
mcp-server-qdrant
An official Qdrant Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementation
Stars: 386
The mcp-server-qdrant repository is an official Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for keeping and retrieving memories in the Qdrant vector search engine. It acts as a semantic memory layer on top of the Qdrant database. The server provides tools like 'qdrant-store' for storing information in the database and 'qdrant-find' for retrieving relevant information. Configuration is done using environment variables, and the server supports different transport protocols. It can be installed using 'uvx' or Docker, and can also be installed via Smithery for Claude Desktop. The server can be used with Cursor/Windsurf as a code search tool by customizing tool descriptions. It can store code snippets and help developers find specific implementations or usage patterns. The repository is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
README:
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open protocol that enables seamless integration between LLM applications and external data sources and tools. Whether you’re building an AI-powered IDE, enhancing a chat interface, or creating custom AI workflows, MCP provides a standardized way to connect LLMs with the context they need.
This repository is an example of how to create a MCP server for Qdrant, a vector search engine.
An official Model Context Protocol server for keeping and retrieving memories in the Qdrant vector search engine. It acts as a semantic memory layer on top of the Qdrant database.
-
qdrant-store- Store some information in the Qdrant database
- Input:
-
information(string): Information to store -
metadata(JSON): Optional metadata to store
-
- Returns: Confirmation message
-
qdrant-find- Retrieve relevant information from the Qdrant database
- Input:
-
query(string): Query to use for searching
-
- Returns: Information stored in the Qdrant database as separate messages
The configuration of the server is done using environment variables:
| Name | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
QDRANT_URL |
URL of the Qdrant server | None |
QDRANT_API_KEY |
API key for the Qdrant server | None |
COLLECTION_NAME |
Name of the collection to use | Required |
QDRANT_LOCAL_PATH |
Path to the local Qdrant database (alternative to QDRANT_URL) |
None |
EMBEDDING_PROVIDER |
Embedding provider to use (currently only "fastembed" is supported) | fastembed |
EMBEDDING_MODEL |
Name of the embedding model to use | sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 |
TOOL_STORE_DESCRIPTION |
Custom description for the store tool | See default in settings.py
|
TOOL_FIND_DESCRIPTION |
Custom description for the find tool | See default in settings.py
|
Note: You cannot provide both QDRANT_URL and QDRANT_LOCAL_PATH at the same time.
[!IMPORTANT] Command-line arguments are not supported anymore! Please use environment variables for all configuration.
When using uvx no specific installation is needed to directly run mcp-server-qdrant.
QDRANT_URL="http://localhost:6333" \
COLLECTION_NAME="my-collection" \
EMBEDDING_MODEL="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2" \
uvx mcp-server-qdrantThe server supports different transport protocols that can be specified using the --transport flag:
QDRANT_URL="http://localhost:6333" \
COLLECTION_NAME="my-collection" \
uvx mcp-server-qdrant --transport sseSupported transport protocols:
-
stdio(default): Standard input/output transport, might only be used by local MCP clients -
sse: Server-Sent Events transport, perfect for remote clients
The default transport is stdio if not specified.
A Dockerfile is available for building and running the MCP server:
# Build the container
docker build -t mcp-server-qdrant .
# Run the container
docker run -p 8000:8000 \
-e QDRANT_URL="http://your-qdrant-server:6333" \
-e QDRANT_API_KEY="your-api-key" \
-e COLLECTION_NAME="your-collection" \
mcp-server-qdrantTo install Qdrant MCP Server for Claude Desktop automatically via Smithery:
npx @smithery/cli install mcp-server-qdrant --client claudeTo use this server with the Claude Desktop app, add the following configuration to the "mcpServers" section of your
claude_desktop_config.json:
{
"qdrant": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-qdrant"],
"env": {
"QDRANT_URL": "https://xyz-example.eu-central.aws.cloud.qdrant.io:6333",
"QDRANT_API_KEY": "your_api_key",
"COLLECTION_NAME": "your-collection-name",
"EMBEDDING_MODEL": "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
}
}
}For local Qdrant mode:
{
"qdrant": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-qdrant"],
"env": {
"QDRANT_LOCAL_PATH": "/path/to/qdrant/database",
"COLLECTION_NAME": "your-collection-name",
"EMBEDDING_MODEL": "sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
}
}
}This MCP server will automatically create a collection with the specified name if it doesn't exist.
By default, the server will use the sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 embedding model to encode memories.
For the time being, only FastEmbed models are supported.
This MCP server can be used with any MCP-compatible client. For example, you can use it with Cursor, which provides built-in support for the Model Context Protocol.
You can configure this MCP server to work as a code search tool for Cursor or Windsurf by customizing the tool descriptions:
QDRANT_URL="http://localhost:6333" \
COLLECTION_NAME="code-snippets" \
TOOL_STORE_DESCRIPTION="Store reusable code snippets for later retrieval. \
The 'information' parameter should contain a natural language description of what the code does, \
while the actual code should be included in the 'metadata' parameter as a 'code' property. \
The value of 'metadata' is a Python dictionary with strings as keys. \
Use this whenever you generate some code snippet." \
TOOL_FIND_DESCRIPTION="Search for relevant code snippets based on natural language descriptions. \
The 'query' parameter should describe what you're looking for, \
and the tool will return the most relevant code snippets. \
Use this when you need to find existing code snippets for reuse or reference." \
uvx mcp-server-qdrant --transport sse # Enable SSE transportIn Cursor/Windsurf, you can then configure the MCP server in your settings by pointing to this running server using SSE transport protocol. The description on how to add an MCP server to Cursor can be found in the Cursor documentation. If you are running Cursor/Windsurf locally, you can use the following URL:
http://localhost:8000/sse
[!TIP] We suggest SSE transport as a preferred way to connect Cursor/Windsurf to the MCP server, as it can support remote connections. That makes it easy to share the server with your team or use it in a cloud environment.
This configuration transforms the Qdrant MCP server into a specialized code search tool that can:
- Store code snippets, documentation, and implementation details
- Retrieve relevant code examples based on semantic search
- Help developers find specific implementations or usage patterns
You can populate the database by storing natural language descriptions of code snippets (in the information parameter)
along with the actual code (in the metadata.code property), and then search for them using natural language queries
that describe what you're looking for.
[!NOTE] The tool descriptions provided above are examples and may need to be customized for your specific use case. Consider adjusting the descriptions to better match your team's workflow and the specific types of code snippets you want to store and retrieve.
If you have successfully installed the mcp-server-qdrant, but still can't get it to work with Cursor, please
consider creating the Cursor rules so the MCP tools are always used when
the agent produces a new code snippet. You can restrict the rules to only work for certain file types, to avoid using
the MCP server for the documentation or other types of content.
You can enhance Claude Code's capabilities by connecting it to this MCP server, enabling semantic search over your existing codebase.
-
Add the MCP server to Claude Code:
# Add mcp-server-qdrant configured for code search claude mcp add code-search \ -e QDRANT_URL="http://localhost:6333" \ -e COLLECTION_NAME="code-repository" \ -e EMBEDDING_MODEL="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2" \ -e TOOL_STORE_DESCRIPTION="Store code snippets with descriptions. The 'information' parameter should contain a natural language description of what the code does, while the actual code should be included in the 'metadata' parameter as a 'code' property." \ -e TOOL_FIND_DESCRIPTION="Search for relevant code snippets using natural language. The 'query' parameter should describe the functionality you're looking for." \ -- uvx mcp-server-qdrant
-
Verify the server was added:
claude mcp list
Tool descriptions, specified in TOOL_STORE_DESCRIPTION and TOOL_FIND_DESCRIPTION, guide Claude Code on how to use
the MCP server. The ones provided above are examples and may need to be customized for your specific use case. However,
Claude Code should be already able to:
- Use the
qdrant-storetool to store code snippets with descriptions. - Use the
qdrant-findtool to search for relevant code snippets using natural language.
If you have suggestions for how mcp-server-qdrant could be improved, or want to report a bug, open an issue! We'd love all and any contributions.
The MCP inspector is a developer tool for testing and debugging MCP servers. It runs both a client UI (default port 5173) and an MCP proxy server (default port 3000). Open the client UI in your browser to use the inspector.
QDRANT_URL=":memory:" COLLECTION_NAME="test" \
mcp dev src/mcp_server_qdrant/server.pyOnce started, open your browser to http://localhost:5173 to access the inspector interface.
This MCP server is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. This means you are free to use, modify, and distribute the software, subject to the terms and conditions of the Apache License 2.0. For more details, please see the LICENSE file in the project repository.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mcp-server-qdrant
Similar Open Source Tools

mcp-server-qdrant
The mcp-server-qdrant repository is an official Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for keeping and retrieving memories in the Qdrant vector search engine. It acts as a semantic memory layer on top of the Qdrant database. The server provides tools like 'qdrant-store' for storing information in the database and 'qdrant-find' for retrieving relevant information. Configuration is done using environment variables, and the server supports different transport protocols. It can be installed using 'uvx' or Docker, and can also be installed via Smithery for Claude Desktop. The server can be used with Cursor/Windsurf as a code search tool by customizing tool descriptions. It can store code snippets and help developers find specific implementations or usage patterns. The repository is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
MCPJungle
MCPJungle is a self-hosted MCP Gateway for private AI agents, serving as a registry for Model Context Protocol Servers. Developers use it to manage servers and tools centrally, while clients discover and consume tools from a single 'Gateway' MCP Server. Suitable for developers using MCP Clients like Claude & Cursor, building production-grade AI Agents, and organizations managing client-server interactions. The tool allows quick start, installation, usage, server and client setup, connection to Claude and Cursor, enabling/disabling tools, managing tool groups, authentication, enterprise features like access control and OpenTelemetry metrics. Limitations include lack of long-running connections to servers and no support for OAuth flow. Contributions are welcome.
mcp
The Snowflake Cortex AI Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server provides tooling for Snowflake Cortex AI, object management, and SQL orchestration. It supports capabilities such as Cortex Search, Cortex Analyst, Cortex Agent, Object Management, SQL Execution, and Semantic View Querying. Users can connect to Snowflake using various authentication methods like username/password, key pair, OAuth, SSO, and MFA. The server is client-agnostic and works with MCP Clients like Claude Desktop, Cursor, fast-agent, Microsoft Visual Studio Code + GitHub Copilot, and Codex. It includes tools for Object Management (creating, dropping, describing, listing objects), SQL Execution (executing SQL statements), and Semantic View Querying (discovering, querying Semantic Views). Troubleshooting can be done using the MCP Inspector tool.
supabase-mcp
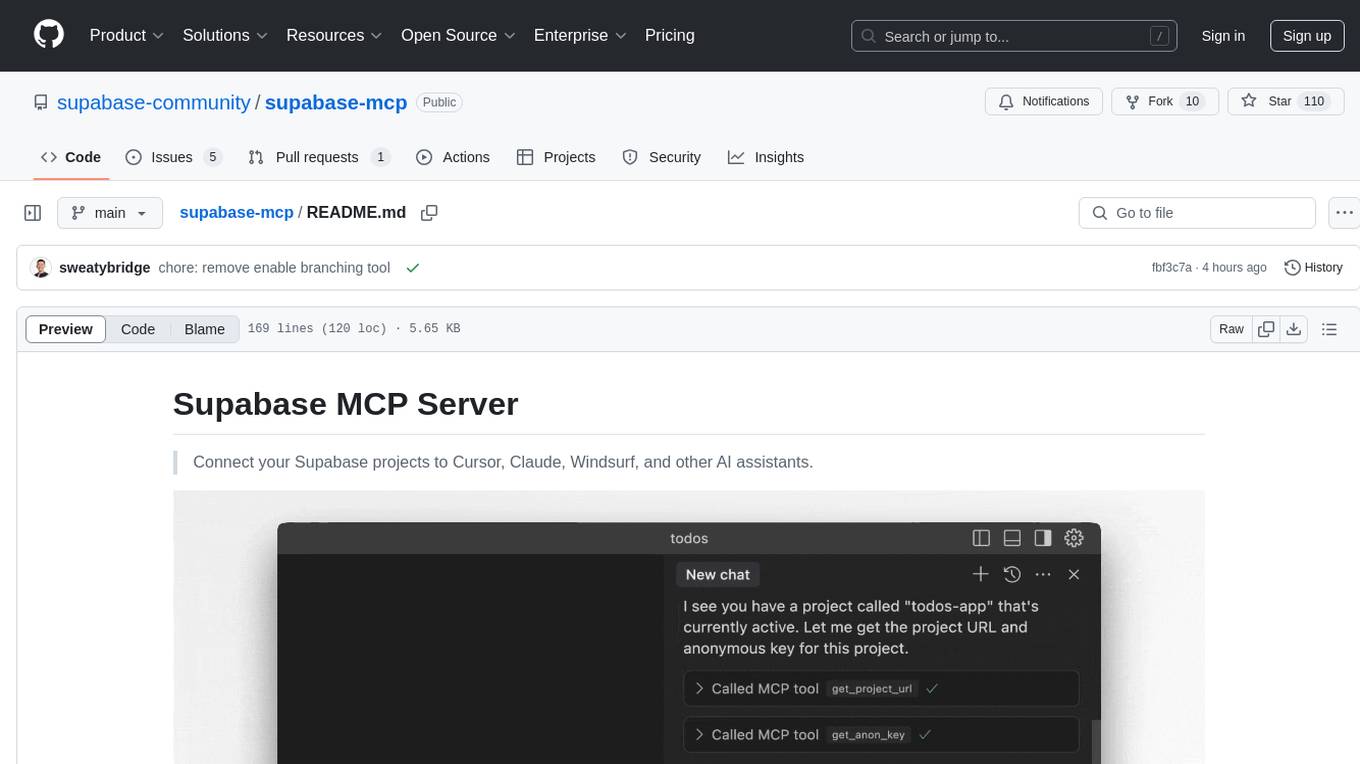
Supabase MCP Server standardizes how Large Language Models (LLMs) interact with Supabase, enabling AI assistants to manage tables, fetch config, and query data. It provides tools for project management, database operations, project configuration, branching (experimental), and development tools. The server is pre-1.0, so expect some breaking changes between versions.

chat-mcp
A Cross-Platform Interface for Large Language Models (LLMs) utilizing the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect and interact with various LLMs. The desktop app, built on Electron, ensures compatibility across Linux, macOS, and Windows. It simplifies understanding MCP principles, facilitates testing of multiple servers and LLMs, and supports dynamic LLM configuration and multi-client management. The UI can be extracted for web use, ensuring consistency across web and desktop versions.
mcp-graphql
mcp-graphql is a Model Context Protocol server that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with GraphQL APIs. It provides schema introspection and query execution capabilities, allowing models to dynamically discover and use GraphQL APIs. The server offers tools for retrieving the GraphQL schema and executing queries against the endpoint. Mutations are disabled by default for security reasons. Users can install mcp-graphql via Smithery or manually to Claude Desktop. It is recommended to carefully consider enabling mutations in production environments to prevent unauthorized data modifications.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
computer-use-mcp
The computer-use-mcp repository is a model context protocol server that allows Claude to control your computer. It is similar to computer use but is easy to set up and use locally. Users should be cautious as the server gives the model complete control of the computer, similar to giving a hyperactive toddler access. The tool communicates with the computer using nut.js and follows Anthropic's official computer use guide with a focus on keyboard shortcuts.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
bedrock-claude-chat
This repository is a sample chatbot using the Anthropic company's LLM Claude, one of the foundational models provided by Amazon Bedrock for generative AI. It allows users to have basic conversations with the chatbot, personalize it with their own instructions and external knowledge, and analyze usage for each user/bot on the administrator dashboard. The chatbot supports various languages, including English, Japanese, Korean, Chinese, French, German, and Spanish. Deployment is straightforward and can be done via the command line or by using AWS CDK. The architecture is built on AWS managed services, eliminating the need for infrastructure management and ensuring scalability, reliability, and security.
tuui
TUUI is a desktop MCP client designed for accelerating AI adoption through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and enabling cross-vendor LLM API orchestration. It is an LLM chat desktop application based on MCP, created using AI-generated components with strict syntax checks and naming conventions. The tool integrates AI tools via MCP, orchestrates LLM APIs, supports automated application testing, TypeScript, multilingual, layout management, global state management, and offers quick support through the GitHub community and official documentation.
magic-cli
Magic CLI is a command line utility that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance command line efficiency. It is inspired by projects like Amazon Q and GitHub Copilot for CLI. The tool allows users to suggest commands, search across command history, and generate commands for specific tasks using local or remote LLM providers. Magic CLI also provides configuration options for LLM selection and response generation. The project is still in early development, so users should expect breaking changes and bugs.
nextjs-openai-doc-search
This starter project is designed to process `.mdx` files in the `pages` directory to use as custom context within OpenAI Text Completion prompts. It involves building a custom ChatGPT style doc search powered by Next.js, OpenAI, and Supabase. The project includes steps for pre-processing knowledge base, storing embeddings in Postgres, performing vector similarity search, and injecting content into OpenAI GPT-3 text completion prompt.
langchain-extract
LangChain Extract is a simple web server that allows you to extract information from text and files using LLMs. It is built using FastAPI, LangChain, and Postgresql. The backend closely follows the extraction use-case documentation and provides a reference implementation of an app that helps to do extraction over data using LLMs. This repository is meant to be a starting point for building your own extraction application which may have slightly different requirements or use cases.
hash
HASH is a self-building, open-source database which grows, structures and checks itself. With it, we're creating a platform for decision-making, which helps you integrate, understand and use data in a variety of different ways.
laragenie
Laragenie is an AI chatbot designed to understand and assist developers with their codebases. It runs on the command line from a Laravel app, helping developers onboard to new projects, understand codebases, and provide daily support. Laragenie accelerates workflow and collaboration by indexing files and directories, allowing users to ask questions and receive AI-generated responses. It supports OpenAI and Pinecone for processing and indexing data, making it a versatile tool for any repo in any language.
For similar tasks
mac-studio-server
This repository provides configuration and scripts for running Ollama LLM server on Apple Silicon Macs in headless mode, optimized for performance and resource usage. It includes features like automatic startup, system resource optimization, external network access, proper logging setup, and SSH-based remote management. Users can customize the Ollama service configuration and enable optional GPU memory optimization and Docker autostart for container applications. The installation process disables unnecessary system services, configures power management, and optimizes for background operation while maintaining Screen Sharing capability for remote management. Performance considerations focus on reducing memory usage, disabling GUI-related services, minimizing background processes, preventing sleep/hibernation, and optimizing for headless operation.

mcp-server-qdrant
The mcp-server-qdrant repository is an official Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed for keeping and retrieving memories in the Qdrant vector search engine. It acts as a semantic memory layer on top of the Qdrant database. The server provides tools like 'qdrant-store' for storing information in the database and 'qdrant-find' for retrieving relevant information. Configuration is done using environment variables, and the server supports different transport protocols. It can be installed using 'uvx' or Docker, and can also be installed via Smithery for Claude Desktop. The server can be used with Cursor/Windsurf as a code search tool by customizing tool descriptions. It can store code snippets and help developers find specific implementations or usage patterns. The repository is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
echokit_box
EchoKit is a tool for setting up and flashing firmware on the EchoKit device. It provides instructions for flashing the device image, installing necessary dependencies, building firmware from source, and flashing the firmware onto the device. The tool also includes steps for resetting the device and configuring it to connect to an EchoKit server for full functionality.
db-ally
db-ally is a library for creating natural language interfaces to data sources. It allows developers to outline specific use cases for a large language model (LLM) to handle, detailing the desired data format and the possible operations to fetch this data. db-ally effectively shields the complexity of the underlying data source from the model, presenting only the essential information needed for solving the specific use cases. Instead of generating arbitrary SQL, the model is asked to generate responses in a simplified query language.
aiocache
Aiocache is an asyncio cache library that supports multiple backends such as memory, redis, and memcached. It provides a simple interface for functions like add, get, set, multi_get, multi_set, exists, increment, delete, clear, and raw. Users can easily install and use the library for caching data in Python applications. Aiocache allows for easy instantiation of caches and setup of cache aliases for reusing configurations. It also provides support for backends, serializers, and plugins to customize cache operations. The library offers detailed documentation and examples for different use cases and configurations.
AirBnB_clone_v2
The AirBnB Clone - The Console project is the first segment of the AirBnB project at Holberton School, aiming to cover fundamental concepts of higher level programming. The goal is to deploy a server as a simple copy of the AirBnB Website (HBnB). The project includes a command interpreter to manage objects for the AirBnB website, allowing users to create new objects, retrieve objects, perform operations on objects, update object attributes, and destroy objects. The project is interpreted/tested on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS using Python 3.4.3.
ask-astro
Ask Astro is an open-source reference implementation of Andreessen Horowitz's LLM Application Architecture built by Astronomer. It provides an end-to-end example of a Q&A LLM application used to answer questions about Apache Airflow® and Astronomer. Ask Astro includes Airflow DAGs for data ingestion, an API for business logic, a Slack bot, a public UI, and DAGs for processing user feedback. The tool is divided into data retrieval & embedding, prompt orchestration, and feedback loops.
ai-tutor-rag-system
The AI Tutor RAG System repository contains Jupyter notebooks supporting the RAG course, focusing on enhancing AI models with retrieval-based methods. It covers foundational and advanced concepts in retrieval-augmented generation, including data retrieval techniques, model integration with retrieval systems, and practical applications of RAG in real-world scenarios.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.