
claude-code-router
Use Claude Code without an Anthropics account and route it to another LLM provider
Stars: 75
This repository is for testing routing Claude Code requests to different models. It implements Normal Mode and Router Mode, using various models like qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct, qwen-max-0125, deepseek-v3, and deepseek-r1. The project aims to reduce the cost of using Claude Code by leveraging free models and KV-Cache. Users can set appropriate ignorePatterns for the project. The Router Mode allows for the separation of tool invocation from coding tasks by using multiple models for different purposes.
README:
This is a repository for testing routing Claude Code requests to different models.
Warning! This project is for testing purposes and may consume a lot of tokens! It may also fail to complete tasks!
-
[x] Mormal Mode and Router Mode
-
[x] Using the qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct model as the routing dispatcher (since it’s currently free on Alibaba Cloud’s official website)
-
[x] Using the qwen-max-0125 model as the tool invoker
-
[x] Using deepseek-v3 as the coder model
-
[x] Using deepseek-r1 as the reasoning model
Thanks to the free qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct model from Alibaba and deepseek’s KV-Cache, we can significantly reduce the cost of using Claude Code. Make sure to set appropriate ignorePatterns for the project. See: https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/agents-and-tools/claude-code/overview
- Install Claude Code
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code- Clone this repo
git clone https://github.com/musistudio/claude-code-reverse.git- Install dependencies
npm i- Start server
# Alternatively, you can create an .env file in the repo directory
# You can refer to the .env.example file to create the .env file
## disable router
ENABLE_ROUTER=false
OPENAI_API_KEY=""
OPENAI_BASE_URL=""
OPENAI_MODEL=""
## enable router
ENABLE_ROUTER=true
export TOOL_AGENT_API_KEY=""
export TOOL_AGENT_BASE_URL=""
export TOOL_AGENT_MODEL="qwen-max-2025-01-25"
export CODER_AGENT_API_KEY=""
export CODER_AGENT_BASE_URL="https://api.deepseek.com"
export CODER_AGENT_MODEL="deepseek-chat"
export THINK_AGENT_API_KEY=""
export THINK_AGENT_BASE_URL="https://api.deepseek.com"
export THINK_AGENT_MODEL="deepseek-reasoner"
export ROUTER_AGENT_API_KEY=""
export ROUTER_AGENT_BASE_URL=""
export ROUTER_AGENT_MODEL="qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct"
node index.mjs- Set environment variable to start claude code
export DISABLE_PROMPT_CACHING=1
export ANTHROPIC_AUTH_TOKEN="test"
export ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL="http://127.0.0.1:3456"
export API_TIMEOUT_MS=600000
claudeThe initial version uses a single model to accomplish all tasks. This model needs to support function calling and must allow for a sufficiently large tool description length, ideally greater than 1754. If the model used in this mode does not support KV Cache, it will consume a significant number of tokens.
Using multiple models to handle different tasks, this mode requires setting ENABLE_ROUTER to true and configuring four models: ROUTER_AGENT_MODEL, TOOL_AGENT_MODEL, CODER_AGENT_MODEL, and THINK_AGENT_MODEL.
ROUTER_AGENT_MODEL does not require high intelligence and is only responsible for request routing. A small model is sufficient for this task (testing has shown that the qwen-coder-3b model performs well). TOOL_AGENT_MODEL must support function calling and allow for a sufficiently large tool description length, ideally greater than 1754. If the model used in this mode does not support KV Cache, it will consume a significant number of tokens.
CODER_AGENT_MODEL and THINK_AGENT_MODEL can use the DeepSeek series of models.
The purpose of router mode is to separate tool invocation from coding tasks, enabling the use of inference models like r1, which do not support function calling.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for claude-code-router
Similar Open Source Tools

claude-code-router
This repository is for testing routing Claude Code requests to different models. It implements Normal Mode and Router Mode, using various models like qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct, qwen-max-0125, deepseek-v3, and deepseek-r1. The project aims to reduce the cost of using Claude Code by leveraging free models and KV-Cache. Users can set appropriate ignorePatterns for the project. The Router Mode allows for the separation of tool invocation from coding tasks by using multiple models for different purposes.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
open-deep-research
Open Deep Research is an open-source project that serves as a clone of Open AI's Deep Research experiment. It utilizes Firecrawl's extract and search method along with a reasoning model to conduct in-depth research on the web. The project features Firecrawl Search + Extract, real-time data feeding to AI via search, structured data extraction from multiple websites, Next.js App Router for advanced routing, React Server Components and Server Actions for server-side rendering, AI SDK for generating text and structured objects, support for various model providers, styling with Tailwind CSS, data persistence with Vercel Postgres and Blob, and simple and secure authentication with NextAuth.js.
vector-vein
VectorVein is a no-code AI workflow software inspired by LangChain and langflow, aiming to combine the powerful capabilities of large language models and enable users to achieve intelligent and automated daily workflows through simple drag-and-drop actions. Users can create powerful workflows without the need for programming, automating all tasks with ease. The software allows users to define inputs, outputs, and processing methods to create customized workflow processes for various tasks such as translation, mind mapping, summarizing web articles, and automatic categorization of customer reviews.
MCP2Lambda
MCP2Lambda is a server that acts as a bridge between MCP clients and AWS Lambda functions, allowing generative AI models to access and run Lambda functions as tools. It enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with Lambda functions without code changes, providing access to private resources, AWS services, private networks, and the public internet. The server supports autodiscovery of Lambda functions and their invocation by name with parameters. It standardizes AI model access to external tools using the MCP protocol.
llm-on-ray
LLM-on-Ray is a comprehensive solution for building, customizing, and deploying Large Language Models (LLMs). It simplifies complex processes into manageable steps by leveraging the power of Ray for distributed computing. The tool supports pretraining, finetuning, and serving LLMs across various hardware setups, incorporating industry and Intel optimizations for performance. It offers modular workflows with intuitive configurations, robust fault tolerance, and scalability. Additionally, it provides an Interactive Web UI for enhanced usability, including a chatbot application for testing and refining models.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
llm-ls
llm-ls is a Language Server Protocol (LSP) server that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance the development experience. It aims to serve as a foundation for IDE extensions by simplifying interactions with LLMs, enabling lightweight extension code. The server offers features such as context-based prompt generation, telemetry for retraining, code completion based on AST analysis, and compatibility with various backends like Hugging Face's APIs and llama.cpp server bindings.
talon-ai-tools
Control large language models and AI tools through voice commands using the Talon Voice dictation engine. This tool is designed to help users quickly edit text, code by voice, reduce keyboard use for those with health issues, and speed up workflow by using AI commands across the desktop. It prompts and extends tools like Github Copilot and OpenAI API for text and image generation. Users can set up the tool by downloading the repo, obtaining an OpenAI API key, and customizing the endpoint URL for preferred models. The tool can be used without an OpenAI key and can be exclusively used with Copilot for those not needing LLM integration.
ai-starter-kit
SambaNova AI Starter Kits is a collection of open-source examples and guides designed to facilitate the deployment of AI-driven use cases for developers and enterprises. The kits cover various categories such as Data Ingestion & Preparation, Model Development & Optimization, Intelligent Information Retrieval, and Advanced AI Capabilities. Users can obtain a free API key using SambaNova Cloud or deploy models using SambaStudio. Most examples are written in Python but can be applied to any programming language. The kits provide resources for tasks like text extraction, fine-tuning embeddings, prompt engineering, question-answering, image search, post-call analysis, and more.
hugescm
HugeSCM is a cloud-based version control system designed to address R&D repository size issues. It effectively manages large repositories and individual large files by separating data storage and utilizing advanced algorithms and data structures. It aims for optimal performance in handling version control operations of large-scale repositories, making it suitable for single large library R&D, AI model development, and game or driver development.
CompressAI-Vision
CompressAI-Vision is a tool that helps you develop, test, and evaluate compression models with standardized tests in the context of compression methods optimized for machine tasks algorithms such as Neural-Network (NN)-based detectors. It currently focuses on two types of pipeline: Video compression for remote inference (`compressai-remote-inference`), which corresponds to the MPEG "Video Coding for Machines" (VCM) activity. Split inference (`compressai-split-inference`), which includes an evaluation framework for compressing intermediate features produced in the context of split models. The software supports all the pipelines considered in the related MPEG activity: "Feature Compression for Machines" (FCM).
InfiniStore
InfiniStore is an open-source high-performance KV store designed to support LLM Inference clusters. It provides high-performance and low-latency KV cache transfer and reuse among inference nodes. In addition to inference clusters, it can be used as a standalone KV store for integration with LLM training or inference services. InfiniStore is currently integrated with vLLM via LMCache and is in progress for integration with SGLang and other inference engines.
Guardrails
Guardrails is a security tool designed to help developers identify and fix security vulnerabilities in their code. It provides automated scanning and analysis of code repositories to detect potential security issues, such as sensitive data exposure, injection attacks, and insecure configurations. By integrating Guardrails into the development workflow, teams can proactively address security concerns and reduce the risk of security breaches. The tool offers detailed reports and actionable recommendations to guide developers in remediation efforts, ultimately improving the overall security posture of the codebase. Guardrails supports multiple programming languages and frameworks, making it versatile and adaptable to different development environments. With its user-friendly interface and seamless integration with popular version control systems, Guardrails empowers developers to prioritize security without compromising productivity.
llm-term
LLM-Term is a Rust-based CLI tool that generates and executes terminal commands using OpenAI's language models or local Ollama models. It offers configurable model and token limits, works on both PowerShell and Unix-like shells, and provides a seamless user experience for generating commands based on prompts. Users can easily set up the tool, customize configurations, and leverage different models for command generation.
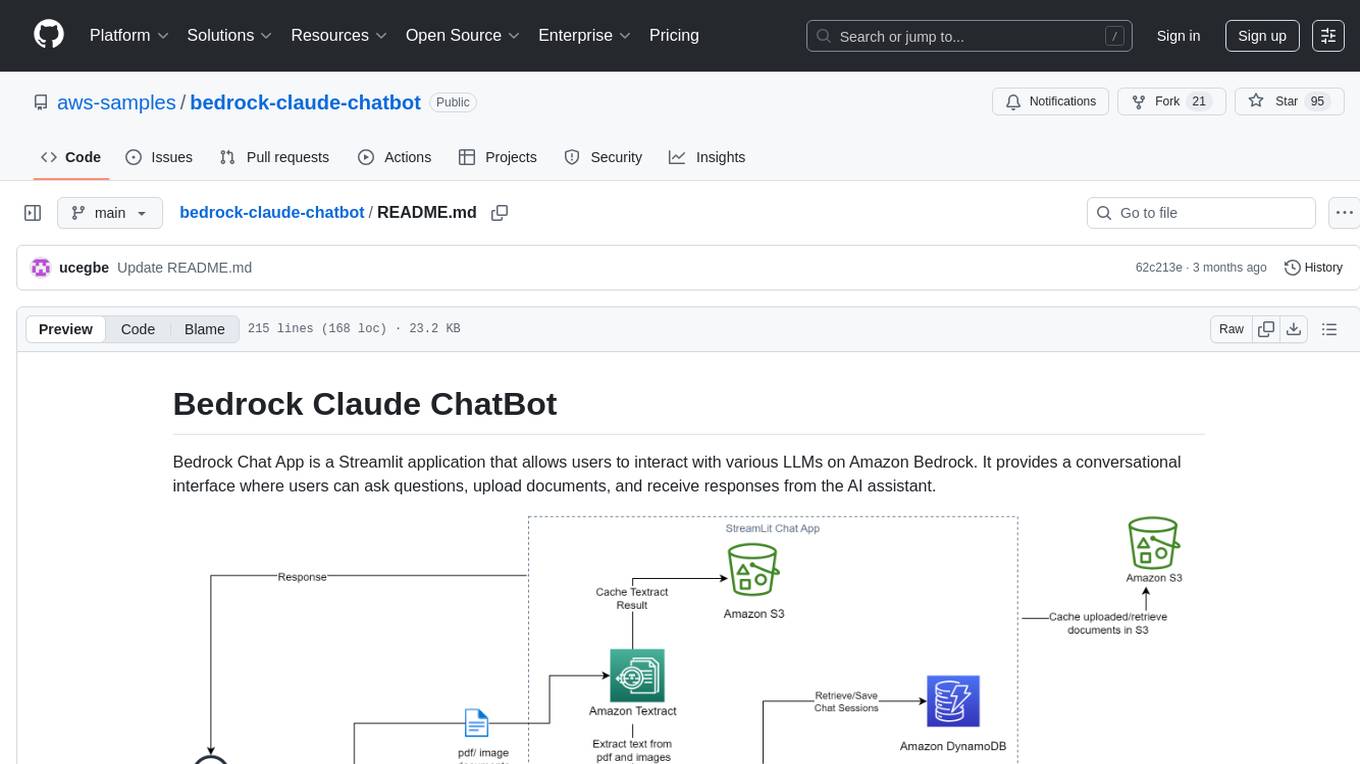
bedrock-claude-chatbot
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.
For similar tasks

claude-code-router
This repository is for testing routing Claude Code requests to different models. It implements Normal Mode and Router Mode, using various models like qwen2.5-coder-3b-instruct, qwen-max-0125, deepseek-v3, and deepseek-r1. The project aims to reduce the cost of using Claude Code by leveraging free models and KV-Cache. Users can set appropriate ignorePatterns for the project. The Router Mode allows for the separation of tool invocation from coding tasks by using multiple models for different purposes.
For similar jobs
ludwig
Ludwig is a declarative deep learning framework designed for scale and efficiency. It is a low-code framework that allows users to build custom AI models like LLMs and other deep neural networks with ease. Ludwig offers features such as optimized scale and efficiency, expert level control, modularity, and extensibility. It is engineered for production with prebuilt Docker containers, support for running with Ray on Kubernetes, and the ability to export models to Torchscript and Triton. Ludwig is hosted by the Linux Foundation AI & Data.
wenda
Wenda is a platform for large-scale language model invocation designed to efficiently generate content for specific environments, considering the limitations of personal and small business computing resources, as well as knowledge security and privacy issues. The platform integrates capabilities such as knowledge base integration, multiple large language models for offline deployment, auto scripts for additional functionality, and other practical capabilities like conversation history management and multi-user simultaneous usage.
LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.

Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B
Chinese-Mixtral-8x7B is an open-source project based on Mistral's Mixtral-8x7B model for incremental pre-training of Chinese vocabulary, aiming to advance research on MoE models in the Chinese natural language processing community. The expanded vocabulary significantly improves the model's encoding and decoding efficiency for Chinese, and the model is pre-trained incrementally on a large-scale open-source corpus, enabling it with powerful Chinese generation and comprehension capabilities. The project includes a large model with expanded Chinese vocabulary and incremental pre-training code.
AI-Horde-Worker
AI-Horde-Worker is a repository containing the original reference implementation for a worker that turns your graphics card(s) into a worker for the AI Horde. It allows users to generate or alchemize images for others. The repository provides instructions for setting up the worker on Windows and Linux, updating the worker code, running with multiple GPUs, and stopping the worker. Users can configure the worker using a WebUI to connect to the horde with their username and API key. The repository also includes information on model usage and running the Docker container with specified environment variables.
openshield
OpenShield is a firewall designed for AI models to protect against various attacks such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, training data poisoning, model denial of service, supply chain vulnerabilities, sensitive information disclosure, insecure plugin design, excessive agency granting, overreliance, and model theft. It provides rate limiting, content filtering, and keyword filtering for AI models. The tool acts as a transparent proxy between AI models and clients, allowing users to set custom rate limits for OpenAI endpoints and perform tokenizer calculations for OpenAI models. OpenShield also supports Python and LLM based rules, with upcoming features including rate limiting per user and model, prompts manager, content filtering, keyword filtering based on LLM/Vector models, OpenMeter integration, and VectorDB integration. The tool requires an OpenAI API key, Postgres, and Redis for operation.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface, independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. It also optimizes interface elements, user registration time support, data operation button positioning, and more.
VoAPI
VoAPI is a new high-value/high-performance AI model interface management and distribution system. It is a closed-source tool for personal learning use only, not for commercial purposes. Users must comply with upstream AI model service providers and legal regulations. The system offers a visually appealing interface with features such as independent development documentation page support, service monitoring page configuration support, and third-party login support. Users can manage user registration time, optimize interface elements, and support features like online recharge, model pricing display, and sensitive word filtering. VoAPI also provides support for various AI models and platforms, with the ability to configure homepage templates, model information, and manufacturer information.


