
cymbal-air-toolbox-demo
None
Stars: 315
Cymbal Air Toolbox Demo is a project that provides a production-quality reference implementation for building Agentic applications using Agents and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to query and interact with data stored in Google Cloud Databases. The demo showcases a customer service assistant for a fictional airline, Cymbal Air, assisting travelers with flight management and providing information about San Francisco International Airport (SFO). It utilizes techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Agent-based Orchestration to enhance responses and handle a wide variety of queries. The architecture includes components like the user-facing application, MCP Toolbox middleware server, and a database, offering advantages such as better security, scalability, and recall for agents.
README:
[!NOTE] This project is for demonstration only and is not an officially supported Google product.
If you're a Googler using this demo, please fill up this form. If you're interested in using our hosted version, please fill up this form.
This project provides a production-quality reference implementation for building Agentic applications that use Agents and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to query and interact with data stored in Google Cloud Databases.
This demonstration features Cymbal Air, a fictional airline. The application showcases a customer service assistant that helps travelers manage flights and find information about San Francisco International Airport (SFO), Cymbal Air's hub. The agent can answer questions like:
- Are there any luxury shops in the terminal?
- Where can I get coffee near gate A6?
- I need to find a gift for my colleague.
- What flights are headed to NYC tomorrow?
One of the best tools for reducing hallucinations is to use Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). RAG is the concept of retrieving some data or information, augmenting your prompt to the agent, and allowing it to generate more accurate responses based on the data included in the prompt. This grounds the model’s response, making it less likely to hallucinate. This technique is also useful for allowing the agent to access data it didn’t have when it was trained. And unlike fine-tuning, the information retrieved for RAG does not alter the model or otherwise leave the context of the request - making it more suitable for use cases where information privacy and security are important.
Cloud databases provide a managed solution for storing and accessing data in a scalable and a reliable way. By connecting an agent to a cloud database, developers can give their applications access to a wider range of information and reduce the risk of hallucinations.
This application uses an Agent-based orchestration model. Instead of a static
chain of calls, the LLM acts as an intelligent Agent that decides which tools to
use and in what order. It is given a set of available tools, each with a
specific function (e.g., find_flights, list_amenities). Based on the user's
query, the agent reasons about the best tool to use to find the answer. This
"thought process" allows the agent to handle a wider variety of queries and to
break down complex questions into smaller, manageable steps.
The architecture consists of three main components:
- Application -- The user-facing agentic app that orchestrates the interaction between the user and the agent.
- MCP Toolbox -- MCP Toolbox is a middleware server that exposes the database operations as a set of tools. The LLM agent connects to the Toolbox to execute these tools. This provides a secure, scalable, and modular way to manage database interactions.
- Database -- The database containing the data the agent can use to answer questions. For this application, the database used was intentionally designed to be interchangeable in order to make it easier to run this on your preferred database.
Using the Toolbox as an intermediary offers several advantages:
- Better Security - The Toolbox handles authentication and authorization, preventing the agent from directly accessing the database and reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities.
- Better scalability - Toolbox allows multiple different Agents to leverage it, as well as allowing it to scale independently. It allows for production best practices such as connection pooling or caching.
- Better recall - Agents perform better when given smaller, discrete tasks they can use to accomplish larger goals. By mapping a specific action to a specific, pre-determined query, via tools, it significantly improves the agent's ability to leverage it successfully.
Head over to the official MCP Toolbox docs for more details.
Deploying Cymbal Air app is a three-step process. You will first download the necessary tools, then perform a one-time setup for your database and Toolbox configuration, and finally launch the Toolbox server and the app.
First, clone this repository and download the MCP Toolbox binary.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cymbal-air-toolbox-demo.git cd cymbal-air-toolbox-demo -
Download MCP Toolbox binary:
Follow these steps to download the binary. This involves running the following commands:
# See the releases page for the latest version export VERSION=0.8.0 curl -O https://storage.googleapis.com/genai-toolbox/v$VERSION/linux/amd64/toolbox chmod +x toolbox
Next, you must perform a one-time setup to create your database instance,
populate it with data, and create the tools.yaml configuration file. This
process uses the Toolbox binary you just downloaded.
[!IMPORTANT] For detailed, step-by-step instructions, follow the Database Setup Guide.
[!NOTE] If you have already configured your own database, you can skip this section.
After your database is initialized and your tools.yaml file is created, you
must run the Toolbox server so the agentic app can connect to it. You can either
run it locally for development or deploy it to Cloud Run for a more robust
setup.
For local development and testing, you can run the Toolbox server directly from your terminal. This is the quickest way to get started.
For instructions, follow the guide to running the Toolbox locally.
The basic command will be:
./toolbox --tools-file "tools.yaml"For a scalable and production-ready setup, you can deploy the Toolbox as a service on Google Cloud Run. This provides a stable, shareable endpoint for your application.
For instructions, follow the guide to deploying the Toolbox on Cloud Run.
Instructions for running app locally
Instructions for cleaning up resources
This demo can serve as a starting point for building your own Agentic applications. You can customize the tools available to the agent by modifying the MCP Toolbox configuration file.
Please refer to the MCP Toolbox documentation for more information on creating and configuring tools.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cymbal-air-toolbox-demo
Similar Open Source Tools

cymbal-air-toolbox-demo
Cymbal Air Toolbox Demo is a project that provides a production-quality reference implementation for building Agentic applications using Agents and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to query and interact with data stored in Google Cloud Databases. The demo showcases a customer service assistant for a fictional airline, Cymbal Air, assisting travelers with flight management and providing information about San Francisco International Airport (SFO). It utilizes techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Agent-based Orchestration to enhance responses and handle a wide variety of queries. The architecture includes components like the user-facing application, MCP Toolbox middleware server, and a database, offering advantages such as better security, scalability, and recall for agents.
ai2apps
AI2Apps is a visual IDE for building LLM-based AI agent applications, enabling developers to efficiently create AI agents through drag-and-drop, with features like design-to-development for rapid prototyping, direct packaging of agents into apps, powerful debugging capabilities, enhanced user interaction, efficient team collaboration, flexible deployment, multilingual support, simplified product maintenance, and extensibility through plugins.
AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.

dataherald
Dataherald is a natural language-to-SQL engine built for enterprise-level question answering over structured data. It allows you to set up an API from your database that can answer questions in plain English. You can use Dataherald to: * Allow business users to get insights from the data warehouse without going through a data analyst * Enable Q+A from your production DBs inside your SaaS application * Create a ChatGPT plug-in from your proprietary data
AgentStack
AgentStack is a command-line tool that helps users create AI agent projects quickly and efficiently. It offers CLI utilities for code generation and simplifies the process of building agents and tasks. The tool is designed to work on macOS, Windows, and Linux, providing a seamless experience for developers. AgentStack aims to streamline the development process by offering pre-built templates, easy access to tools, and a curated experience on top of popular agent frameworks and LLM providers. It is not a low-code solution but rather a head-start for starting agent projects from scratch.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
WilmerAI
WilmerAI is a middleware system designed to process prompts before sending them to Large Language Models (LLMs). It categorizes prompts, routes them to appropriate workflows, and generates manageable prompts for local models. It acts as an intermediary between the user interface and LLM APIs, supporting multiple backend LLMs simultaneously. WilmerAI provides API endpoints compatible with OpenAI API, supports prompt templates, and offers flexible connections to various LLM APIs. The project is under heavy development and may contain bugs or incomplete code.
paddler
Paddler is an open-source LLM load balancer and serving platform designed for digital products and users who prioritize privacy, reliability, cost control, and independence from closed-source model providers. It allows running inference, deploying, and scaling LLMs on personal infrastructure, offering a seamless developer experience. Key features include inference through llama.cpp engine, LLM-specific load balancing, dynamic model swapping, request buffering, and built-in web admin panel for management and monitoring. Paddler is suitable for product teams needing LLM inference, DevOps/LLMOps teams deploying LLMs at scale, organizations handling sensitive data, and product leaders aiming for predictable LLM costs and reliable model performance.
magic
Magic Cloud is a software development automation platform based on AI, Low-Code, and No-Code. It allows dynamic code creation and orchestration using Hyperlambda, generative AI, and meta programming. The platform includes features like CRUD generation, No-Code AI, Hyperlambda programming language, AI agents creation, and various components for software development. Magic is suitable for backend development, AI-related tasks, and creating AI chatbots. It offers high-level programming capabilities, productivity gains, and reduced technical debt.
ask-astro
Ask Astro is an open-source reference implementation of Andreessen Horowitz's LLM Application Architecture built by Astronomer. It provides an end-to-end example of a Q&A LLM application used to answer questions about Apache Airflow® and Astronomer. Ask Astro includes Airflow DAGs for data ingestion, an API for business logic, a Slack bot, a public UI, and DAGs for processing user feedback. The tool is divided into data retrieval & embedding, prompt orchestration, and feedback loops.
mastra
Mastra is an opinionated Typescript framework designed to help users quickly build AI applications and features. It provides primitives such as workflows, agents, RAG, integrations, syncs, and evals. Users can run Mastra locally or deploy it to a serverless cloud. The framework supports various LLM providers, offers tools for building language models, workflows, and accessing knowledge bases. It includes features like durable graph-based state machines, retrieval-augmented generation, integrations, syncs, and automated tests for evaluating LLM outputs.
mahilo
Mahilo is a flexible framework for creating multi-agent systems that can interact with humans while sharing context internally. It allows developers to set up complex agent networks for various applications, from customer service to emergency response simulations. Agents can communicate with each other and with humans, making the system efficient by handling context from multiple agents and helping humans stay focused on specific problems. The system supports Realtime API for voice interactions, WebSocket-based communication, flexible communication patterns, session management, and easy agent definition.
wave-apps
Wave Apps is a directory of sample applications built on H2O Wave, allowing users to build AI apps faster. The apps cover various use cases such as explainable hotel ratings, human-in-the-loop credit risk assessment, mitigating churn risk, online shopping recommendations, and sales forecasting EDA. Users can download, modify, and integrate these sample apps into their own projects to learn about app development and AI model deployment.
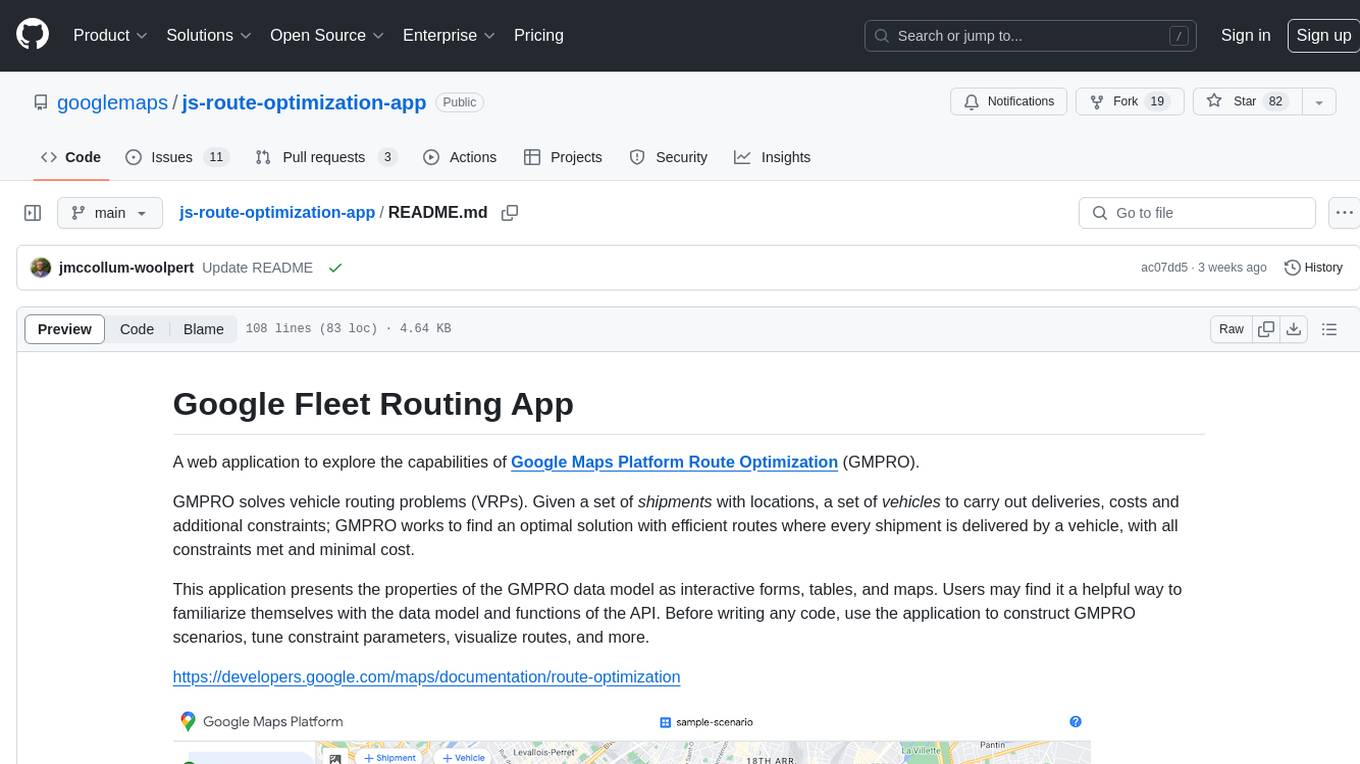
js-route-optimization-app
A web application to explore the capabilities of Google Maps Platform Route Optimization (GMPRO). It helps users understand the data model and functions of the API by presenting interactive forms, tables, and maps. The tool is intended for exploratory use only and should not be deployed in production. Users can construct scenarios, tune constraint parameters, and visualize routes before implementing their own solutions for integrating Route Optimization into their business processes. The application incurs charges related to cloud resources and API usage, and users should be cautious about generating high usage volumes, especially for large scenarios.
agents-js
LiveKit Agents for Node.js is a framework designed for building realtime, programmable voice agents that can see, hear, and understand. It includes support for OpenAI Realtime API, allowing for ultra-low latency WebRTC transport between GPT-4o and users' devices. The framework provides concepts like Agents, Workers, and Plugins to create complex tasks. It offers a CLI interface for running agents and a versatile web frontend called 'playground' for building and testing agents. The framework is suitable for developers looking to create conversational voice agents with advanced capabilities.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
