
aiodns
Simple DNS resolver for asyncio
Stars: 570
aiodns is a simple DNS resolver for asyncio that provides a way for asynchronous DNS resolutions using pycares. It offers functions like query, gethostbyname, gethostbyaddr, and cancel for DNS resolution and reverse lookup. The library supports various query types such as A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, NS, PTR, SOA, SRV, and TXT. Note that Windows users need to set the asyncio loop to SelectorEventLoop. The tool is licensed under MIT and welcomes contributions.
README:
.. image:: https://badge.fury.io/py/aiodns.png :target: https://pypi.org/project/aiodns/
.. image:: https://github.com/saghul/aiodns/workflows/CI/badge.svg :target: https://github.com/saghul/aiodns/actions
aiodns provides a simple way for doing asynchronous DNS resolutions using pycares <https://github.com/saghul/pycares>_.
.. code:: python
import asyncio
import aiodns
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
resolver = aiodns.DNSResolver(loop=loop)
async def query(name, query_type):
return await resolver.query(name, query_type)
coro = query('google.com', 'A')
result = loop.run_until_complete(coro)
The following query types are supported: A, AAAA, ANY, CAA, CNAME, MX, NAPTR, NS, PTR, SOA, SRV, TXT.
The API is pretty simple, the following functions are provided in the DNSResolver class:
-
query(host, type): Do a DNS resolution of the given type for the given hostname. It returns an instance ofasyncio.Future. The actual result of the DNS query is taken directly from pycares. As of version 1.0.0 of aiodns (and pycares, for that matter) results are always namedtuple-like objects with different attributes. Please check thedocumentation <http://pycares.readthedocs.org/latest/channel.html#pycares.Channel.query>_ for the result fields. -
gethostbyname(host, socket_family): Do a DNS resolution for the given hostname and the desired type of address family (i.e.socket.AF_INET). Whilequery()always performs a request to a DNS server,gethostbyname()first looks into/etc/hostsand thus can resolve local hostnames (such aslocalhost). Please checkthe documentation <http://pycares.readthedocs.io/latest/channel.html#pycares.Channel.gethostbyname>_ for the result fields. The actual result of the call is aasyncio.Future. -
gethostbyaddr(name): Make a reverse lookup for an address. -
cancel(): Cancel all pending DNS queries. All futures will getDNSErrorexception set, withARES_ECANCELLEDerrno. -
close(): Close the resolver. This releases all resources and cancels any pending queries. It must be called when the resolver is no longer needed (e.g., application shutdown). The resolver should only be closed from the event loop that created the resolver.
While not recommended for typical use cases, DNSResolver can be used as an async context manager
for scenarios where automatic cleanup is desired:
.. code:: python
async with aiodns.DNSResolver() as resolver:
result = await resolver.query('example.com', 'A')
# resolver.close() is called automatically when exiting the context
Important: This pattern is discouraged for most applications because DNSResolver instances
are designed to be long-lived and reused for many queries. Creating and destroying resolvers
frequently adds unnecessary overhead. Use the context manager pattern only when you specifically
need automatic cleanup for short-lived resolver instances, such as in tests or one-off scripts.
This library requires the use of an asyncio.SelectorEventLoop or winloop on Windows
only when using a custom build of pycares that links against a system-
provided c-ares library without thread-safety support. This is because
non-thread-safe builds of c-ares are incompatible with the default
ProactorEventLoop on Windows.
If you're using the official prebuilt pycares wheels on PyPI (version 4.7.0 or
later), which include a thread-safe version of c-ares, this limitation does
not apply and can be safely ignored.
The default event loop can be changed as follows (do this very early in your application):
.. code:: python
asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(asyncio.WindowsSelectorEventLoopPolicy())
This may have other implications for the rest of your codebase, so make sure to test thoroughly.
To run the test suite: python tests.py
Saúl Ibarra Corretgé [email protected]
aiodns uses the MIT license, check LICENSE file.
If you'd like to contribute, fork the project, make a patch and send a pull request. Have a look at the surrounding code and please, make yours look alike :-)
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aiodns
Similar Open Source Tools

aiodns
aiodns is a simple DNS resolver for asyncio that provides a way for asynchronous DNS resolutions using pycares. It offers functions like query, gethostbyname, gethostbyaddr, and cancel for DNS resolution and reverse lookup. The library supports various query types such as A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, NS, PTR, SOA, SRV, and TXT. Note that Windows users need to set the asyncio loop to SelectorEventLoop. The tool is licensed under MIT and welcomes contributions.
lightspeed-service
OpenShift LightSpeed (OLS) is an AI powered assistant that runs on OpenShift and provides answers to product questions using backend LLM services. It supports various LLM providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, OpenShift AI, RHEL AI, and Watsonx. Users can configure the service, manage API keys securely, and deploy it locally or on OpenShift. The project structure includes REST API handlers, configuration loader, LLM providers registry, and more. Additional tools include generating OpenAPI schema, requirements.txt file, and uploading artifacts to an S3 bucket. The project is open source under the Apache 2.0 License.
goclaw
goclaw is a powerful AI Agent framework written in Go language. It provides a complete tool system for FileSystem, Shell, Web, and Browser with Docker sandbox support and permission control. The framework includes a skill system compatible with OpenClaw and AgentSkills specifications, supporting automatic discovery and environment gating. It also offers persistent session storage, multi-channel support for Telegram, WhatsApp, Feishu, QQ, and WeWork, flexible configuration with YAML/JSON support, multiple LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and OpenRouter, WebSocket Gateway, Cron scheduling, and Browser automation based on Chrome DevTools Protocol.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
lm-proxy
lm-proxy is a lightweight and efficient tool for managing HTTP/HTTPS proxies. It provides a simple interface to easily rotate, validate, and use proxies in web scraping, data mining, and automation tasks. With lm-proxy, users can seamlessly handle proxy management without the need for complex configurations or setups.

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.
jadx-mcp-server
JADX-MCP-SERVER is a standalone Python server that interacts with JADX-AI-MCP Plugin to analyze Android APKs using LLMs like Claude. It enables live communication with decompiled Android app context, uncovering vulnerabilities, parsing manifests, and facilitating reverse engineering effortlessly. The tool combines JADX-AI-MCP and JADX MCP SERVER to provide real-time reverse engineering support with LLMs, offering features like quick analysis, vulnerability detection, AI code modification, static analysis, and reverse engineering helpers. It supports various MCP tools for fetching class information, text, methods, fields, smali code, AndroidManifest.xml content, strings.xml file, resource files, and more. Tested on Claude Desktop, it aims to support other LLMs in the future, enhancing Android reverse engineering and APK modification tools connectivity for easier reverse engineering purely from vibes.
llms
llms.py is a lightweight CLI, API, and ChatGPT-like alternative to Open WebUI for accessing multiple LLMs. It operates entirely offline, ensuring all data is kept private in browser storage. The tool provides a convenient way to interact with various LLM models without the need for an internet connection, prioritizing user privacy and data security.

hyper-mcp
hyper-mcp is a fast and secure MCP server that enables adding AI capabilities to applications through WebAssembly plugins. It supports writing plugins in various languages, distributing them via standard OCI registries, and running them in resource-constrained environments. The tool offers sandboxing with WASM for limiting access, cross-platform compatibility, and deployment flexibility. Security features include sandboxed plugins, memory-safe execution, secure plugin distribution, and fine-grained access control. Users can configure the tool for global or project-specific use, start the server with different transport options, and utilize available plugins for tasks like time calculations, QR code generation, hash generation, IP retrieval, and webpage fetching.
dbeaver
DBeaver is a free multi-platform database tool designed for developers, SQL programmers, database administrators, and analysts. It offers a wide range of features including schema editor, SQL editor, data editor, AI integration, ER diagrams, data export/import/migration, SQL execution plans, database administration tools, database dashboards, Spatial data viewer, proxy and SSH tunnelling, custom database drivers editor, etc. It supports over 100 database drivers out of the box and is compatible with any database that has a JDBC or ODBC driver. DBeaver also supports smart AI completion and code generation with OpenAI or Copilot.
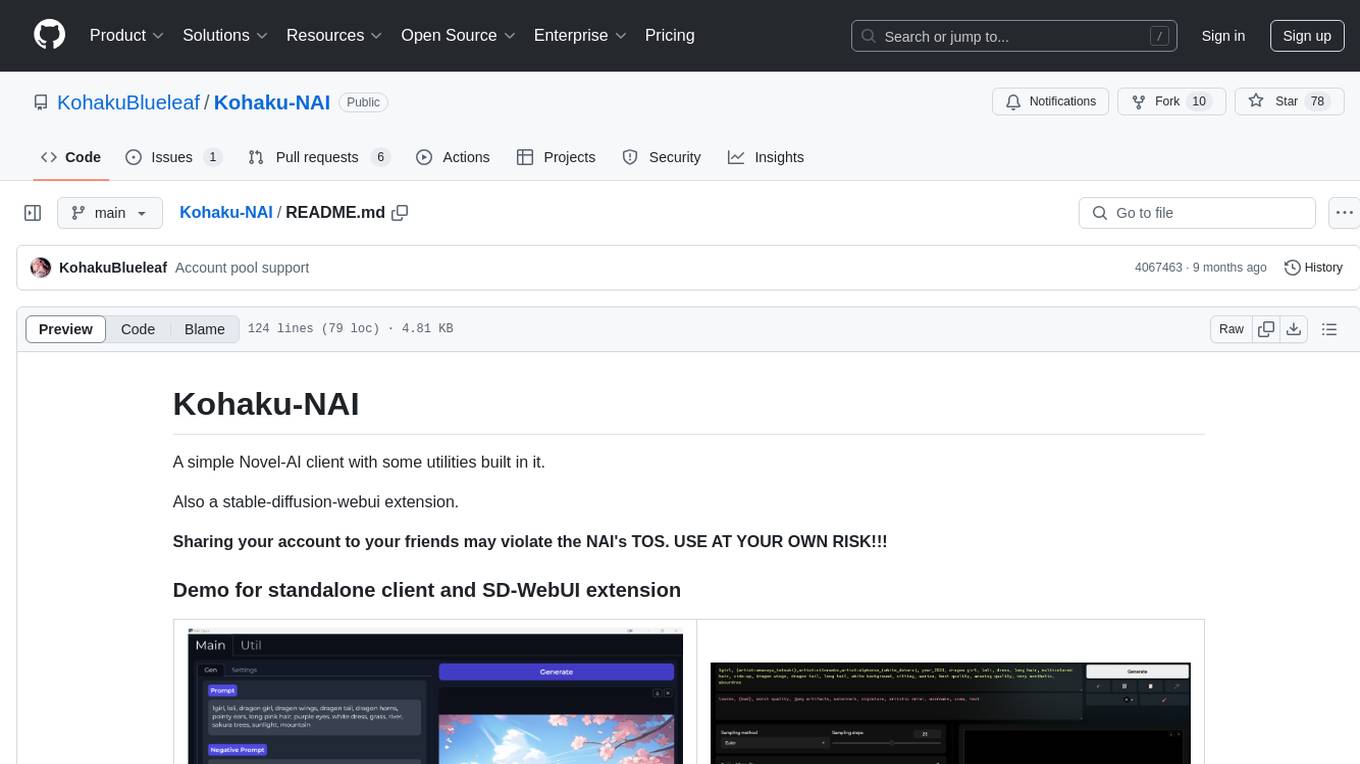
Kohaku-NAI
Kohaku-NAI is a simple Novel-AI client with utilities like a generation server, saving images automatically, account pool, and an auth system. It also includes a standalone client, a DC bot based on the generation server, and a stable-diffusion-webui extension. Users can use it to generate images with NAI API within sd-webui, as a standalone client, gen server, or DC bot. The project aims to add features like QoS system, better client, random prompts, and fetch account info in the future.
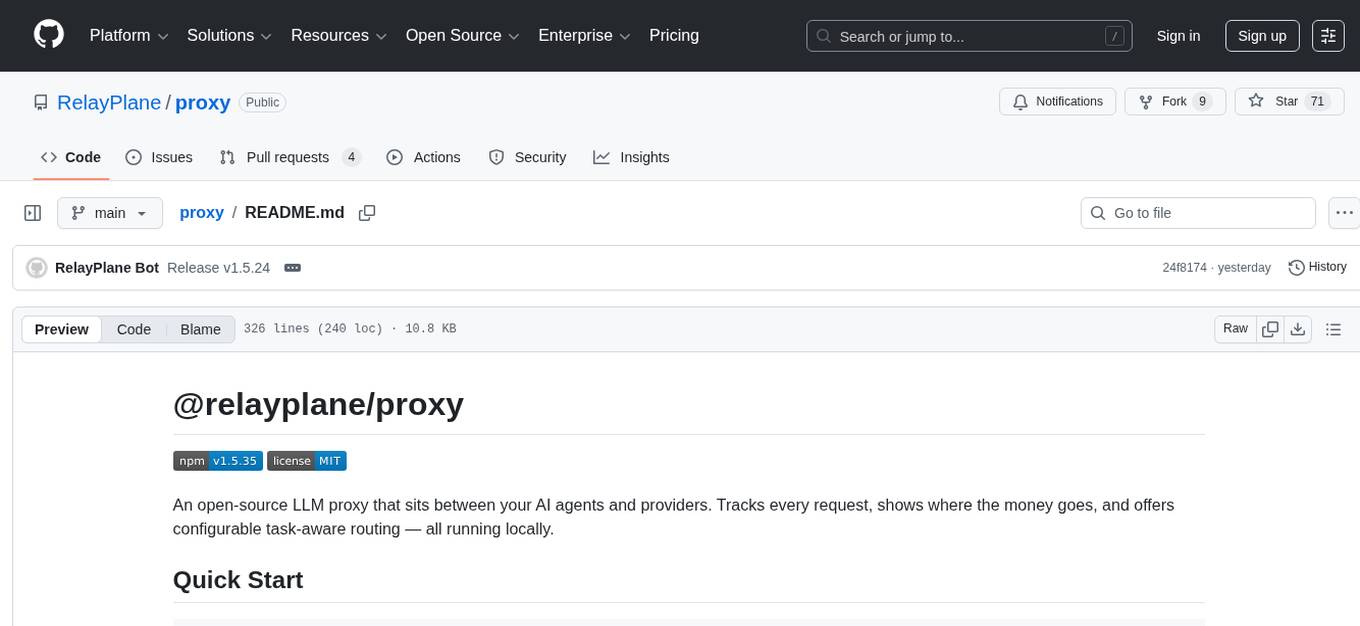
proxy
An open-source local HTTP proxy tool that sits between AI agents and providers, tracking requests, offering task-aware routing, and providing a dashboard for monitoring. It works with various agent frameworks communicating with OpenAI or Anthropic APIs, allowing users to classify tasks, route requests to specific models, and record telemetry data locally. Users can configure complexity-based routing, model overrides, cascade mode, smart aliases, and routing suffixes for routing preferences. The tool ensures provider reliability with cooldowns, supports hybrid authentication for expensive models, and offers telemetry features for monitoring usage. The dashboard displays request statistics, cost breakdowns, routing decisions, and provider health status.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.
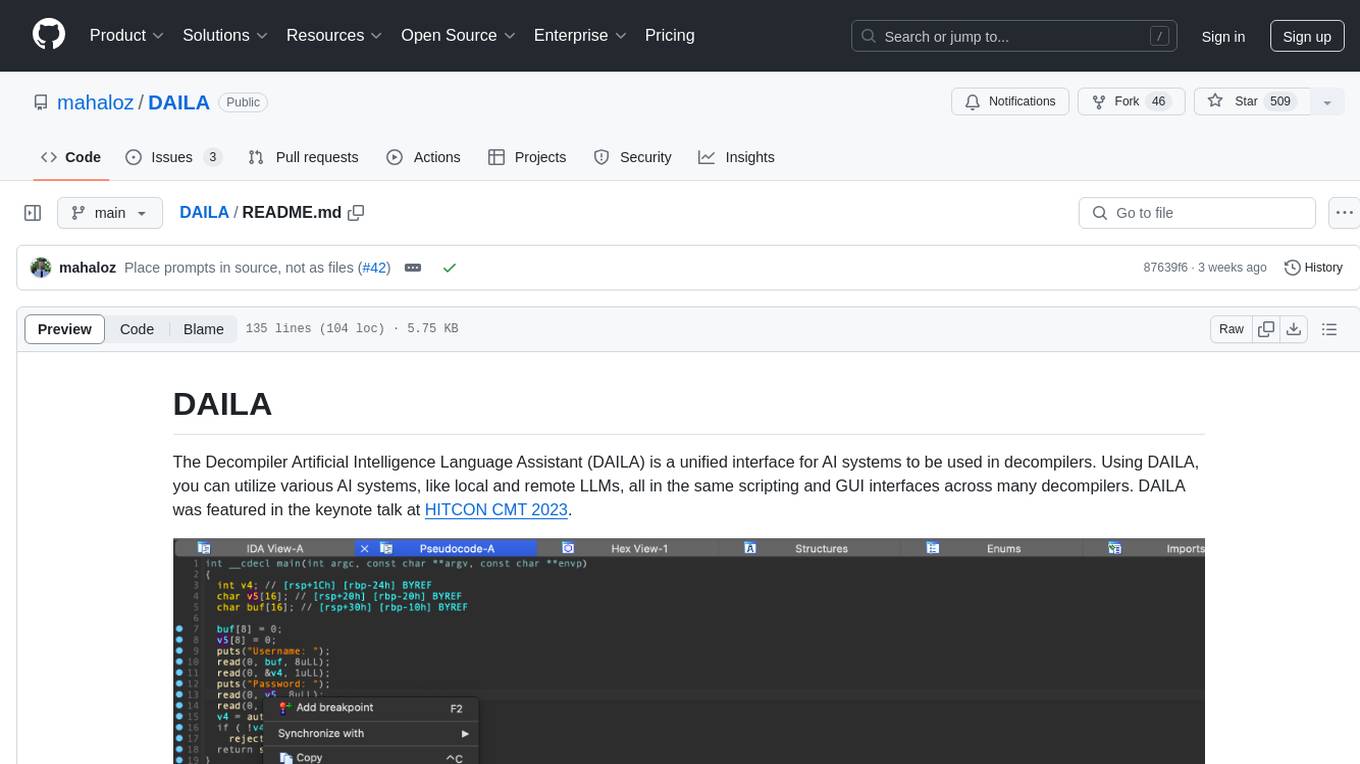
DAILA
DAILA is a unified interface for AI systems in decompilers, supporting various decompilers and AI systems. It allows users to utilize local and remote LLMs, like ChatGPT and Claude, and local models such as VarBERT. DAILA can be used as a decompiler plugin with GUI or as a scripting library. It also provides a Docker container for offline installations and supports tasks like summarizing functions and renaming variables in decompilation.
ollama4j
Ollama4j is a Java library that serves as a wrapper or binding for the Ollama server. It allows users to communicate with the Ollama server and manage models for various deployment scenarios. The library provides APIs for interacting with Ollama, generating fake data, testing UI interactions, translating messages, and building web UIs. Users can easily integrate Ollama4j into their Java projects to leverage the functionalities offered by the Ollama server.
llm
The 'llm' package for Emacs provides an interface for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It abstracts functionality to a higher level, concealing API variations and ensuring compatibility with various LLMs. Users can set up providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Vertex, Claude, Ollama, GPT4All, and a fake client for testing. The package allows for chat interactions, embeddings, token counting, and function calling. It also offers advanced prompt creation and logging capabilities. Users can handle conversations, create prompts with placeholders, and contribute by creating providers.
For similar tasks

aiodns
aiodns is a simple DNS resolver for asyncio that provides a way for asynchronous DNS resolutions using pycares. It offers functions like query, gethostbyname, gethostbyaddr, and cancel for DNS resolution and reverse lookup. The library supports various query types such as A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, NS, PTR, SOA, SRV, and TXT. Note that Windows users need to set the asyncio loop to SelectorEventLoop. The tool is licensed under MIT and welcomes contributions.
For similar jobs

AirGo
AirGo is a front and rear end separation, multi user, multi protocol proxy service management system, simple and easy to use. It supports vless, vmess, shadowsocks, and hysteria2.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
llm-code-interpreter
The 'llm-code-interpreter' repository is a deprecated plugin that provides a code interpreter on steroids for ChatGPT by E2B. It gives ChatGPT access to a sandboxed cloud environment with capabilities like running any code, accessing Linux OS, installing programs, using filesystem, running processes, and accessing the internet. The plugin exposes commands to run shell commands, read files, and write files, enabling various possibilities such as running different languages, installing programs, starting servers, deploying websites, and more. It is powered by the E2B API and is designed for agents to freely experiment within a sandboxed environment.

pezzo
Pezzo is a fully cloud-native and open-source LLMOps platform that allows users to observe and monitor AI operations, troubleshoot issues, save costs and latency, collaborate, manage prompts, and deliver AI changes instantly. It supports various clients for prompt management, observability, and caching. Users can run the full Pezzo stack locally using Docker Compose, with prerequisites including Node.js 18+, Docker, and a GraphQL Language Feature Support VSCode Extension. Contributions are welcome, and the source code is available under the Apache 2.0 License.
learn-generative-ai
Learn Cloud Applied Generative AI Engineering (GenEng) is a course focusing on the application of generative AI technologies in various industries. The course covers topics such as the economic impact of generative AI, the role of developers in adopting and integrating generative AI technologies, and the future trends in generative AI. Students will learn about tools like OpenAI API, LangChain, and Pinecone, and how to build and deploy Large Language Models (LLMs) for different applications. The course also explores the convergence of generative AI with Web 3.0 and its potential implications for decentralized intelligence.
gcloud-aio
This repository contains shared codebase for two projects: gcloud-aio and gcloud-rest. gcloud-aio is built for Python 3's asyncio, while gcloud-rest is a threadsafe requests-based implementation. It provides clients for Google Cloud services like Auth, BigQuery, Datastore, KMS, PubSub, Storage, and Task Queue. Users can install the library using pip and refer to the documentation for usage details. Developers can contribute to the project by following the contribution guide.
fluid
Fluid is an open source Kubernetes-native Distributed Dataset Orchestrator and Accelerator for data-intensive applications, such as big data and AI applications. It implements dataset abstraction, scalable cache runtime, automated data operations, elasticity and scheduling, and is runtime platform agnostic. Key concepts include Dataset and Runtime. Prerequisites include Kubernetes version > 1.16, Golang 1.18+, and Helm 3. The tool offers features like accelerating remote file accessing, machine learning, accelerating PVC, preloading dataset, and on-the-fly dataset cache scaling. Contributions are welcomed, and the project is under the Apache 2.0 license with a vendor-neutral approach.
aiges
AIGES is a core component of the Athena Serving Framework, designed as a universal encapsulation tool for AI developers to deploy AI algorithm models and engines quickly. By integrating AIGES, you can deploy AI algorithm models and engines rapidly and host them on the Athena Serving Framework, utilizing supporting auxiliary systems for networking, distribution strategies, data processing, etc. The Athena Serving Framework aims to accelerate the cloud service of AI algorithm models and engines, providing multiple guarantees for cloud service stability through cloud-native architecture. You can efficiently and securely deploy, upgrade, scale, operate, and monitor models and engines without focusing on underlying infrastructure and service-related development, governance, and operations.