
NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
NBA sports betting using machine learning
Stars: 1053
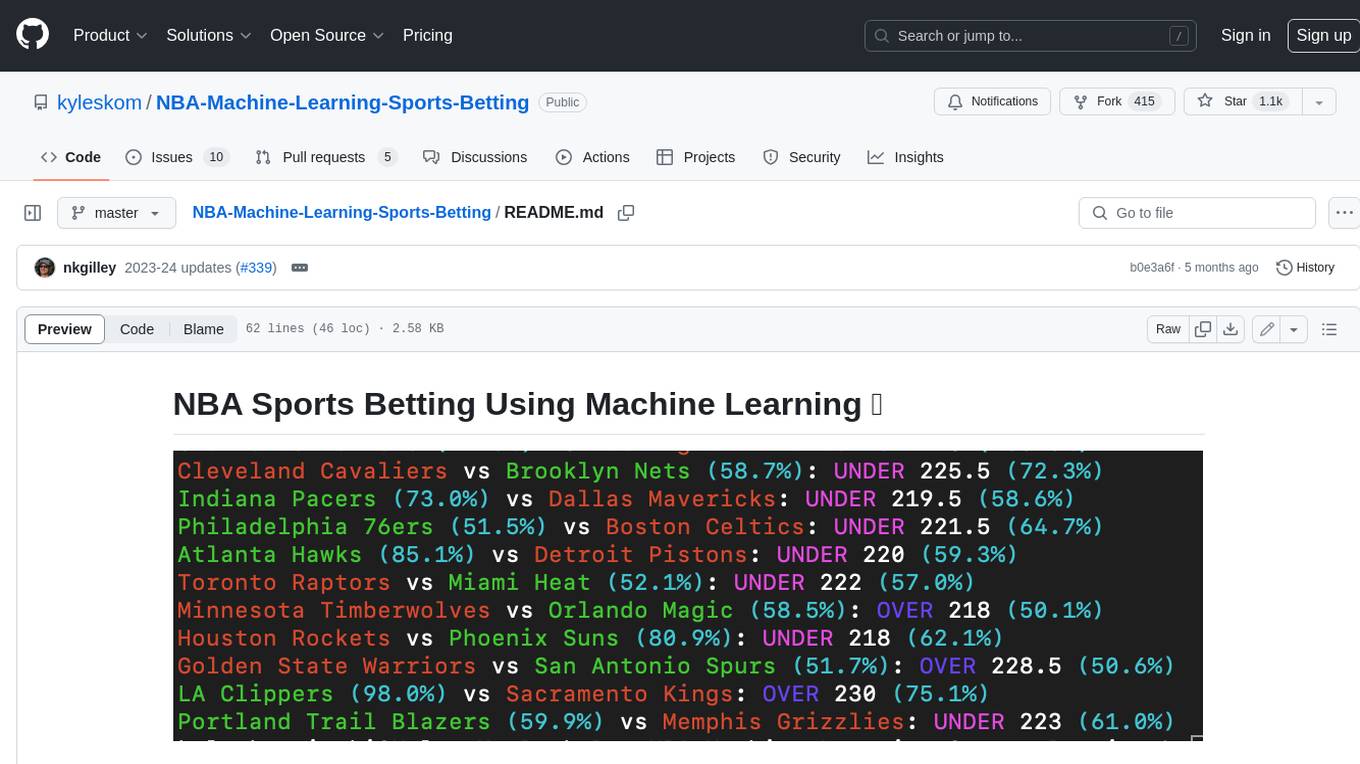
This tool is a machine learning AI used to predict the winners and under/overs of NBA games. It takes all team data from the 2007-08 season to the current season, matched with odds of those games, and uses a neural network to predict winning bets for today's games. The tool achieves ~69% accuracy on money lines and ~55% on under/overs. It outputs expected value for teams' money lines to provide better insight and the fraction of your bankroll to bet based on the Kelly Criterion. A popular, less risky approach is to bet 50% of the stake recommended by the Kelly Criterion.
README:
A machine learning AI used to predict the winners and under/overs of NBA games. Takes all team data from the 2007-08 season to current season, matched with odds of those games, using a neural network to predict winning bets for today's games. Achieves ~69% accuracy on money lines and ~55% on under/overs. Outputs expected value for teams money lines to provide better insight. The fraction of your bankroll to bet based on the Kelly Criterion is also outputted. Note that a popular, less risky approach is to bet 50% of the stake recommended by the Kelly Criterion.
Use Python 3.11. In particular the packages/libraries used are...
- Tensorflow - Machine learning library
- XGBoost - Gradient boosting framework
- Numpy - Package for scientific computing in Python
- Pandas - Data manipulation and analysis
- Colorama - Color text output
- Tqdm - Progress bars
- Requests - Http library
- Scikit_learn - Machine learning library
Make sure all packages above are installed.
$ git clone https://github.com/kyleskom/NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting.git
$ cd NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
$ python3 main.py -xgb -odds=fanduelOdds data will be automatically fetched from sbrodds if the -odds option is provided with a sportsbook. Options include: fanduel, draftkings, betmgm, pointsbet, caesars, wynn, bet_rivers_ny
If -odds is not given, enter the under/over and odds for today's games manually after starting the script.
Optionally, you can add '-kc' as a command line argument to see the recommended fraction of your bankroll to wager based on the model's edge
This repo also includes a small Flask application to help view the data from this tool in the browser. To run it:
cd Flask
flask --debug run
# Create dataset with the latest data for 2023-24 season
cd src/Process-Data
python -m Get_Data
python -m Get_Odds_Data
python -m Create_Games
# Train models
cd ../Train-Models
python -m XGBoost_Model_ML
python -m XGBoost_Model_UO
All contributions welcomed and encouraged.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
Similar Open Source Tools

NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
This tool is a machine learning AI used to predict the winners and under/overs of NBA games. It takes all team data from the 2007-08 season to the current season, matched with odds of those games, and uses a neural network to predict winning bets for today's games. The tool achieves ~69% accuracy on money lines and ~55% on under/overs. It outputs expected value for teams' money lines to provide better insight and the fraction of your bankroll to bet based on the Kelly Criterion. A popular, less risky approach is to bet 50% of the stake recommended by the Kelly Criterion.
sports-betting
Sports-betting is a Python library for implementing betting strategies and analyzing sports data. It provides tools for collecting, processing, and visualizing sports data to make informed betting decisions. The library includes modules for scraping data from sports websites, calculating odds, simulating betting strategies, and evaluating performance. With sports-betting, users can automate betting processes, test different strategies, and improve their betting outcomes.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
maxtext
MaxText is a high performance, highly scalable, open-source Large Language Model (LLM) written in pure Python/Jax targeting Google Cloud TPUs and GPUs for training and inference. It aims to be a launching off point for ambitious LLM projects in research and production, supporting TPUs and GPUs, models like Llama2, Mistral, and Gemma. MaxText provides specific instructions for getting started, runtime performance results, comparison to alternatives, and features like stack trace collection, ahead of time compilation for TPUs and GPUs, and automatic upload of logs to Vertex Tensorboard.
tetris-ai
A bot that plays Tetris using deep reinforcement learning. The agent learns to play by training itself with a neural network and Q Learning algorithm. It explores different 'paths' to achieve higher scores and makes decisions based on predicted scores for possible moves. The game state includes attributes like lines cleared, holes, bumpiness, and total height. The agent is implemented in Python using Keras framework with a deep neural network structure. Training involves a replay queue, random sampling, and optimization techniques. Results show the agent's progress in achieving higher scores over episodes.
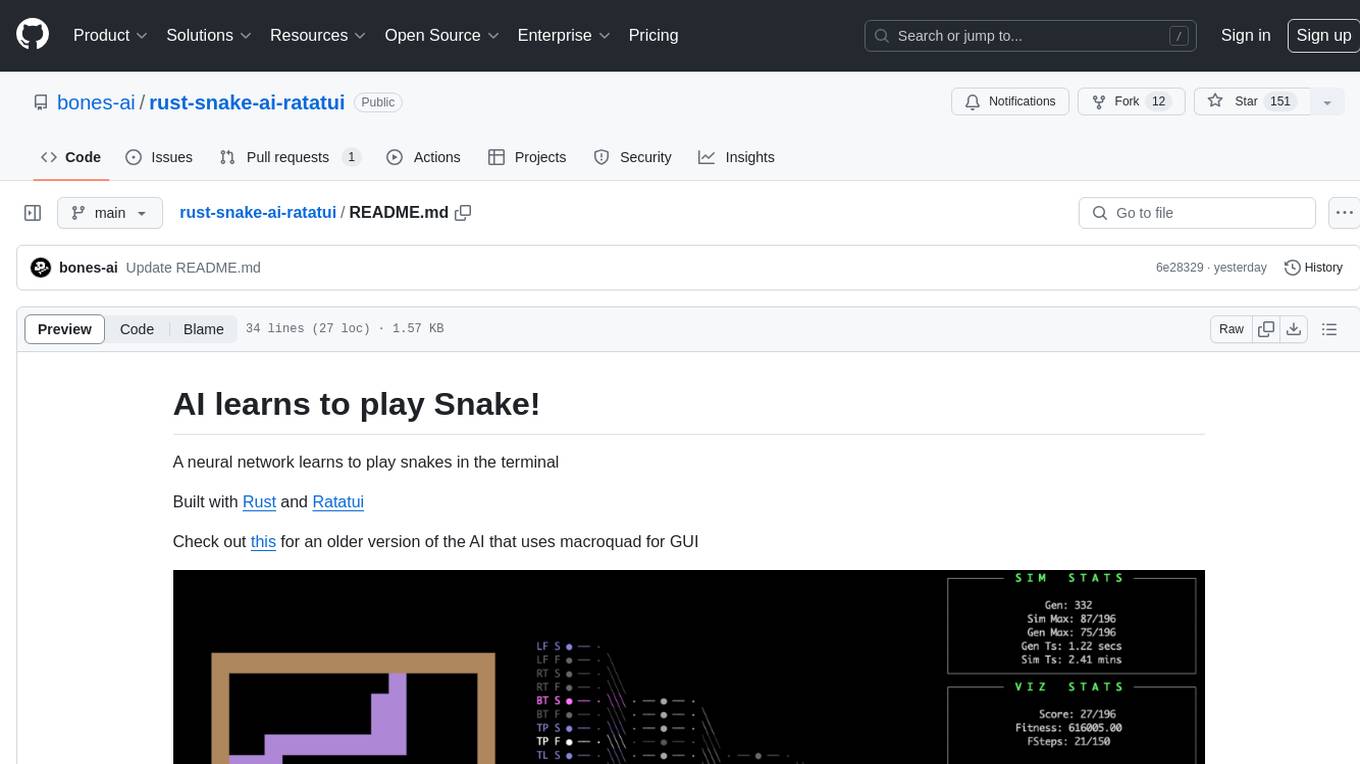
rust-snake-ai-ratatui
This repository contains an AI implementation that learns to play the classic game Snake in the terminal. The AI is built using Rust and Ratatui. Users can clone the repo, run the simulation, and configure various settings to customize the AI's behavior. The project also provides options for minimal UI, training custom networks, and watching the AI complete the game on different board sizes. The developer shares updates and insights about the project on Twitter and plans to create a detailed blog post explaining the AI's workings.

physical-AI-interpretability
Physical AI Interpretability is a toolkit for transformer-based Physical AI and robotics models, providing tools for attention mapping, feature extraction, and out-of-distribution detection. It includes methods for post-hoc attention analysis, applying Dictionary Learning into robotics, and training sparse autoencoders. The toolkit aims to enhance interpretability and understanding of AI models in physical environments.
Aidan-Bench
Aidan Bench is a tool that rewards creativity, reliability, contextual attention, and instruction following. It is weakly correlated with Lmsys, has no score ceiling, and aligns with real-world open-ended use. The tool involves giving LLMs open-ended questions and evaluating their answers based on novelty scores. Users can set up the tool by installing required libraries and setting up API keys. The project allows users to run benchmarks for different models and provides flexibility in threading options.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
swt-bench
SWT-Bench is a benchmark tool for evaluating large language models on testing generation for real world software issues collected from GitHub. It tasks a language model with generating a reproducing test that fails in the original state of the code base and passes after a patch resolving the issue has been applied. The tool operates in unit test mode or reproduction script mode to assess model predictions and success rates. Users can run evaluations on SWT-Bench Lite using the evaluation harness with specific commands. The tool provides instructions for setting up and building SWT-Bench, as well as guidelines for contributing to the project. It also offers datasets and evaluation results for public access and provides a citation for referencing the work.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
llm.c
LLM training in simple, pure C/CUDA. There is no need for 245MB of PyTorch or 107MB of cPython. For example, training GPT-2 (CPU, fp32) is ~1,000 lines of clean code in a single file. It compiles and runs instantly, and exactly matches the PyTorch reference implementation. I chose GPT-2 as the first working example because it is the grand-daddy of LLMs, the first time the modern stack was put together.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
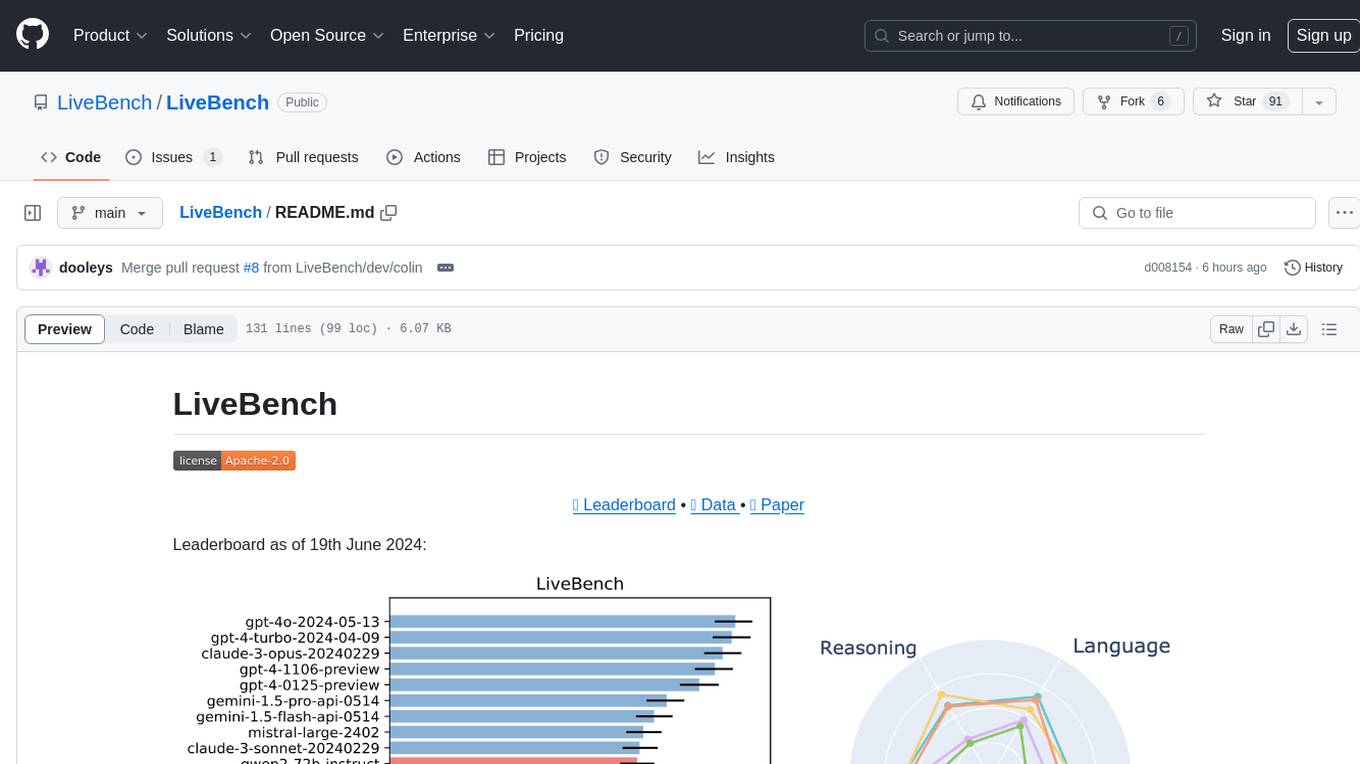
LiveBench
LiveBench is a benchmark tool designed for Language Model Models (LLMs) with a focus on limiting contamination through monthly new questions based on recent datasets, arXiv papers, news articles, and IMDb movie synopses. It provides verifiable, objective ground-truth answers for accurate scoring without an LLM judge. The tool offers 18 diverse tasks across 6 categories and promises to release more challenging tasks over time. LiveBench is built on FastChat's llm_judge module and incorporates code from LiveCodeBench and IFEval.
sunone_aimbot
Sunone Aimbot is an AI-powered aim bot for first-person shooter games. It leverages YOLOv8 and YOLOv10 models, PyTorch, and various tools to automatically target and aim at enemies within the game. The AI model has been trained on more than 30,000 images from popular first-person shooter games like Warface, Destiny 2, Battlefield 2042, CS:GO, Fortnite, The Finals, CS2, and more. The aimbot can be configured through the `config.ini` file to adjust various settings related to object search, capture methods, aiming behavior, hotkeys, mouse settings, shooting options, Arduino integration, AI model parameters, overlay display, debug window, and more. Users are advised to follow specific recommendations to optimize performance and avoid potential issues while using the aimbot.
For similar tasks

NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
This tool is a machine learning AI used to predict the winners and under/overs of NBA games. It takes all team data from the 2007-08 season to the current season, matched with odds of those games, and uses a neural network to predict winning bets for today's games. The tool achieves ~69% accuracy on money lines and ~55% on under/overs. It outputs expected value for teams' money lines to provide better insight and the fraction of your bankroll to bet based on the Kelly Criterion. A popular, less risky approach is to bet 50% of the stake recommended by the Kelly Criterion.
For similar jobs

NBA-Machine-Learning-Sports-Betting
This tool is a machine learning AI used to predict the winners and under/overs of NBA games. It takes all team data from the 2007-08 season to the current season, matched with odds of those games, and uses a neural network to predict winning bets for today's games. The tool achieves ~69% accuracy on money lines and ~55% on under/overs. It outputs expected value for teams' money lines to provide better insight and the fraction of your bankroll to bet based on the Kelly Criterion. A popular, less risky approach is to bet 50% of the stake recommended by the Kelly Criterion.
FBP
FootBallPrediction (FBP) is a software project that utilizes big data and machine learning to predict the outcome of football matches based on odds from gambling companies. The software has achieved an accuracy rate of over 80% in predicting match results. The current version, 22.0, successfully predicted eight out of nine matches from major football leagues. The project has a community of over 60 members who benefit from the predicted results. The author is seeking collaboration to further enhance the project and welcomes interested individuals to join. AI-FBP is a subscription service that provides daily football game predictions.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.


