Awesome-Story-Generation
This repository collects an extensive list of awesome papers about Story Generation / Storytelling, primarily focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs).
Stars: 390
Awesome-Story-Generation is a repository that curates a comprehensive list of papers related to Story Generation and Storytelling, focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository includes papers on various topics such as Literature Review, Large Language Model, Plot Development, Better Storytelling, Story Character, Writing Style, Story Planning, Controllable Story, Reasonable Story, and Benchmark. It aims to provide a chronological collection of influential papers in the field, with a focus on citation counts for LLMs-era papers and some earlier influential papers. The repository also encourages contributions and feedback from the community to improve the collection.
README:
🔥 Previously, we couldn't display citation counts for all papers due to Semantic Scholar API limitations. Now we've solved this issue and can show citations for all papers. Cheers! 🍻
Thanks to all the fellow enthusiasts in story generation for your stars! We'll gradually add new papers from recent months to this repo! 😊
This repository collects an extensive list of awesome papers about Story Generation / Storytelling, primarily focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs).
All papers are sorted in chronological order, with the most recent ones appearing at the top.
Due to limited energy and time, there may be omissions and errors. If you notice any issues or mistakes, please feel free to open issues or submit PRs!
If you have any suggestions or questions, please do not hesitate to reach out to me:
mayingpeng33 [AT] gmail [DOT] com
Eg. ACL-2023 Title [paper] [code] .. [authors]
-
CHI-2024The Value, Benefits, and Concerns of Generative AI-Powered Assistance in Writing [paper] [Zhuoyan Li, Chen Liang, Jing Peng, Ming Yin] -
EMNLP-2023Creative Natural Language Generation [paper] [Tuhin Chakrabarty, Vishakh Padmakumar, He He, Nanyun Peng] -
Neurocomputing-2023Open-world story generation with structured knowledge enhancement: A comprehensive survey [paper] [Yuxin Wang, Jieru Lin, Zhiwei Yu, Wei Hu, Börje F. Karlsson] -
WNU-2022What is Wrong with Language Models that Can Not Tell a Story? [paper] [Ivan P. Yamshchikov, Alexey Tikhonov] -
ACM Computing Surveys-2021Automatic Story Generation [paper] [Arwa I. Alhussain, Aqil M. Azmi] -
NUSE-2021Automatic Story Generation: Challenges and Attempts [paper] [Amal Alabdulkarim, Siyan Li, Xiangyu Peng]
-
EACL-2024Creating Suspenseful Stories: Iterative Planning with Large Language Models [paper] [Kaige Xie, Mark Riedl] -
Arxiv-2024SWAG: Storytelling With Action Guidance [paper] [Zeeshan Patel, Karim El-Refai, Jonathan Pei, Tianle Li] -
Arxiv-2024Weaver: Foundation Models for Creative Writing [paper] [Tiannan Wang, Jiamin Chen, Qingrui Jia, Shuai Wang, Ruoyu Fang, ... , Yuchen Eleanor Jiang, Wangchunshu Zhou] -
ArXiv-2023AutoAgents: A Framework for Automatic Agent Generation [paper] [Guangyao Chen, Siwei Dong, Yu Shu, Ge Zhang, Jaward Sesay, Börje F. Karlsson, Jie Fu, Yemin Shi] -
ArXiv-2023RecurrentGPT: Interactive Generation of (Arbitrarily) Long Text [paper] [code] [Wangchunshu Zhou, Yuchen Eleanor Jiang, Peng Cui, Tiannan Wang, Zhenxin Xiao, Yifan Hou, Ryan Cotterell, Mrinmaya Sachan]
-
Stanford CS224N Custom Project-2023Novelty: Optimizing StreamingLLM for Novel Plot Generation [paper] [Joyce Chen, Megan Mou] -
ArXiv-2023End-to-End Story Plot Generator [paper] [Hanlin Zhu, Andrew Cohen, Danqing Wang, Kevin Yang, Xiaomeng Yang, Jiantao Jiao, Yuandong Tian] -
AAAI Workshop-2023Conveying the Predicted Future to Users: A Case Study of Story Plot Prediction [paper] [Chieh-Yang Huang, Saniya Naphade, Kavya Laalasa Karanam, Ting-Hao 'Kenneth' Huang] -
RANLP-2023Coherent Story Generation with Structured Knowledge [paper] [Congda Ma, Kotaro Funakoshi, Kiyoaki Shirai, Manabu Okumura] -
EMNLP-2022EtriCA: Event-triggered context-aware story generation augmented by cross attention [paper] [Chen Tang, Chenghua Lin, Henglin Huang, Frank Guerin, Zhihao Zhang] -
INLG-2022Plot Writing From Pre-Trained Language Models [paper] [Yiping Jin, Vishakha Kadam, Dittaya Wanvarie] -
AAAI-2020Story Realization: Expanding Plot Events into Sentences [paper] [code] [Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Ethan Tien, Wesley Cheung, Zhaochen Luo, William Ma, Lara J. Martin, Mark O. Riedl]
-
ArXiv-2024With Greater Text Comes Greater Necessity: Inference-Time Training Helps Long Text Generation [paper] [Y. Wang, D. Ma, D. Cai] -
PAKDD-2024LongStory: Coherent, Complete and Length Controlled Long story Generation [paper] [Kyeongman Park, Nakyeong Yang, Kyomin Jung] -
EMNLP Findings-2023Affective and Dynamic Beam Search for Story Generation [paper] [Tenghao Huang, Ehsan Qasemi, Bangzheng Li, He Wang, Faeze Brahman, Muhao Chen, Snigdha Chaturvedi] -
EMNLP Findings-2023GROVE: A Retrieval-augmented Complex Story Generation Framework with A Forest of Evidence [paper] [Zhihua Wen, Zhiliang Tian, Wei Wu, Yuxin Yang, Yanqi Shi, Zhen Huang, Dongsheng Li] -
ACL-2023Open-ended Long Text Generation via Masked Language Modeling [paper] [Xiaobo Liang, Zecheng Tang, Juntao Li, Min Zhang] -
ArXiv-2022Future Sight: Dynamic Story Generation with Large Pretrained Language Models [paper] [Brian D. Zimmerman, Gaurav Sahu, Olga Vechtomova] -
ACL Workshop-2022Coherent Long Text Generation by Contrastive Soft Prompt [paper] [Guandan Chen, Jiashu Pu, Yadong Xi, Rongsheng Zhang] -
AACL-2022Improving Chinese Story Generation via Awareness of Syntactic Dependencies and Semantics [paper] [Henglin Huang, Chen Tang, Tyler Loakman, Frank Guerin, Chenghua Lin] -
AAAI-2022Generating Coherent Narratives by Learning Dynamic and Discrete Entity States with a Contrastive Framework [paper] [Jian Guan, Zhenyu Yang, Rongsheng Zhang, Zhipeng Hu, Minlie Huang] -
PhD Thesis-2022Great Expectations: Unsupervised Inference of Suspense, Surprise and Salience in Storytelling [paper] [David Wilmot] -
NAACL-2022Go Back in Time: Generating Flashbacks in Stories with Event Temporal Prompts [paper] [Rujun Han, Hong Chen, Yufei Tian, Nanyun Peng] -
ACL Findings-2022Event Transition Planning for Open-ended Text Generation [paper] [Qintong Li, Piji Li, Wei Bi, Zhaochun Ren, Yuxuan Lai, Lingpeng Kong] -
ICASSP-2022Clseg: Contrastive learning of story ending generation [paper] [Yuqiang Xie, Yue Hu, Luxi Xing, Yunpeng Li, Wei Peng, Ping Guo] -
ICML-2022Towards Coherent and Consistent Use of Entities in Narrative Generation [paper] [Pinelopi Papalampidi, Kris Cao, Tomas Kocisky] -
EMNLP Findings-2021Guiding Neural Story Generation with Reader Models [paper] [Xiangyu Peng, Kaige Xie, Amal Alabdulkarim, Harshith Kayam, Samihan Dani, Mark O. Riedl] -
ArXiv-2021Goal-Directed Story Generation: Augmenting Generative Language Models with Reinforcement Learning [paper] [Amal Alabdulkarim, Winston Li, Lara J. Martin, Mark O. Riedl] -
ArXiv-2021Automated Story Generation as Question-Answering [paper] [Louis Castricato, Spencer Frazier, Jonathan Balloch, Nitya Tarakad, Mark Riedl] -
ACL-2021Long text generation by modeling sentence-level and discourse-level coherence [paper] [Jian Guan, Xiaoxi Mao, Changjie Fan, Zitao Liu, Wenbiao Ding, Minlie Huang] -
AACL-2020Cue Me In: Content-Inducing Approaches to Interactive Story Generation [paper] [Faeze Brahman, Alexandru Petrusca, Snigdha Chaturvedi]
-
FDG-2024StoryVerse: Towards Co-authoring Dynamic Plot with LLM-based Character Simulation via Narrative Planning [paper] [Yi Wang, Qian Zhou, David Ledo] -
ArXiv-2024Large Language Models Fall Short: Understanding Complex Relationships in Detective Narratives [paper] [Runcong Zhao, Qinglin Zhu, Hainiu Xu, Jiazheng Li, Yuxiang Zhou, Yulan He, Lin Gui] -
EMNLP-2022Towards Inter-character Relationship-driven Story Generation [paper] [Anvesh Rao Vijjini, Faeze Brahman, Snigdha Chaturvedi] -
COLING-2022CHAE: Fine-Grained Controllable Story Generation with Characters, Actions and Emotions [paper] [Xinpeng Wang, Han Jiang, Zhihua Wei, Shanlin Zhou] -
ArXiv-2022A Benchmark for Understanding and Generating Dialogue between Characters in Stories [paper] [Jianzhu Yao, Ziqi Liu, Jian Guan, Minlie Huang] -
ECML/PKDD-2022An Ion Exchange Mechanism Inspired Story Ending Generator for Different Characters [paper] [Xinyu Jiang, Qi Zhang, Chongyang Shi, Kaiying Jiang, Liang Hu, Shoujin Wang] -
NAACL-2022Persona-Guided Planning for Controlling the Protagonist’s Persona in Story Generation [paper] [code] [Zhexin Zhang, Jiaxin Wen, Jian Guan, Minlie Huang] -
ACL-2021Unsupervised Enrichment of Persona-grounded Dialog with Background Stories [paper] [Bodhisattwa Prasad Majumder, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Julian McAuley, Harsh Jhamtani] -
SIGDIAL-2021Telling Stories through Multi-User Dialogue by Modeling Character Relations [paper] [Wai Man Si, Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Mark O. Riedl]
-
ArXiv-2025Pastiche Novel Generation Creating: Fan Fiction You Love in Your Favorite Author's Style [paper] [Xueran Han, Yuhan Liu, Mingzhe Li, Wei Liu, Sen Hu, Rui Yan, Zhiqiang Xu, Xiuying Chen] -
ArXiv-2025Whose story is it? Personalizing story generation by inferring author styles [paper] [Nischal Ashok Kumar, Chau Minh Pham, Mohit Iyyer, Andrew Lan] -
ArXiv-2024CAT-LLM: Prompting Large Language Models with Text Style Definition for Chinese Article-style Transfer [paper] [Zhen Tao, Dinghao Xi, Zhiyu Li, Liumin Tang, Wei Xu] -
ArXiv-2023Learning to Generate Text in Arbitrary Writing Styles [paper] [Aleem Khan, Andrew Wang, Sophia Hager, Nicholas Andrews] -
ACL-2023StoryTrans: Non-Parallel Story Author-Style Transfer with Discourse Representations and Content Enhancing [paper] [Xuekai Zhu, Jian Guan, Minlie Huang, Juan Liu] -
ACL-2021Stylized story generation with style-guided planning [paper] [Xiangzhe Kong, Jialiang Huang, Ziquan Tung, Jian Guan, Minlie Huang] -
ACL-2020Story-level Text Style Transfer: A Proposal [paper] [Yusu Qian]
-
ArXiv-2024Navigating the Path of Writing: Outline-guided Text Generation with Large Language Models [paper] [Yukyung Lee, Soonwon Ka, Bokyung Son, Pilsung Kang, Jaewook Kang] -
EMNLP Findings-2023Improving Pacing in Long-Form Story Planning [paper] [Yichen Wang, Kevin Yang, Xiaoming Liu, Dan Klein] -
ArXiv-2023EIPE-text: Evaluation-Guided Iterative Plan Extraction for Long-Form Narrative Text Generation [paper] [Wang You, Wenshan Wu, Yaobo Liang, Shaoguang Mao, Chenfei Wu, Maosong Cao, Yuzhe Cai, Yiduo Guo, Yan Xia, Furu Wei, Nan Duan] -
ArXiv-2023RLCD: Reinforcement Learning from Contrast Distillation for Language Model Alignment [paper] [Kevin Yang, Dan Klein, Asli Celikyilmaz, Nanyun Peng, Yuandong Tian] -
ArXiv-2023Enhancing Generation through Summarization Duality and Explicit Outline Control [paper] [Yunzhe Li, Qian Chen, Weixiang Yan, Wen Wang, Qinglin Zhang, Hari Sundaram] -
ArXiv-2022Little Red Riding Hood Goes Around the Globe:Crosslingual Story Planning and Generation with Large Language Models [paper] [Evgeniia Razumovskaia, Joshua Maynez, Annie Louis, Mirella Lapata, Shashi Narayan] -
ACL-2023DOC: Improving Long Story Coherence With Detailed Outline Control [paper] [code] [Kevin Yang, Dan Klein, Nanyun Peng, Yuandong Tian] -
ArXiv-2022Neural Story Planning [paper] [Anbang Ye, Christopher Cui, Taiwei Shi, Mark O. Riedl] -
EMNLP-2022Re3: Generating longer stories with recursive reprompting and revision [paper] [Kevin Yang, Yuandong Tian, Nanyun Peng, Dan Klein] -
AAAI-2021Narrative Plan Generation with Self-Supervised Learning [paper] [Mihai Polceanu, Julie Porteous, Alan Lindsay, Marc Cavazza] -
INLG-2021GraphPlan: Story Generation by Planning with Event Graph [paper] [Hong Chen, Raphael Shu, Hiroya Takamura, Hideki Nakayama] -
EMNLP-2020Content Planning for Neural Story Generation with Aristotelian Rescoring [paper] [Seraphina Goldfarb-Tarrant, Tuhin Chakrabarty, Ralph Weischedel, Nanyun Peng] -
AAAI-2020Draft and Edit: Automatic Storytelling Through Multi-Pass Hierarchical Conditional Variational Autoencoder [paper] [Meng-Hsuan Yu, Juntao Li, Danyang Liu, Dongyan Zhao, Rui Yan, Bo Tang, Haisong Zhang] -
ACL-2019Strategies for Structuring Story Generation [paper] [Angela Fan, Mike Lewis, Yann Dauphin] -
AAAI-2019Plan-And-Write: Towards Better Automatic Storytelling [paper] [code] [Lili Yao, Nanyun Peng, Ralph Weischedel, Kevin Knight, Dongyan Zhao, Rui Yan] -
EMNLP-2018A Skeleton-Based Model for Promoting Coherence Among Sentences in Narrative Story Generation [paper] [code] [Jingjing Xu, Xuancheng Ren, Yi Zhang, Qi Zeng, Xiaoyan Cai, Xu Sun] -
ACL-2018Hierarchical Neural Story Generation [paper] [code] [writing prompt] [Angela Fan, Mike Lewis, Yann Dauphin] -
AAAI-2018Event Representations for Automated Story Generation with Deep Neural Nets [paper] [code] [Lara J. Martin, Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Xinyu Wang, William Hancock, Shruti Singh, Brent Harrison, Mark O. Riedl]
-
ACL-2024MoPS: Modular Story Premise Synthesis for Open-Ended Automatic Story Generation [paper] [code] [Yan Ma, Yu Qiao, Pengfei Liu] -
ArXiv-2024Returning to the Start: Generating Narratives with Related Endpoints [paper] [code] [Anneliese Brei, Chao Zhao, Snigdha Chaturvedi] -
ArXiv-2024LiFi: Lightweight Controlled Text Generation with Fine-Grained Control Codes [paper] [Chufan Shi, Deng Cai, Yujiu Yang] -
INLG-2023Controlling keywords and their positions in text generation [paper] [Yuichi Sasazawa, Terufumi Morishita, Hiroaki Ozaki, Osamu Imaichi, Yasuhiro Sogawa] -
COLING-2022Psychology-guided Controllable Story Generation [paper] [Yuqiang Xie, Yue Hu, Yunpeng Li, Guanqun Bi, Luxi Xing, Wei Peng] -
WWW-2022Genre-controllable story generation via supervised contrastive learning [paper] [JinUk Cho, MinSu Jeong, JinYeong Bak, Yun-Gyung Cheong] -
EMNLP Findings-2021A Plug-and-Play Method for Controlled Text Generation [paper] [code] [Damian Pascual, Beni Egressy, Clara Meister, Ryan Cotterell, Roger Wattenhofer] -
NUSE-2021Plug-and-Blend: A Framework for Controllable Story Generation with Blended Control Codes [paper] [code] [Zhiyu Lin, Mark Riedl] -
ArXiv-2021Transformer-based Conditional Variational Autoencoder for Controllable Story Generation [paper] [code] [Le Fang, Tao Zeng, Chaochun Liu, Liefeng Bo, Wen Dong, Changyou Chen] -
ArXiv-2021Outline to Story: Fine-grained Controllable Story Generation from Cascaded Events [paper] [Le Fang, Tao Zeng, Chaochun Liu, Liefeng Bo, Wen Dong, Changyou Chen] -
EMNLP-2020Controllable Story Generation with External Knowledge Using Large-Scale Language Models [paper] [Peng Xu, Mostofa Patwary, Mohammad Shoeybi, Raul Puri, Pascale Fung, Anima Anandkumar, Bryan Catanzaro] -
ACL-2019Learning to Control the Fine-grained Sentiment for Story Ending Generation [paper] [Fuli Luo, Damai Dai, Pengcheng Yang, Tianyu Liu, Baobao Chang, Zhifang Sui, Xu Sun] -
IJCAI-2019Controllable Neural Story Plot Generation via Reward Shaping [paper] [Pradyumna Tambwekar, Murtaza Dhuliawala, Lara J. Martin, Animesh Mehta, Brent Harrison, Mark O. Riedl] -
ACL-2018Towards Controllable Story Generation [paper] [Nanyun Peng, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Jonathan May, Kevin Knight]
-
SIGIR-2022What makes the story forward? inferring commonsense explanations as prompts for future event generation [paper] [Li Lin, Yixin Cao, Lifu Huang, Shu'ang Li, Xuming Hu, Lijie Wen, Jianmin Wang] -
EMNLP Findings-2022Inferring the Reader: Guiding Automated Story Generation with Commonsense Reasoning [paper] [Xiangyu Peng, Siyan Li, Sarah Wiegreffe, Mark Riedl] -
AAAI-2021Automated Storytelling via Causal, Commonsense Plot Ordering [paper] [Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Wesley Cheung, William Broniec, Mark O. Riedl] -
AIIDE-2020Bringing Stories Alive: Generating Interactive Fiction Worlds [paper] [code] [Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, Wesley Cheung, Dan Tu, William Broniec, Mark O. Riedl] -
TACL-2020A Knowledge-Enhanced Pretraining Model for Commonsense Story Generation [paper] [Jian Guan, Fei Huang, Zhihao Zhao, Xiaoyan Zhu, Minlie Huang] -
EMNLP-2020Improving Neural Story Generation by Targeted Common Sense Grounding [paper] [code] [Huanru Henry Mao, Bodhisattwa Prasad Majumder, Julian McAuley, Garrison W. Cottrell] -
AAAI-2019Story Ending Generation with Incremental Encoding and Commonsense Knowledge [paper] [Jian Guan, Yansen Wang, Minlie Huang]
-
TACL-2024Do Language Models Enjoy Their Own Stories? Prompting Large Language Models for Automatic Story Evaluation [paper] [Cyril Chhun, Fabian M. Suchanek, Chloé Clavel] -
Arxiv-2024Reading Subtext: Evaluating Large Language Models on Short Story Summarization with Writers [paper] [Melanie Subbiah, Sean Zhang, Lydia B. Chilton, Kathleen McKeown] -
ArXiv-2023Experimental Narratives: A Comparison of Human Crowdsourced Storytelling and AI Storytelling [paper] [Nina Begus] -
ArXiv-2023Learning Personalized Alignment for Evaluating Open-ended Text Generation [paper] [Danqing Wang, Kevin Yang, Hanlin Zhu, Xiaomeng Yang, Andrew Cohen, Lei Li, Yuandong Tian] -
ArXiv-2023BooookScore: A systematic exploration of book-length summarization in the era of LLMs[paper][Yapei Chang, Kyle Lo, Tanya Goyal, Mohit Iyyer] -
ArXiv-2023TIGERScore: Towards Building Explainable Metric for All Text Generation Tasks[paper][Dongfu Jiang, Yishan Li, Ge Zhang, Wenhao Huang, Bill Yuchen Lin, Wenhu Chen] -
CHI-2023Art or Artifice? Large Language Models and the False Promise of Creativity [paper] [Tuhin Chakrabarty, Philippe Laban, Divyansh Agarwal, Smaranda Muresan, Chien-Sheng Wu] -
ACL-2023HAUSER: Towards Holistic and Automatic Evaluation of Simile Generation [paper] [Qianyu He, Yikai Zhang, Jiaqing Liang, Yuncheng Huang, Yanghua Xiao, Yunwen Chen] -
ACL-2023Can Large Language Models Be an Alternative to Human Evaluations? [paper] [Cheng-Han Chiang, Hung-yi Lee] -
ArXiv-2023DeltaScore: Evaluating Story Generation with Differentiating Perturbations [paper] [Zhuohan Xie, Miao Li, Trevor Cohn, Jey Han Lau] -
INLG-2023The Next Chapter: A Study of Large Language Models in Storytelling [paper] [Zhuohan Xie, Trevor Cohn, Jey Han Lau] -
IEEE Access-2023Comparison of Evaluation Metrics for Short Story Generation [paper] [P. Netisopakul, Usanisa Taoto] -
EMNLP-2022StoryER: Automatic Story Evaluation via Ranking, Rating and Reasoning [paper] [Hong Chen, Duc Minh Vo, Hiroya Takamura, Yusuke Miyao, Hideki Nakayama] -
COLING-2022Of Human Criteria and Automatic Metrics: A Benchmark of the Evaluation of Story Generation [paper] [Cyril Chhun, Pierre Colombo, Chloé Clavel, Fabian M. Suchanek] -
TACL-2022LOT: A story-centric benchmark for evaluating Chinese long text understanding and generation [paper] [Jian Guan, Zhuoer Feng, Yamei Chen, Ruilin He, Xiaoxi Mao, Changjie Fan, Minlie Huang] -
ACL-2021Openmeva: A benchmark for evaluating open-ended story generation metrics [paper] [Jian Guan, Zhexin Zhang, Zhuoer Feng, Zitao Liu, Wenbiao Ding, Xiaoxi Mao, Changjie Fan, Minlie Huang] -
EMNLP-2020Union: An unreferenced metric for evaluating open-ended story generation [paper] [code] [Jian Guan, Minlie Huang] -
CoNLL-2019Do Massively Pretrained Language Models Make Better Storytellers? [paper] [code] [Abigail See, Aneesh Pappu, Rohun Saxena, Akhila Yerukola, Christopher D. Manning] -
NAACL-2016A Corpus and Evaluation Framework for Deeper Understanding of Commonsense Stories [paper] [Nasrin Mostafazadeh, Nathanael Chambers, Xiaodong He, Devi Parikh, Dhruv Batra, Lucy Vanderwende, Pushmeet Kohli, James Allen]
-
ArXiv-2024CollabStory: Multi-LLM Collaborative Story Generation and Authorship Analysis [paper] [Saranya Venkatraman, Nafis Irtiza Tripto, Dongwon Lee] -
IREC-COLING-2024Reflections & Resonance: Two-Agent Partnership for Advancing LLM-based Story Annotation [paper] [Yuetian Chen, Mei Si] -
ArXiv-2024CMDAG: A Chinese Metaphor Dataset with Annotated Grounds as CoT for Boosting Metaphor Generation [paper] [Yujie Shao, Xinrong Yao, Xingwei Qu, Chenghua Lin, Shi Wang, Stephen W. Huang, Ge Zhang, Jie Fu] -
ArXiv-2023STONYBOOK: A System and Resource for Large-Scale Analysis of Novels [paper] [Charuta Pethe, Allen Kim, Rajesh Prabhakar, Tanzir Pial, Steven Skiena] -
ACL-2023StoryWars: A Dataset and Instruction Tuning Baselines for Collaborative Story Understanding and Generation [paper] [Yulun Du, Lydia Chilton] -
TACL-2023PASTA: A Dataset for Modeling Participant States in Narratives [paper] [Sayontan Ghosh, Mahnaz Koupaee, Isabella Chen, Francis Ferraro, Nathanael Chambers, Niranjan Balasubramanian] -
NAACL-2022A corpus for understanding and generating moral stories [paper] [Jian Guan, Ziqi Liu, Minlie Huang] -
EVAL4NLP-2021StoryDB: Broad Multi-language Narrative Dataset [paper] [Alexey Tikhonov, Igor Samenko, Ivan P. Yamshchikov] -
ACL-2022SummScreen: A Dataset for Abstractive Screenplay Summarization [paper] [data] [Mingda Chen, Zewei Chu, Sam Wiseman, Kevin Gimpel] -
Arxiv-2021TVStoryGen: A Dataset for Generating Stories with Character Descriptions [paper] [Mingda Chen, Kevin Gimpel] -
EMNLP-2020STORIUM: A Dataset and Evaluation Platform for Machine-in-the-Loop Story Generation [paper] [Nader Akoury, Shufan Wang, Josh Whiting, Stephen Hood, Nanyun Peng, Mohit Iyyer]
Click to view details of other related papers:
-
ArXiv-2024Ai.llude: Encouraging Rewriting AI-Generated Text to Support Creative Expression [paper] [David Zhou, Sarah Sterman] -
ArXiv-2024Word2World: Generating Stories and Worlds through Large Language Models [paper] [code] [Muhammad U. Nasir, Steven James, Julian Togelius] -
ArXiv-2024Let Storytelling Tell Vivid Stories: An Expressive and Fluent Multimodal Storyteller [paper] [Chuanqi Zang, Jiji Tang, Rongsheng Zhang, Zeng Zhao, Tangjie Lv, Mingtao Pei, Wei Liang] -
CHI-2024Shaping Human-AI Collaboration: Varied Scaffolding Levels in Co-writing with Language Models [paper] [Paramveer S. Dhillon, Somayeh Molaei, Jiaqi Li, Maximilian Golub, Shaochun Zheng, Lionel P. Robert] -
Arxiv-2024GhostWriter: Augmenting Collaborative Human-AI Writing Experiences Through Personalization and Agency [paper] [Catherine Yeh, Gonzalo Ramos, Rachel Ng, Andy Huntington, Richard Banks] -
ArXiv-2023Inspo: Writing Stories with a Flock of AIs and Humans [paper] [Chieh-Yang Huang, Sanjana Gautam, Shannon McClellan Brooks, Ya-Fang Lin, Ting-Hao 'Kenneth' Huang] -
AAAI-2023SceneCraft: Automating Interactive Narrative Scene Generation in Digital Games with Large Language Models [paper] [Vikram Kumaran, Jonathan Rowe, Bradford Mott, James Lester] -
ArXiv-2023PEARL: Personalizing Large Language Model Writing Assistants with Generation-Calibrated Retrievers [paper] [Sheshera Mysore, Zhuoran Lu, Mengting Wan, Longqi Yang, Steve Menezes, Tina Baghaee, Emmanuel Barajas Gonzalez, Jennifer Neville, Tara Safavi] -
EMNLP Findings-2023Are NLP Models Good at Tracing Thoughts: An Overview of Narrative Understanding [paper] [Lixing Zhu, Runcong Zhao, Lin Gui, Yulan He] -
CoNLL Workshop-2023BabyStories: Can Reinforcement Learning Teach Baby Language Models to Write Better Stories? [paper] [Xingmeng Zhao, Tongnian Wang, Sheri Osborn, Anthony Rios] -
ArXiv-2023Creativity Support in the Age of Large Language Models: An Empirical Study Involving Emerging Writers [paper] [Tuhin Chakrabarty, Vishakh Padmakumar, Faeze Brahman, Smaranda Muresan] -
UIST-2023Storyfier: Exploring Vocabulary Learning Support with Text Generation Models [paper] [Zhenhui Peng, Xingbo Wang, Qiushi Han, Junkai Zhu, Xiaojuan Ma, Huamin Qu] -
PACLIC-2023Generating Character Lines in Four-Panel Manga [paper] [Michimasa Inaba] -
ArXiv-2022Creative Writing with an AI-Powered Writing Assistant: Perspectives from Professional Writers [paper] [Daphne Ippolito, Ann Yuan, Andy Coenen, Sehmon Burnam] -
ArXiv-2022Survey: Automatic Movie Plot and Script Generation [paper] [Prerak Gandhi, Pushpak Bhattacharyya] -
CHI-2022TaleBrush: Sketching Stories with Generative Pretrained Language Models [paper] [John Joon Young Chung, Wooseok Kim, Kang Min Yoo, Hwaran Lee, Eytan Adar, Minsuk Chang] -
EMNLP-2022Help me write a poem: Instruction Tuning as a Vehicle for Collaborative Poetry Writing [paper] [Tuhin Chakrabarty, Vishakh Padmakumar, He He] -
CHI-2023Co-Writing Screenplays and Theatre Scripts with Language Models: An Evaluation by Industry Professionals [paper] [Piotr Mirowski, Kory W. Mathewson, Jaylen Pittman, Richard Evans] -
NeurIPS-2022Factuality Enhanced Language Models for Open-Ended Text Generation [paper] [Nayeon Lee, Wei Ping, Peng Xu, Mostofa Patwary, Mohammad Shoeybi, Bryan Catanzaro] -
FDG-2022TropeTwist: Trope-based Narrative Structure Generation [paper] [Alberto Alvarez, Jose Font] -
IUI-2022Wordcraft: Story Writing With Large Language Models [paper] [Ann Yuan, Andy Coenen, Emily Reif, Daphne Ippolito] -
ACM Computing Surveys-2023A Survey of Controllable Text Generation Using Transformer-based Pre-trained Language Models [paper] [Hanqing Zhang, Haolin Song, Shaoyu Li, Ming Zhou, Dawei Song] -
ACL-IJCNLP-2021KuiLeiXi: a Chinese Open-Ended Text Adventure Game [paper] [Heng Ji, Jong C. Park, Rui Xia] -
IJCAI AI4Narratives-2020THEaiTRE: Artificial Intelligence to Write a Theatre Play [paper] [Rudolf Rosa, Ondřej Dušek, Tom Kocmi, David Mareček, Tomáš Musil, Patrícia Schmidtová, Dominik Jurko, Ondřej Bojar, Daniel Hrbek, David Košťák, Martina Kinská, Josef Doležal, Klára Vosecká] -
ICCC-2020Toward Automated Quest Generation in Text-Adventure Games [paper] [Prithviraj Ammanabrolu, William Broniec, Alex Mueller, Jeremy Paul, Mark O. Riedl]
- Understanding AI for Stories serves as a survey blog that delves into the application of AI in the realm of story generation, shedding light on its potential as well as the challenges that it encounters.
- ROC Stories is a compilation of 100,000 five-sentence stories and 3,742 Story Cloze Test stories, capturing a rich array of causal and temporal commonsense connections between everyday events, making it suitable for story generation tasks.
- CommonGen was developed by combining crowdsourced and existing caption corpora, containing 79k commonsense descriptions across 35k distinct concept-sets.
- CMU Movie Summary Corpus offers access to a dataset containing movie plot summaries and related metadata.
- Scifi TV Show Plot Summaries & Events is a collection of plot synopses for long-running (80+ episodes) science fiction TV shows, sourced from Fandom.com wikis.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-Story-Generation
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-Story-Generation
Awesome-Story-Generation is a repository that curates a comprehensive list of papers related to Story Generation and Storytelling, focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository includes papers on various topics such as Literature Review, Large Language Model, Plot Development, Better Storytelling, Story Character, Writing Style, Story Planning, Controllable Story, Reasonable Story, and Benchmark. It aims to provide a chronological collection of influential papers in the field, with a focus on citation counts for LLMs-era papers and some earlier influential papers. The repository also encourages contributions and feedback from the community to improve the collection.
Awesome-Latent-CoT
This repository contains a regularly updated paper list for Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning in latent space. Reasoning in latent space allows for more flexible and efficient thought representation beyond language tokens, bringing AI closer to human-like cognition. The repository covers various aspects of LLMs, including pre-training, supervised finetuning, analysis, interpretability, multimodal reasoning, and applications. It aims to showcase the advancements in reasoning with latent thoughts and continuous concepts in AI models.
Awesome-Segment-Anything
Awesome-Segment-Anything is a powerful tool for segmenting and extracting information from various types of data. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily define segmentation rules and apply them to text, images, and other data formats. The tool supports both supervised and unsupervised segmentation methods, allowing users to customize the segmentation process based on their specific needs. With its versatile functionality and intuitive design, Awesome-Segment-Anything is ideal for data analysts, researchers, content creators, and anyone looking to efficiently extract valuable insights from complex datasets.
llm-misinformation-survey
The 'llm-misinformation-survey' repository is dedicated to the survey on combating misinformation in the age of Large Language Models (LLMs). It explores the opportunities and challenges of utilizing LLMs to combat misinformation, providing insights into the history of combating misinformation, current efforts, and future outlook. The repository serves as a resource hub for the initiative 'LLMs Meet Misinformation' and welcomes contributions of relevant research papers and resources. The goal is to facilitate interdisciplinary efforts in combating LLM-generated misinformation and promoting the responsible use of LLMs in fighting misinformation.
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-Openai-o1-Survey
The repository 'Awesome LLM Reasoning Openai-o1 Survey' provides a collection of survey papers and related works on OpenAI o1, focusing on topics such as LLM reasoning, self-play reinforcement learning, complex logic reasoning, and scaling law. It includes papers from various institutions and researchers, showcasing advancements in reasoning bootstrapping, reasoning scaling law, self-play learning, step-wise and process-based optimization, and applications beyond math. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reasoning techniques.
awesome-open-ended
A curated list of open-ended learning AI resources focusing on algorithms that invent new and complex tasks endlessly, inspired by human advancements. The repository includes papers, safety considerations, surveys, perspectives, and blog posts related to open-ended AI research.
Everything-LLMs-And-Robotics
The Everything-LLMs-And-Robotics repository is the world's largest GitHub repository focusing on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Robotics. It provides educational resources, research papers, project demos, and Twitter threads related to LLMs, Robotics, and their combination. The repository covers topics such as reasoning, planning, manipulation, instructions and navigation, simulation frameworks, perception, and more, showcasing the latest advancements in the field.
Awesome-LLM-Robotics
This repository contains a curated list of **papers using Large Language/Multi-Modal Models for Robotics/RL**. Template from awesome-Implicit-NeRF-Robotics Please feel free to send me pull requests or email to add papers! If you find this repository useful, please consider citing and STARing this list. Feel free to share this list with others! ## Overview * Surveys * Reasoning * Planning * Manipulation * Instructions and Navigation * Simulation Frameworks * Citation
latentbox
Latent Box is a curated collection of resources for AI, creativity, and art. It aims to bridge the information gap with high-quality content, promote diversity and interdisciplinary collaboration, and maintain updates through community co-creation. The website features a wide range of resources, including articles, tutorials, tools, and datasets, covering various topics such as machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, generative art, and creative coding.
awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona
Awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona is a curated list of resources for large language models for role-playing with assigned personas. It includes papers and resources related to persona-based dialogue systems, personalized response generation, psychology of LLMs, biases in LLMs, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of research papers and tools for exploring role-playing abilities of large language models in various contexts.
LLM-IR-Bias-Fairness-Survey
LLM-IR-Bias-Fairness-Survey is a collection of papers related to bias and fairness in Information Retrieval (IR) with Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository organizes papers according to a survey paper titled 'Bias and Unfairness in Information Retrieval Systems: New Challenges in the LLM Era'. The survey provides a comprehensive review of emerging issues related to bias and unfairness in the integration of LLMs into IR systems, categorizing mitigation strategies into data sampling and distribution reconstruction approaches.
simpletransformers
Simple Transformers is a library based on the Transformers library by HuggingFace, allowing users to quickly train and evaluate Transformer models with only 3 lines of code. It supports various tasks such as Information Retrieval, Language Models, Encoder Model Training, Sequence Classification, Token Classification, Question Answering, Language Generation, T5 Model, Seq2Seq Tasks, Multi-Modal Classification, and Conversational AI.
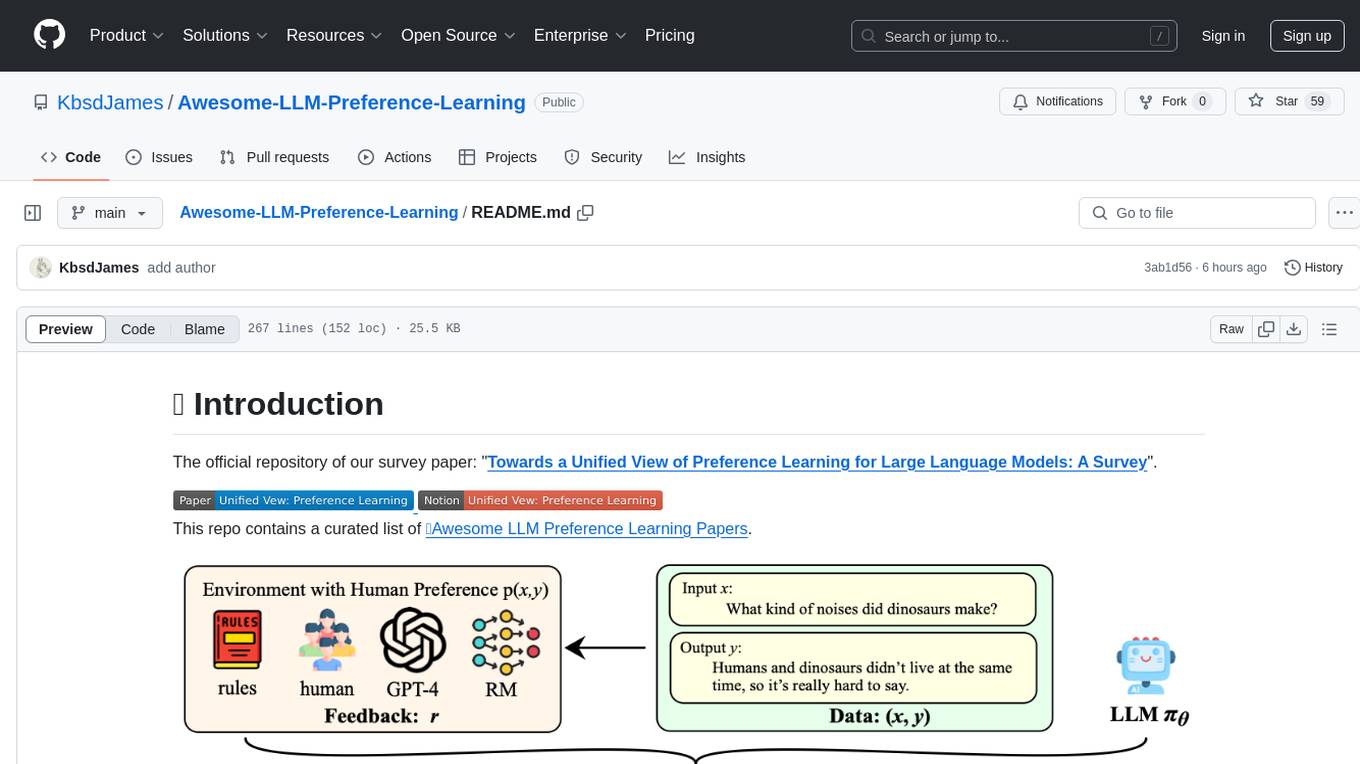
Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning
The repository 'Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning' is the official repository of a survey paper titled 'Towards a Unified View of Preference Learning for Large Language Models: A Survey'. It contains a curated list of papers related to preference learning for Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository covers various aspects of preference learning, including on-policy and off-policy methods, feedback mechanisms, reward models, algorithms, evaluation techniques, and more. The papers included in the repository explore different approaches to aligning LLMs with human preferences, improving mathematical reasoning in LLMs, enhancing code generation, and optimizing language model performance.
For similar tasks

Awesome-Story-Generation
Awesome-Story-Generation is a repository that curates a comprehensive list of papers related to Story Generation and Storytelling, focusing on the era of Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository includes papers on various topics such as Literature Review, Large Language Model, Plot Development, Better Storytelling, Story Character, Writing Style, Story Planning, Controllable Story, Reasonable Story, and Benchmark. It aims to provide a chronological collection of influential papers in the field, with a focus on citation counts for LLMs-era papers and some earlier influential papers. The repository also encourages contributions and feedback from the community to improve the collection.
EasyNovelAssistant
EasyNovelAssistant is a simple novel generation assistant powered by a lightweight and uncensored Japanese local LLM 'LightChatAssistant-TypeB'. It allows for perpetual generation with 'Generate forever' feature, stacking up lucky gacha draws. It also supports text-to-speech. Users can directly utilize KoboldCpp and Style-Bert-VITS2 internally or use EasySdxlWebUi to generate images while using the tool. The tool is designed for local novel generation with a focus on ease of use and flexibility.
SillyTavern
SillyTavern is a user interface you can install on your computer (and Android phones) that allows you to interact with text generation AIs and chat/roleplay with characters you or the community create. SillyTavern is a fork of TavernAI 1.2.8 which is under more active development and has added many major features. At this point, they can be thought of as completely independent programs.
agnai
Agnaistic is an AI roleplay chat tool that allows users to interact with personalized characters using their favorite AI services. It supports multiple AI services, persona schema formats, and features such as group conversations, user authentication, and memory/lore books. Agnaistic can be self-hosted or run using Docker, and it provides a range of customization options through its settings.json file. The tool is designed to be user-friendly and accessible, making it suitable for both casual users and developers.
ComfyUI-IF_AI_tools
ComfyUI-IF_AI_tools is a set of custom nodes for ComfyUI that allows you to generate prompts using a local Large Language Model (LLM) via Ollama. This tool enables you to enhance your image generation workflow by leveraging the power of language models.
ai-game-development-tools
Here we will keep track of the AI Game Development Tools, including LLM, Agent, Code, Writer, Image, Texture, Shader, 3D Model, Animation, Video, Audio, Music, Singing Voice and Analytics. 🔥 * Tool (AI LLM) * Game (Agent) * Code * Framework * Writer * Image * Texture * Shader * 3D Model * Avatar * Animation * Video * Audio * Music * Singing Voice * Speech * Analytics * Video Tool
RisuAI
RisuAI, or Risu for short, is a cross-platform AI chatting software/web application with powerful features such as multiple API support, assets in the chat, regex functions, and much more.
llm-x
LLM X is a ChatGPT-style UI for the niche group of folks who run Ollama (think of this like an offline chat gpt server) locally. It supports sending and receiving images and text and works offline through PWA (Progressive Web App) standards. The project utilizes React, Typescript, Lodash, Mobx State Tree, Tailwind css, DaisyUI, NextUI, Highlight.js, React Markdown, kbar, Yet Another React Lightbox, Vite, and Vite PWA plugin. It is inspired by ollama-ui's project and Perplexity.ai's UI advancements in the LLM UI space. The project is still under development, but it is already a great way to get started with building your own LLM UI.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.