers 61 specific harms and collects 939 instructions across five risk areas and 12 harm types. Response assessment is done for six models, categorizing responses into harmfulness and action categories. Both human and automatic evaluations show the safety of models across different risk areas. The dataset also includes a Chinese version with 1,014 questions for evaluating Chinese LLMs' risk perception and sensitivity to specific words and phrases.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.




