Best AI tools for< Understand Model Mechanisms >
20 - AI tool Sites

John Schulman's Homepage
John Schulman's Homepage is an AI tool developed by a researcher at Anthropic. The website focuses on aligning large language models, scalable oversight, and developing better written specifications of model behavior. It showcases the researcher's work in the field of AI, including projects like ChatGPT and the OpenAI API. The homepage also highlights the researcher's academic background, including a PhD in Computer Science from UC Berkeley with a focus on robotics and reinforcement learning.

SnapMeasureAI
SnapMeasureAI is an AI application that specializes in automated AI image labeling, precise 3D body measurements, and video-based motion capture. It uses advanced AI technology to accurately understand and model the human body, working with any body type, skin tone, pose, or background. The application caters to various industries such as retail, fitness & health, AI training data, and security, offering a free demo for interested users.
Diffusion Chat
Diffusion Chat is a text-to-image AI tool that allows users to generate images from text prompts. The tool uses a large language model to understand the user's prompt and then generates an image that matches the description. Diffusion Chat is still in development, but it has already shown great promise for creating realistic and creative images.
xAI Grok
xAI Grok is a visual analytics platform that helps users understand and interpret machine learning models. It provides a variety of tools for visualizing and exploring model data, including interactive charts, graphs, and tables. xAI Grok also includes a library of pre-built visualizations that can be used to quickly get started with model analysis.
Censius
Censius is an AI Observability Platform for Enterprise ML Teams. It provides end-to-end visibility of structured and unstructured production models, enabling proactive model management and continuous delivery of reliable ML. Key features include model monitoring, explainability, and analytics.
Storia AI
Storia AI is an AI tool designed to assist software engineering teams in understanding and generating code. It provides a Perplexity-like chat experience where users can interact with an AI expert that has access to the latest versions of open-source software. The tool aims to improve code understanding and generation by providing responses backed with links to implementations, API references, GitHub issues, and more. Storia AI is developed by a team of natural language processing researchers from Google and Amazon Alexa, with a mission to build the most reliable AI pair programmer for engineering teams.
AIby.email
AIby.email is an AI-powered email assistant that helps you write better emails, faster. It uses natural language processing to understand your intent and generate personalized email responses. AIby.email also offers a variety of other features, such as email scheduling, tracking, and analytics.
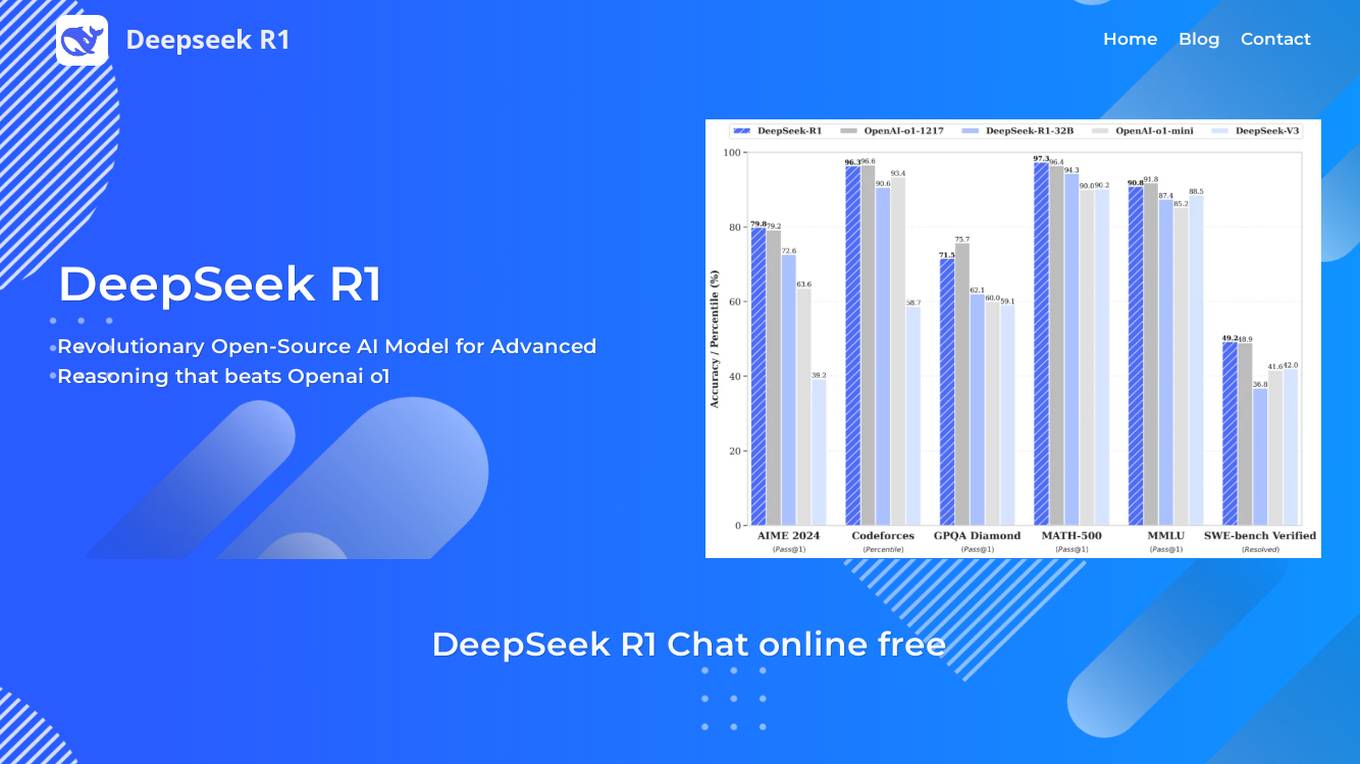
DeepSeek R1
DeepSeek R1 is a revolutionary open-source AI model for advanced reasoning that outperforms leading AI models in mathematics, coding, and general reasoning tasks. It utilizes a sophisticated MoE architecture with 37B active/671B total parameters and 128K context length, incorporating advanced reinforcement learning techniques. DeepSeek R1 offers multiple variants and distilled models optimized for complex problem-solving, multilingual understanding, and production-grade code generation. It provides cost-effective pricing compared to competitors like OpenAI o1, making it an attractive choice for developers and enterprises.
MindpoolAI
MindpoolAI is a tool that allows users to access multiple leading AI models with a single query. This means that users can get the answers they are looking for, spark ideas, and fuel their work, creativity, and curiosity. MindpoolAI is easy to use and does not require any technical expertise. Users simply need to enter their prompt and select the AI models they want to compare. MindpoolAI will then send the query to the selected models and present the results in an easy-to-understand format.
Image Translator
Image Translator is an AI-powered photo translation tool that seamlessly translates text on images in over 25 languages. Users can upload images, select the target language, and get accurate translations while preserving the original design and layout. The tool offers advanced capabilities such as accurate text translation, AI-powered processing, high-quality results, support for over 25 languages, custom instructions, and secure processing. Users can translate various types of text on images including menus, posters, documents, product labels, and more, making it ideal for travelers, students, professionals, and language enthusiasts.

Luma AI
Luma AI is an AI-powered platform that specializes in video generation using advanced models like Ray2 and Dream Machine. The platform offers director-grade control over style, character, and setting, allowing users to reshape videos with ease. Luma AI aims to build multimodal general intelligence that can generate, understand, and operate in the physical world, paving the way for creative, immersive, and interactive systems beyond traditional text-based approaches. The platform caters to creatives in various industries, offering powerful tools for worldbuilding, storytelling, and creative expression.

ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a large language model developed by OpenAI. It is designed to understand and generate human-like text, and can be used for a variety of tasks such as answering questions, writing stories, and translating languages. ChatGPT is free to use, and can be accessed through a web interface or via an API.
Zephyr 7B
Zephyr 7B is a state-of-the-art language model developed by WebPilot.AI with 7 billion parameters. It can understand and generate human-like text with remarkable accuracy and coherence. The model is built upon the latest advancements in natural language processing and machine learning, trained on a vast corpus of text data from diverse sources. Zephyr 7B offers capabilities such as natural language understanding, text generation, language translation, text summarization, sentiment analysis, and question answering. It represents a significant advancement in natural language processing, making it a powerful tool for content creation, customer support, research, and more.

Re-View
Re-View is an AI-powered platform that enables users to conduct surveys that capture more than words by utilizing user-friendly video survey forms. The platform allows users to understand emotions, uncover insights, and collect more and better data through authentic emotional connections. With features like automatic insights, efficient research at scale, stunning simplicity, and powerful research capabilities, Re-View offers a practical pricing model that makes research accessible to all. Users can easily create surveys, analyze responses with AI assistance, and gain valuable research reports to support decision-making.
Ray 3
Ray 3 is the first video AI application for reasoning developed by Luma. It offers users the ability to create stunning videos with advanced visual effects and HDR generation. Ray 3 utilizes state-of-the-art visual intelligence to understand user intent, think through concepts, and deliver high-quality video outputs. With features like visual reasoning, 16-bit HDR generation, Draft Mode for faster iteration, and Chain of Thought for interpreting prompts, Ray 3 provides a seamless video creation experience for professionals across various industries.

DORA
DORA is a research program by Google Cloud that focuses on understanding the capabilities driving software delivery and operations performance. It helps teams apply these capabilities to enhance organizational performance. The program introduces the DORA AI Capabilities Model, identifying key technical and cultural practices that amplify the positive impacts of AI on performance. DORA offers resources, guides, and tools like the DORA Quick Check to help organizations improve their software delivery goals.

Molmo AI
Molmo AI is a powerful, open-source multimodal AI model revolutionizing visual understanding. It helps developers easily build tools that can understand images and interact with the world in useful ways. Molmo AI offers exceptional image understanding, efficient data usage, open and accessible features, on-device compatibility, and a new era in multimodal AI development. It closes the gap between open and closed AI models, empowers the AI community with open access, and efficiently utilizes data for superior performance.
How Attractive Am I
How Attractive Am I is an AI-powered tool that analyzes facial features to calculate an attractiveness score. By evaluating symmetry and proportions, the tool provides personalized beauty scores. Users can upload a photo to discover their true beauty potential. The tool ensures accuracy by providing guidelines for taking photos and offers a fun and insightful way to understand facial appeal.
Rerun
Rerun is an SDK, time-series database, and visualizer for temporal and multimodal data. It is used in fields like robotics, spatial computing, 2D/3D simulation, and finance to verify, debug, and explain data. Rerun allows users to log data like tensors, point clouds, and text to create streams, visualize and interact with live and recorded streams, build layouts, customize visualizations, and extend data and UI functionalities. The application provides a composable data model, dynamic schemas, and custom views for enhanced data visualization and analysis.
Photosolve
Photosolve is an AI-powered educational tool that helps students, teachers, researchers, and writers to quickly find accurate answers to their questions. It offers a Chrome extension and mobile app for easy access to its features. With over 10 million questions answered and growing, Photosolve revolutionizes learning by providing detailed explanations along with answers. Users can upload materials for analysis, have conversations with AI, generate flashcards, and enhance their knowledge with customizable quizzes. The application uses a custom-built AI model for higher accuracy compared to general AI models, ensuring reliable results for academic success.
1 - Open Source AI Tools
Awesome-Interpretability-in-Large-Language-Models
This repository is a collection of resources focused on interpretability in large language models (LLMs). It aims to help beginners get started in the area and keep researchers updated on the latest progress. It includes libraries, blogs, tutorials, forums, tools, programs, papers, and more related to interpretability in LLMs.
20 - OpenAI Gpts
Octorate Code Companion
I help developers understand and use APIs, referencing a YAML model.
CTMU Sage
Bot that guides users in understanding the Cognitive-Theoretic Model of the Universe
Back Propagation
I'm Back Propagation, here to help you understand and apply back propagation techniques to your AI models.
Psychological Analysis of Fictional Characters
This prompt is designed to act as an expert psychologist in personality analysis, using three different psychological models: the Big Five Factor model, the Myers-Briggs Sixteen Types model, and the Enneagram model.
Mental Models Maven
Explains mental models with examples, inspired by thinkers like Charlie Munger.
Experto en Toxina Botulínica
Este modelo de GPT proporciona información general sobre la toxina botulínica, incluyendo su historia, usos comunes y datos de interés. Está diseñado para educar y ofrecer una visión general basada en fuentes de información públicas y conocidas. No proporciona consejos médicos
AInatomy
An expert in Human Anatomy, be it for art or science or education, anything relating to the human body, come ask me. I will provide photo-realistic visual aids and AI created models to expound on different parts of the anatomy
Tech Tutor
A tech guide for software engineers, focusing on the latest tools and foundational knowledge.
MITRE Interpreter
This GPT helps you understand and apply the MITRE ATT&CK Framework, whether you are familiar with the concepts or not.