Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
A series of technical report on Slow Thinking with LLM
Stars: 618
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.
README:
We are STILL exploring the uncharted territory of o1-like reasoning systems.
- [28 Mar 2025] ⚡️⚡️ OlymMATH: We introduce OlymMATH, a challenging benchmark of 200 Olympiad-level math problems across algebra, geometry, number theory, and combinatorics in both English and Chinese. Even the most advanced models achieve only moderate accuracy on OlymMATH-EN-HARD, highlighting significant room for improvement in mathematical reasoning. We open-source our dataset, evaluation code, and paper. For more details, please refer to our project page and huggingface 🤗.
- [9 Mar 2025] ⚡️⚡️ R1-Searcher: We propose R1-Searcher, a novel two-stage outcome-based RL approach designed to enhance the search capabilities of LLMs.
- This method allows LLMs to autonomously invoke external search systems to access additional knowledge during the reasoning process.
- Our framework relies exclusively on RL, without requiring process rewards or distillation for a cold start.
- We conduct training on both base models (zero-shot) and fine-tuned models, analyzing key research questions arising during the training process.
- **We open-source our models: Qwen-2.5-7B-Base-RL and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-RL, code and data.
- [7 Mar 2025] ⚡️⚡️ STILL-3: We propose STILL-3, An Empirical Study on Eliciting and Improving R1-like Reasoning Models.
- We systematically experiment with and document the effects of various factors influencing RL training, conducting experiments on both base models (zero) and fine-tuned models.
- Beyond RL training, we also explore the use of tool manipulation, finding that it significantly boosts the reasoning performance of large reasoning models.
- [1 Mar 2025] STILL-3-Tool-32B: We propose STILL-3-Tool-32B, leveraging python code to help the reasoning process. During evaluation, STILL-3-Tool-32B achieves 81.70% accuracy on AIME 2024, matching the performance of o3-mini, outperforming o1 and DeepSeek-R1. We open-source our code, model, and data. For more details, please refer to our Notion page.
- [26 Jan 2025] STILL-3-1.5B-preview: We release STILL-3-1.5B-preview, a 1.5B slow-thinking reasoning model achieves 39.33% accuracy on AIME benchmark! We utilize 30k queries to adapt reinforcement learning on 1.5B model (DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B) and observe the continuous performance improvement as the number of training steps increased. For better reproducing our work and advancing research progress, we open-source our code, model, and data.
- [6 Jan 2025] Virgo: We develop Virgo, a multi-modal slow-thinking reasoning model, based on Qwen2-VL-72B-Instruct, which achieves leading performance on four challenging multi-modal benchmarks. We demonstrate that the slow-thinking reasoning ability can be transferred from text to vision. We open-source the model and training data.
- [3 Jan 2025] STILL-Hallucination Mitigation: We propose HaluSearch, a framework that integrates tree search algorithms and a dynamic system switch mechanism, inspired by dual process theory, to reduce LLM hallucinations during inference.
- [22 Dec 2024] We open-source part of the training data in Github or HuggingFace and the model for community researchers to use for research purposes.
- [12 Dec 2024] STILL-2: We preliminarily reproduce a slow-thinking reasoning system, achieving competitive performance compared to industry-level reasoning systems on these benchmarks! And we also release the technical report, which presents the details about our reproduction.
- [18 Nov 2024] STILL-1: We release our first technical report, where we leverage reward-guided tree search algorithm to assist LLM reasoning process and largely enhance the performance of LLM on complex reasoning tasks.
OlymMATH: Challenging the Boundaries of Reasoning: An Olympiad-Level Math Benchmark for Large Language Models [Report]
-
🧮 We introduce OlymMATH, a meticulously curated benchmark of 200 high-quality Olympiad-level math problems spanning algebra, geometry, number theory, and combinatorics.
-
🌐 Our benchmark features fully parallel English and Chinese problem sets (OlymMATH-EN and OlymMATH-ZH), enabling comprehensive multilingual evaluation of mathematical reasoning capabilities.
-
📊 OlymMATH is strategically divided into two difficulty levels: The EASY subset closely aligns with AIME-level difficulty, providing an effective evaluation for standard reasoning approaches The HARD subset is specifically designed to challenge state-of-the-art reasoning models, pushing the boundaries of their capabilities.
-
🔍 Our experiments reveal that even the most advanced models struggle with OlymMATH-HARD, highlighting significant room for improvement in mathematical reasoning.
-
🧠 We observe that LLMs often resort to empirical guessing rather than rigorous reasoning, using pattern matching, heuristic methods, or proposition simplification to arrive at answers without systematic derivation. OlymMATH-HARD effectively challenges these "shortcut" approaches, as its complex problems require deeper mathematical understanding.
R1-Searcher: Incentivizing the Search Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning [Report]
- The core motivation lies in incentivizing the search capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by enabling exploration within an external retrieval environment. A two-stage outcome-based reinforcement learning (RL) framework is designed to guide the model in freely exploring how to invoke an external retrieval system for acquiring relevant information.
- The proposed methodology relies solely on outcome-based reinforcement learning, eliminating the need for distillation techniques or cold-start strategies based on supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Moreover, it is effective for both base models (zero-shot) and fine-tuned models.
- A modified RL training method is introduced, building on Reinforce++ with RAG-based rollout and retrieval mask-based loss calculation. The RAG-based rollout strategy enhances the model's ability to utilize retrieved information effectively during the reasoning process. Additionally, retrieval mask-based loss calculation ensures precise capture of the relevance of retrieved information during training while minimizing interference from irrelevant data.
- 🔥 Here are our model: Qwen-2.5-7B-Base-RL and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-RL, code and data.
STILL-3: An Empirical Study on Eliciting and Improving R1-like Reasoning Models [Report]
- The performance of large reasoning models is heavily influenced by the settings of RL.
- We thoroughly investigate and document these effects by testing a range of parameter configurations. Following this, we provide a recommendation for RL training.
- After pre-training, the base models already exhibit the potential to perform individual complex reasoning actions. The RL process effectively activates this capability, enabling the model to integrate these actions into a coherent and deliberate thinking process.
- Our RL training approach consistently improves the QWEN2.5-32B base model, enhancing both response length and test accuracy.
- Response length serves as an important indicator of the success of RL training; however, it is a consequence, not a cause, of performance improvement. Designing specialized reward functions to explicitly encourage the model to produce longer responses may lead to issues such as reward hacking, which can’t inherently enhance the model’s reasoning capabilities.
- RL training consistently improves the performance of fine-tuned models, encompassing both short and long CoT reasoning models.
- Even after Qwen2.5-1.5B attains a high level of performance through training with distilled data, RL training further elevates its capabilities, achieving a remarkable accuracy of 39.33 on AIME 2024 (STILL-3-1.5B-Preview).
- Through supervised fine-tuning, LRMs can acquire the capability to manipulate external tools, leading to a significant enhancement in the model’s performance.
- By effectively utilizing tool manipulation, STILL-3-TOOL-32B achieves an impressive accuracy of 86.67 (greedy search) on AIME 2024.
- Remarkably, this ability can be activated with only a small number of high-quality training instances.
- We will soon open-source our model, code, and data.
✨ STILL-3-Tool-32B: Empowering Reasoning Models with Wings: Tool Manipulation Significantly Enhances the Reasoning Ability of O1- and R1-like LLMs
- 🧑💻 We attempt to activate the tool manipulation capability of the long CoT thinking model, enabling it to spontaneously generate code and call upon tools to assist in the problem-solving process.
- 📈 To our surprise, we find that our approach outperform the comparative baseline models (such as DeepSeek-R1, o1, o3-mini-medium) on AIME 24, and its average performance across three math competitions was on par with DeepSeek-R1!
- 📝 We have detailed the training process, data construction, and case studies of STILL-3-Tool-32B in our Notion page.
- 🔥 Here are our model, code and data.
- To delve deeper into the potential of reinforcement learning, we applied this training method to the publicly released SFT model by DeepSeek, known as DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B, which has enhanced by complex reasoning capacities.
- Throughout the RL process, we noticed a progressive expansion in both the training and test sets. This led to a substantial enhancement in the model's reasoning skills, culminating in a 39.33% accuracy score on the American Invitational Mathematics Examination (AIME) leaderboard.
- We are open-sourcing all of the relevant code (based on OpenRLHF), model, and training data (30k from MATH,NuminaMathCoT, and AIME 1983-2023) to foster further research and development in the field of reinforcement learning algorithms.
We evaluated the model on four benchmarks: MATH, AIME, OMNI, and LiveAOPS. For MATH and AIME, we employed a sampling decoding setup with a sampling temperature of 0.6 and a top-p sampling probability of 0.95. Each question was sampled 64 times, and the average score was calculated. For OMNI and LiveAOPS (August-November 2024), we randomly sampled a subset of answers as integers to facilitate automated evaluation, and used greedy search decoding for the evaluation. The trained model, STILL-3-1.5B-preview, achieved significant improvement. The accuracy on the AIME task increased from 28.67% to 39.33%, resulting in a relative improvement of 37.18%.
| MATH | AIME | OMNI | LiveAOPS | Avg. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen-2.5-Math-7B-Instruct | 83.60 | 16.67 | - | - | - |
| Qwen-2.5-Math-72B-Instruct | 85.90 | 30.00 | - | - | - |
| O1-preview | 85.50 | 44.60 | - | - | - |
| STILL-2 | 90.20 | 46.67 | - | - | - |
| QwQ-32B | 90.60 | 50.00 | - | - | - |
| DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B | 84.04 | 28.67 | 25.60 | 33.33 | 42.91 |
| STILL-3-1.5B-preview | 85.48 | 39.33 | 33.00 | 39.50 | 49.33 |
🚀 Imitate, Explore, and Self-Improve: A Reproduction Report on Slow-thinking Reasoning Systems [Report]
-
Slow-thinking reasoning systems, such as o1, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in solving complex reasoning tasks, and are primarily developed and maintained by industry, with their core techniques not publicly disclosed. This paper presents a reproduction report on implementing o1-like reasoning systems. We introduce an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework as our primary technical approach to train the reasoning model. In the initial phase, we use distilled long-form thought data to fine-tune the reasoning model, enabling it to invoke a slow-thinking mode. The model is then encouraged to explore challenging problems by generating multiple rollouts, which can result in increasingly more high-quality trajectories that lead to correct answers. Furthermore, the model undergoes self-improvement by iteratively refining its training dataset.


from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# Load model and tokenizer
model_path = "RUC-AIBOX/STILL-2"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
# PROMPT
PROMPT = 'Your role as an assistant involves thoroughly exploring questions through a systematic long thinking process before providing the final precise and accurate solutions. This requires engaging in a comprehensive cycle of analysis, summarizing, exploration, reassessment, reflection, backtracing, and iteration to develop well-considered thinking process.\n\nPlease structure your response into two main sections: Thought and Solution.\n\nIn the Thought section, detail your reasoning process using the specified format:\n\n```\n<|begin_of_thought|>\n{thought with steps seperated with "\n\n"}\n<|end_of_thought|>\n```\n\nEach step should include detailed considerations such as analisying questions, summarizing relevant findings, brainstorming new ideas, verifying the accuracy of the current steps, refining any errors, and revisiting previous steps. Try to use casual, genuine phrases like: "Hmm...", "This is interesting because...", "Wait, let me think about...", "Actually...", "Now that I look at it...", "This reminds me of...", "I wonder if...", "But then again...", "Let\'s see if...", "Alternatively...", "Let\'s summaize existing information...", "This might mean that...", "why/how/when/where...", etc, to make your thought process be coherent, clear, and logically sound, effectively simulating human cognitive processes.\n\nIn the Solution section, based on various attempts, explorations, and reflections from the Thought section, systematically present the final solution that you deem correct. The solution should remain a logical, accurate, concise expression style and detail necessary step needed to reach the conclusion, formatted as follows:\n\n```\n<|begin_of_solution|>\n{final formatted, precise, and clear solution}\n<|end_of_solution|>\n```\n\nNow, try to solve the following question through the above guidlines:\n'
# Input text
question = "Convert the point $(0,3)$ in rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates. Enter your answer in the form $(r,\\theta),$ where $r > 0$ and $0 \\le \\theta < 2 \\pi.$"
input_prompts = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
[{"role": "user", "content": PROMPT + question}],
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
)
# Params
stop_words = ["<|im_end|>", "<|endoftext|>"]
llm = LLM(
model=model_path,
tensor_parallel_size=8,
max_model_len=int(1.5 * 20000),
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95,
dtype="bfloat16",
)
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature=0,
top_p=1.0,
max_tokens=20000,
stop=stop_words,
seed=42,
skip_special_tokens=False,
)
# Completion
responses = llm.generate(input_prompts, sampling_params)
print(responses[0].outputs[0].text)🚀 Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Reward-guided Tree Search [Report]
-
Recently, test-time scaling has garnered significant attention from the research community, largely due to the substantial advancements of the o1 model released by OpenAI. However, develop an o1-like reasoning approach is challenging, and researchers have been making various attempts to advance this open area of research. In this paper, we present a preliminary exploration into enhancing the reasoning abilities of LLMs through reward-guided tree search algorithms. This framework is implemented by integrating the policy model, reward model, and search algorithm. It is primarily constructed around a tree search algorithm, where the policy model navigates a dynamically expanding tree guided by a specially trained reward model.

🚀 Think More, Hallucinate Less: Mitigating Hallucinations via Dual Process of Fast and Slow Thinking [Report]
-
Large language models demonstrate exceptional capabilities, yet still face the hallucination issue. We propose HaluSearch, a novel framework that incorporates tree search-based algorithms to enable an explicit slow thinking generation process for mitigating hallucinations of LLMs during inference. HaluSearch frames text generation as a step-by-step reasoning process, using a self-evaluation reward model to score each generation step and guide the tree search towards the most reliable generation pathway. To balance efficiency and quality, we introduce a hierarchical thinking system switch mechanism inspired by the dual process theory in cognitive science, which dynamically alternates between fast and slow thinking modes at both the instance and step levels.

🚀 Virgo: A Preliminary Exploration on Reproducing o1-like MLLM [Report]
- There is a growing interest in reproducing o1-like MLLM in the research community. We explore a straightforward approach by fine-tuning a capable MLLM with a small amount of textual long-form thought data, resulting in a multimodal slow-thinking model, Virgo (Visual reasoning with long thought). We find that these long-form reasoning processes, expressed in natural language, can be effectively transferred to MLLMs. Moreover, it seems that such textual reasoning data can be even more effective than visual reasoning data in eliciting the slow-thinking capacities of MLLMs.
Despite the promising results, our exploration remains preliminary, and there is still a substantial capacity gap compared to industry-level systems. As future work, we plan to investigate how to scale our training approach and extend its capacity to more complex tasks.
As always, we are committed to keeping our technical approach open, and we will release the data, model, and other resources. We welcome collaboration and support in computational resources.
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to DataCanvas Alaya NeW and BAAI for their generous computational resources and support.
Additionally, we are deeply thankful for the OpenRLHF open-source training framework, which has provided an invaluable foundation for our work.
Please kindly cite our reports if they are helpful for your research.
@article{Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs_1,
title={Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Reward-guided Tree Search},
author={Jiang, Jinhao and Chen, Zhipeng and Min, Yingqian and Chen, Jie and Cheng, Xiaoxue and Wang, Jiapeng and Tang, Yiru and Sun, Haoxiang and Deng, Jia and Zhao, Wayne Xin and Liu, Zheng and Yan, Dong and Xie, Jian and Wang, Zhongyuan and Wen, Ji-Rong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.11694},
year={2024}
}
@article{Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs_2,
title={Imitate, Explore, and Self-Improve: A Reproduction Report on Slow-thinking Reasoning Systems},
author={Min, Yingqian and Chen, Zhipeng and Jiang, Jinhao and Chen, Jie and Deng, Jia and Hu, Yiwen and Tang, Yiru and Wang, Jiapeng and Cheng, Xiaoxue and Song, Huatong and Zhao, Wayne Xin and Liu, Zheng and Wang, Zhongyuan and Wen, Ji-Rong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.09413},
year={2024}
}
@article{Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs_3,
title={An Empirical Study on Eliciting and Improving R1-like Reasoning Models},
author={Chen, Zhipeng and Min, Yingqian and Zhang, Beichen and Chen, Jie and Jiang, Jinhao and Cheng, Daixuan and Zhao, Wayne Xin and Liu, Zheng and Miao, Xu and Lu, Yang and Fang, Lei and Wang, Zhongyuan and Wen, Ji-Rong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.04548},
year={2025}
}
@article{cheng2025think,
title={Think More, Hallucinate Less: Mitigating Hallucinations via Dual Process of Fast and Slow Thinking},
author={Cheng, Xiaoxue and Li, Junyi and Zhao, Wayne Xin and Wen, Ji-Rong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.01306},
year={2025}
}
@article{du2025virgo,
title={Virgo: A Preliminary Exploration on Reproducing o1-like MLLM},
author={Yifan Du and Zikang Liu and Yifan Li and Wayne Xin Zhao and Yuqi Huo and Bingning Wang and Weipeng Chen and Zheng Liu and Zhongyuan Wang and Ji-Rong Wen},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.01904},
year={2025}
}
@article{R1-searcher,
title={R1-searcher: Stimulating the Search Capability of LLM from Zero via Reinforcement Learning},
author={Huatong Song, Jinhao Jiang, Yingqian Min, Jie Chen, Zhipeng Chen, Wayne Xin Zhao, Ji-Rong Wen, Yang Lu, Xu Miu},
url={https://github.com/SsmallSong/R1-searcher},
year={2025}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
Similar Open Source Tools

Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).
AgentGym-RL
AgentGym-RL is a framework designed to train Long-Long Memory (LLM) agents for multi-turn interactive decision-making through Reinforcement Learning. It addresses challenges in training agents for real-world scenarios by supporting mainstream RL algorithms and introducing the ScalingInter-RL method for stable optimization. The framework includes modular components for environment, agent reasoning, and training pipelines. It offers diverse environments like Web Navigation, Deep Search, Digital Games, Embodied Tasks, and Scientific Tasks. AgentGym-RL also supports various online RL algorithms and post-training strategies. The tool aims to enhance agent performance and exploration capabilities through long-horizon planning and interaction with the environment.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
MathPile
MathPile is a generative AI tool designed for math, offering a diverse and high-quality math-centric corpus comprising about 9.5 billion tokens. It draws from various sources such as textbooks, arXiv, Wikipedia, ProofWiki, StackExchange, and web pages, catering to different educational levels and math competitions. The corpus is meticulously processed to ensure data quality, with extensive documentation and data contamination detection. MathPile aims to enhance mathematical reasoning abilities of language models.
llms-learning
A repository sharing literatures and resources about Large Language Models (LLMs) and beyond. It includes tutorials, notebooks, course assignments, development stages, modeling, inference, training, applications, study, and basics related to LLMs. The repository covers various topics such as language models, transformers, state space models, multi-modal language models, training recipes, applications in autonomous driving, code, math, embodied intelligence, and more. The content is organized by different categories and provides comprehensive information on LLMs and related topics.

AgentCPM
AgentCPM is a series of open-source LLM agents jointly developed by THUNLP, Renmin University of China, ModelBest, and the OpenBMB community. It addresses challenges faced by agents in real-world applications such as limited long-horizon capability, autonomy, and generalization. The team focuses on building deep research capabilities for agents, releasing AgentCPM-Explore, a deep-search LLM agent, and AgentCPM-Report, a deep-research LLM agent. AgentCPM-Explore is the first open-source agent model with 4B parameters to appear on widely used long-horizon agent benchmarks. AgentCPM-Report is built on the 8B-parameter base model MiniCPM4.1, autonomously generating long-form reports with extreme performance and minimal footprint, designed for high-privacy scenarios with offline and agile local deployment.
Reflection_Tuning
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.
learn-agentic-ai
Learn Agentic AI is a repository that is part of the Panaversity Certified Agentic and Robotic AI Engineer program. It covers AI-201 and AI-202 courses, providing fundamentals and advanced knowledge in Agentic AI. The repository includes video playlists, projects, and project submission guidelines for students to enhance their understanding and skills in the field of AI engineering.
MMStar
MMStar is an elite vision-indispensable multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,500 challenge samples meticulously selected by humans. It addresses two key issues in current LLM evaluation: the unnecessary use of visual content in many samples and the existence of unintentional data leakage in LLM and LVLM training. MMStar evaluates 6 core capabilities across 18 detailed axes, ensuring a balanced distribution of samples across all dimensions.
ai-notes
Notes on AI state of the art, with a focus on generative and large language models. These are the "raw materials" for the https://lspace.swyx.io/ newsletter. This repo used to be called https://github.com/sw-yx/prompt-eng, but was renamed because Prompt Engineering is Overhyped. This is now an AI Engineering notes repo.
siiRL
siiRL is a novel, fully distributed reinforcement learning (RL) framework designed to break the scaling barriers in Large Language Models (LLMs) post-training. Developed by researchers from Shanghai Innovation Institute, siiRL delivers near-linear scalability, dramatic throughput gains, and unprecedented flexibility for RL-based LLM development. It eliminates the centralized controller common in other frameworks, enabling scalability to thousands of GPUs, achieving state-of-the-art throughput, and supporting cross-hardware compatibility. siiRL is extensively benchmarked and excels in data-intensive workloads such as long-context and multi-modal training.
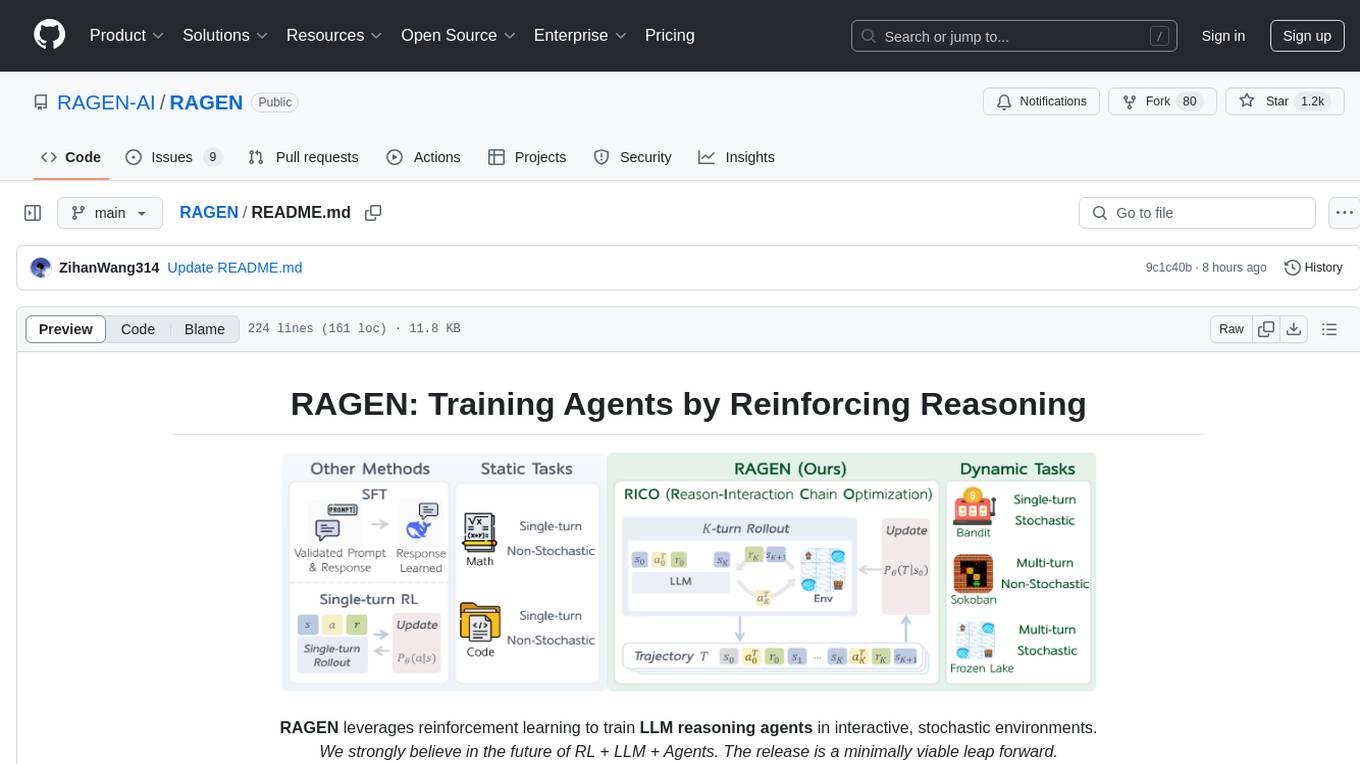
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework consists of MDP formulation, RICO algorithm with rollout and update stages, and reward normalization strategies to stabilize training. RAGEN aims to optimize reasoning and action strategies for LLM agents operating in complex environments.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
OpenNARS-for-Applications
OpenNARS-for-Applications is an implementation of a Non-Axiomatic Reasoning System, a general-purpose reasoner that adapts under the Assumption of Insufficient Knowledge and Resources. The system combines the logic and conceptual ideas of OpenNARS, event handling and procedure learning capabilities of ANSNA and 20NAR1, and the control model from ALANN. It is written in C, offers improved reasoning performance, and has been compared with Reinforcement Learning and means-end reasoning approaches. The system has been used in real-world applications such as assisting first responders, real-time traffic surveillance, and experiments with autonomous robots. It has been developed with a pragmatic mindset focusing on effective implementation of existing theory.
For similar tasks

Slow_Thinking_with_LLMs
STILL is an open-source project exploring slow-thinking reasoning systems, focusing on o1-like reasoning systems. The project has released technical reports on enhancing LLM reasoning with reward-guided tree search algorithms and implementing slow-thinking reasoning systems using an imitate, explore, and self-improve framework. The project aims to replicate the capabilities of industry-level reasoning systems by fine-tuning reasoning models with long-form thought data and iteratively refining training datasets.

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
one-click-llms
The one-click-llms repository provides templates for quickly setting up an API for language models. It includes advanced inferencing scripts for function calling and offers various models for text generation and fine-tuning tasks. Users can choose between Runpod and Vast.AI for different GPU configurations, with recommendations for optimal performance. The repository also supports Trelis Research and offers templates for different model sizes and types, including multi-modal APIs and chat models.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
enhance_llm
The enhance_llm repository contains three main parts: 1. Vector model domain fine-tuning based on llama_index and qwen fine-tuning BGE vector model. 2. Large model domain fine-tuning based on PEFT fine-tuning qwen1.5-7b-chat, with sft and dpo. 3. High-order retrieval enhanced generation (RAG) system based on the above domain work, implementing a two-stage RAG system. It includes query rewriting, recall reordering, retrieval reordering, multi-turn dialogue, and more. The repository also provides hardware and environment configurations along with star history and licensing information.
fms-fsdp
The 'fms-fsdp' repository is a companion to the Foundation Model Stack, providing a (pre)training example to efficiently train FMS models, specifically Llama2, using native PyTorch features like FSDP for training and SDPA implementation of Flash attention v2. It focuses on leveraging FSDP for training efficiently, not as an end-to-end framework. The repo benchmarks training throughput on different GPUs, shares strategies, and provides installation and training instructions. It trained a model on IBM curated data achieving high efficiency and performance metrics.

CogVLM2
CogVLM2 is a new generation of open source models that offer significant improvements in benchmarks such as TextVQA and DocVQA. It supports 8K content length, image resolution up to 1344 * 1344, and both Chinese and English languages. The project provides basic calling methods, fine-tuning examples, and OpenAI API format calling examples to help developers quickly get started with the model.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.