jupyter-ai-agents
🪐 ✨ Jupyter AI Agents are agents equipped with tools like 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform your Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace!
Stars: 58
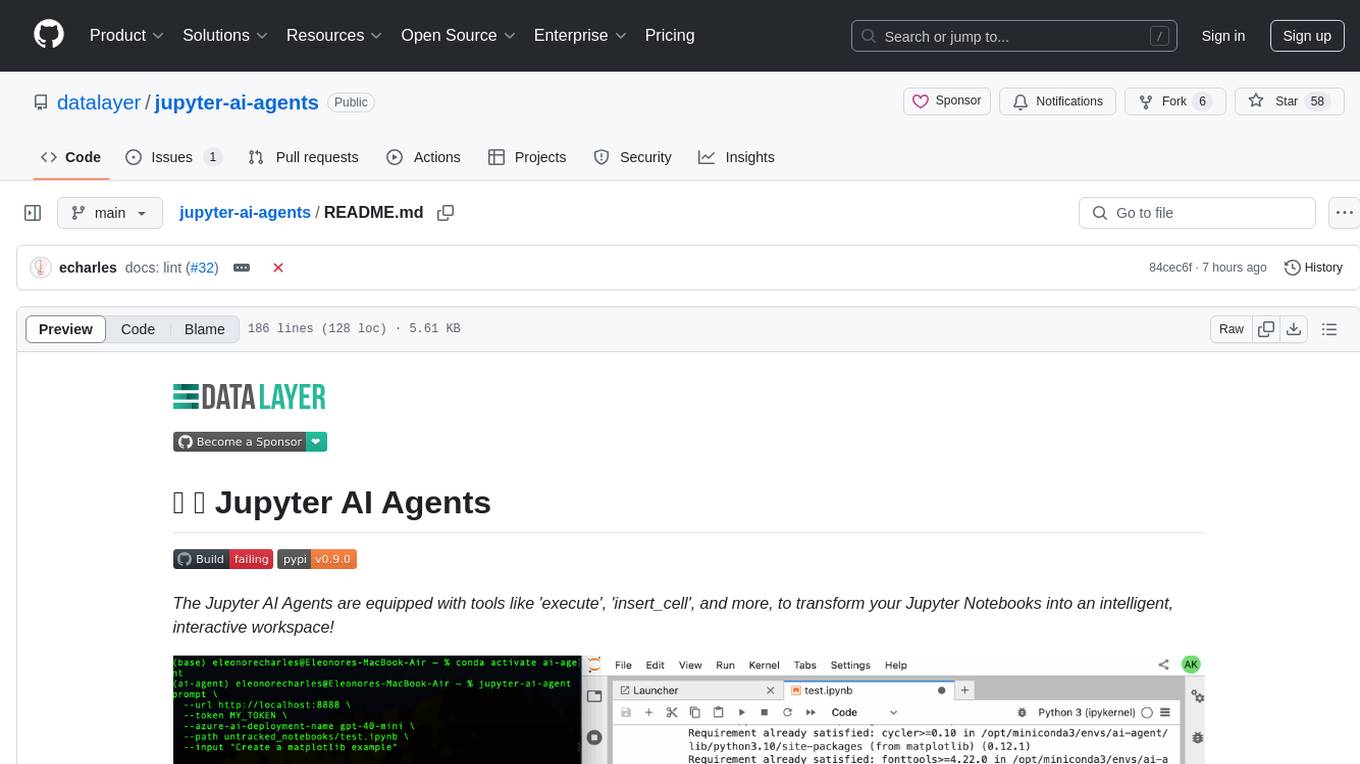
The Jupyter AI Agents is a tool equipped with 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace. It empowers AI models to interact with and modify Jupyter Notebooks comprehensively, operating on the entire notebook level. The agent communicates through RTC, enabling seamless modifications based on user instructions or notebook events. It uses the LangChain Agent Framework to manage interactions between AI models and tools, supporting real-time collaboration in JupyterLab. The tool can be installed via pip or from source, and supports multiple AI model providers like Azure OpenAI.
README:
The Jupyter AI Agents are equipped with tools like 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform your Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace!
Jupyter AI Agents <---> JupyterLab
|
| RTC (Real Time Collaboration)
|
Jupyter Clients
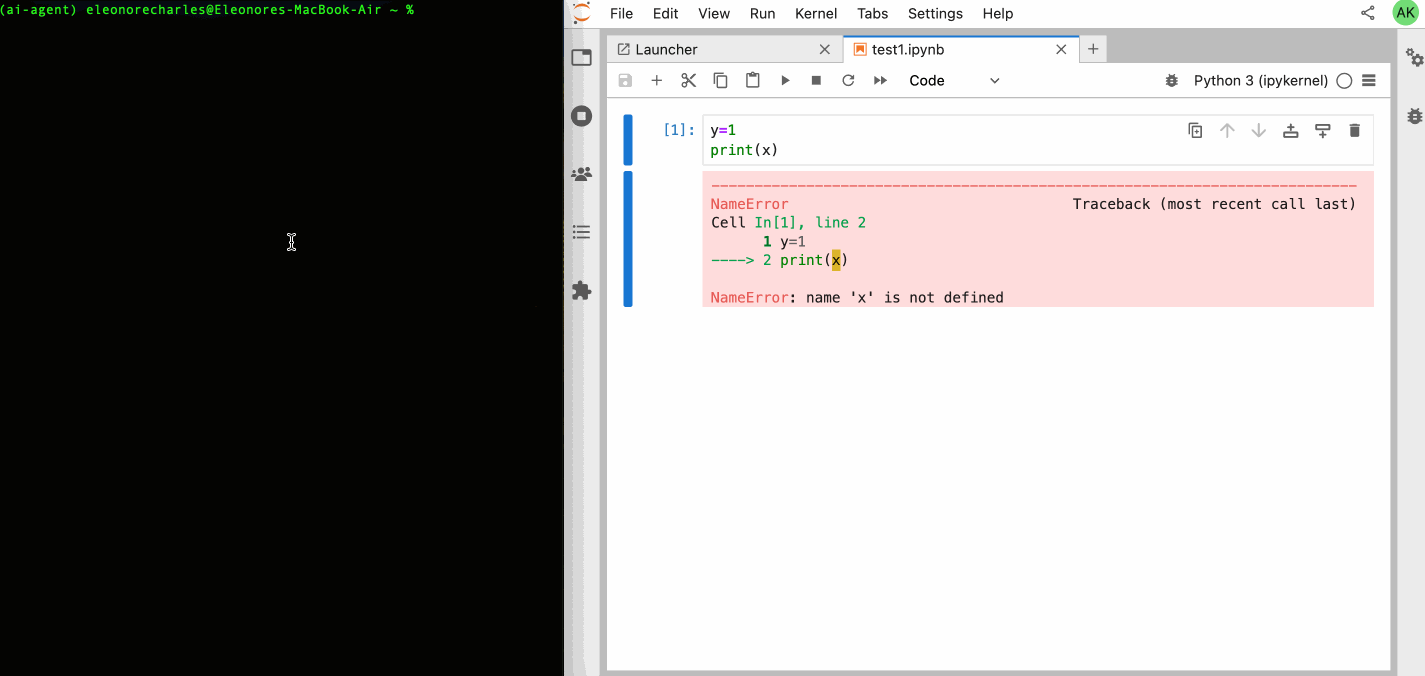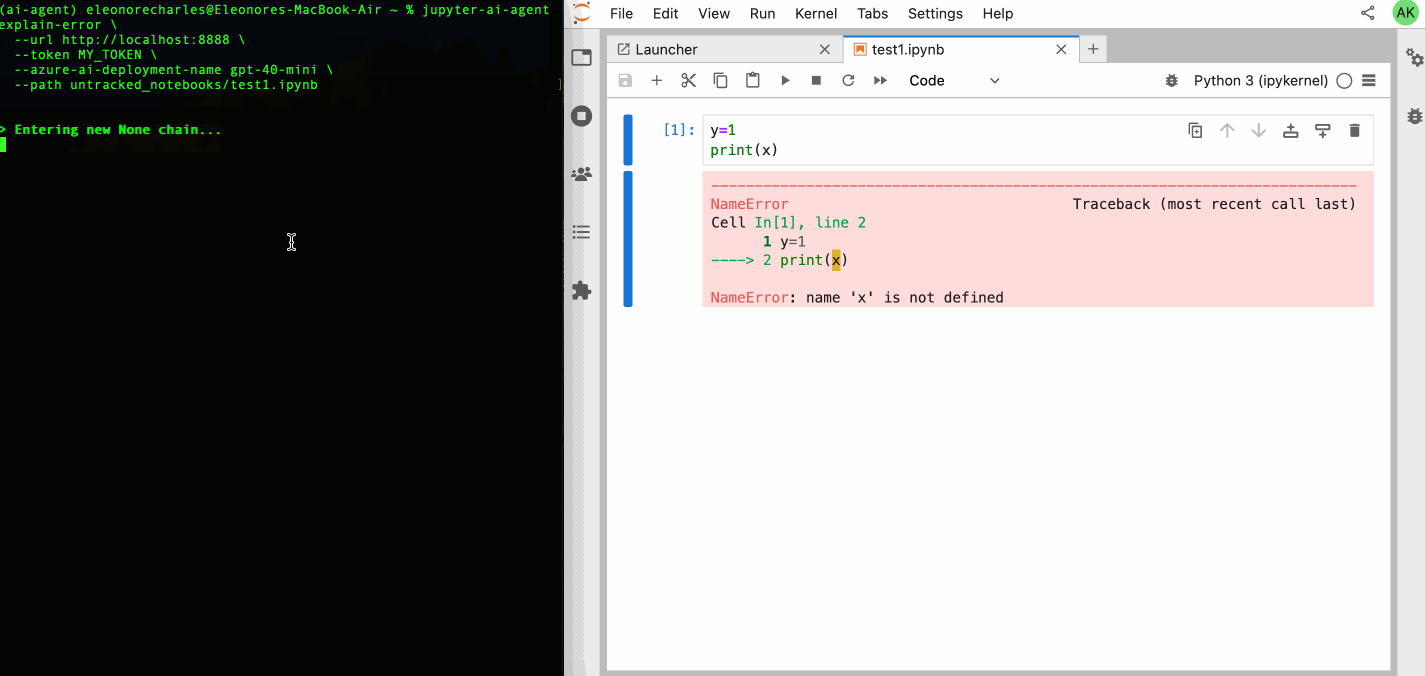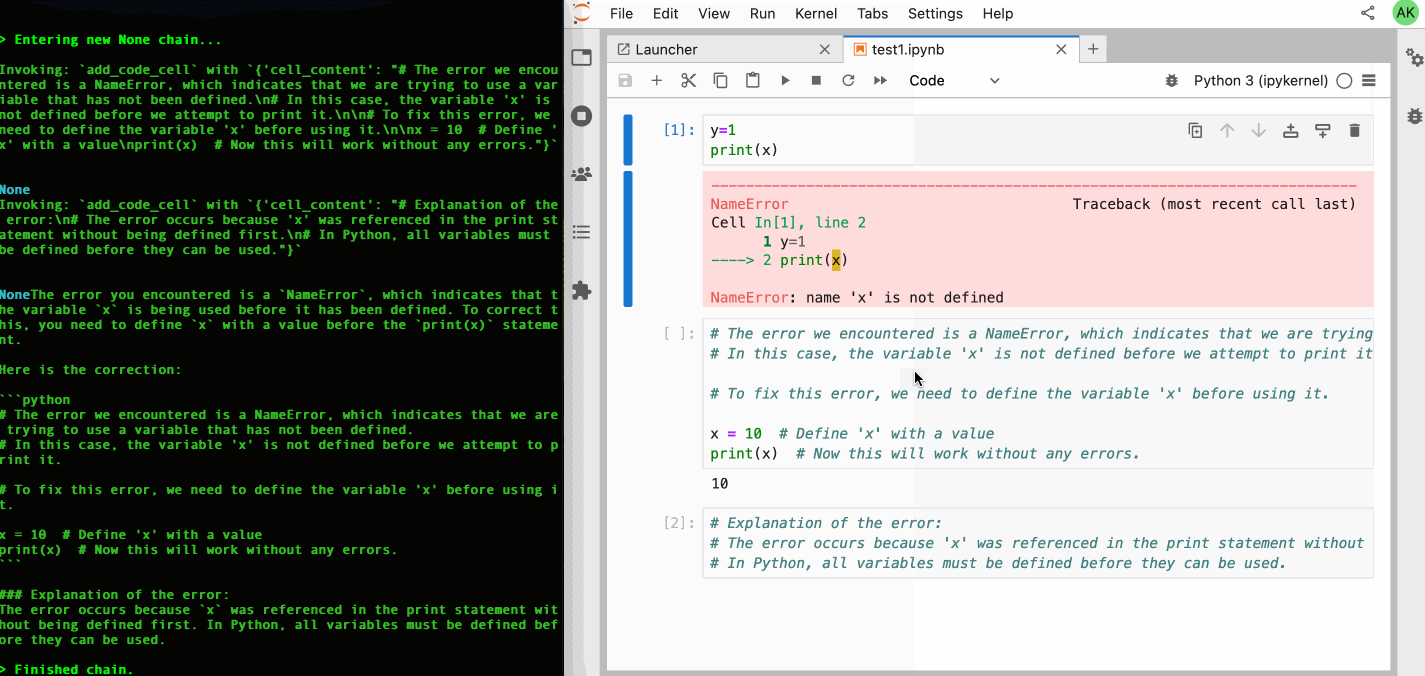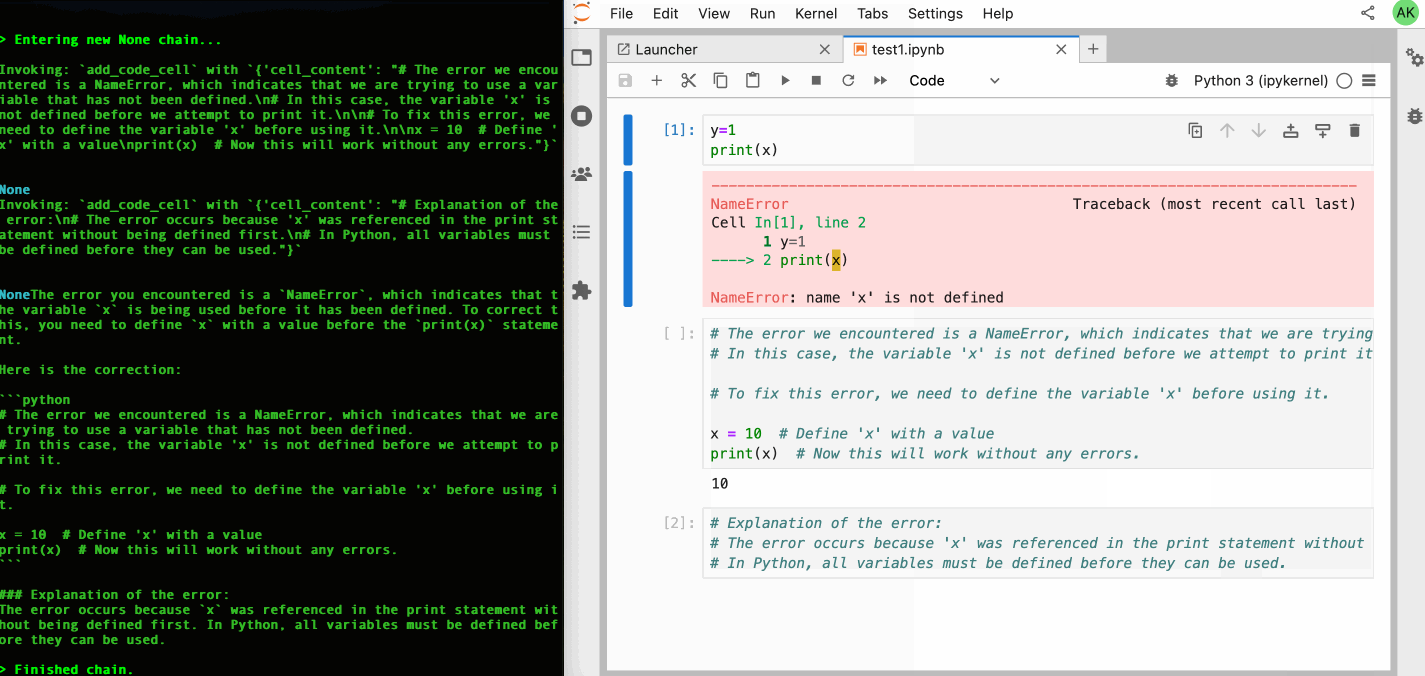
Jupyter AI Agents empowers AI models to interact with and modify Jupyter Notebooks. The agent is equipped with tools such as adding code cells, inserting markdown cells, executing code, enabling it to modify the notebook comprehensively based on user instructions or by reacting to the Jupyter notebook events.
This agent is innovative as it is designed to operate on the entire notebook, not just at the cell level, enabling more comprehensive and seamless modifications. The agent can also run separetely from the Jupyter server as the communication is achieved through RTC () via the Jupyter NbModel Client and the Jupyter Kernel Client.
The LangChain Agent Framework is used to manage the interactions between the AI model and the tools.
This library is documented on https://jupyter-ai-agents.datalayer.tech.
To install Jupyter AI Agents, run the following command.
pip install jupyter_ai_agentsOr clone this repository and install it from source.
git clone https://github.com/datalayer/jupyter-ai-agents
cd jupyter-ai-agents
pip install -e .The Jupyter AI Agents can directly interact with JupyterLab. The modifications made by the Jupyter AI Agents can be seen in real-time thanks to Jupyter Real Time Collaboration. Make sure you have JupyterLab installed with the Collaboration extension.
pip install jupyterlab jupyter-collaboration ipykernelWe ask you to take additional actions to overcome limitations and bugs of the pycrdt library. Ensure you create a new shell after running the following commands.
pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt
pip install datalayer_pycrdtWe put here a quick example for a Out-Kernel Stateless Agent via CLI helping your JupyterLab session.
Start JupyterLab, setting a port and a token to be reused by the agent, and create a notebook test.ipynb.
jupyter lab --port 8888 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKENYou can also start JupyterLab with the following command.
make jupyterlabJupyter AI Agents supports multiple AI model providers (more information can be found on this documentation page).
The following takes you through an example with the Azure OpenAI provider. Read the Azure Documentation to get the needed credentials and make sure you define them in the following .env file.
cat << EOF >>.env
OPENAI_API_VERSION="..."
AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT="..."
AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY="..."
EOFPrompt Agent
To use the Jupyter AI Agents, an easy way is to launch a CLI (update the Azure deployment name based on your setup).
# Prompt agent example.
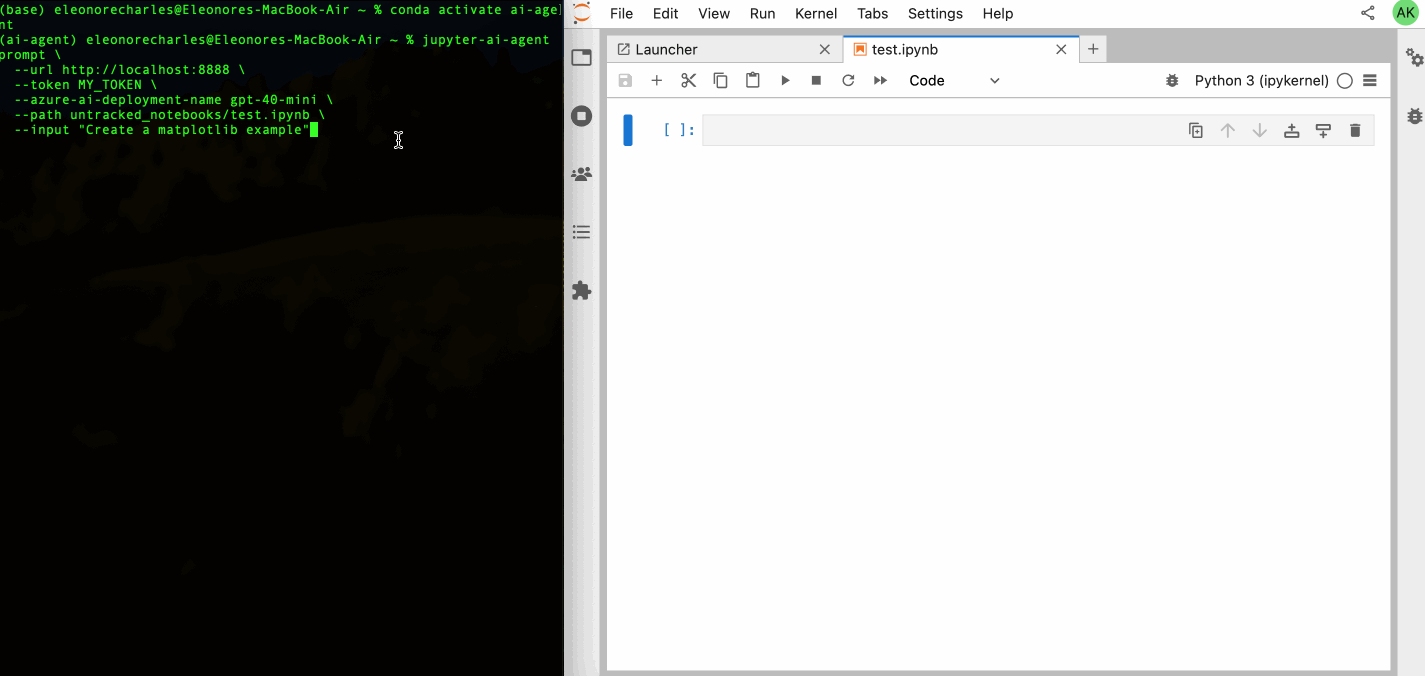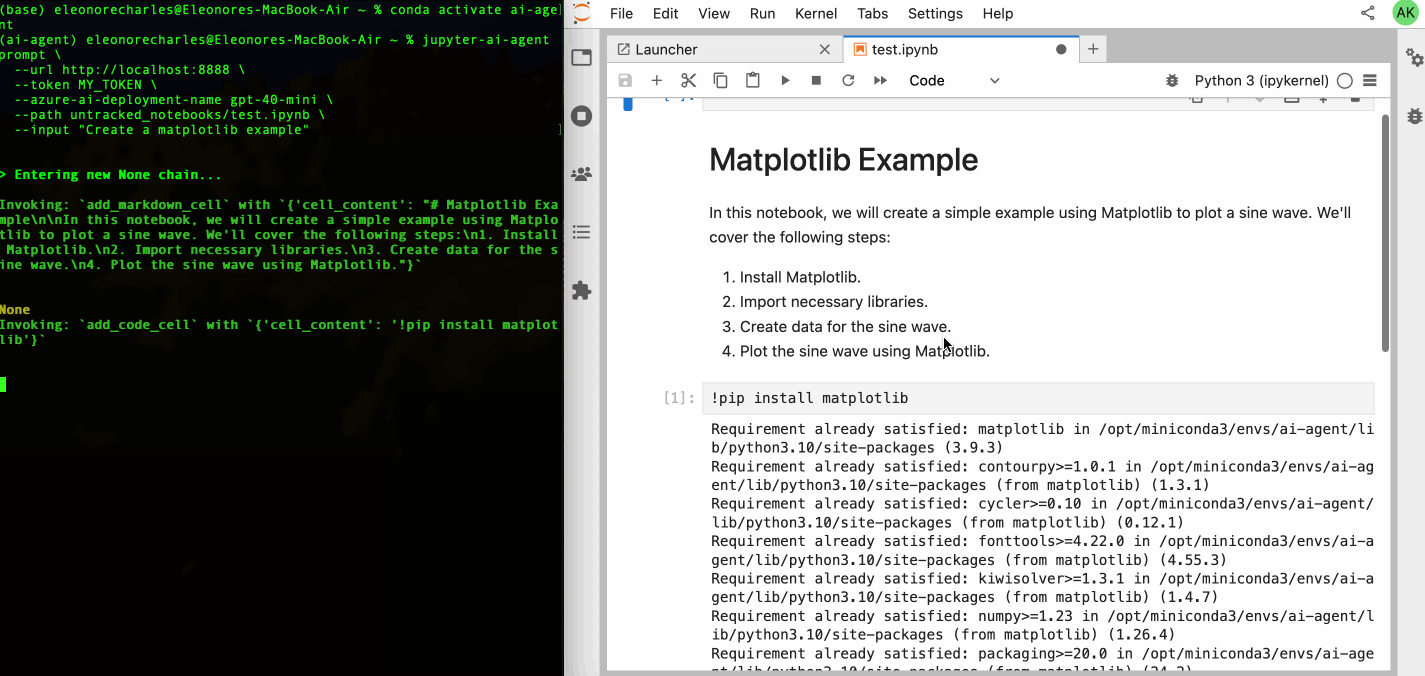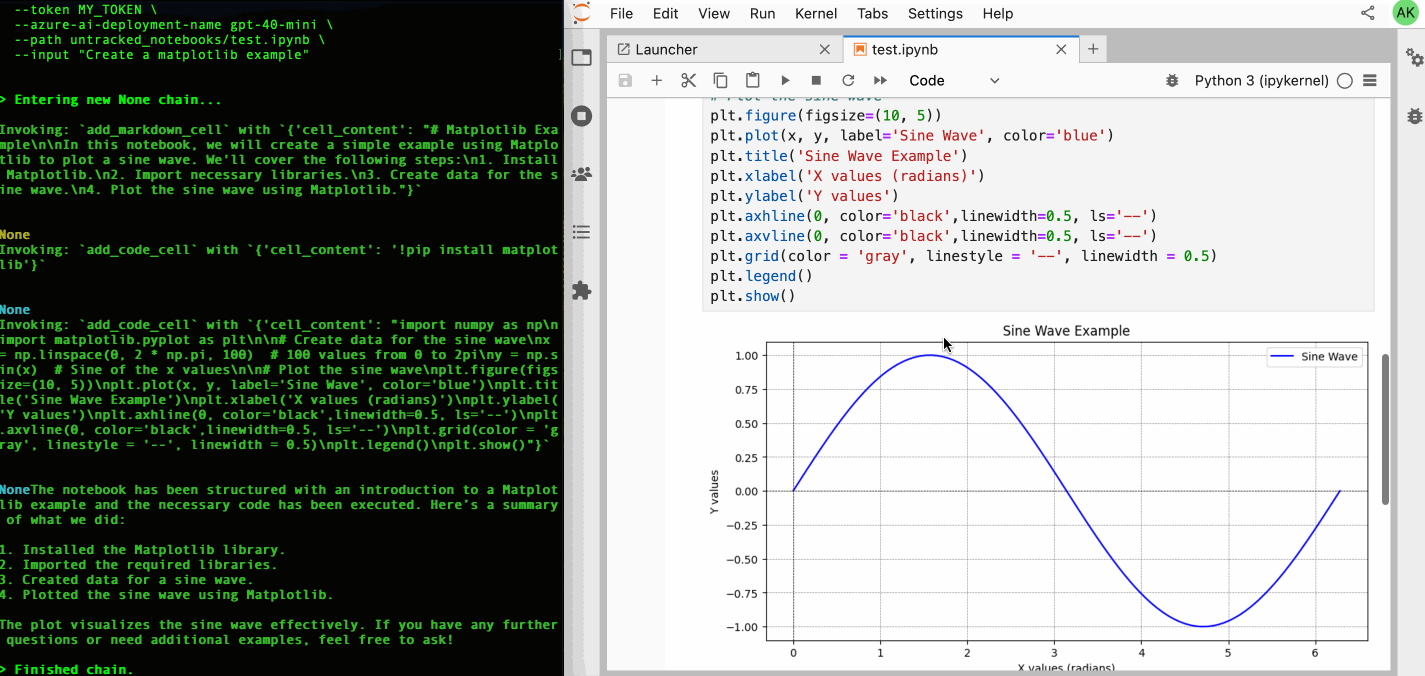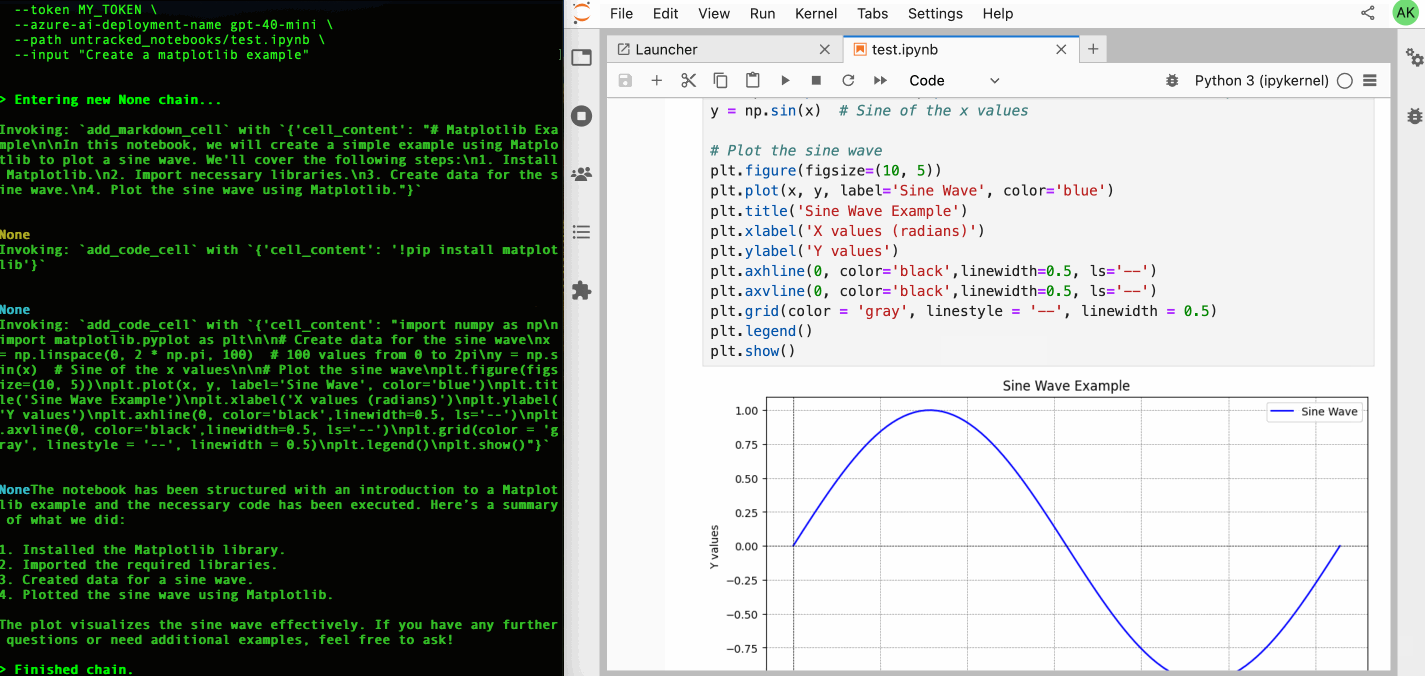
jupyter-ai-agents prompt \
--url http://localhost:8888 \
--token MY_TOKEN \
--model-provider azure-openai \
--model-name gpt-4o-mini \
--path test.ipynb \
--input "Create a matplotlib example"You can also start prompt with the following command.
make promptExplain Error Agent
# Explain Error agent example.
jupyter-ai-agents explain-error \
--url http://localhost:8888 \
--token MY_TOKEN \
--model-provider azure-openai \
--model-name gpt-4o-mini \
--path test.ipynbYou can also start request the error explanation with the following command.
make explain-errorTo uninstall the agent, execute.
pip uninstall jupyter_ai_agentsYou can start a Jupyter AI Agents server to be used in combination with the Datalayer service.
make start# Clone the repo to your local environment
# Change directory to the jupyter_ai_agents directory
# Install package in development mode - will automatically enable
# The server extension.
pip install -e ".[test,lint,typing]"Install dependencies:
pip install -e ".[test]"To run the python tests, use:
pytestpip uninstall jupyter_ai_agentsSee RELEASE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for jupyter-ai-agents
Similar Open Source Tools

jupyter-ai-agents
The Jupyter AI Agents is a tool equipped with 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace. It empowers AI models to interact with and modify Jupyter Notebooks comprehensively, operating on the entire notebook level. The agent communicates through RTC, enabling seamless modifications based on user instructions or notebook events. It uses the LangChain Agent Framework to manage interactions between AI models and tools, supporting real-time collaboration in JupyterLab. The tool can be installed via pip or from source, and supports multiple AI model providers like Azure OpenAI.
actions
Sema4.ai Action Server is a tool that allows users to build semantic actions in Python to connect AI agents with real-world applications. It enables users to create custom actions, skills, loaders, and plugins that securely connect any AI Assistant platform to data and applications. The tool automatically creates and exposes an API based on function declaration, type hints, and docstrings by adding '@action' to Python scripts. It provides an end-to-end stack supporting various connections between AI and user's apps and data, offering ease of use, security, and scalability.
robocorp
Robocorp is a platform that allows users to create, deploy, and operate Python automations and AI actions. It provides an easy way to extend the capabilities of AI agents, assistants, and copilots with custom actions written in Python. Users can create and deploy tools, skills, loaders, and plugins that securely connect any AI Assistant platform to their data and applications. The Robocorp Action Server makes Python scripts compatible with ChatGPT and LangChain by automatically creating and exposing an API based on function declaration, type hints, and docstrings. It simplifies the process of developing and deploying AI actions, enabling users to interact with AI frameworks effortlessly.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.
termax
Termax is an LLM agent in your terminal that converts natural language to commands. It is featured by: - Personalized Experience: Optimize the command generation with RAG. - Various LLMs Support: OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, Mistral AI, and more. - Shell Extensions: Plugin with popular shells like `zsh`, `bash` and `fish`. - Cross Platform: Able to run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.
ai-town
AI Town is a virtual town where AI characters live, chat, and socialize. This project provides a deployable starter kit for building and customizing your own version of AI Town. It features a game engine, database, vector search, auth, text model, deployment, pixel art generation, background music generation, and local inference. You can customize your own simulation by creating characters and stories, updating spritesheets, changing the background, and modifying the background music.
qrev
QRev is an open-source alternative to Salesforce, offering AI agents to scale sales organizations infinitely. It aims to provide digital workers for various sales roles or a superagent named Qai. The tech stack includes TypeScript for frontend, NodeJS for backend, MongoDB for app server database, ChromaDB for vector database, SQLite for AI server SQL relational database, and Langchain for LLM tooling. The tool allows users to run client app, app server, and AI server components. It requires Node.js and MongoDB to be installed, and provides detailed setup instructions in the README file.
seer
Seer is a service that provides AI capabilities to Sentry by running inference on Sentry issues and providing user insights. It is currently in early development and not yet compatible with self-hosted Sentry instances. The tool requires access to internal Sentry resources and is intended for internal Sentry employees. Users can set up the environment, download model artifacts, integrate with local Sentry, run evaluations for Autofix AI agent, and deploy to a sandbox staging environment. Development commands include applying database migrations, creating new migrations, running tests, and more. The tool also supports VCRs for recording and replaying HTTP requests.
btp-genai-starter-kit
This repository provides a quick way for users of the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) to learn how to use generative AI with BTP services. It guides users through setting up the necessary infrastructure, deploying AI models, and running genAI experiments on SAP BTP. The repository includes scripts, examples, and instructions to help users get started with generative AI on the SAP BTP platform.
NeoGPT
NeoGPT is an AI assistant that transforms your local workspace into a powerhouse of productivity from your CLI. With features like code interpretation, multi-RAG support, vision models, and LLM integration, NeoGPT redefines how you work and create. It supports executing code seamlessly, multiple RAG techniques, vision models, and interacting with various language models. Users can run the CLI to start using NeoGPT and access features like Code Interpreter, building vector database, running Streamlit UI, and changing LLM models. The tool also offers magic commands for chat sessions, such as resetting chat history, saving conversations, exporting settings, and more. Join the NeoGPT community to experience a new era of efficiency and contribute to its evolution.
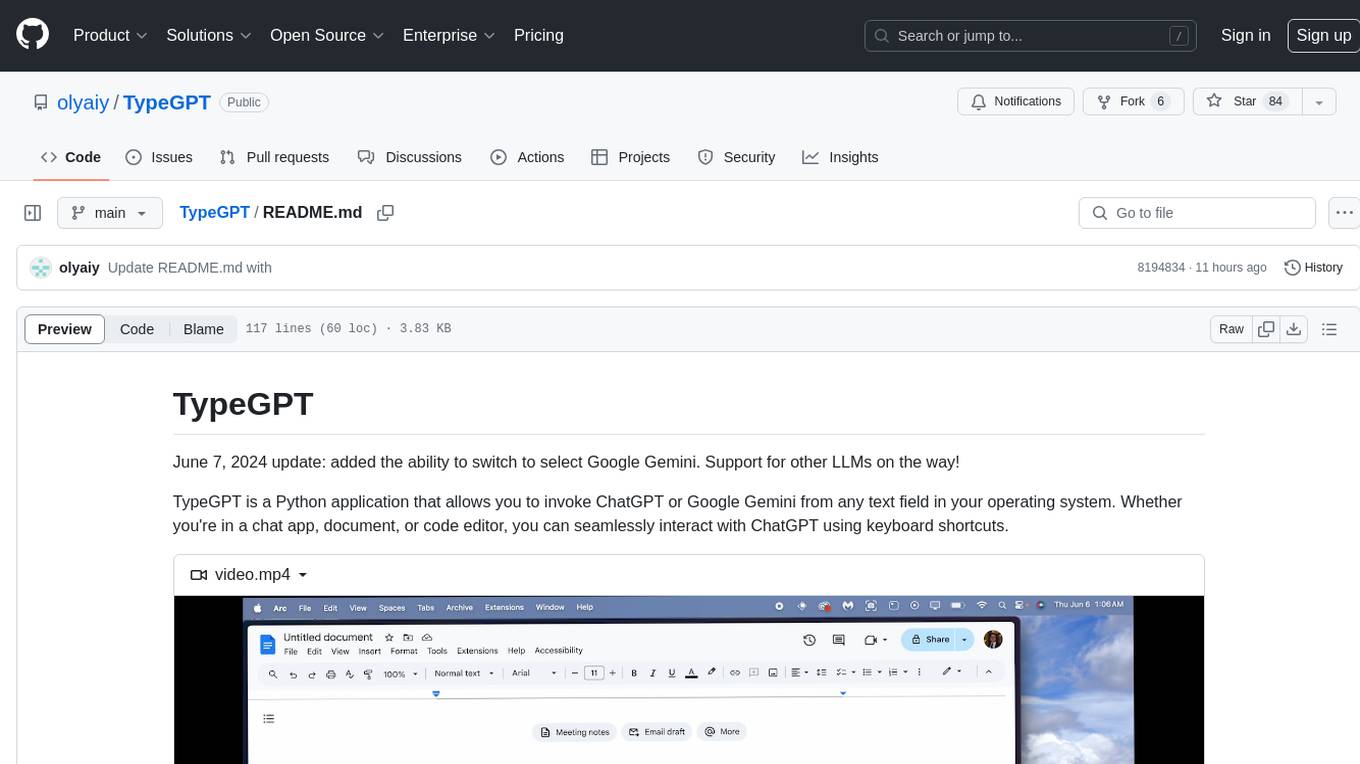
TypeGPT
TypeGPT is a Python application that enables users to interact with ChatGPT or Google Gemini from any text field in their operating system using keyboard shortcuts. It provides global accessibility, keyboard shortcuts for communication, and clipboard integration for larger text inputs. Users need to have Python 3.x installed along with specific packages and API keys from OpenAI for ChatGPT access. The tool allows users to run the program normally or in the background, manage processes, and stop the program. Users can use keyboard shortcuts like `/ask`, `/see`, `/stop`, `/chatgpt`, `/gemini`, `/check`, and `Shift + Cmd + Enter` to interact with the application in any text field. Customization options are available by modifying files like `keys.txt` and `system_prompt.txt`. Contributions are welcome, and future plans include adding support for other APIs and a user-friendly GUI.

joinly
joinly.ai is a connector middleware designed to enable AI agents to actively participate in video calls, providing essential meeting tools for AI agents to perform tasks and interact in real time. It supports live interaction, conversational flow, cross-platform compatibility, bring-your-own-LLM, and choose-your-preferred-TTS/STT services. The tool is 100% open-source, self-hosted, and privacy-first, aiming to make meetings accessible to AI agents by joining and participating in video calls.

aider-composer
Aider Composer is a VSCode extension that integrates Aider into your development workflow. It allows users to easily add and remove files, toggle between read-only and editable modes, review code changes, use different chat modes, and reference files in the chat. The extension supports multiple models, code generation, code snippets, and settings customization. It has limitations such as lack of support for multiple workspaces, Git repository features, linting, testing, voice features, in-chat commands, and configuration options.

moly-ai
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust that showcases the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius. It supports various AI providers, including OpenAI-compatible providers, Moly Server for local LLM exploration, and MoFa Servers for building AI agents. Users can download pre-built releases for different platforms and contribute to extending the list of supported providers. Moly can be used for tasks like chat completions, AI agent interactions, and custom client creation.
For similar tasks

jupyter-ai-agents
The Jupyter AI Agents is a tool equipped with 'execute', 'insert_cell', and more, to transform Jupyter Notebooks into an intelligent, interactive workspace. It empowers AI models to interact with and modify Jupyter Notebooks comprehensively, operating on the entire notebook level. The agent communicates through RTC, enabling seamless modifications based on user instructions or notebook events. It uses the LangChain Agent Framework to manage interactions between AI models and tools, supporting real-time collaboration in JupyterLab. The tool can be installed via pip or from source, and supports multiple AI model providers like Azure OpenAI.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
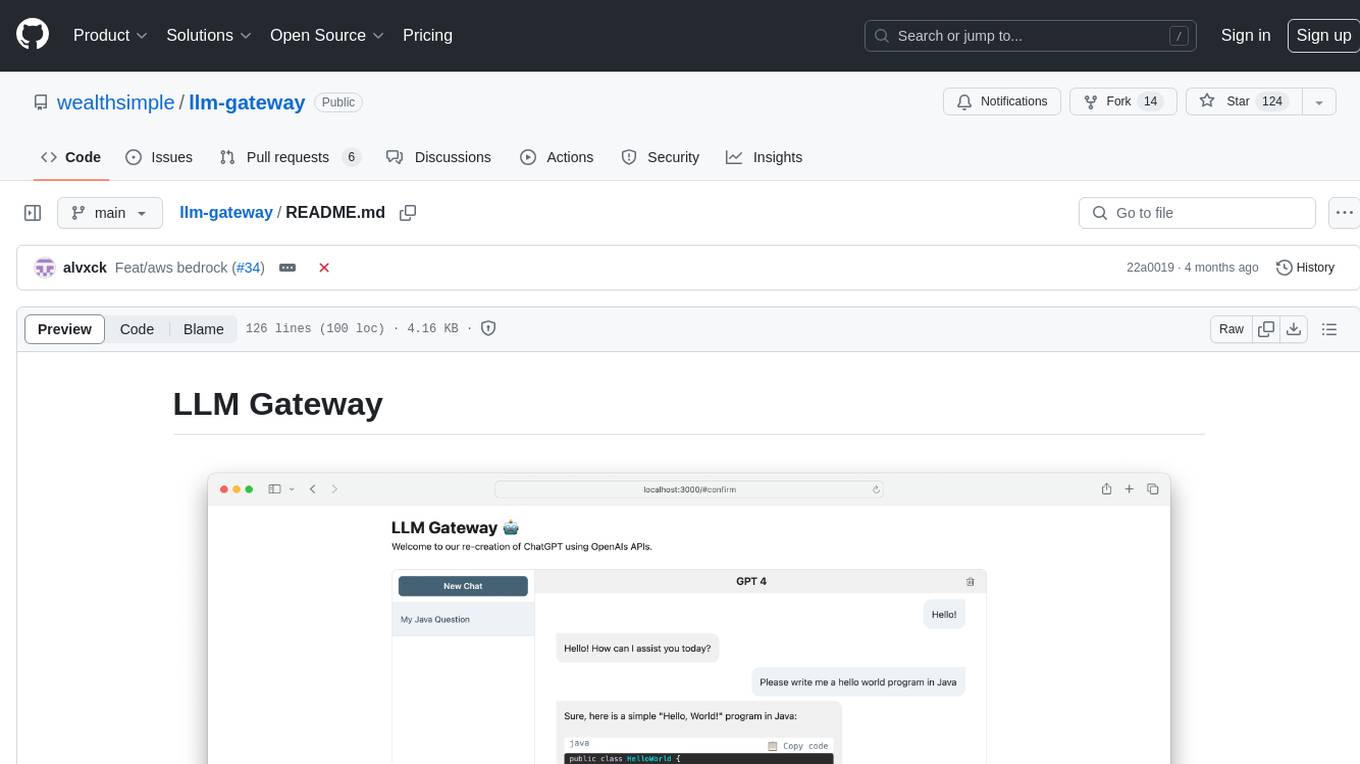
llm-gateway
llm-gateway is a gateway tool designed for interacting with third-party LLM providers such as OpenAI, Cohere, etc. It tracks data exchanged with these providers in a postgres database, applies PII scrubbing heuristics, and ensures safe communication with OpenAI's services. The tool supports various models from different providers and offers API and Python usage examples. Developers can set up the tool using Poetry, Pyenv, npm, and yarn for dependency management. The project also includes Docker setup for backend and frontend development.
Ollamac
Ollamac is a macOS app designed for interacting with Ollama models. It is optimized for macOS, allowing users to easily use any model from the Ollama library. The app features a user-friendly interface, chat archive for saving interactions, and real-time communication using HTTP streaming technology. Ollamac is open-source, enabling users to contribute to its development and enhance its capabilities. It requires macOS 14 or later and the Ollama system to be installed on the user's Mac with at least one Ollama model downloaded.
llmops-duke-aipi
LLMOps Duke AIPI is a course focused on operationalizing Large Language Models, teaching methodologies for developing applications using software development best practices with large language models. The course covers various topics such as generative AI concepts, setting up development environments, interacting with large language models, using local large language models, applied solutions with LLMs, extensibility using plugins and functions, retrieval augmented generation, introduction to Python web frameworks for APIs, DevOps principles, deploying machine learning APIs, LLM platforms, and final presentations. Students will learn to build, share, and present portfolios using Github, YouTube, and Linkedin, as well as develop non-linear life-long learning skills. Prerequisites include basic Linux and programming skills, with coursework available in Python or Rust. Additional resources and references are provided for further learning and exploration.
mistral-ai-kmp
Mistral AI SDK for Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) allows communication with Mistral API to get AI models, start a chat with the assistant, and create embeddings. The library is based on Mistral API documentation and built with Kotlin Multiplatform and Ktor client library. Sample projects like ZeChat showcase the capabilities of Mistral AI SDK. Users can interact with different Mistral AI models through ZeChat apps on Android, Desktop, and Web platforms. The library is not yet published on Maven, but users can fork the project and use it as a module dependency in their apps.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
ell
ell is a command-line interface for Language Model Models (LLMs) written in Bash. It allows users to interact with LLMs from the terminal, supports piping, context bringing, and chatting with LLMs. Users can also call functions and use templates. The tool requires bash, jq for JSON parsing, curl for HTTPS requests, and perl for PCRE. Configuration involves setting variables for different LLM models and APIs. Usage examples include asking questions, specifying models, recording input/output, running in interactive mode, and using templates. The tool is lightweight, easy to install, and pipe-friendly, making it suitable for interacting with LLMs in a terminal environment.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.