
AgroTech-AI
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture
Stars: 54
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more. The platform implements machine learning algorithms to provide functionalities like fertilizer prediction, crop prediction, soil quality prediction, yield prediction, and mushroom edibility prediction.
README:
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more.
Make sure you star the repository and show your love to us💗
Contributing in open source increases your opportunities to work with different projects and mentors, getting to know various insights and ideas. It is a platform where contributors grow together with a construvtive and a positive attitude. This repository also provides one such platforms where contributers come over and put their ideas and make our website as interactive as much they can!
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more.
It implements machine learning algorithms to implement 3 basic functionalities:
Aims to predict the appropriate fertilizer based on environmental and soil conditions. The dataset contains various features like temperature, humidity, moisture, soil type, crop type, and the levels of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus in the soil. The model aims to recommend the correct fertilizer to use, improving crop yield and soil health.
Fertilizer Prediction.csv (Uploaded under notebooks)
A Random Forest Classifier was chosen as the primary model due to its robustness and high accuracy in classification tasks. The dataset was split into training and testing sets in an 80:20 ratio. Key steps:
Categorical variables (Soil Type, Crop Type, and Fertilizer Name) were encoded using LabelEncoder.
A Random Forest model was trained using the training data.
A grid search with cross-validation was applied to find the optimal parameters for the Random Forest model.
Develop a machine learning-based crop recommendation system that uses various classification algorithms to predict the optimal crop for farming based on soil and environmental factors. The model takes inputs such as Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), temperature, humidity, pH level, and rainfall, and outputs the most suitable crop for specific conditions.
Crop_recommendation.csv
Four different models were trained on the dataset to predict the crop: The results of each model are as follows:
- Logistic Regression: 96.18%
- Decision Tree Classifier: 97.82%
- Gaussian Naive Bayes: 99.45%
- Random Forest Classifier: 99.45% The final model selected for deployment is the Random Forest Classifier.
Implements machine learning models to classify soil quality based on various features like nitrogen content, pH levels, organic carbon, and other nutrients. The goal of the model is to predict the quality of soil using logistic regression and a Support Vector Machine (SVM) model.
Soil_Quality.csv (Uploaded under notebooks)
-
Logistic Regression Logistic Regression is used to model the soil quality based on the provided features. The dataset is split into training and testing sets, and the logistic regression model is trained on the training data.
-
Support Vector Machine (SVM) A Support Vector Machine with an RBF (Radial Basis Function) kernel is trained as an alternative model. The SVM model aims to find the decision boundary that best separates different soil quality classes.
-
Performance Evaluation The performance of both models is evaluated using accuracy. The accuracy of each model is calculated by comparing the predicted soil quality labels with the actual labels in the test dataset.
Aims to develop a machine learning-based model for predicting crop yields based on various environmental and agricultural factors. The primary objective of this project is to create a model that predicts the total crop yield for a given region using data such as Area and type of crop, Year of cultivation, Average rainfall (in mm per year), Pesticide usage (in tonnes), Average temperature (in °C)
yield_df.csv (Uploaded under notebooks)
Various machine learning regression algorithms are applied, and the performance is evaluated based on metrics like Mean Squared Error (MSE). The results of the models used are as follows:
-
Linear Regression Mean Squared Error : 80852.08620158922 Score 0.09879301553673503
-
K Neighbors Regressor Mean Squared Error : 55183.1146293406 Score 0.5801883304861266
-
Decision Tree Regressor Mean Squared Error : 13211.190235825037 Score 0.9759383181169221
-
Random Forest Regressor Mean Squared Error : 10135.46523142438 Score 0.9858378410451943
-
Gradient Boosting Regressor Mean Squared Error : 34773.822585474634 Score 0.833295640875001
-
XGB Regressor Mean Squared Error : 13451.947664464684 Score 0.975053338957936Linear Regression Mean Squared Error : 80852.08620158922 Score 0.09879301553673503
The Random Forest Regressor was found to have the lowest MSE, making it the most suitable model for crop yield prediction. This model was selected for deployment and future predictions.
Develop a machine learning model that predicts whether a mushroom is edible or not, depending on it's physical features and environment. The model takes various inputs regarding the physical characteristics of the mushroom and outputs if the mushroom is edible or poisonous.
mushrooms.csv
Five different models were trained on the dataset to predict mushroom edibility. The accuracy of each model are as follows:
- Logistic Regression: 0.94
- Decision Tree Classifier: 1.0
- K Nearest Neighbors: 0.99
- Random Forest Classifier: 1.0
- XGB Classifier: 1.0
The final model selected for deployment is the XGBoost Classifier as it can handle missing datas better than the other models.
- React
- Tailwind
- python - Flask
- Node
- MongoDB
- Express
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
Ready to contribute to this fun project? Here's how to set up your development environment:
Make sure you follow our contributing guidlines:- here
-
Fork this repository 🍴 and clone it to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/manikumarreddyu/AgroTech-AI.git
-
Install the node modules in frontend directory:
npm install
-
Start the react server ⚡:
npm run dev
-
Install the node modules for backend directory 🧩:
npm install
-
Run the backend server ⚡:
npm start
- Open your browser at
http://localhost:5173to see the project running! 🌟
Please note that this project is released with a Code of Conduct. By participating in this project you agree to abide by its terms.
If you would like to contribute to the project then kindly go through Contributing Guidelines to understand everything from setup to necessary instructions.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AgroTech-AI
Similar Open Source Tools

AgroTech-AI
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more. The platform implements machine learning algorithms to provide functionalities like fertilizer prediction, crop prediction, soil quality prediction, yield prediction, and mushroom edibility prediction.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.
nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool that learns correctional residuals between preferred and dispreferred answers using a small model. It can be directly applied to various open-source and API-based models with only one-off training, suitable for rapid iteration and improving model performance. Aligner has shown significant improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions across different large language models.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
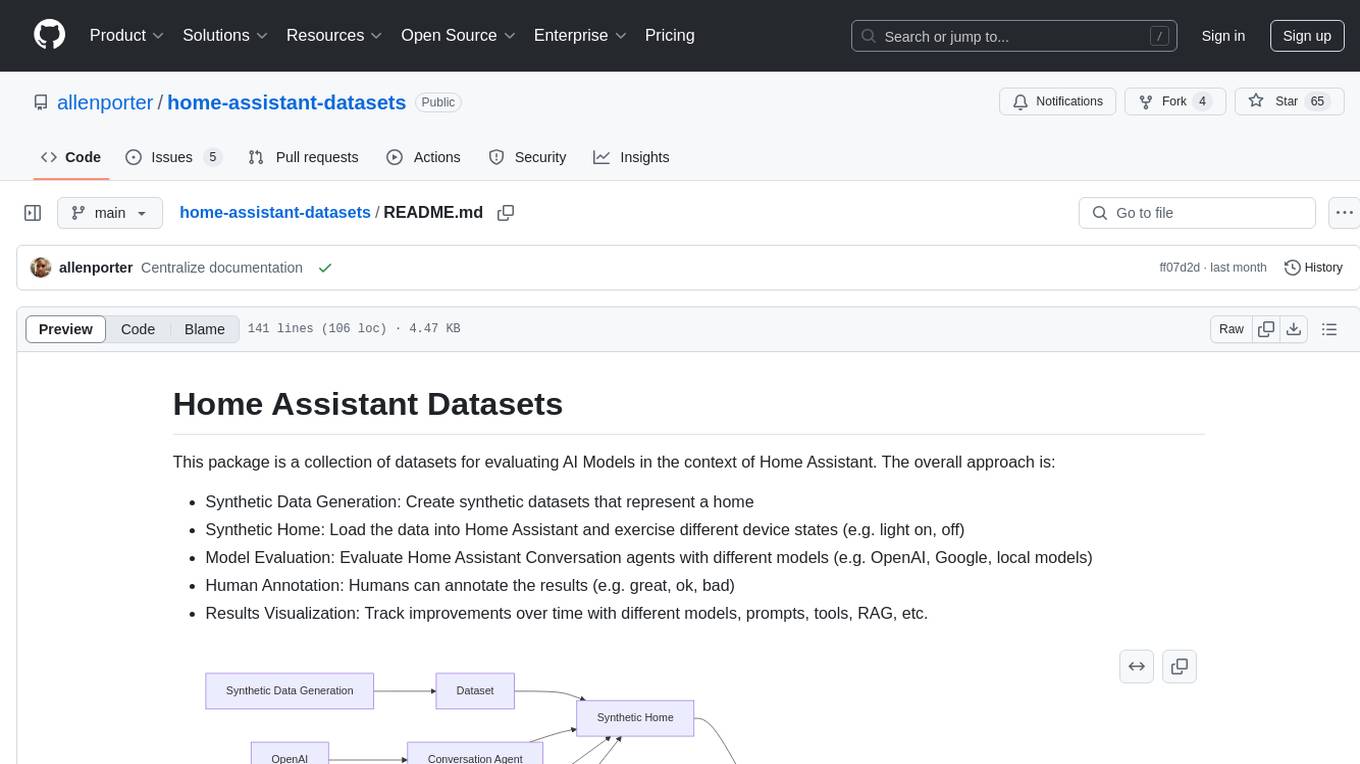
home-assistant-datasets
This package provides a collection of datasets for evaluating AI Models in the context of Home Assistant. It includes synthetic data generation, loading data into Home Assistant, model evaluation with different conversation agents, human annotation of results, and visualization of improvements over time. The datasets cover home descriptions, area descriptions, device descriptions, and summaries that can be performed on a home. The tool aims to build datasets for future training purposes.

GrAIdient
GrAIdient is a framework designed to enable the development of deep learning models using the internal GPU of a Mac. It provides access to the graph of layers, allowing for unique model design with greater understanding, control, and reproducibility. The goal is to challenge the understanding of deep learning models, transitioning from black box to white box models. Key features include direct access to layers, native Mac GPU support, Swift language implementation, gradient checking, PyTorch interoperability, and more. The documentation covers main concepts, architecture, and examples. GrAIdient is MIT licensed.
LLM-Geo
LLM-Geo is an AI-powered geographic information system (GIS) that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for automatic spatial data collection, analysis, and visualization. By adopting LLM as the reasoning core, it addresses spatial problems with self-generating, self-organizing, self-verifying, self-executing, and self-growing capabilities. The tool aims to make spatial analysis easier, faster, and more accessible by reducing manual operation time and delivering accurate results through case studies. It uses GPT-4 API in a Python environment and advocates for further research and development in autonomous GIS.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.

onnx
Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types. Currently, we focus on the capabilities needed for inferencing (scoring). ONNX is widely supported and can be found in many frameworks, tools, and hardware, enabling interoperability between different frameworks and streamlining the path from research to production to increase the speed of innovation in the AI community. Join us to further evolve ONNX.
R1-Searcher
R1-searcher is a tool designed to incentivize the search capability in large reasoning models (LRMs) via reinforcement learning. It enables LRMs to invoke web search and obtain external information during the reasoning process by utilizing a two-stage outcome-supervision reinforcement learning approach. The tool does not require instruction fine-tuning for cold start and is compatible with existing Base LLMs or Chat LLMs. It includes training code, inference code, model checkpoints, and a detailed technical report.
BitMat
BitMat is a Python package designed to optimize matrix multiplication operations by utilizing custom kernels written in Triton. It leverages the principles outlined in the "1bit-LLM Era" paper, specifically utilizing packed int8 data to enhance computational efficiency and performance in deep learning and numerical computing tasks.
baal
Baal is an active learning library that supports both industrial applications and research use cases. It provides a framework for Bayesian active learning methods such as Monte-Carlo Dropout, MCDropConnect, Deep ensembles, and Semi-supervised learning. Baal helps in labeling the most uncertain items in the dataset pool to improve model performance and reduce annotation effort. The library is actively maintained by a dedicated team and has been used in various research papers for production and experimentation.
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.
For similar tasks

AgroTech-AI
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more. The platform implements machine learning algorithms to provide functionalities like fertilizer prediction, crop prediction, soil quality prediction, yield prediction, and mushroom edibility prediction.
AgriTech
AgriTech is an AI-powered smart agriculture platform designed to assist farmers with crop recommendations, yield prediction, plant disease detection, and community-driven collaboration—enabling sustainable and data-driven farming practices. It offers AI-driven decision support for modern agriculture, early-stage plant disease detection, crop yield forecasting using machine learning models, and a collaborative ecosystem for farmers and stakeholders. The platform includes features like crop recommendation, yield prediction, disease detection, an AI chatbot for platform guidance and agriculture support, a farmer community, and shopkeeper listings. AgriTech's AI chatbot provides comprehensive support for farmers with features like platform guidance, agriculture support, decision making, image analysis, and 24/7 support. The tech stack includes frontend technologies like HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, backend technologies like Python (Flask) and optional Node.js, machine learning libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, OpenCV, and database & DevOps tools like MySQL, MongoDB, Firebase, Docker, and GitHub Actions.
For similar jobs
farmvibes-ai
FarmVibes.AI is a repository focused on developing multi-modal geospatial machine learning models for agriculture and sustainability. It enables users to fuse various geospatial and spatiotemporal datasets, such as satellite imagery, drone imagery, and weather data, to generate robust insights for agriculture-related problems. The repository provides fusion workflows, data preparation tools, model training notebooks, and an inference engine to facilitate the creation of geospatial models tailored for agriculture and farming. Users can interact with the tools via a local cluster, REST API, or a Python client, and the repository includes documentation and notebook examples to guide users in utilizing FarmVibes.AI for tasks like harvest date detection, climate impact estimation, micro climate prediction, and crop identification.

AgroTech-AI
AgroTech AI platform is a comprehensive web-based tool where users can access various machine learning models for making accurate predictions related to agriculture. It offers solutions for crop management, soil health assessment, pest control, and more. The platform implements machine learning algorithms to provide functionalities like fertilizer prediction, crop prediction, soil quality prediction, yield prediction, and mushroom edibility prediction.

AgriTech
AgriTech is an AI-powered smart agriculture platform designed to assist farmers with crop recommendations, yield prediction, plant disease detection, and community-driven collaboration—enabling sustainable and data-driven farming practices. It offers AI-driven decision support for modern agriculture, early-stage plant disease detection, crop yield forecasting using machine learning models, and a collaborative ecosystem for farmers and stakeholders. The platform includes features like crop recommendation, yield prediction, disease detection, an AI chatbot for platform guidance and agriculture support, a farmer community, and shopkeeper listings. AgriTech's AI chatbot provides comprehensive support for farmers with features like platform guidance, agriculture support, decision making, image analysis, and 24/7 support. The tech stack includes frontend technologies like HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, backend technologies like Python (Flask) and optional Node.js, machine learning libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, OpenCV, and database & DevOps tools like MySQL, MongoDB, Firebase, Docker, and GitHub Actions.
plants_disease_detection
This repository contains code for the AI challenger competition on plant disease detection. The goal is to classify nearly 50,000 plant leaf photos into 61 categories based on 'species-disease-severity'. The framework used is Keras with TensorFlow backend, implementing DenseNet for image classification. Data is uploaded to a private dataset on Kaggle for model training. The code includes data preparation, model training, and prediction steps.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.





