
Better-Ruozhiba
【逐条处理完成】人为审核+修改每一条的弱智吧精选问题QA数据集
Stars: 245
Better Ruozhiba is a modified version of the GPT-4 model for Chinese text generation. Contributors manually reviewed and corrected original text errors, aiming to improve the Chinese language corpus for large language models. The project provides enhanced answers to questions, with a focus on improving the quality of generated responses.
README:
license: apache-2.0 task_categories:
- text-generation language:
- zh
原项目为 https://huggingface.co/datasets/LooksJuicy/ruozhiba,原部分答案为 GPT-4 生成。贡献者们人为审阅了每一条的原文和回复,剔除了一些原文中的格式错误,修改或重写了部分答案。希望对大语言模型的中文语料有所帮助。
PS. 正儿八经回答弱智吧的问题,真是一种奇妙的感觉
如果有意参与贡献,请查看此 issue
如果本项目对你有所帮助,请引用:
@misc{better-ruozhiba,
title={Better Ruozhiba},
author={Ruozhiba and FunnySaltyFish and Misdirection and Xinsu,Liu},
year={2024},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/FunnySaltyFish/Better-Ruozhiba}}
} 我的更多项目列表:https://web.funnysaltyfish.fun/
另一个语料相关项目:基于 B 站评论区数据构建大语言模型训练用对话数据集
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Better-Ruozhiba
Similar Open Source Tools

Better-Ruozhiba
Better Ruozhiba is a modified version of the GPT-4 model for Chinese text generation. Contributors manually reviewed and corrected original text errors, aiming to improve the Chinese language corpus for large language models. The project provides enhanced answers to questions, with a focus on improving the quality of generated responses.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
LLMRec
LLMRec is a PyTorch implementation for the WSDM 2024 paper 'Large Language Models with Graph Augmentation for Recommendation'. It is a novel framework that enhances recommenders by applying LLM-based graph augmentation strategies to recommendation systems. The tool aims to make the most of content within online platforms to augment interaction graphs by reinforcing u-i interactive edges, enhancing item node attributes, and conducting user node profiling from a natural language perspective.
scikit-llm
Scikit-LLM is a tool that seamlessly integrates powerful language models like ChatGPT into scikit-learn for enhanced text analysis tasks. It allows users to leverage large language models for various text analysis applications within the familiar scikit-learn framework. The tool simplifies the process of incorporating advanced language processing capabilities into machine learning pipelines, enabling users to benefit from the latest advancements in natural language processing.
langchaingo
LangChain Go is a Go language implementation of LangChain, a framework for building applications with LLMs through composability. It provides a simple and easy-to-use API for interacting with LLMs, making it easy to add language-based features to your applications.
eino
Eino is an ultimate LLM application development framework in Golang, emphasizing simplicity, scalability, reliability, and effectiveness. It provides a curated list of component abstractions, a powerful composition framework, meticulously designed APIs, best practices, and tools covering the entire development cycle. Eino standardizes and improves efficiency in AI application development by offering rich components, powerful orchestration, complete stream processing, highly extensible aspects, and a comprehensive framework structure.
lionagi
LionAGI is a powerful intelligent workflow automation framework that introduces advanced ML models into any existing workflows and data infrastructure. It can interact with almost any model, run interactions in parallel for most models, produce structured pydantic outputs with flexible usage, automate workflow via graph based agents, use advanced prompting techniques, and more. LionAGI aims to provide a centralized agent-managed framework for "ML-powered tools coordination" and to dramatically lower the barrier of entries for creating use-case/domain specific tools. It is designed to be asynchronous only and requires Python 3.10 or higher.

EasySteer
EasySteer is a unified framework built on vLLM for high-performance LLM steering. It offers fast, flexible, and easy-to-use steering capabilities with features like high performance, modular design, fine-grained control, pre-computed steering vectors, and an interactive demo. Users can interactively configure models, adjust steering parameters, and test interventions without writing code. The tool supports OpenAI-compatible APIs and provides modules for hidden states extraction, analysis-based steering, learning-based steering, and a frontend web interface for interactive steering and ReFT interventions.
LTEngine
LTEngine is a free and open-source local AI machine translation API written in Rust. It is self-hosted and compatible with LibreTranslate. LTEngine utilizes large language models (LLMs) via llama.cpp, offering high-quality translations that rival or surpass DeepL for certain languages. It supports various accelerators like CUDA, Metal, and Vulkan, with the largest model 'gemma3-27b' fitting on a single consumer RTX 3090. LTEngine is actively developed, with a roadmap outlining future enhancements and features.
omnihuman
OmniHuman is an AI model designed to understand humanoids and text. It provides functionalities to process images and videos, generating text descriptions for human actions depicted in the visual content. The tool offers support for various tasks related to human pose recognition and action understanding. Users can easily integrate OmniHuman into their projects to enhance the capabilities of their applications in recognizing and interpreting human actions in images and videos.
flow-prompt
Flow Prompt is a dynamic library for managing and optimizing prompts for large language models. It facilitates budget-aware operations, dynamic data integration, and efficient load distribution. Features include CI/CD testing, dynamic prompt development, multi-model support, real-time insights, and prompt testing and evolution.
sophia
Sophia is an open-source TypeScript platform designed for autonomous AI agents and LLM based workflows. It aims to automate processes, review code, assist with refactorings, and support various integrations. The platform offers features like advanced autonomous agents, reasoning/planning inspired by Google's Self-Discover paper, memory and function call history, adaptive iterative planning, and more. Sophia supports multiple LLMs/services, CLI and web interface, human-in-the-loop interactions, flexible deployment options, observability with OpenTelemetry tracing, and specific agents for code editing, software engineering, and code review. It provides a flexible platform for the TypeScript community to expand and support various use cases and integrations.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.
Endia
Endia is a dynamic Array library for Scientific Computing, offering automatic differentiation of arbitrary order, complex number support, dual API with PyTorch-like imperative or JAX-like functional interface, and JIT Compilation for speeding up training and inference. It can handle complex valued functions, perform both forward and reverse-mode automatic differentiation, and has a builtin JIT compiler. Endia aims to advance AI & Scientific Computing by pushing boundaries with clear algorithms, providing high-performance open-source code that remains readable and pythonic, and prioritizing clarity and educational value over exhaustive features.
educhain
Educhain is a powerful Python package that leverages Generative AI to create engaging and personalized educational content. It enables users to generate multiple-choice questions, create lesson plans, and support various LLM models. Users can export questions to JSON, PDF, and CSV formats, customize prompt templates, and generate questions from text, PDF, URL files, youtube videos, and images. Educhain outperforms traditional methods in content generation speed and quality. It offers advanced configuration options and has a roadmap for future enhancements, including integration with popular Learning Management Systems and a mobile app for content generation on-the-go.

LightRAG
LightRAG is a PyTorch library designed for building and optimizing Retriever-Agent-Generator (RAG) pipelines. It follows principles of simplicity, quality, and optimization, offering developers maximum customizability with minimal abstraction. The library includes components for model interaction, output parsing, and structured data generation. LightRAG facilitates tasks like providing explanations and examples for concepts through a question-answering pipeline.
For similar tasks

Better-Ruozhiba
Better Ruozhiba is a modified version of the GPT-4 model for Chinese text generation. Contributors manually reviewed and corrected original text errors, aiming to improve the Chinese language corpus for large language models. The project provides enhanced answers to questions, with a focus on improving the quality of generated responses.
semantic-router
Semantic Router is a superfast decision-making layer for your LLMs and agents. Rather than waiting for slow LLM generations to make tool-use decisions, we use the magic of semantic vector space to make those decisions — _routing_ our requests using _semantic_ meaning.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.
luna-ai
Luna AI is a virtual streamer driven by a 'brain' composed of ChatterBot, GPT, Claude, langchain, chatglm, text-generation-webui, 讯飞星火, 智谱AI. It can interact with viewers in real-time during live streams on platforms like Bilibili, Douyin, Kuaishou, Douyu, or chat with you locally. Luna AI uses natural language processing and text-to-speech technologies like Edge-TTS, VITS-Fast, elevenlabs, bark-gui, VALL-E-X to generate responses to viewer questions and can change voice using so-vits-svc, DDSP-SVC. It can also collaborate with Stable Diffusion for drawing displays and loop custom texts. This project is completely free, and any identical copycat selling programs are pirated, please stop them promptly.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.

cria
Cria is a Python library designed for running Large Language Models with minimal configuration. It provides an easy and concise way to interact with LLMs, offering advanced features such as custom models, streams, message history management, and running multiple models in parallel. Cria simplifies the process of using LLMs by providing a straightforward API that requires only a few lines of code to get started. It also handles model installation automatically, making it efficient and user-friendly for various natural language processing tasks.
beyondllm
Beyond LLM offers an all-in-one toolkit for experimentation, evaluation, and deployment of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It simplifies the process with automated integration, customizable evaluation metrics, and support for various Large Language Models (LLMs) tailored to specific needs. The aim is to reduce LLM hallucination risks and enhance reliability.
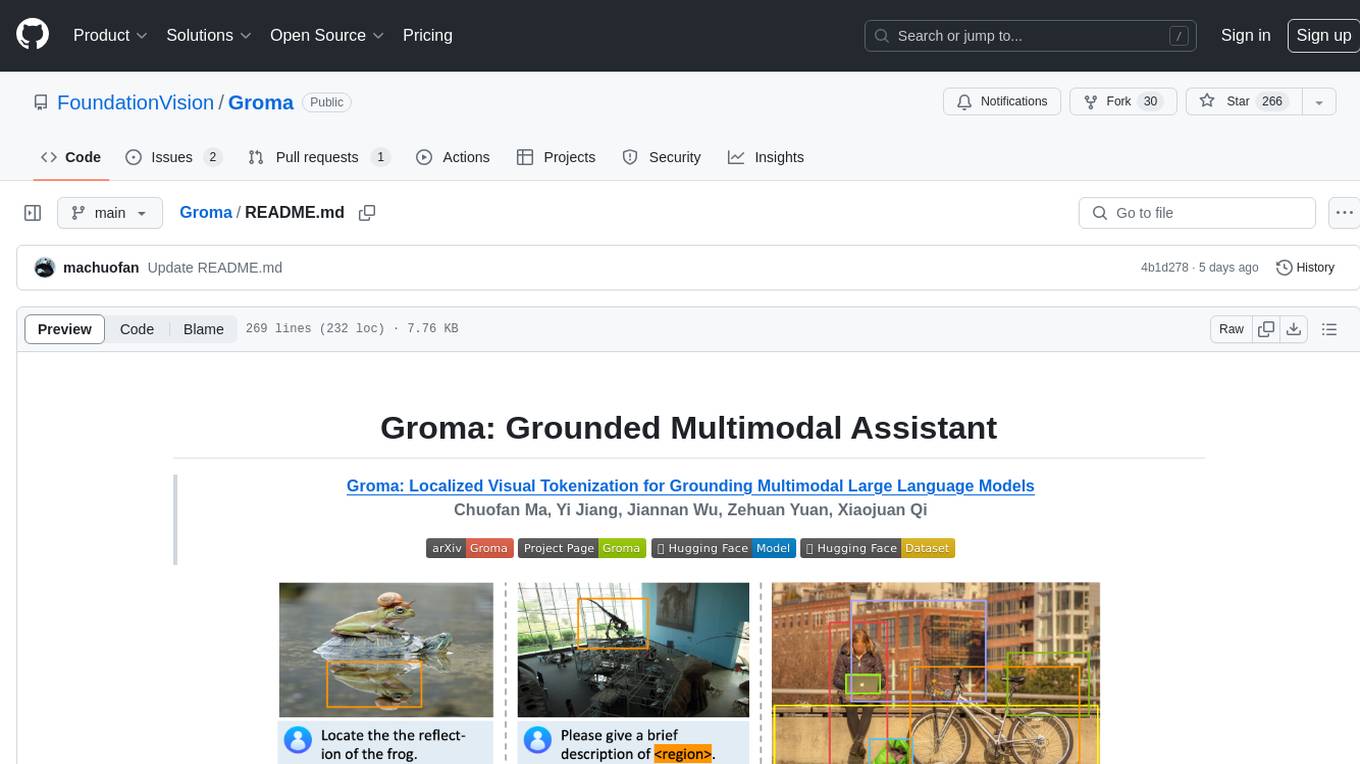
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.