env-doctor
One CLI to validate GPU, CUDA, and AI stacks across local, Docker, and CI
Stars: 88
Env-Doctor is a tool designed to diagnose and fix mismatched CUDA versions between NVIDIA driver, system toolkit, cuDNN, and Python libraries, providing a quick solution to the common frustration in GPU computing. It offers one-command diagnosis, safe install commands, extension library support, AI model compatibility checks, WSL2 GPU support, deep CUDA analysis, container validation, MCP server integration, and CI/CD readiness. The tool helps users identify and resolve environment issues efficiently, ensuring smooth operation of AI libraries on their GPUs.
README:
The missing link between your GPU and Python AI libraries
"Why does my PyTorch crash with CUDA errors when I just installed it?"
Because your driver supports CUDA 11.8, but
pip install torchgave you CUDA 12.4 wheels.
Env-Doctor diagnoses and fixes the #1 frustration in GPU computing: mismatched CUDA versions between your NVIDIA driver, system toolkit, cuDNN, and Python libraries.
It takes 5 seconds to find out if your environment is broken - and exactly how to fix it.
| Feature | What It Does |
|---|---|
| One-Command Diagnosis | Check compatibility: GPU Driver → CUDA Toolkit → cuDNN → PyTorch/TensorFlow/JAX |
| Safe Install Commands | Get the exact pip install command that works with YOUR driver |
| Extension Library Support | Install compilation packages (flash-attn, SageAttention, auto-gptq, apex, xformers) with CUDA version matching |
| AI Model Compatibility | Check if LLMs, Diffusion, or Audio models fit on your GPU before downloading |
| WSL2 GPU Support | Validate GPU forwarding, detect driver conflicts within WSL2 env for Windows users |
| Deep CUDA Analysis | Find multiple installations, PATH issues, environment misconfigurations |
| Container Validation | Catch GPU config errors in Dockerfiles before you build |
| MCP Server | Expose diagnostics to AI assistants (Claude Desktop, Zed) via Model Context Protocol |
| CI/CD Ready | JSON output and proper exit codes for automation |
pip install env-doctorOr from source:
git clone https://github.com/mitulgarg/env-doctor.git
cd env-doctor
pip install -e .env-doctor checkExample output:
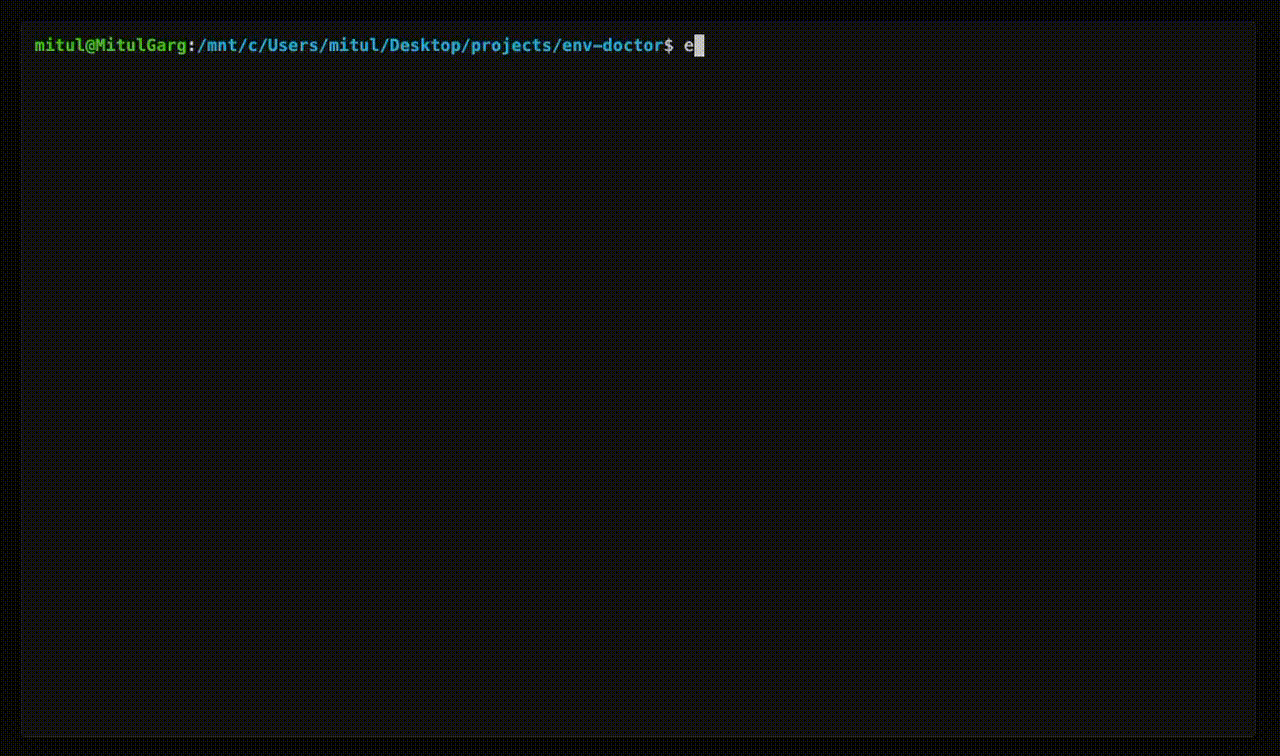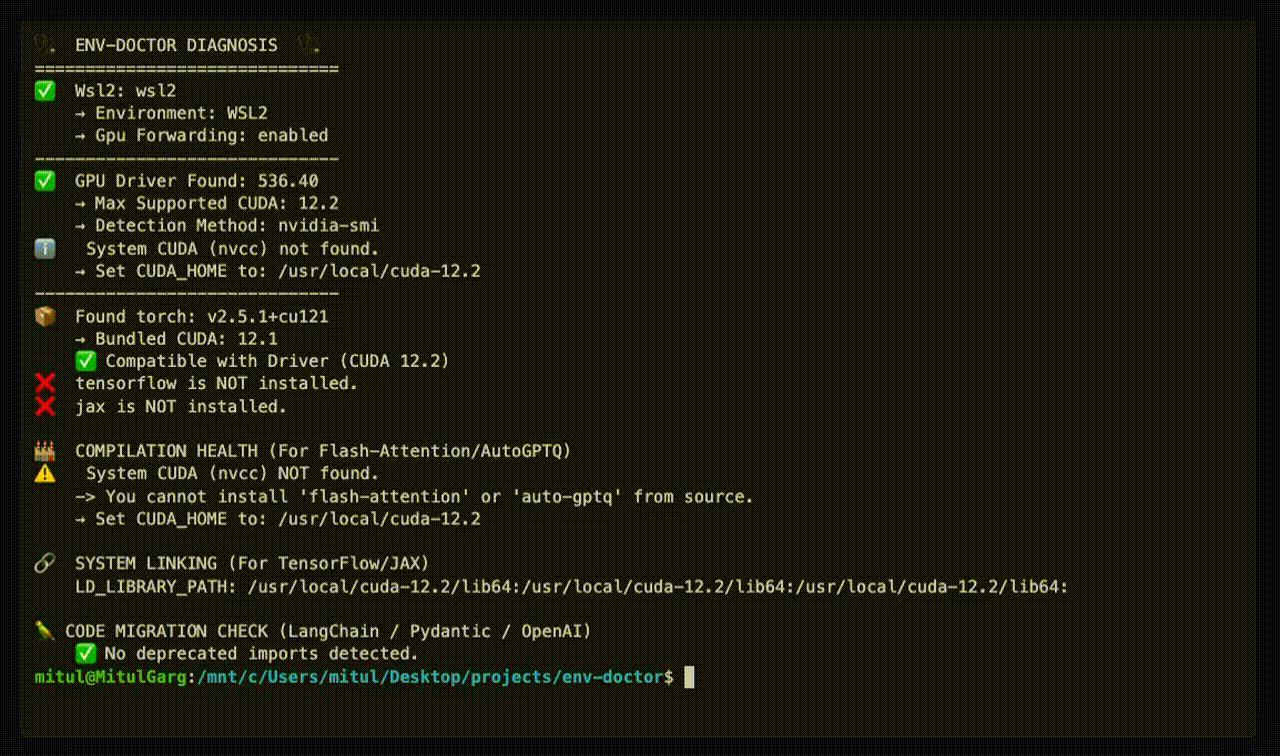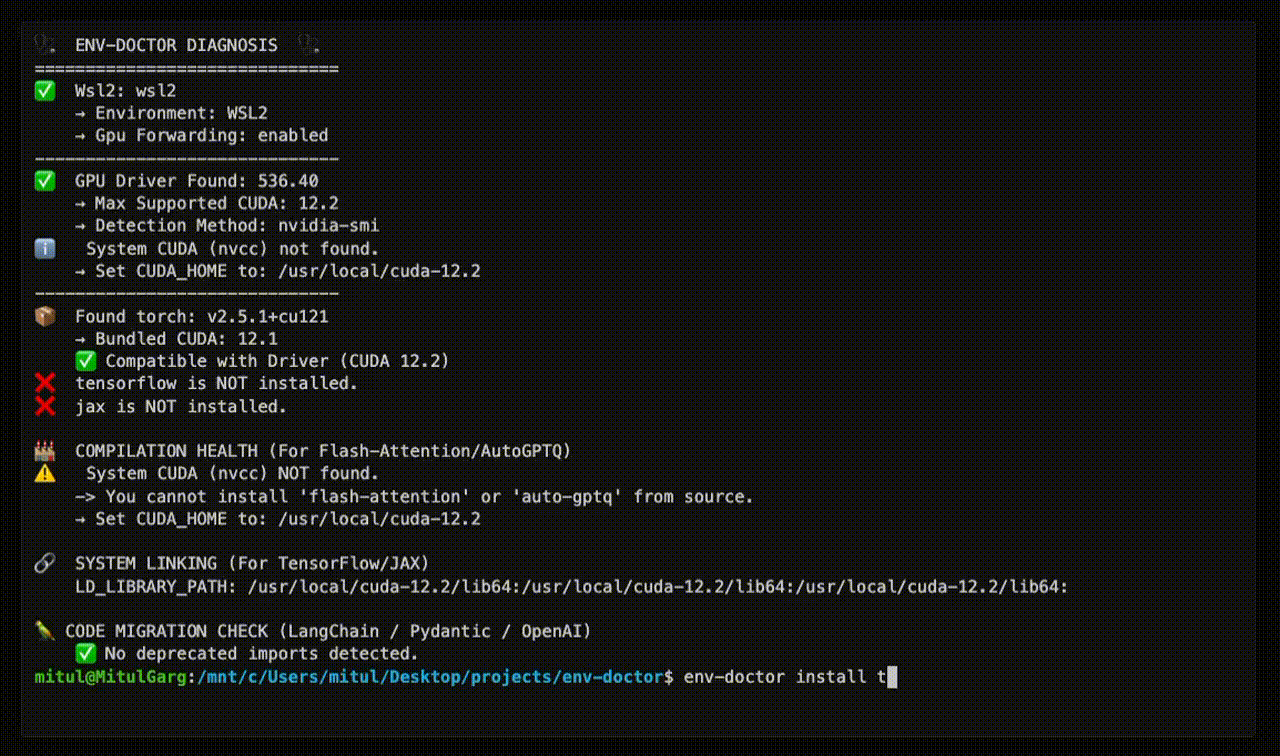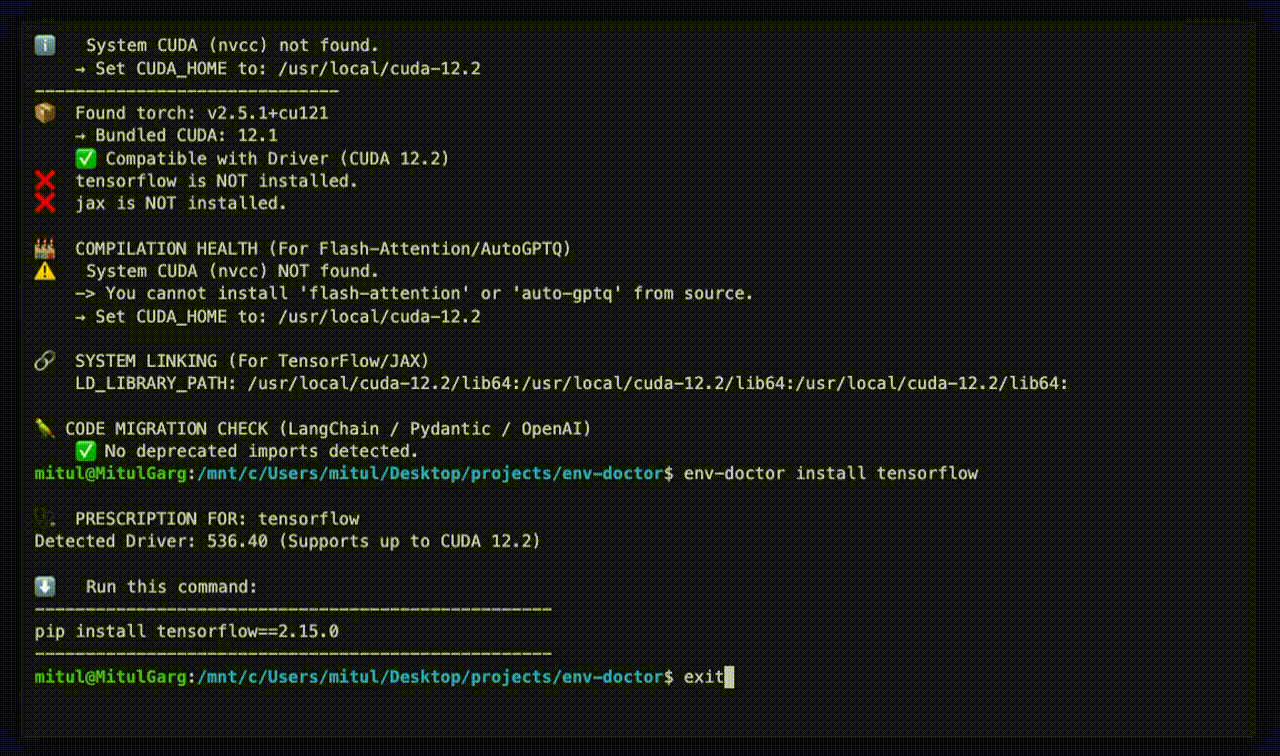
🩺 ENV-DOCTOR DIAGNOSIS
============================================================
🖥️ Environment: Native Linux
🎮 GPU Driver
✅ NVIDIA Driver: 535.146.02
└─ Max CUDA: 12.2
🔧 CUDA Toolkit
✅ System CUDA: 12.1.1
📦 Python Libraries
✅ torch 2.1.0+cu121
✅ All checks passed!
env-doctor install torch⬇️ Run this command to install the SAFE version:
---------------------------------------------------
pip install torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
---------------------------------------------------
For extension libraries like flash-attn, SageAttention, auto-gptq, apex, and xformers that require compilation from source, env-doctor provides special guidance to handle CUDA version mismatches:
env-doctor install flash-attnExample output (with CUDA mismatch):
🩺 PRESCRIPTION FOR: flash-attn
⚠️ CUDA VERSION MISMATCH DETECTED
System nvcc: 12.1.1
PyTorch CUDA: 12.4.1
🔧 flash-attn requires EXACT CUDA version match for compilation.
You have TWO options to fix this:
============================================================
📦 OPTION 1: Install PyTorch matching your nvcc (12.1)
============================================================
Trade-offs:
✅ No system changes needed
✅ Faster to implement
❌ Older PyTorch version (may lack new features)
Commands:
# Uninstall current PyTorch
pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# Install PyTorch for CUDA 12.1
pip install torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
# Install flash-attn
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
============================================================
⚙️ OPTION 2: Upgrade nvcc to match PyTorch (12.4)
============================================================
Trade-offs:
✅ Keep latest PyTorch
✅ Better long-term solution
❌ Requires system-level changes
❌ Verify driver supports CUDA 12.4
Steps:
1. Check driver compatibility:
env-doctor check
2. Download CUDA Toolkit 12.4:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-12-4-0-download-archive
3. Install CUDA Toolkit (follow NVIDIA's platform-specific guide)
4. Verify installation:
nvcc --version
5. Install flash-attn:
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
============================================================
env-doctor model llama-3-8b🤖 Checking: LLAMA-3-8B (8.0B params)
🖥️ Your Hardware: RTX 3090 (24GB)
💾 VRAM Requirements:
✅ FP16: 19.2GB - fits with 4.8GB free
✅ INT4: 4.8GB - fits with 19.2GB free
✅ This model WILL FIT on your GPU!
List all models: env-doctor model --list
Automatic HuggingFace Support (New ✨) If a model isn't found locally, env-doctor automatically checks the HuggingFace Hub, fetches its parameter metadata, and caches it locally for future runs — no manual setup required.
# Fetches from HuggingFace on first run, cached afterward
env-doctor model bert-base-uncased
env-doctor model sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2Output:
🤖 Checking: BERT-BASE-UNCASED
(Fetched from HuggingFace API - cached for future use)
Parameters: 0.11B
HuggingFace: bert-base-uncased
🖥️ Your Hardware:
RTX 3090 (24GB VRAM)
💾 VRAM Requirements & Compatibility
✅ FP16: 264 MB - Fits easily!
💡 Recommendations:
1. Use fp16 for best quality on your GPU
env-doctor dockerfile🐳 DOCKERFILE VALIDATION
❌ Line 1: CPU-only base image: python:3.10
Fix: FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu22.04
❌ Line 8: PyTorch missing --index-url
Fix: pip install torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
env-doctor check |
Full environment diagnosis |
env-doctor install <lib> |
Safe install command for PyTorch/TensorFlow/JAX, extension libraries (flash-attn, auto-gptq, apex, xformers, SageAttention, etc.) |
env-doctor model <name> |
Check model VRAM requirements |
env-doctor cuda-info |
Detailed CUDA toolkit analysis |
env-doctor cudnn-info |
cuDNN library analysis |
env-doctor dockerfile |
Validate Dockerfile |
env-doctor docker-compose |
Validate docker-compose.yml |
env-doctor scan |
Scan for deprecated imports |
env-doctor debug |
Verbose detector output |
# JSON output for scripting
env-doctor check --json
# CI mode with exit codes (0=pass, 1=warn, 2=error)
env-doctor check --ciGitHub Actions example:
- run: pip install env-doctor
- run: env-doctor check --ciEnv-Doctor includes a built-in Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that exposes diagnostic tools to AI assistants like Claude Desktop.
-
Install env-doctor:
pip install env-doctor
-
Add to Claude Desktop config (
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json):{ "mcpServers": { "env-doctor": { "command": "env-doctor-mcp" } } } -
Restart Claude Desktop - the tools will be available automatically.
-
env_check- Full GPU/CUDA environment diagnostics -
env_check_component- Check specific component (driver, CUDA, cuDNN, etc.) -
model_check- Analyze if AI models fit on your GPU -
model_list- List all available models in database -
dockerfile_validate- Validate Dockerfiles for GPU issues
Ask Claude Desktop:
- "Check my GPU environment"
- "Can I run Llama 3 70B on my GPU?"
- "Validate this Dockerfile for GPU issues"
- "What CUDA version does my PyTorch require?"
Learn more: MCP Integration Guide
Full documentation: https://mitulgarg.github.io/env-doctor/
- Getting Started
- Command Reference
- MCP Integration Guide
- WSL2 GPU Guide
- CI/CD Integration
- Architecture
Contributions welcome! See CONTRIBUTING.md for details.
MIT License - see LICENSE
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for env-doctor
Similar Open Source Tools

env-doctor
Env-Doctor is a tool designed to diagnose and fix mismatched CUDA versions between NVIDIA driver, system toolkit, cuDNN, and Python libraries, providing a quick solution to the common frustration in GPU computing. It offers one-command diagnosis, safe install commands, extension library support, AI model compatibility checks, WSL2 GPU support, deep CUDA analysis, container validation, MCP server integration, and CI/CD readiness. The tool helps users identify and resolve environment issues efficiently, ensuring smooth operation of AI libraries on their GPUs.
ryoma
Ryoma is an AI Powered Data Agent framework that offers a comprehensive solution for data analysis, engineering, and visualization. It leverages cutting-edge technologies like Langchain, Reflex, Apache Arrow, Jupyter Ai Magics, Amundsen, Ibis, and Feast to provide seamless integration of language models, build interactive web applications, handle in-memory data efficiently, work with AI models, and manage machine learning features in production. Ryoma also supports various data sources like Snowflake, Sqlite, BigQuery, Postgres, MySQL, and different engines like Apache Spark and Apache Flink. The tool enables users to connect to databases, run SQL queries, and interact with data and AI models through a user-friendly UI called Ryoma Lab.

LLaVA-OneVision-1.5
LLaVA-OneVision 1.5 is a fully open framework for democratized multimodal training, introducing a novel family of large multimodal models achieving state-of-the-art performance at lower cost through training on native resolution images. It offers superior performance across multiple benchmarks, high-quality data at scale with concept-balanced and diverse caption data, and an ultra-efficient training framework with support for MoE, FP8, and long sequence parallelization. The framework is fully open for community access and reproducibility, providing high-quality pre-training & SFT data, complete training framework & code, training recipes & configurations, and comprehensive training logs & metrics.

nncase
nncase is a neural network compiler for AI accelerators that supports multiple inputs and outputs, static memory allocation, operators fusion and optimizations, float and quantized uint8 inference, post quantization from float model with calibration dataset, and flat model with zero copy loading. It can be installed via pip and supports TFLite, Caffe, and ONNX ops. Users can compile nncase from source using Ninja or make. The tool is suitable for tasks like image classification, object detection, image segmentation, pose estimation, and more.
ai-trend-publish
AI TrendPublish is an AI-based trend discovery and content publishing system that supports multi-source data collection, intelligent summarization, and automatic publishing to WeChat official accounts. It features data collection from various sources, AI-powered content processing using DeepseekAI Together, key information extraction, intelligent title generation, automatic article publishing to WeChat official accounts with custom templates and scheduled tasks, notification system integration with Bark for task status updates and error alerts. The tool offers multiple templates for content customization and is built using Node.js + TypeScript with AI services from DeepseekAI Together, data sources including Twitter/X API and FireCrawl, and uses node-cron for scheduling tasks and EJS as the template engine.
turing
Viglet Turing is an enterprise search platform that combines semantic navigation, chatbots, and generative artificial intelligence. It offers integrations for authentication APIs, OCR, content indexing, CMS connectors, web crawling, database connectors, and file system indexing.
aiocron
aiocron is a Python library that provides crontab functionality for asyncio. It allows users to schedule functions to run at specific times using a decorator or as an object. Users can also await a crontab, use it as a sleep coroutine, and customize functions without decorator magic. aiocron has switched from croniter to cronsim for cron expression parsing since Dec 31, 2024.
aiohttp
aiohttp is an async http client/server framework that supports both client and server side of HTTP protocol. It also supports both client and server Web-Sockets out-of-the-box and avoids Callback Hell. aiohttp provides a Web-server with middleware and pluggable routing.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
bce-qianfan-sdk
The Qianfan SDK provides best practices for large model toolchains, allowing AI workflows and AI-native applications to access the Qianfan large model platform elegantly and conveniently. The core capabilities of the SDK include three parts: large model reasoning, large model training, and general and extension: * `Large model reasoning`: Implements interface encapsulation for reasoning of Yuyan (ERNIE-Bot) series, open source large models, etc., supporting dialogue, completion, Embedding, etc. * `Large model training`: Based on platform capabilities, it supports end-to-end large model training process, including training data, fine-tuning/pre-training, and model services. * `General and extension`: General capabilities include common AI development tools such as Prompt/Debug/Client. The extension capability is based on the characteristics of Qianfan to adapt to common middleware frameworks.
mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
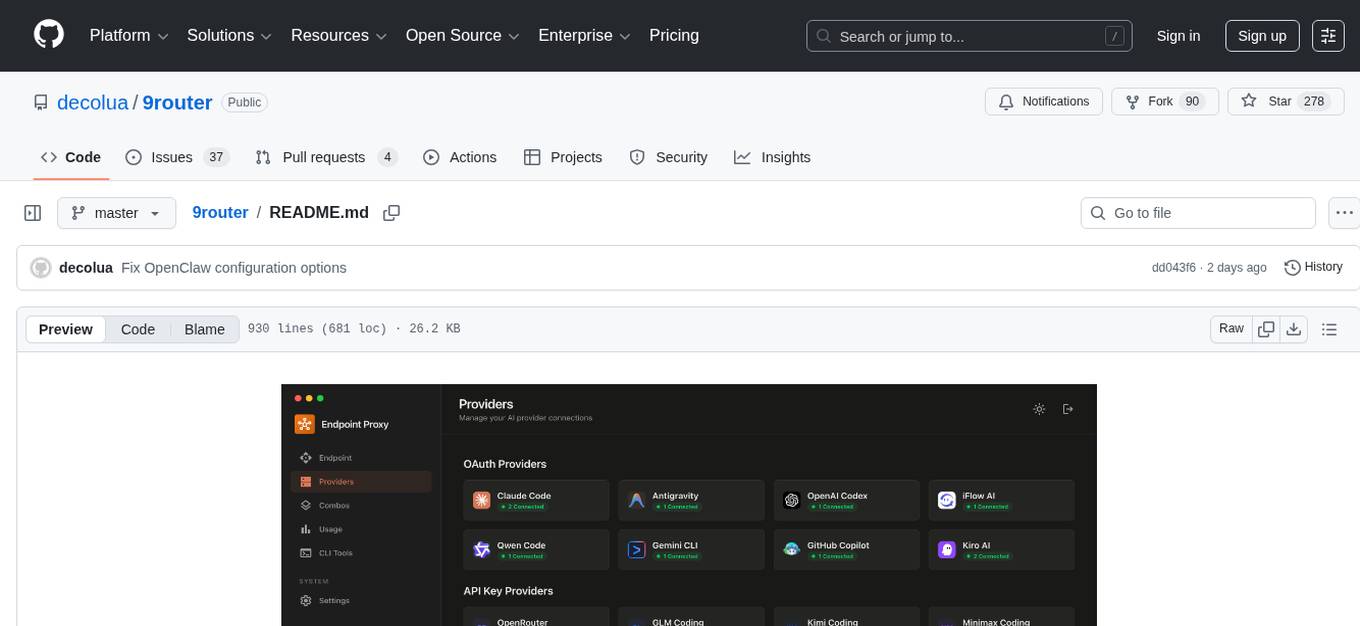
9router
9Router is a free AI router tool designed to help developers maximize their AI subscriptions, auto-route to free and cheap AI models with smart fallback, and avoid hitting limits and wasting money. It offers features like real-time quota tracking, format translation between OpenAI, Claude, and Gemini, multi-account support, auto token refresh, custom model combinations, request logging, cloud sync, usage analytics, and flexible deployment options. The tool supports various providers like Claude Code, Codex, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, GLM, MiniMax, iFlow, Qwen, and Kiro, and allows users to create combos for different scenarios. Users can connect to the tool via CLI tools like Cursor, Claude Code, Codex, OpenClaw, and Cline, and deploy it on VPS, Docker, or Cloudflare Workers.
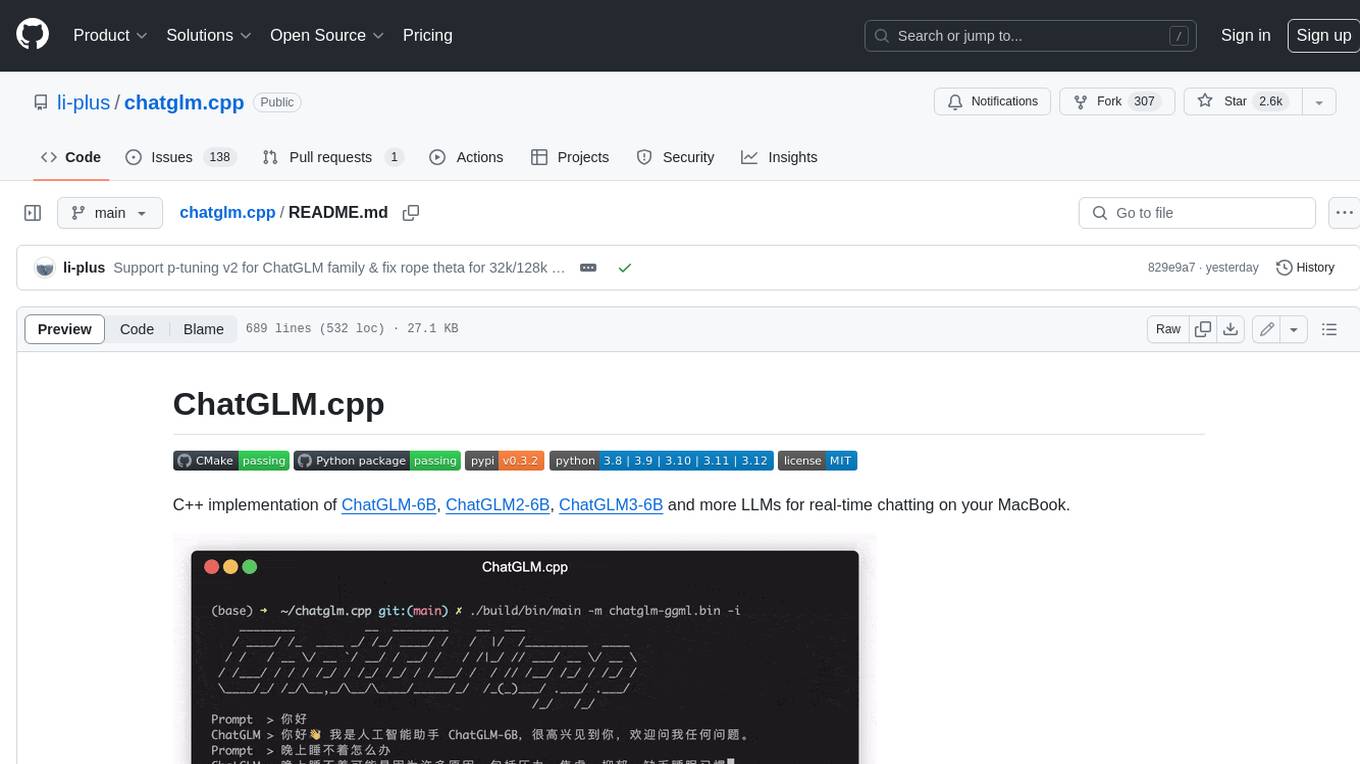
chatglm.cpp
ChatGLM.cpp is a C++ implementation of ChatGLM-6B, ChatGLM2-6B, ChatGLM3-6B and more LLMs for real-time chatting on your MacBook. It is based on ggml, working in the same way as llama.cpp. ChatGLM.cpp features accelerated memory-efficient CPU inference with int4/int8 quantization, optimized KV cache and parallel computing. It also supports P-Tuning v2 and LoRA finetuned models, streaming generation with typewriter effect, Python binding, web demo, api servers and more possibilities.
Thor
Thor is a powerful AI model management tool designed for unified management and usage of various AI models. It offers features such as user, channel, and token management, data statistics preview, log viewing, system settings, external chat link integration, and Alipay account balance purchase. Thor supports multiple AI models including OpenAI, Kimi, Starfire, Claudia, Zhilu AI, Ollama, Tongyi Qianwen, AzureOpenAI, and Tencent Hybrid models. It also supports various databases like SqlServer, PostgreSql, Sqlite, and MySql, allowing users to choose the appropriate database based on their needs.
ddddocr
ddddocr is a Rust version of a simple OCR API server that provides easy deployment for captcha recognition without relying on the OpenCV library. It offers a user-friendly general-purpose captcha recognition Rust library. The tool supports recognizing various types of captchas, including single-line text, transparent black PNG images, target detection, and slider matching algorithms. Users can also import custom OCR training models and utilize the OCR API server for flexible OCR result control and range limitation. The tool is cross-platform and can be easily deployed.
TechFlow
TechFlow is a platform that allows users to build their own AI workflows through drag-and-drop functionality. It features a visually appealing interface with clear layout and intuitive navigation. TechFlow supports multiple models beyond Language Models (LLM) and offers flexible integration capabilities. It provides a powerful SDK for developers to easily integrate generated workflows into existing systems, enhancing flexibility and scalability. The platform aims to embed AI capabilities as modules into existing functionalities to enhance business competitiveness.
For similar tasks

env-doctor
Env-Doctor is a tool designed to diagnose and fix mismatched CUDA versions between NVIDIA driver, system toolkit, cuDNN, and Python libraries, providing a quick solution to the common frustration in GPU computing. It offers one-command diagnosis, safe install commands, extension library support, AI model compatibility checks, WSL2 GPU support, deep CUDA analysis, container validation, MCP server integration, and CI/CD readiness. The tool helps users identify and resolve environment issues efficiently, ensuring smooth operation of AI libraries on their GPUs.
azhpc-images
This repository contains scripts for installing HPC and AI libraries and tools to build Azure HPC/AI images. It streamlines the process of provisioning compute-intensive workloads and crafting advanced AI models in the cloud, ensuring efficiency and reliability in deployments.
Aidan-Bench
Aidan Bench is a tool that rewards creativity, reliability, contextual attention, and instruction following. It is weakly correlated with Lmsys, has no score ceiling, and aligns with real-world open-ended use. The tool involves giving LLMs open-ended questions and evaluating their answers based on novelty scores. Users can set up the tool by installing required libraries and setting up API keys. The project allows users to run benchmarks for different models and provides flexibility in threading options.

llm-chatbot-python
This repository provides resources for building a chatbot backed by Neo4j using Python. It includes instructions on running the application, setting up tests, and installing necessary libraries. The chatbot is designed to interact with users and provide recommendations based on data stored in a Neo4j database. The repository is part of the Neo4j GraphAcademy course on building chatbots with Python.
AI-windows-whl
AI-windows-whl is a curated collection of pre-compiled Python wheels for difficult-to-install AI/ML libraries on Windows. It addresses the common pain point of building complex Python packages from source on Windows by providing direct links to pre-compiled `.whl` files for essential libraries like PyTorch, Flash Attention, xformers, SageAttention, NATTEN, Triton, bitsandbytes, and other packages. The goal is to save time for AI enthusiasts and developers on Windows, allowing them to focus on creating amazing things with AI.

chunkhound
ChunkHound is a modern tool for transforming your codebase into a searchable knowledge base for AI assistants. It utilizes semantic search via the cAST algorithm and regex search, integrating with AI assistants through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). With features like cAST Algorithm, Multi-Hop Semantic Search, Regex search, and support for 22 languages, ChunkHound offers a local-first approach to code analysis and discovery. It provides intelligent code discovery, universal language support, and real-time indexing capabilities, making it a powerful tool for developers looking to enhance their coding experience.
ApeRAG
ApeRAG is a production-ready platform for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that combines Graph RAG, vector search, and full-text search with advanced AI agents. It is ideal for building Knowledge Graphs, Context Engineering, and deploying intelligent AI agents for autonomous search and reasoning across knowledge bases. The platform offers features like advanced index types, intelligent AI agents with MCP support, enhanced Graph RAG with entity normalization, multimodal processing, hybrid retrieval engine, MinerU integration for document parsing, production-grade deployment with Kubernetes, enterprise management features, MCP integration, and developer-friendly tools for customization and contribution.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.