TensorRT-LLM
TensorRT LLM provides users with an easy-to-use Python API to define Large Language Models (LLMs) and supports state-of-the-art optimizations to perform inference efficiently on NVIDIA GPUs. TensorRT LLM also contains components to create Python and C++ runtimes that orchestrate the inference execution in a performant way.
Stars: 12915
TensorRT-LLM is an easy-to-use Python API to define Large Language Models (LLMs) and build TensorRT engines that contain state-of-the-art optimizations to perform inference efficiently on NVIDIA GPUs. TensorRT-LLM contains components to create Python and C++ runtimes that execute those TensorRT engines. It also includes a backend for integration with the NVIDIA Triton Inference Server; a production-quality system to serve LLMs. Models built with TensorRT-LLM can be executed on a wide range of configurations going from a single GPU to multiple nodes with multiple GPUs (using Tensor Parallelism and/or Pipeline Parallelism).
README:
TensorRT LLM provides users with an easy-to-use Python API to define Large Language Models (LLMs) and supports state-of-the-art optimizations to perform inference efficiently on NVIDIA GPUs.
Architecture | Performance | Examples | Documentation | Roadmap
-
[02/06] Accelerating Long-Context Inference with Skip Softmax Attention ✨ ➡️ link
-
[01/09] Optimizing DeepSeek-V3.2 on NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs ✨ ➡️ link
-
[10/13] Scaling Expert Parallelism in TensorRT LLM (Part 3: Pushing the Performance Boundary) ✨ ➡️ link
-
[09/26] Inference Time Compute Implementation in TensorRT LLM ✨ ➡️ link
-
[09/19] Combining Guided Decoding and Speculative Decoding: Making CPU and GPU Cooperate Seamlessly ✨ ➡️ link
-
[08/29] ADP Balance Strategy ✨ ➡️ link
-
[08/05] Running a High-Performance GPT-OSS-120B Inference Server with TensorRT LLM ✨ ➡️ link
-
[08/01] Scaling Expert Parallelism in TensorRT LLM (Part 2: Performance Status and Optimization) ✨ ➡️ link
-
[07/26] N-Gram Speculative Decoding in TensorRT LLM ✨ ➡️ link
-
[06/19] Disaggregated Serving in TensorRT LLM ✨ ➡️ link
-
[06/05] Scaling Expert Parallelism in TensorRT LLM (Part 1: Design and Implementation of Large-scale EP) ✨ ➡️ link
-
[05/30] Optimizing DeepSeek R1 Throughput on NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs: A Deep Dive for Developers ✨ ➡️ link
-
[05/23] DeepSeek R1 MTP Implementation and Optimization ✨ ➡️ link
-
[05/16] Pushing Latency Boundaries: Optimizing DeepSeek-R1 Performance on NVIDIA B200 GPUs ✨ ➡️ link
-
[08/05] 🌟 TensorRT LLM delivers Day-0 support for OpenAI's latest open-weights models: GPT-OSS-120B ➡️ link and GPT-OSS-20B ➡️ link
-
[07/15] 🌟 TensorRT LLM delivers Day-0 support for LG AI Research's latest model, EXAONE 4.0 ➡️ link
-
[06/17] Join NVIDIA and DeepInfra for a developer meetup on June 26 ✨ ➡️ link
-
[05/22] Blackwell Breaks the 1,000 TPS/User Barrier With Meta’s Llama 4 Maverick ✨ ➡️ link
-
[04/10] TensorRT LLM DeepSeek R1 performance benchmarking best practices now published. ✨ ➡️ link
-
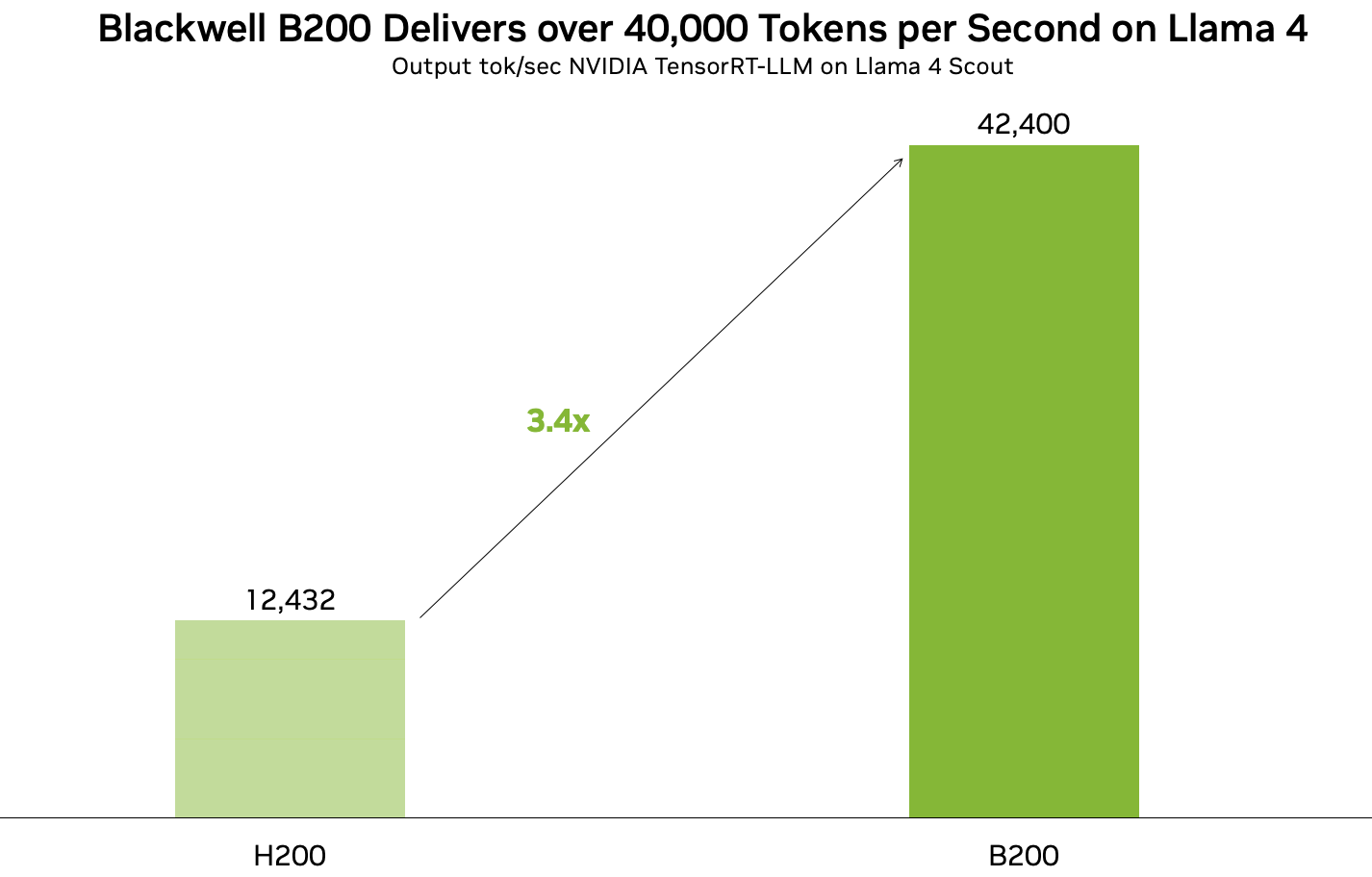
[04/05] TensorRT LLM can run Llama 4 at over 40,000 tokens per second on B200 GPUs!
-
[03/22] TensorRT LLM is now fully open-source, with developments moved to GitHub!
-
[03/18] 🚀🚀 NVIDIA Blackwell Delivers World-Record DeepSeek-R1 Inference Performance with TensorRT LLM ➡️ Link
-
[02/28] 🌟 NAVER Place Optimizes SLM-Based Vertical Services with TensorRT LLM ➡️ Link
-
[02/25] 🌟 DeepSeek-R1 performance now optimized for Blackwell ➡️ Link
-
[02/20] Explore the complete guide to achieve great accuracy, high throughput, and low latency at the lowest cost for your business here.
-
[02/18] Unlock #LLM inference with auto-scaling on @AWS EKS ✨ ➡️ link
-
[02/12] 🦸⚡ Automating GPU Kernel Generation with DeepSeek-R1 and Inference Time Scaling ➡️ link
-
[02/12] 🌟 How Scaling Laws Drive Smarter, More Powerful AI ➡️ link
Previous News
-
[2025/01/25] Nvidia moves AI focus to inference cost, efficiency ➡️ link
-
[2025/01/24] 🏎️ Optimize AI Inference Performance with NVIDIA Full-Stack Solutions ➡️ link
-
[2025/01/23] 🚀 Fast, Low-Cost Inference Offers Key to Profitable AI ➡️ link
-
[2025/01/16] Introducing New KV Cache Reuse Optimizations in TensorRT LLM ➡️ link
-
[2025/01/14] 📣 Bing's Transition to LLM/SLM Models: Optimizing Search with TensorRT LLM ➡️ link
-
[2025/01/04] ⚡Boost Llama 3.3 70B Inference Throughput 3x with TensorRT LLM Speculative Decoding ➡️ link
-
[2024/12/10] ⚡ Llama 3.3 70B from AI at Meta is accelerated by TensorRT-LLM. 🌟 State-of-the-art model on par with Llama 3.1 405B for reasoning, math, instruction following and tool use. Explore the preview ➡️ link
-
[2024/12/03] 🌟 Boost your AI inference throughput by up to 3.6x. We now support speculative decoding and tripling token throughput with our NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM. Perfect for your generative AI apps. ⚡Learn how in this technical deep dive ➡️ link
-
[2024/12/02] Working on deploying ONNX models for performance-critical applications? Try our NVIDIA Nsight Deep Learning Designer ⚡ A user-friendly GUI and tight integration with NVIDIA TensorRT that offers: ✅ Intuitive visualization of ONNX model graphs ✅ Quick tweaking of model architecture and parameters ✅ Detailed performance profiling with either ORT or TensorRT ✅ Easy building of TensorRT engines ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/26] 📣 Introducing TensorRT LLM for Jetson AGX Orin, making it even easier to deploy on Jetson AGX Orin with initial support in JetPack 6.1 via the v0.12.0-jetson branch of the TensorRT LLM repo. ✅ Pre-compiled TensorRT LLM wheels & containers for easy integration ✅ Comprehensive guides & docs to get you started ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/21] NVIDIA TensorRT LLM Multiblock Attention Boosts Throughput by More Than 3x for Long Sequence Lengths on NVIDIA HGX H200 ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/19] Llama 3.2 Full-Stack Optimizations Unlock High Performance on NVIDIA GPUs ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/09] 🚀🚀🚀 3x Faster AllReduce with NVSwitch and TensorRT LLM MultiShot ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/09] ✨ NVIDIA advances the AI ecosystem with the AI model of LG AI Research 🙌 ➡️ link
-
[2024/11/02] 🌟🌟🌟 NVIDIA and LlamaIndex Developer Contest 🙌 Enter for a chance to win prizes including an NVIDIA® GeForce RTX™ 4080 SUPER GPU, DLI credits, and more🙌 ➡️ link
-
[2024/10/28] 🏎️🏎️🏎️ NVIDIA GH200 Superchip Accelerates Inference by 2x in Multiturn Interactions with Llama Models ➡️ link
-
[2024/10/22] New 📝 Step-by-step instructions on how to ✅ Optimize LLMs with NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, ✅ Deploy the optimized models with Triton Inference Server, ✅ Autoscale LLMs deployment in a Kubernetes environment. 🙌 Technical Deep Dive: ➡️ link
-
[2024/10/07] 🚀🚀🚀Optimizing Microsoft Bing Visual Search with NVIDIA Accelerated Libraries ➡️ link
-
[2024/09/29] 🌟 AI at Meta PyTorch + TensorRT v2.4 🌟 ⚡TensorRT 10.1 ⚡PyTorch 2.4 ⚡CUDA 12.4 ⚡Python 3.12 ➡️ link
-
[2024/09/17] ✨ NVIDIA TensorRT LLM Meetup ➡️ link
-
[2024/09/17] ✨ Accelerating LLM Inference at Databricks with TensorRT-LLM ➡️ link
-
[2024/09/17] ✨ TensorRT LLM @ Baseten ➡️ link
-
[2024/09/04] 🏎️🏎️🏎️ Best Practices for Tuning TensorRT LLM for Optimal Serving with BentoML ➡️ link
-
[2024/08/20] 🏎️SDXL with #Model Optimizer ⏱️⚡ 🏁 cache diffusion 🏁 quantization aware training 🏁 QLoRA 🏁 #Python 3.12 ➡️ link
-
[2024/08/13] 🐍 DIY Code Completion with #Mamba ⚡ #TensorRT #LLM for speed 🤖 NIM for ease ☁️ deploy anywhere ➡️ link
-
[2024/08/06] 🗫 Multilingual Challenge Accepted 🗫 🤖 #TensorRT #LLM boosts low-resource languages like Hebrew, Indonesian and Vietnamese ⚡➡️ link
-
[2024/07/30] Introducing🍊 @SliceXAI ELM Turbo 🤖 train ELM once ⚡ #TensorRT #LLM optimize ☁️ deploy anywhere ➡️ link
-
[2024/07/23] 👀 @AIatMeta Llama 3.1 405B trained on 16K NVIDIA H100s - inference is #TensorRT #LLM optimized ⚡ 🦙 400 tok/s - per node 🦙 37 tok/s - per user 🦙 1 node inference ➡️ link
-
[2024/07/09] Checklist to maximize multi-language performance of @meta #Llama3 with #TensorRT #LLM inference: ✅ MultiLingual ✅ NIM ✅ LoRA tuned adaptors➡️ Tech blog
-
[2024/07/02] Let the @MistralAI MoE tokens fly 📈 🚀 #Mixtral 8x7B with NVIDIA #TensorRT #LLM on #H100. ➡️ Tech blog
-
[2024/06/24] Enhanced with NVIDIA #TensorRT #LLM, @upstage.ai’s solar-10.7B-instruct is ready to power your developer projects through our API catalog 🏎️. ✨➡️ link
-
[2024/06/18] CYMI: 🤩 Stable Diffusion 3 dropped last week 🎊 🏎️ Speed up your SD3 with #TensorRT INT8 Quantization➡️ link
-
[2024/06/18] 🧰Deploying ComfyUI with TensorRT? Here’s your setup guide ➡️ link
-
[2024/06/11] ✨#TensorRT Weight-Stripped Engines ✨ Technical Deep Dive for serious coders ✅+99% compression ✅1 set of weights → ** GPUs ✅0 performance loss ✅** models…LLM, CNN, etc.➡️ link
-
[2024/06/04] ✨ #TensorRT and GeForce #RTX unlock ComfyUI SD superhero powers 🦸⚡ 🎥 Demo: ➡️ link 📗 DIY notebook: ➡️ link
-
[2024/05/28] ✨#TensorRT weight stripping for ResNet-50 ✨ ✅+99% compression ✅1 set of weights → ** GPUs\ ✅0 performance loss ✅** models…LLM, CNN, etc 👀 📚 DIY ➡️ link
-
[2024/05/21] ✨@modal_labs has the codes for serverless @AIatMeta Llama 3 on #TensorRT #LLM ✨👀 📚 Marvelous Modal Manual: Serverless TensorRT LLM (LLaMA 3 8B) | Modal Docs ➡️ link
-
[2024/05/08] NVIDIA Model Optimizer -- the newest member of the #TensorRT ecosystem is a library of post-training and training-in-the-loop model optimization techniques ✅quantization ✅sparsity ✅QAT ➡️ blog
-
[2024/05/07] 🦙🦙🦙 24,000 tokens per second 🛫Meta Llama 3 takes off with #TensorRT #LLM 📚➡️ link
-
[2024/02/06] 🚀 Speed up inference with SOTA quantization techniques in TRT-LLM
-
[2024/01/30] New XQA-kernel provides 2.4x more Llama-70B throughput within the same latency budget
-
[2023/12/04] Falcon-180B on a single H200 GPU with INT4 AWQ, and 6.7x faster Llama-70B over A100
-
[2023/11/27] SageMaker LMI now supports TensorRT LLM - improves throughput by 60%, compared to previous version
-
[2023/11/13] H200 achieves nearly 12,000 tok/sec on Llama2-13B
-
[2023/10/22] 🚀 RAG on Windows using TensorRT LLM and LlamaIndex 🦙
-
[2023/10/19] Getting Started Guide - Optimizing Inference on Large Language Models with NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, Now Publicly Available
-
[2023/10/17] Large Language Models up to 4x Faster on RTX With TensorRT LLM for Windows
TensorRT LLM is an open-sourced library for optimizing Large Language Model (LLM) inference. It provides state-of-the-art optimizations, including custom attention kernels, inflight batching, paged KV caching, quantization (FP8, FP4, INT4 AWQ, INT8 SmoothQuant, ...), speculative decoding, and much more, to perform inference efficiently on NVIDIA GPUs.
Architected on PyTorch, TensorRT LLM provides a high-level Python LLM API that supports a wide range of inference setups - from single-GPU to multi-GPU or multi-node deployments. It includes built-in support for various parallelism strategies and advanced features. The LLM API integrates seamlessly with the broader inference ecosystem, including NVIDIA Dynamo and the Triton Inference Server.
TensorRT LLM is designed to be modular and easy to modify. Its PyTorch-native architecture allows developers to experiment with the runtime or extend functionality. Several popular models are also pre-defined and can be customized using native PyTorch code, making it easy to adapt the system to specific needs.
To get started with TensorRT-LLM, visit our documentation:
- Quick Start Guide
- Installation Guide for Linux
- Installation Guide for Grace Hopper
- Supported Hardware, Models, and other Software
- Benchmarking Performance
- Release Notes
Deprecation is used to inform developers that some APIs and tools are no longer recommended for use. Beginning with version 1.0, TensorRT LLM has the following deprecation policy:
- Communication of Deprecation
- Deprecation notices are documented in the Release Notes.
- Deprecated APIs, methods, classes, or parameters include a statement in the source code indicating when they were deprecated.
- If used, deprecated methods, classes, or parameters issue runtime deprecation warnings.
- Migration Period
- TensorRT LLM provides a 3-month migration period after deprecation.
- During this period, deprecated APIs, tools, or parameters continue to work but trigger warnings.
- Scope of Deprecation
- Full API/Method/Class Deprecation: The entire API/method/class is marked for removal.
- Partial Deprecation: If only specific parameters of an API/method are deprecated (e.g., param1 in LLM.generate(param1, param2)), the method itself remains functional, but the deprecated parameters will be removed in a future release.
- Removal After Migration Period
- After the 3-month migration period ends, deprecated APIs, tools, or parameters are removed in a manner consistent with semantic versioning (major version changes may include breaking removals).
- Quantized models on Hugging Face: A growing collection of quantized (e.g., FP8, FP4) and optimized LLMs, including DeepSeek FP4, ready for fast inference with TensorRT LLM.
- NVIDIA Dynamo: A datacenter scale distributed inference serving framework that works seamlessly with TensorRT LLM.
- AutoDeploy: A beta backend for TensorRT LLM to simplify and accelerate the deployment of PyTorch models.
- WeChat Discussion Group: A real-time channel for TensorRT LLM Q&A and news.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TensorRT-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

TensorRT-LLM
TensorRT-LLM is an easy-to-use Python API to define Large Language Models (LLMs) and build TensorRT engines that contain state-of-the-art optimizations to perform inference efficiently on NVIDIA GPUs. TensorRT-LLM contains components to create Python and C++ runtimes that execute those TensorRT engines. It also includes a backend for integration with the NVIDIA Triton Inference Server; a production-quality system to serve LLMs. Models built with TensorRT-LLM can be executed on a wide range of configurations going from a single GPU to multiple nodes with multiple GPUs (using Tensor Parallelism and/or Pipeline Parallelism).
ST-LLM
ST-LLM is a temporal-sensitive video large language model that incorporates joint spatial-temporal modeling, dynamic masking strategy, and global-local input module for effective video understanding. It has achieved state-of-the-art results on various video benchmarks. The repository provides code and weights for the model, along with demo scripts for easy usage. Users can train, validate, and use the model for tasks like video description, action identification, and reasoning.

VideoRefer
VideoRefer Suite is a tool designed to enhance the fine-grained spatial-temporal understanding capabilities of Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs). It consists of three primary components: Model (VideoRefer) for perceiving, reasoning, and retrieval for user-defined regions at any specified timestamps, Dataset (VideoRefer-700K) for high-quality object-level video instruction data, and Benchmark (VideoRefer-Bench) to evaluate object-level video understanding capabilities. The tool can understand any object within a video.

llama.cpp
The main goal of llama.cpp is to enable LLM inference with minimal setup and state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of hardware - locally and in the cloud. It provides a Plain C/C++ implementation without any dependencies, optimized for Apple silicon via ARM NEON, Accelerate and Metal frameworks, and supports various architectures like AVX, AVX2, AVX512, and AMX. It offers integer quantization for faster inference, custom CUDA kernels for NVIDIA GPUs, Vulkan and SYCL backend support, and CPU+GPU hybrid inference. llama.cpp is the main playground for developing new features for the ggml library, supporting various models and providing tools and infrastructure for LLM deployment.

intel-extension-for-transformers
Intel® Extension for Transformers is an innovative toolkit designed to accelerate GenAI/LLM everywhere with the optimal performance of Transformer-based models on various Intel platforms, including Intel Gaudi2, Intel CPU, and Intel GPU. The toolkit provides the below key features and examples: * Seamless user experience of model compressions on Transformer-based models by extending [Hugging Face transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) APIs and leveraging [Intel® Neural Compressor](https://github.com/intel/neural-compressor) * Advanced software optimizations and unique compression-aware runtime (released with NeurIPS 2022's paper [Fast Distilbert on CPUs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.07715) and [QuaLA-MiniLM: a Quantized Length Adaptive MiniLM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17114), and NeurIPS 2021's paper [Prune Once for All: Sparse Pre-Trained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.05754)) * Optimized Transformer-based model packages such as [Stable Diffusion](examples/huggingface/pytorch/text-to-image/deployment/stable_diffusion), [GPT-J-6B](examples/huggingface/pytorch/text-generation/deployment), [GPT-NEOX](examples/huggingface/pytorch/language-modeling/quantization#2-validated-model-list), [BLOOM-176B](examples/huggingface/pytorch/language-modeling/inference#BLOOM-176B), [T5](examples/huggingface/pytorch/summarization/quantization#2-validated-model-list), [Flan-T5](examples/huggingface/pytorch/summarization/quantization#2-validated-model-list), and end-to-end workflows such as [SetFit-based text classification](docs/tutorials/pytorch/text-classification/SetFit_model_compression_AGNews.ipynb) and [document level sentiment analysis (DLSA)](workflows/dlsa) * [NeuralChat](intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat), a customizable chatbot framework to create your own chatbot within minutes by leveraging a rich set of [plugins](https://github.com/intel/intel-extension-for-transformers/blob/main/intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat/docs/advanced_features.md) such as [Knowledge Retrieval](./intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat/pipeline/plugins/retrieval/README.md), [Speech Interaction](./intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat/pipeline/plugins/audio/README.md), [Query Caching](./intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat/pipeline/plugins/caching/README.md), and [Security Guardrail](./intel_extension_for_transformers/neural_chat/pipeline/plugins/security/README.md). This framework supports Intel Gaudi2/CPU/GPU. * [Inference](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main) of Large Language Model (LLM) in pure C/C++ with weight-only quantization kernels for Intel CPU and Intel GPU (TBD), supporting [GPT-NEOX](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/gptneox), [LLAMA](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/llama), [MPT](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/mpt), [FALCON](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/falcon), [BLOOM-7B](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/bloom), [OPT](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/opt), [ChatGLM2-6B](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/chatglm), [GPT-J-6B](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/gptj), and [Dolly-v2-3B](https://github.com/intel/neural-speed/tree/main/neural_speed/models/gptneox). Support AMX, VNNI, AVX512F and AVX2 instruction set. We've boosted the performance of Intel CPUs, with a particular focus on the 4th generation Intel Xeon Scalable processor, codenamed [Sapphire Rapids](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/docs/processors/xeon-accelerated/4th-gen-xeon-scalable-processors.html).
Open-Sora-Plan
Open-Sora-Plan is a project that aims to create a simple and scalable repo to reproduce Sora (OpenAI, but we prefer to call it "ClosedAI"). The project is still in its early stages, but the team is working hard to improve it and make it more accessible to the open-source community. The project is currently focused on training an unconditional model on a landscape dataset, but the team plans to expand the scope of the project in the future to include text2video experiments, training on video2text datasets, and controlling the model with more conditions.

llama.cpp
llama.cpp is a C++ implementation of LLaMA, a large language model from Meta. It provides a command-line interface for inference and can be used for a variety of tasks, including text generation, translation, and question answering. llama.cpp is highly optimized for performance and can be run on a variety of hardware, including CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs.
LLaMA-Factory
LLaMA Factory is a unified framework for fine-tuning 100+ large language models (LLMs) with various methods, including pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, PPO, DPO and ORPO. It features integrated algorithms like GaLore, BAdam, DoRA, LongLoRA, LLaMA Pro, LoRA+, LoftQ and Agent tuning, as well as practical tricks like FlashAttention-2, Unsloth, RoPE scaling, NEFTune and rsLoRA. LLaMA Factory provides experiment monitors like LlamaBoard, TensorBoard, Wandb, MLflow, etc., and supports faster inference with OpenAI-style API, Gradio UI and CLI with vLLM worker. Compared to ChatGLM's P-Tuning, LLaMA Factory's LoRA tuning offers up to 3.7 times faster training speed with a better Rouge score on the advertising text generation task. By leveraging 4-bit quantization technique, LLaMA Factory's QLoRA further improves the efficiency regarding the GPU memory.
lmdeploy
LMDeploy is a toolkit for compressing, deploying, and serving LLM, developed by the MMRazor and MMDeploy teams. It has the following core features: * **Efficient Inference** : LMDeploy delivers up to 1.8x higher request throughput than vLLM, by introducing key features like persistent batch(a.k.a. continuous batching), blocked KV cache, dynamic split&fuse, tensor parallelism, high-performance CUDA kernels and so on. * **Effective Quantization** : LMDeploy supports weight-only and k/v quantization, and the 4-bit inference performance is 2.4x higher than FP16. The quantization quality has been confirmed via OpenCompass evaluation. * **Effortless Distribution Server** : Leveraging the request distribution service, LMDeploy facilitates an easy and efficient deployment of multi-model services across multiple machines and cards. * **Interactive Inference Mode** : By caching the k/v of attention during multi-round dialogue processes, the engine remembers dialogue history, thus avoiding repetitive processing of historical sessions.
Awesome-Colorful-LLM
Awesome-Colorful-LLM is a meticulously assembled anthology of vibrant multimodal research focusing on advancements propelled by large language models (LLMs) in domains such as Vision, Audio, Agent, Robotics, and Fundamental Sciences like Mathematics. The repository contains curated collections of works, datasets, benchmarks, projects, and tools related to LLMs and multimodal learning. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the intersection of language models and various modalities for tasks like image understanding, video pretraining, 3D modeling, document understanding, audio analysis, agent learning, robotic applications, and mathematical research.
For similar tasks
litgpt
LitGPT is a command-line tool designed to easily finetune, pretrain, evaluate, and deploy 20+ LLMs **on your own data**. It features highly-optimized training recipes for the world's most powerful open-source large-language-models (LLMs).
llm-engine
Scale's LLM Engine is an open-source Python library, CLI, and Helm chart that provides everything you need to serve and fine-tune foundation models, whether you use Scale's hosted infrastructure or do it in your own cloud infrastructure using Kubernetes.

LLaMA-Factory
LLaMA Factory is a unified framework for fine-tuning 100+ large language models (LLMs) with various methods, including pre-training, supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, PPO, DPO and ORPO. It features integrated algorithms like GaLore, BAdam, DoRA, LongLoRA, LLaMA Pro, LoRA+, LoftQ and Agent tuning, as well as practical tricks like FlashAttention-2, Unsloth, RoPE scaling, NEFTune and rsLoRA. LLaMA Factory provides experiment monitors like LlamaBoard, TensorBoard, Wandb, MLflow, etc., and supports faster inference with OpenAI-style API, Gradio UI and CLI with vLLM worker. Compared to ChatGLM's P-Tuning, LLaMA Factory's LoRA tuning offers up to 3.7 times faster training speed with a better Rouge score on the advertising text generation task. By leveraging 4-bit quantization technique, LLaMA Factory's QLoRA further improves the efficiency regarding the GPU memory.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
llm-foundry
LLM Foundry is a codebase for training, finetuning, evaluating, and deploying LLMs for inference with Composer and the MosaicML platform. It is designed to be easy-to-use, efficient _and_ flexible, enabling rapid experimentation with the latest techniques. You'll find in this repo: * `llmfoundry/` - source code for models, datasets, callbacks, utilities, etc. * `scripts/` - scripts to run LLM workloads * `data_prep/` - convert text data from original sources to StreamingDataset format * `train/` - train or finetune HuggingFace and MPT models from 125M - 70B parameters * `train/benchmarking` - profile training throughput and MFU * `inference/` - convert models to HuggingFace or ONNX format, and generate responses * `inference/benchmarking` - profile inference latency and throughput * `eval/` - evaluate LLMs on academic (or custom) in-context-learning tasks * `mcli/` - launch any of these workloads using MCLI and the MosaicML platform * `TUTORIAL.md` - a deeper dive into the repo, example workflows, and FAQs
EdgeChains
EdgeChains is an open-source chain-of-thought engineering framework tailored for Large Language Models (LLMs)- like OpenAI GPT, LLama2, Falcon, etc. - With a focus on enterprise-grade deployability and scalability. EdgeChains is specifically designed to **orchestrate** such applications. At EdgeChains, we take a unique approach to Generative AI - we think Generative AI is a deployment and configuration management challenge rather than a UI and library design pattern challenge. We build on top of a tech that has solved this problem in a different domain - Kubernetes Config Management - and bring that to Generative AI. Edgechains is built on top of jsonnet, originally built by Google based on their experience managing a vast amount of configuration code in the Borg infrastructure.
llm-action
This repository provides a comprehensive guide to large language models (LLMs), covering various aspects such as training, fine-tuning, compression, and applications. It includes detailed tutorials, code examples, and explanations of key concepts and techniques. The repository is maintained by Liguo Dong, an AI researcher and engineer with expertise in LLM research and development.

llm-on-openshift
This repository provides resources, demos, and recipes for working with Large Language Models (LLMs) on OpenShift using OpenShift AI or Open Data Hub. It includes instructions for deploying inference servers for LLMs, such as vLLM, Hugging Face TGI, Caikit-TGIS-Serving, and Ollama. Additionally, it offers guidance on deploying serving runtimes, such as vLLM Serving Runtime and Hugging Face Text Generation Inference, in the Single-Model Serving stack of Open Data Hub or OpenShift AI. The repository also covers vector databases that can be used as a Vector Store for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications, including Milvus, PostgreSQL+pgvector, and Redis. Furthermore, it provides examples of inference and application usage, such as Caikit, Langchain, Langflow, and UI examples.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.