
llm_benchmark
None
Stars: 775
The 'llm_benchmark' repository is a personal evaluation project that tracks and tests various large models in areas such as logic, mathematics, programming, and human intuition. The evaluation consists of a private question bank with around 30 questions and 240 test cases, updated monthly. The scoring method involves assigning points based on correct deductions and meeting specific requirements, with scores normalized to a scale of 10. The repository aims to observe the long-term evolution trends of different large models from a subjective perspective, providing insights and a testing approach for individuals to assess large models.
README:
- 本评测是个人性质,使用滚动更新的私有题库进行长期跟踪评测。
- 本评测侧重模型对逻辑,数学,编程,人类直觉等问题的测试。不够权威,不够全面。仅从一个侧面观察各个大模型的长期进化趋势。
- 本评测的题库规模不大,长期维持在30题/240个用例以内,不使用任何互联网公开题目。题目每月会有滚动更新。题目不公开,意图是分享一种评测思路,以及个人见解。每个人应该根据自己所需,对大模型进行考察。不可盲信任何评测。
- 因为题目会每月增减,每个模型的成绩在每个月榜单中会有正负4分左右的变化,属于正常现象。大致排序保持稳定。
- 每道题设置若干个得分点,有些题目每个用例通过记1分,有些题目每答出一个符合要求的数据/文本记1分。每题有至少1个得分点。最终得分是计分除以得分点总数,再乘以10。(即每道题满分10分)
- 每题要求推导过程必须正确,猜对的答案不得分。部分题目有额外要求,输出多余答案会扣分,避免枚举。
- 要求回答必须完全符合题目要求,如果明确要求不写解释,不得编程等,而回答包含了解释或编程部分,即使正确,也记0分。
- 评测统一使用官方API或OpenRouter中转。官方有明确建议的温度值,使用官方温度,否则使用默认温度值0.1,推理模型限制思考长度30K,输出长度10K,无法分别设置的模型,设置总输出为40K。非推理模型设置输出长度10K。模型支持的MaxToken达不到上限,就按模型上限。其他参数均默认。部分不提供API的模型使用官网问答。每道题测3遍,取最高分。
2、文本摘要:阅读包含误导信息的文本,提取正确信息,按要求格式输出
4、魔方旋转:按规则拧魔方后求魔方颜色
11、岛屿面积:给定字符形式地图,求图中岛屿面积
16、插件调用:给定插件描述,要求根据文本信息输出正确插件调用和参数
24、数字规律:给2个示例,找数字变换规律
28、符号定义:重新定义数学符号含义,求数学计算式值
29、符号还原:将数学符号含义打乱,给表达式,要求推导符号原始含义
30、日记整理:阅读长文本,按给定条件和多个要求整理文本,考察指令遵循
31、棋盘图案:求经过棋盘上给定2个点的最大面积等腰三角形顶点
32、干支纪年:天干中删除部分,求历史某一年的干支
37、投影问题:给三维投影视图,求对应的立方体体积
38、函数求交:给多个函数求所有交点
39、火车售票:多个车次,多人次操作购票退票,求最终售票情况
40、代码推导:给100行算法代码和输入,要求纸面推导输出结果
41、交织文本解读:从多段交织混合文本中寻找问题答案
42、长文本总结:从文本中提炼关键数据,输出核心摘要
43、目标数:通过数学运算将给定数字组合,计算得到目标数字
44、工具组合:给定若干工具,通过使用工具,得到指定输出
45、程序编写:完成复杂约束下的python编程
46、字母组合:从字母序列中找出存在的单词
48、字符处理:根据规则对一段文本进行字符级别处理和统计
49、激光布局:根据条件约束,在10x10空间中部署满足要求的激光器
50、日志分析:在约20K的生产服务器日志中找到有效线索进行归纳
51、复杂计算:综合考察K12范围内的数学公式和计算能力
52、观棋不语:从一场没有解说的对局中归纳游戏规则
53、管道疏通:使用一定手段使阻塞的管道通畅
54、高级拼图:从多块拼图中选择部分拼图完成图形
55、寻路问题:在给出的地图中寻找符合条件的通路
- 新模型测试后,总榜实时更新
- 每月25号做一次成绩归档
- 每个模型的详细评测首发在知乎个人号: 知乎主页,和微信公众号:大模型观测员
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm_benchmark
Similar Open Source Tools

llm_benchmark
The 'llm_benchmark' repository is a personal evaluation project that tracks and tests various large models in areas such as logic, mathematics, programming, and human intuition. The evaluation consists of a private question bank with around 30 questions and 240 test cases, updated monthly. The scoring method involves assigning points based on correct deductions and meeting specific requirements, with scores normalized to a scale of 10. The repository aims to observe the long-term evolution trends of different large models from a subjective perspective, providing insights and a testing approach for individuals to assess large models.
TurtleBenchmark
Turtle Benchmark is a novel and cheat-proof benchmark test used to evaluate large language models (LLMs). It is based on the Turtle Soup game, focusing on logical reasoning and context understanding abilities. The benchmark does not require background knowledge or model memory, providing all necessary information for judgment from stories under 200 words. The results are objective and unbiased, quantifiable as correct/incorrect/unknown, and impossible to cheat due to using real user-generated questions and dynamic data generation during online gameplay.
awesome-hallucination-detection
This repository provides a curated list of papers, datasets, and resources related to the detection and mitigation of hallucinations in large language models (LLMs). Hallucinations refer to the generation of factually incorrect or nonsensical text by LLMs, which can be a significant challenge for their use in real-world applications. The resources in this repository aim to help researchers and practitioners better understand and address this issue.
nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.
HuixiangDou2
HuixiangDou2 is a robustly optimized GraphRAG approach that integrates multiple open-source projects to improve performance in graph-based augmented generation. It conducts comparative experiments and achieves a significant score increase, leading to a GraphRAG implementation with recognized performance. The repository provides code improvements, dense retrieval for querying entities and relationships, real domain knowledge testing, and impact analysis on accuracy.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
This repository compiles a list of academic papers that evaluate, align, simulate, and provide surveys or perspectives on the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Social Science. The papers cover various aspects of LLM research, including assessing their alignment with human values, evaluating their capabilities in tasks such as opinion formation and moral reasoning, and exploring their potential for simulating social interactions and addressing issues in diverse fields of Social Science. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of LLMs and Social Science.
long-llms-learning
A repository sharing the panorama of the methodology literature on Transformer architecture upgrades in Large Language Models for handling extensive context windows, with real-time updating the newest published works. It includes a survey on advancing Transformer architecture in long-context large language models, flash-ReRoPE implementation, latest news on data engineering, lightning attention, Kimi AI assistant, chatglm-6b-128k, gpt-4-turbo-preview, benchmarks like InfiniteBench and LongBench, long-LLMs-evals for evaluating methods for enhancing long-context capabilities, and LLMs-learning for learning technologies and applicated tasks about Large Language Models.
Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.
MMStar
MMStar is an elite vision-indispensable multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,500 challenge samples meticulously selected by humans. It addresses two key issues in current LLM evaluation: the unnecessary use of visual content in many samples and the existence of unintentional data leakage in LLM and LVLM training. MMStar evaluates 6 core capabilities across 18 detailed axes, ensuring a balanced distribution of samples across all dimensions.
ChatLaw
ChatLaw is an open-source legal large language model tailored for Chinese legal scenarios. It aims to combine LLM and knowledge bases to provide solutions for legal scenarios. The models include ChatLaw-13B and ChatLaw-33B, trained on various legal texts to construct dialogue data. The project focuses on improving logical reasoning abilities and plans to train models with parameters exceeding 30B for better performance. The dataset consists of forum posts, news, legal texts, judicial interpretations, legal consultations, exam questions, and court judgments, cleaned and enhanced to create dialogue data. The tool is designed to assist in legal tasks requiring complex logical reasoning, with a focus on accuracy and reliability.
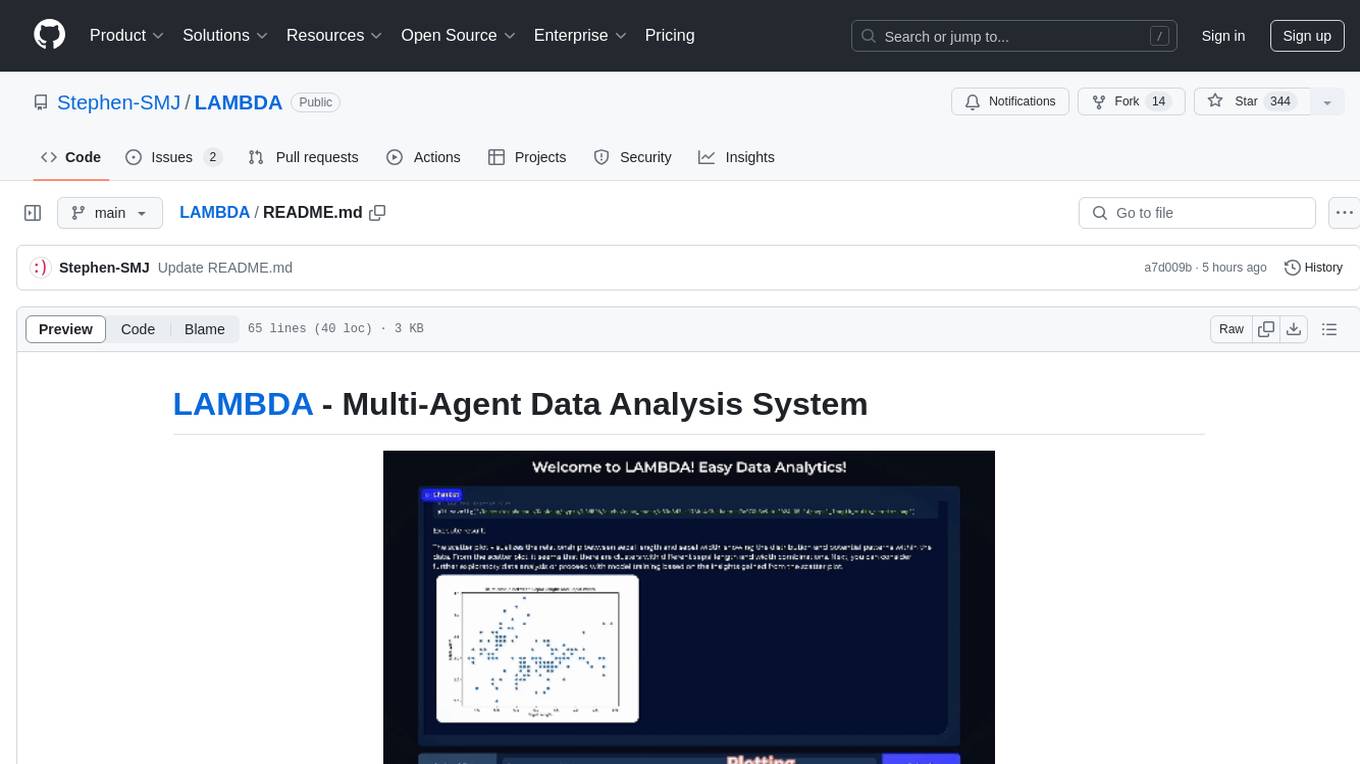
LAMBDA
LAMBDA is a code-free multi-agent data analysis system that utilizes large models to address data analysis challenges in complex data-driven applications. It allows users to perform complex data analysis tasks through human language instruction, seamlessly generate and debug code using two key agent roles, integrate external models and algorithms, and automatically generate reports. The system has demonstrated strong performance on various machine learning datasets, enhancing data science practice by integrating human and artificial intelligence.
DataDreamer
DataDreamer is a powerful open-source Python library designed for prompting, synthetic data generation, and training workflows. It is simple, efficient, and research-grade, allowing users to create prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets, and train models with ease. The library is built for researchers, by researchers, focusing on correctness, best practices, and reproducibility. It offers features like aggressive caching, resumability, support for bleeding-edge techniques, and easy sharing of datasets and models. DataDreamer enables users to run multi-step prompting workflows, generate synthetic datasets for various tasks, and train models by aligning, fine-tuning, instruction-tuning, and distilling them using existing or synthetic data.

AutoPatent
AutoPatent is a multi-agent framework designed for automatic patent generation. It challenges large language models to generate full-length patents based on initial drafts. The framework leverages planner, writer, and examiner agents along with PGTree and RRAG to craft lengthy, intricate, and high-quality patent documents. It introduces a new metric, IRR (Inverse Repetition Rate), to measure sentence repetition within patents. The tool aims to streamline the patent generation process by automating the creation of detailed and specialized patent documents.
LLMsForTimeSeries
LLMsForTimeSeries is a repository that questions the usefulness of language models in time series forecasting. The work shows that simple baselines outperform most language model-based time series forecasting models. It includes ablation studies on LLM-based TSF methods and introduces the PAttn method, showcasing the performance of patching and attention structures in forecasting. The repository provides datasets, setup instructions, and scripts for running ablations on different datasets.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.