
awesome-llm-security
A curation of awesome tools, documents and projects about LLM Security.
Stars: 777
Awesome LLM Security is a curated collection of tools, documents, and projects related to Large Language Model (LLM) security. It covers various aspects of LLM security including white-box, black-box, and backdoor attacks, defense mechanisms, platform security, and surveys. The repository provides resources for researchers and practitioners interested in understanding and safeguarding LLMs against adversarial attacks. It also includes a list of tools specifically designed for testing and enhancing LLM security.
README:
A curation of awesome tools, documents and projects about LLM Security.
Contributions are always welcome. Please read the Contribution Guidelines before contributing.
- "Visual Adversarial Examples Jailbreak Large Language Models", 2023-06, AAAI(Oral) 24,
multi-modal, [paper] [repo] - "Are aligned neural networks adversarially aligned?", 2023-06, NeurIPS(Poster) 23,
multi-modal, [paper] - "(Ab)using Images and Sounds for Indirect Instruction Injection in Multi-Modal LLMs", 2023-07,
multi-modal[paper] - "Universal and Transferable Adversarial Attacks on Aligned Language Models", 2023-07,
transfer, [paper] [repo] [page] - "Jailbreak in pieces: Compositional Adversarial Attacks on Multi-Modal Language Models", 2023-07,
multi-modal, [paper] - "Image Hijacking: Adversarial Images can Control Generative Models at Runtime", 2023-09,
multi-modal, [paper] [repo] [site] - "Weak-to-Strong Jailbreaking on Large Language Models", 2024-04,
token-prob, [paper] [repo]
- "Not what you've signed up for: Compromising Real-World LLM-Integrated Applications with Indirect Prompt Injection", 2023-02, AISec@CCS 23 [paper]
- "Jailbroken: How Does LLM Safety Training Fail?", 2023-07, NeurIPS(Oral) 23, [paper]
- "Latent Jailbreak: A Benchmark for Evaluating Text Safety and Output Robustness of Large Language Models", 2023-07, [paper] [repo]
- "Effective Prompt Extraction from Language Models", 2023-07,
prompt-extraction, [paper] - "Multi-step Jailbreaking Privacy Attacks on ChatGPT", 2023-04, EMNLP 23,
privacy, [paper] - "LLM Censorship: A Machine Learning Challenge or a Computer Security Problem?", 2023-07, [paper]
- "Jailbreaking chatgpt via prompt engineering: An empirical study", 2023-05, [paper]
- "Prompt Injection attack against LLM-integrated Applications", 2023-06, [paper] [repo]
- "MasterKey: Automated Jailbreak Across Multiple Large Language Model Chatbots", 2023-07,
time-side-channel, [paper] - "GPT-4 Is Too Smart To Be Safe: Stealthy Chat with LLMs via Cipher", 2023-08, ICLR 24,
cipher, [paper] [repo] - "Use of LLMs for Illicit Purposes: Threats, Prevention Measures, and Vulnerabilities", 2023-08, [paper]
- "Do-Not-Answer: A Dataset for Evaluating Safeguards in LLMs", 2023-08, [paper] [repo] [dataset]
- "Detecting Language Model Attacks with Perplexity", 2023-08, [paper]
- "Open Sesame! Universal Black Box Jailbreaking of Large Language Models", 2023-09,
gene-algorithm, [paper] - "Fine-tuning Aligned Language Models Compromises Safety, Even When Users Do Not Intend To!", 2023-10, ICLR(oral) 24, [paper] [repo] [site] [dataset]
- "AutoDAN: Generating Stealthy Jailbreak Prompts on Aligned Large Language Models", 2023-10, ICLR(poster) 24,
gene-algorithm,new-criterion, [paper] - "Jailbreak and Guard Aligned Language Models with Only Few In-Context Demonstrations", 2023-10, CoRR 23,
ICL, [paper] - "Multilingual Jailbreak Challenges in Large Language Models", 2023-10, ICLR(poster) 24, [paper] [repo]
- "Scalable and Transferable Black-Box Jailbreaks for Language Models via Persona Modulation", 2023-11, SoLaR(poster) 24, [paper]
- "DeepInception: Hypnotize Large Language Model to Be Jailbreaker", 2023-11, [paper] [repo] [site]
- "A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing: Generalized Nested Jailbreak Prompts can Fool Large Language Models Easily", 2023-11, NAACL 24, [paper] [repo]
- "AutoDAN: Automatic and Interpretable Adversarial Attacks on Large Language Models", 2023-10, [paper]
- "Language Model Inversion", 2023-11, ICLR(poster) 24, [paper] [repo]
- "An LLM can Fool Itself: A Prompt-Based Adversarial Attack", 2023-10, ICLR(poster) 24, [paper] [repo]
- "GPTFUZZER: Red Teaming Large Language Models with Auto-Generated Jailbreak Prompts", 2023-09, [paper] [repo] [site]
- "Many-shot Jailbreaking", 2024-04, [paper]
- "Rethinking How to Evaluate Language Model Jailbreak", 2024-04, [paper] [repo]
- "BITE: Textual Backdoor Attacks with Iterative Trigger Injection", 2022-05, ACL 23,
defense[paper] - "Prompt as Triggers for Backdoor Attack: Examining the Vulnerability in Language Models", 2023-05, EMNLP 23, [paper]
- "Backdooring Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models with Virtual Prompt Injection", 2023-07, NAACL 24, [paper] [repo] [site]
- "Baseline Defenses for Adversarial Attacks Against Aligned Language Models", 2023-09, [paper] [repo]
- "LLM Self Defense: By Self Examination, LLMs Know They Are Being Tricked", 2023-08, ICLR 24 Tiny Paper,
self-filtered, [paper] [repo] [site] - "Defending Against Alignment-Breaking Attacks via Robustly Aligned LLM", 2023-09,
random-mask-filter, [paper] - "Benchmarking and Defending Against Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks on Large Language Models", 2023-12, [paper] [repo]
- "AutoDefense: Multi-Agent LLM Defense against Jailbreak Attacks", 2024-03, [paper] [repo]
- "Protecting Your LLMs with Information Bottleneck", 2024-04, [paper] [repo]
- "PARDEN, Can You Repeat That? Defending against Jailbreaks via Repetition", 2024-05, ICML 24, [paper] [repo]
- “Adversarial Tuning: Defending Against Jailbreak Attacks for LLMs”, 2024-06, [paper]
- "LLM Platform Security: Applying a Systematic Evaluation Framework to OpenAI’s ChatGPT Plugins", 2023-09, [paper] [repo]
- "Survey of Vulnerabilities in Large Language Models Revealed by Adversarial Attacks", 2023-10, ACL 24, [paper]
- "Security and Privacy Challenges of Large Language Models: A Survey", 2024-02, [paper]
- "Breaking Down the Defenses: A Comparative Survey of Attacks on Large Language Models", 2024-03, [paper]
-
Plexiglass: a security toolbox for testing and safeguarding LLMs
-
PurpleLlama: set of tools to assess and improve LLM security.
-
Rebuff: a self-hardening prompt injection detector
-
Garak: a LLM vulnerability scanner
-
LLMFuzzer: a fuzzing framework for LLMs
-
LLM Guard: a security toolkit for LLM Interactions
-
Vigil: a LLM prompt injection detection toolkit
-
jailbreak-evaluation: an easy-to-use Python package for language model jailbreak evaluation
-
Prompt Fuzzer: the open-source tool to help you harden your GenAI applications
- Hacking Auto-GPT and escaping its docker container
- Prompt Injection Cheat Sheet: How To Manipulate AI Language Models
- Indirect Prompt Injection Threats
- Prompt injection: What’s the worst that can happen?
- OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications
- PoisonGPT: How we hid a lobotomized LLM on Hugging Face to spread fake news
- ChatGPT Plugins: Data Exfiltration via Images & Cross Plugin Request Forgery
- Jailbreaking GPT-4's code interpreter
- Securing LLM Systems Against Prompt Injection
- The AI Attack Surface Map v1.0
- Adversarial Attacks on LLMs
- How Anyone can Hack ChatGPT - GPT4o
- (0din GenAI Bug Bounty from Mozilla)(https://0din.ai): The 0Day Investigative Network is a bug bounty program focusing on flaws within GenAI models. Vulnerability classes include Prompt Injection, Training Data Poisoning, DoS, and more.
- Gandalf: a prompt injection wargame
- LangChain vulnerable to code injection - CVE-2023-29374
- Jailbreak Chat
- Adversarial Prompting
- Epivolis: a prompt injection aware chatbot designed to mitigate adversarial efforts
- LLM Security Problems at DEFCON31 Quals: the world's top security competition
- PromptBounty.io
- PALLMs (Payloads for Attacking Large Language Models)
- Twitter: @llm_sec
- Blog: LLM Security authored by @llm_sec
- Blog: Embrace The Red
- Blog: Kai's Blog
- Newsletter: AI safety takes
- Newsletter & Blog: Hackstery
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-llm-security
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-llm-security
Awesome LLM Security is a curated collection of tools, documents, and projects related to Large Language Model (LLM) security. It covers various aspects of LLM security including white-box, black-box, and backdoor attacks, defense mechanisms, platform security, and surveys. The repository provides resources for researchers and practitioners interested in understanding and safeguarding LLMs against adversarial attacks. It also includes a list of tools specifically designed for testing and enhancing LLM security.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
awesome-deliberative-prompting
The 'awesome-deliberative-prompting' repository focuses on how to ask Large Language Models (LLMs) to produce reliable reasoning and make reason-responsive decisions through deliberative prompting. It includes success stories, prompting patterns and strategies, multi-agent deliberation, reflection and meta-cognition, text generation techniques, self-correction methods, reasoning analytics, limitations, failures, puzzles, datasets, tools, and other resources related to deliberative prompting. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of research, techniques, and tools for enhancing reasoning capabilities of LLMs.
DeepResearch
Tongyi DeepResearch is an agentic large language model with 30.5 billion total parameters, designed for long-horizon, deep information-seeking tasks. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across various search benchmarks. The model features a fully automated synthetic data generation pipeline, large-scale continual pre-training on agentic data, end-to-end reinforcement learning, and compatibility with two inference paradigms. Users can download the model directly from HuggingFace or ModelScope. The repository also provides benchmark evaluation scripts and information on the Deep Research Agent Family.
LTEngine
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
TheoremExplainAgent
TheoremExplainAgent is an AI system that generates long-form Manim videos to visually explain theorems, proving its deep understanding while uncovering reasoning flaws that text alone often hides. The codebase for the paper 'TheoremExplainAgent: Towards Multimodal Explanations for LLM Theorem Understanding' is available in this repository. It provides a tool for creating multimodal explanations for theorem understanding using AI technology.
unitxt
Unitxt is a customizable library for textual data preparation and evaluation tailored to generative language models. It natively integrates with common libraries like HuggingFace and LM-eval-harness and deconstructs processing flows into modular components, enabling easy customization and sharing between practitioners. These components encompass model-specific formats, task prompts, and many other comprehensive dataset processing definitions. The Unitxt-Catalog centralizes these components, fostering collaboration and exploration in modern textual data workflows. Beyond being a tool, Unitxt is a community-driven platform, empowering users to build, share, and advance their pipelines collaboratively.
LLMRec
LLMRec is a PyTorch implementation for the WSDM 2024 paper 'Large Language Models with Graph Augmentation for Recommendation'. It is a novel framework that enhances recommenders by applying LLM-based graph augmentation strategies to recommendation systems. The tool aims to make the most of content within online platforms to augment interaction graphs by reinforcing u-i interactive edges, enhancing item node attributes, and conducting user node profiling from a natural language perspective.
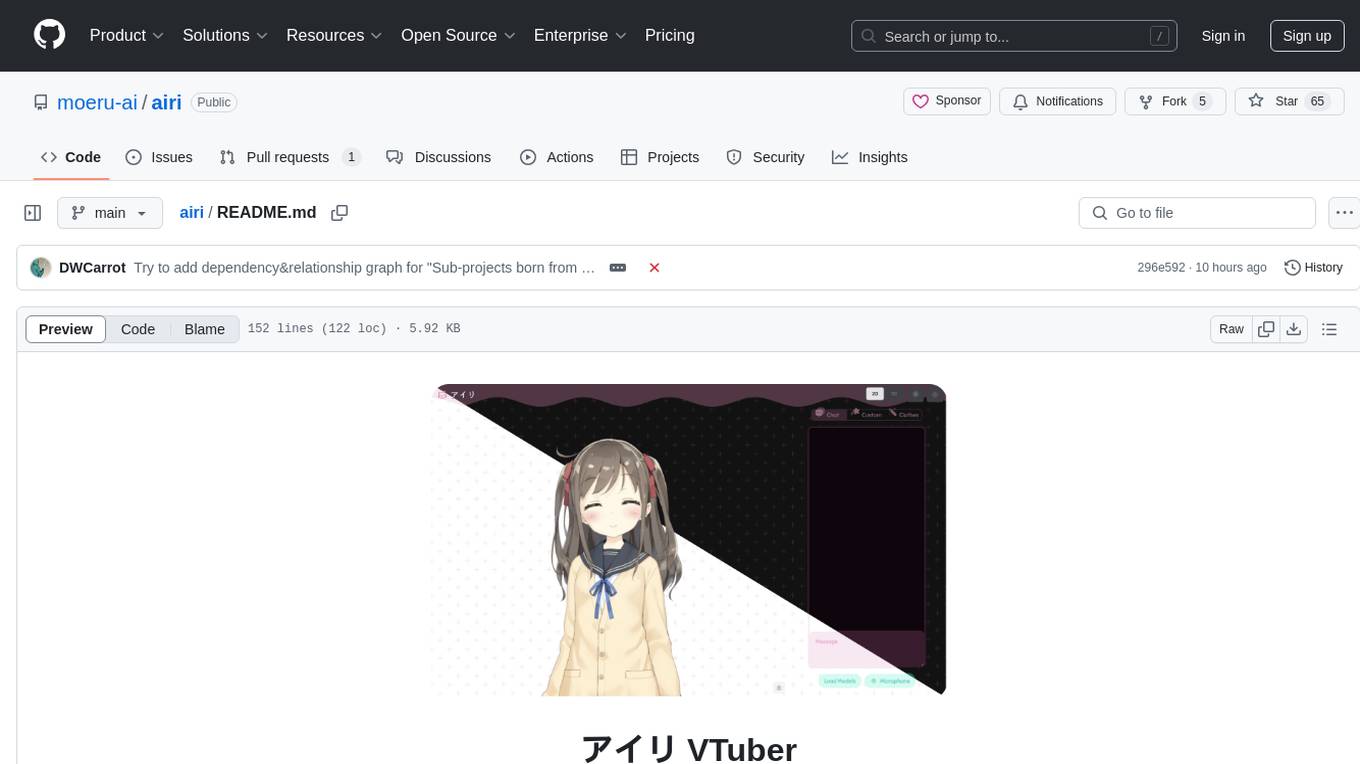
airi
Airi is a VTuber project heavily inspired by Neuro-sama. It is capable of various functions such as playing Minecraft, chatting in Telegram and Discord, audio input from browser and Discord, client side speech recognition, VRM and Live2D model support with animations, and more. The project also includes sub-projects like unspeech, hfup, Drizzle ORM driver for DuckDB WASM, and various other tools. Airi uses models like whisper-large-v3-turbo from Hugging Face and is similar to projects like z-waif, amica, eliza, AI-Waifu-Vtuber, and AIVTuber. The project acknowledges contributions from various sources and implements packages to interact with LLMs and models.
DeepMesh
DeepMesh is an auto-regressive artist-mesh creation tool that utilizes reinforcement learning to generate high-quality meshes conditioned on a given point cloud. It offers pretrained weights and allows users to generate obj/ply files based on specific input parameters. The tool has been tested on Ubuntu 22 with CUDA 11.8 and supports A100, A800, and A6000 GPUs. Users can clone the repository, create a conda environment, install pretrained model weights, and use command line inference to generate meshes.
Acontext
Acontext is a context data platform designed for production AI agents, offering unified storage, built-in context management, and observability features. It helps agents scale from local demos to production without the need to rebuild context infrastructure. The platform provides solutions for challenges like scattered context data, long-running agents requiring context management, and tracking states from multi-modal agents. Acontext offers core features such as context storage, session management, disk storage, agent skills management, and sandbox for code execution and analysis. Users can connect to Acontext, install SDKs, initialize clients, store and retrieve messages, perform context engineering, and utilize agent storage tools. The platform also supports building agents using end-to-end scripts in Python and Typescript, with various templates available. Acontext's architecture includes client layer, backend with API and core components, infrastructure with PostgreSQL, S3, Redis, and RabbitMQ, and a web dashboard. Join the Acontext community on Discord and follow updates on GitHub.
PPTAgent
PPTAgent is an innovative system that automatically generates presentations from documents. It employs a two-step process for quality assurance and introduces PPTEval for comprehensive evaluation. With dynamic content generation, smart reference learning, and quality assessment, PPTAgent aims to streamline presentation creation. The tool follows an analysis phase to learn from reference presentations and a generation phase to develop structured outlines and cohesive slides. PPTEval evaluates presentations based on content accuracy, visual appeal, and logical coherence.
langcorn
LangCorn is an API server that enables you to serve LangChain models and pipelines with ease, leveraging the power of FastAPI for a robust and efficient experience. It offers features such as easy deployment of LangChain models and pipelines, ready-to-use authentication functionality, high-performance FastAPI framework for serving requests, scalability and robustness for language processing applications, support for custom pipelines and processing, well-documented RESTful API endpoints, and asynchronous processing for faster response times.
superlinked
Superlinked is a compute framework for information retrieval and feature engineering systems, focusing on converting complex data into vector embeddings for RAG, Search, RecSys, and Analytics stack integration. It enables custom model performance in machine learning with pre-trained model convenience. The tool allows users to build multimodal vectors, define weights at query time, and avoid postprocessing & rerank requirements. Users can explore the computational model through simple scripts and python notebooks, with a future release planned for production usage with built-in data infra and vector database integrations.

aderyn
Aderyn is a powerful Solidity static analyzer designed to help protocol engineers and security researchers find vulnerabilities in Solidity code bases. It provides off-the-shelf support for Foundry and Hardhat projects, allows for custom frameworks through a configuration file, and generates reports in Markdown, JSON, and Sarif formats. Users can install Aderyn using Cyfrinup, curl, Homebrew, or npm, and quickly identify vulnerabilities in their Solidity code. The tool also offers a VS Code extension for seamless integration with the IDE.
ChatTTS
ChatTTS is a generative speech model optimized for dialogue scenarios, providing natural and expressive speech synthesis with fine-grained control over prosodic features. It supports multiple speakers and surpasses most open-source TTS models in terms of prosody. The model is trained with 100,000+ hours of Chinese and English audio data, and the open-source version on HuggingFace is a 40,000-hour pre-trained model without SFT. The roadmap includes open-sourcing additional features like VQ encoder, multi-emotion control, and streaming audio generation. The tool is intended for academic and research use only, with precautions taken to limit potential misuse.
For similar tasks

awesome-llm-security
Awesome LLM Security is a curated collection of tools, documents, and projects related to Large Language Model (LLM) security. It covers various aspects of LLM security including white-box, black-box, and backdoor attacks, defense mechanisms, platform security, and surveys. The repository provides resources for researchers and practitioners interested in understanding and safeguarding LLMs against adversarial attacks. It also includes a list of tools specifically designed for testing and enhancing LLM security.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.









