
Evaluator
Open-source library for scalable, reproducible evaluation of AI models and benchmarks.
Stars: 194
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.
README:
-
TAU2-Bench (
tau2-bench): Conversational agents in dual-control environments (telecom, airline, retail) -
RULER (
long-context-eval): Long-context evaluation with configurable sequence lengths (4K to 1M tokens) -
CoDec (
contamination-detection): Contamination detection - practical and accurate method to detect and quantify training data contamination in large language models -
MTEB (
mteb): Massive Text Embedding Benchmark
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables you to run hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. Evaluations execute in open-source Docker containers for auditable and trustworthy results. The platform's containerized architecture allows for the rapid integration of public benchmarks and private datasets.
NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles to provide a reliable and versatile evaluation experience:
- Reproducibility by Default: All configurations, random seeds, and software provenance are captured automatically for auditable and repeatable evaluations.
- Scale Anywhere: Run evaluations from a local machine to a Slurm cluster or cloud-native backends like Lepton AI without changing your workflow.
- State-of-the-Art Benchmarking: Access a comprehensive suite of over 100 benchmarks from 18 popular open-source evaluation harnesses. See the full list of Supported benchmarks and evaluation harnesses.
- Extensible and Customizable: Integrate new evaluation harnesses, add custom benchmarks with proprietary data, and define custom result exporters for existing MLOps tooling.
The platform consists of two main components:
-
nemo-evaluator(The Evaluation Core Engine): A Python library that manages the interaction between an evaluation harness and the model being tested. -
nemo-evaluator-launcher(The CLI and Orchestration): The primary user interface and orchestration layer. It handles configuration, selects the execution environment, and launches the appropriate container to run the evaluation.
Most users typically interact with nemo-evaluator-launcher, which serves as a universal gateway to different benchmarks and harnesses. However, it is also possible to interact directly with nemo-evaluator by following this guide.
NeMo Evaluator Launcher provides pre-built evaluation containers for different evaluation harnesses through the NVIDIA NGC catalog. Each harness supports a variety of benchmarks, which can then be called via nemo-evaluator. This table provides a list of benchmark names per harness. A more detailed list of task names can be found in the list of NGC containers.
| Container | Description | NGC Catalog | Latest Tag | Supported benchmarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bfcl | Function calling | Link | 26.01 |
BFCL v2 and v3 |
| bigcode-evaluation-harness | Code generation evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
MBPP, MBPP-Plus, HumanEval, HumanEval+, Multiple (cpp, cs, d, go, java, jl, js, lua, php, pl, py, r, rb, rkt, rs, scala, sh, swift, ts) |
| compute-eval | CUDA code evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
CCCL, Combined Problems, CUDA |
| CoDec | Contamination detection | Link | 26.01 |
CoDec |
| garak | Safety and vulnerability testing | Link | 26.01 |
Garak |
| genai-perf | GenAI performance benchmarking | Link | 26.01 |
GenAI Perf Generation & Summarization |
| helm | Holistic evaluation framework | Link | 26.01 |
MedHelm |
| hle | Academic knowledge and problem solving | Link | 26.01 |
HLE |
| ifbench | Instruction following | Link | 26.01 |
IFBench |
| livecodebench | Coding | Link | 26.01 |
LiveCodeBench (v1-v6, 0724_0125, 0824_0225) |
| lm-evaluation-harness | Language model benchmarks | Link | 26.01 |
ARC Challenge (also multilingual), GSM8K, HumanEval, HumanEval+, MBPP, MBPP+, MINERVA Math, RACE, AGIEval, BBH, BBQ, CSQA, Frames, Global MMLU, GPQA-D, HellaSwag (also multilingual), IFEval, MGSM, MMLU, MMLU-Pro, MMLU-ProX (de, es, fr, it, ja), MMLU-Redux, MUSR, OpenbookQA, Piqa, Social IQa, TruthfulQA, WikiLingua, WinoGrande |
| long-context-eval | Long context evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
Ruler |
| mmath | Multilingual math reasoning | Link | 26.01 |
EN, ZH, AR, ES, FR, JA, KO, PT, TH, VI |
| mtbench | Multi-turn conversation evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
MT-Bench |
| MTEB | Multimodal toolbox for evaluating embeddings and retrieval systems | Link | 26.01 |
fiqa, miracl, ViDoRe |
| nemo-skills | Language model benchmarks (science, math, agentic) | Link | 26.01 |
AIME 24 & 25, BFCL_v3, GPQA, HLE, LiveCodeBench, MMLU, MMLU-Pro |
| profbench | Professional domains in Business and Scientific Research | Link | 26.01 |
ProfBench |
| safety-harness | Safety and bias evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
Aegis v2, WildGuard |
| scicode | Coding for scientific research | Link | 26.01 |
SciCode |
| simple-evals | Common evaluation tasks | Link | 26.01 |
GPQA-D, MATH-500, AIME 24 & 25, HumanEval, HumanEval+, MGSM, MMLU (also multilingual), MMLU-Pro, MMLU-lite (AR, BN, DE, EN, ES, FR, HI, ID, IT, JA, KO, MY, PT, SW, YO, ZH), SimpleQA, BrowseComp, HealthBench |
| tau2-bench | TAU2 benchmark evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
TAU2-Bench telecom, airline, retail |
| tooltalk | Tool usage evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
ToolTalk |
| vlmevalkit | Vision-language model evaluation | Link | 26.01 |
AI2D, ChartQA, MMMU, MathVista-MINI, OCRBench, SlideVQA |
Get your first evaluation result in minutes. This guide uses your local machine to run a small benchmark against an OpenAI API-compatible endpoint.
The launcher is the only package required to get started.
pip install nemo-evaluator-launcherNeMo Evaluator works with any model that exposes an OpenAI-compatible endpoint. For this quickstart, we will use the OpenAI API.
What is an OpenAI-compatible endpoint? A server that exposes /v1/chat/completions and /v1/completions endpoints, matching the OpenAI API specification.
Options for model endpoints:
- Hosted endpoints (fastest): Use ready-to-use hosted models from providers like build.nvidia.com that expose OpenAI-compatible APIs with no hosting required.
- Self-hosted options: Host your own models using tools like NVIDIA NIM, vLLM, or TensorRT-LLM for full control over your evaluation environment.
- Models trained with NeMo framework: Host your models trained with NeMo framework by deploying them as OpenAI-compatible endpoints using NeMo Export-Deploy. More detailed user guide here.
Getting an NGC API Key for build.nvidia.com:
To use out-of-the-box build.nvidia.com APIs, you need an API key:
- Register an account at build.nvidia.com.
- In the Setup menu under Keys/Secrets, generate an API key.
- Set the environment variable by executing
export NGC_API_KEY=<YOUR_API_KEY>.
Run a small evaluation on your local machine. The launcher automatically pulls the correct container and executes the benchmark. The list of benchmarks is directly configured in the YAML file.
Configuration Examples: Explore ready-to-use configuration files in packages/nemo-evaluator-launcher/examples/ for local, Lepton, and Slurm deployments with various model hosting options (vLLM, NIM, hosted endpoints).
Once you have the example configuration file, either by cloning this repository or downloading one directly such as local_nvidia_nemotron_nano_9b_v2.yaml, you can run the following command:
nemo-evaluator-launcher run --config packages/nemo-evaluator-launcher/examples/local_nvidia_nemotron_nano_9b_v2.yaml -o execution.output_dir=<YOUR_OUTPUT_LOCAL_DIR>After running this command, you will see a job_id, which can be used to track the job and its results. All logs will be available in your <YOUR_OUTPUT_LOCAL_DIR>.
Results, logs, and run configurations are saved locally. Inspect the status of the evaluation job by using the corresponding job_id:
nemo-evaluator-launcher status <job_id_or_invocation_id>We welcome community contributions. Please see our Contribution Guide for instructions on submitting pull requests, reporting issues, and suggesting features.
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. See the LICENSE file for details.
- Issues: GitHub Issues
- Discussions: GitHub Discussions
- Documentation: NeMo Evaluator Documentation
-
nel lsmight require docker authenthication and currently does not support fetching credentials from known password management systems such as MacOS's Keychain or GNOME Keyring.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Evaluator
Similar Open Source Tools
For similar tasks
ai4math-papers
The 'ai4math-papers' repository contains a collection of research papers related to AI applications in mathematics, including automated theorem proving, synthetic theorem generation, autoformalization, proof refactoring, premise selection, benchmarks, human-in-the-loop interactions, and constructing examples/counterexamples. The papers cover various topics such as neural theorem proving, reinforcement learning for theorem proving, generative language modeling, formal mathematics statement curriculum learning, and more. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of AI and mathematics.
Evaluator
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.
AirspeedVelocity.jl
AirspeedVelocity.jl is a tool designed to simplify benchmarking of Julia packages over their lifetime. It provides a CLI to generate benchmarks, compare commits/tags/branches, plot benchmarks, and run benchmark comparisons for every submitted PR as a GitHub action. The tool freezes the benchmark script at a specific revision to prevent old history from affecting benchmarks. Users can configure options using CLI flags and visualize benchmark results. AirspeedVelocity.jl can be used to benchmark any Julia package and offers features like generating tables and plots of benchmark results. It also supports custom benchmarks and can be integrated into GitHub actions for automated benchmarking of PRs.
hallucination-leaderboard
This leaderboard evaluates the hallucination rate of various Large Language Models (LLMs) when summarizing documents. It uses a model trained by Vectara to detect hallucinations in LLM outputs. The leaderboard includes models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and others. The evaluation is based on 831 documents that were summarized by all the models. The leaderboard shows the hallucination rate, factual consistency rate, answer rate, and average summary length for each model.

h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
llm-jp-eval
LLM-jp-eval is a tool designed to automatically evaluate Japanese large language models across multiple datasets. It provides functionalities such as converting existing Japanese evaluation data to text generation task evaluation datasets, executing evaluations of large language models across multiple datasets, and generating instruction data (jaster) in the format of evaluation data prompts. Users can manage the evaluation settings through a config file and use Hydra to load them. The tool supports saving evaluation results and logs using wandb. Users can add new evaluation datasets by following specific steps and guidelines provided in the tool's documentation. It is important to note that using jaster for instruction tuning can lead to artificially high evaluation scores, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
For similar jobs

llm-jp-eval
LLM-jp-eval is a tool designed to automatically evaluate Japanese large language models across multiple datasets. It provides functionalities such as converting existing Japanese evaluation data to text generation task evaluation datasets, executing evaluations of large language models across multiple datasets, and generating instruction data (jaster) in the format of evaluation data prompts. Users can manage the evaluation settings through a config file and use Hydra to load them. The tool supports saving evaluation results and logs using wandb. Users can add new evaluation datasets by following specific steps and guidelines provided in the tool's documentation. It is important to note that using jaster for instruction tuning can lead to artificially high evaluation scores, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
AlignBench
AlignBench is the first comprehensive evaluation benchmark for assessing the alignment level of Chinese large models across multiple dimensions. It includes introduction information, data, and code related to AlignBench. The benchmark aims to evaluate the alignment performance of Chinese large language models through a multi-dimensional and rule-calibrated evaluation method, enhancing reliability and interpretability.
LiveBench
LiveBench is a benchmark tool designed for Language Model Models (LLMs) with a focus on limiting contamination through monthly new questions based on recent datasets, arXiv papers, news articles, and IMDb movie synopses. It provides verifiable, objective ground-truth answers for accurate scoring without an LLM judge. The tool offers 18 diverse tasks across 6 categories and promises to release more challenging tasks over time. LiveBench is built on FastChat's llm_judge module and incorporates code from LiveCodeBench and IFEval.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
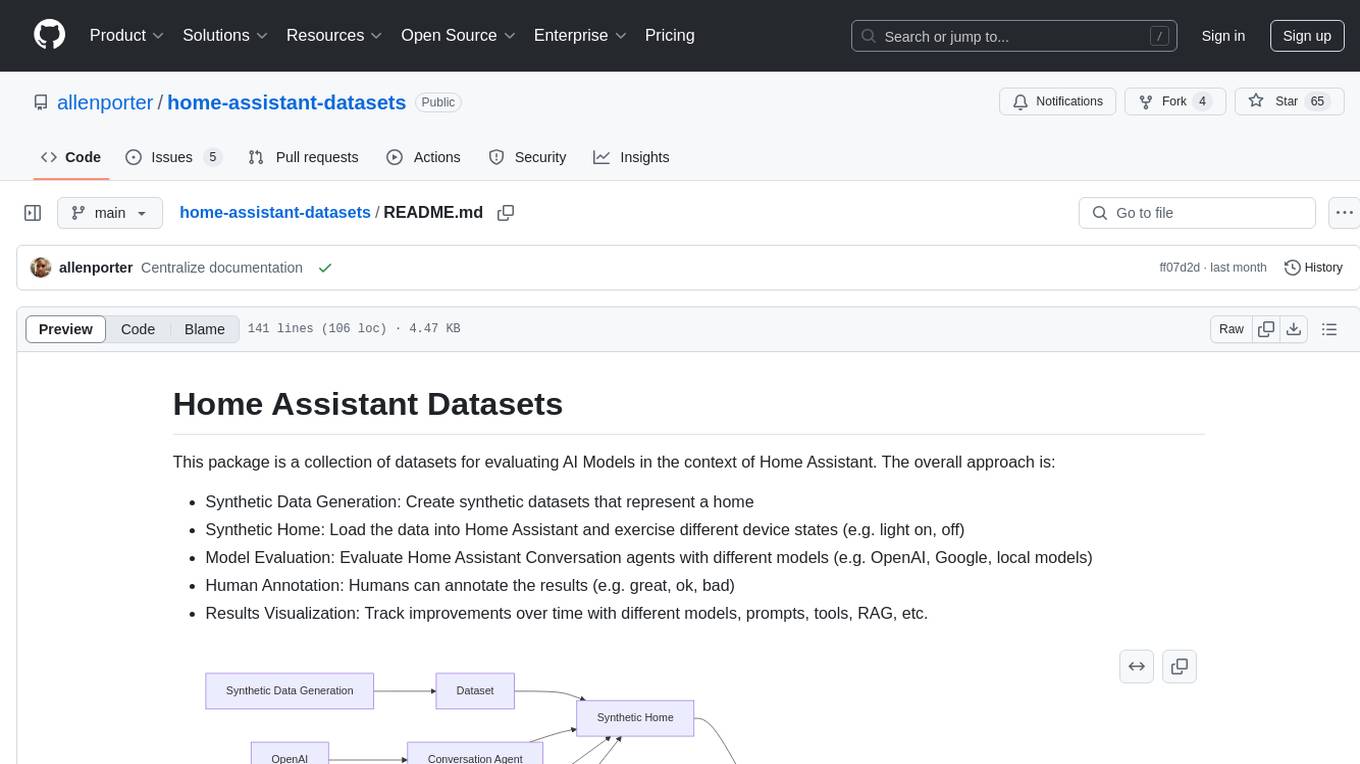
home-assistant-datasets
This package provides a collection of datasets for evaluating AI Models in the context of Home Assistant. It includes synthetic data generation, loading data into Home Assistant, model evaluation with different conversation agents, human annotation of results, and visualization of improvements over time. The datasets cover home descriptions, area descriptions, device descriptions, and summaries that can be performed on a home. The tool aims to build datasets for future training purposes.
Evaluator
NeMo Evaluator SDK is an open-source platform for robust, reproducible, and scalable evaluation of Large Language Models. It enables running hundreds of benchmarks across popular evaluation harnesses against any OpenAI-compatible model API. The platform ensures auditable and trustworthy results by executing evaluations in open-source Docker containers. NeMo Evaluator SDK is built on four core principles: Reproducibility by Default, Scale Anywhere, State-of-the-Art Benchmarking, and Extensible and Customizable.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.







