
CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
Use locally run models (OpenAI compatible APIs, Tabby, Ollama) to generate code suggestions for Xcode.
Stars: 71
This repository provides a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing users to enhance code suggestions using chat models. It supports different suggestion services and strategies for generating code suggestions. Users can customize prompt formats and utilize local models for code completion.
README:
This extension offers a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing you to leverage a chat model to enhance the suggestions provided as you write code.
- Install the application in the Applications folder.
- Launch the application.
- Open Copilot for Xcode and navigate to "Extensions".
- Click "Select Extensions" and enable this extension.
- You can now set this application as the suggestion provider in the suggestion settings.
To update the app, you can do so directly within the app itself. Once updated, you should perform one of the following steps to ensure Copilot for Xcode recognizes the new version:
- Restart the
CopilotForXcodeExtensionService. - Alternatively, terminate the "Custom Suggestion Service (CopilotForXcodeExtensionService)" process, open the extension manager in Copilot for Xcode, and click "Restart Extensions".
We are exploring better methods to tweak the update process.
The app supports three types of suggestion services:
- Models with chat completions API
- Models with completions API
- Models with FIM API
- Tabby
If you are new to running a model locally, you can try Ollama and LM Studio.
-
Use Tabby since they have extensive experience in code completion.
-
Use models with completions API with Fill-in-the-Middle support (for example, codellama:7b-code), and use the "Fill-in-the-Middle" strategy.
You can find some examples here.
-
Use models with FIM API.
When using custom models to generate suggestions, it is recommended to setup a lower suggestion limit for faster generation.
In other situations, it is advisable to use a custom model with the completions API over a chat completions API, and employ the default request strategy.
Ensure that the prompt format remains as simple as the following:
{System}
{User}
{Assistant}
The template format differs in different tools.
- Fill-in-the-Middle: It uses special tokens to guide the models to generate suggestions. The models need to support FIM to use it (codellama:xb-code, startcoder, etc.). You need to setup a prompt format to allow it to work properly. The default prompt format is for codellama.
- Fill-in-the-Middle with System Prompt: The previous one doesn't have a system prompt telling it what to do. You can try to use it in models that don't support FIM.
- Anthropic Optimized: This strategy is optimized for Anthropic chat models. You can try it on other chat models, too.
- Default: This strategy meticulously explains the context to the model, prompting it to generate a suggestion.
- Naive: This strategy rearranges the code in a naive way to trick the model into believing it's appending code at the end of a file.
- Continue: This strategy employs the "Please Continue" technique to persuade the model that it has started a suggestion and must continue to complete it. (Only effective with the chat completion API).
- Load
qwen2.5-coder:32bwith Ollama. - Setup the model with the completions API.
- Set the request strategy to "Fill-in-the-Middle".
- Set prompt format to
<|fim_prefix|>{prefix}<|fim_suffix|>{suffix}<|fim_middle|>and turn on Raw Prompt.
Prompt engineering is a challenging task, and your assistance is invaluable.
The most complex things are located within the Core package.
- To add a new service, please refer to the
CodeCompletionServicefolder. - To add new request strategies, check out the
SuggestionServicefolder. - To add a new instructions of using a local model, update the
Example Use of Local Modelsin the README.md.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
Similar Open Source Tools

CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
This repository provides a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing users to enhance code suggestions using chat models. It supports different suggestion services and strategies for generating code suggestions. Users can customize prompt formats and utilize local models for code completion.
sublayer
Sublayer is a model-agnostic Ruby AI Agent framework that provides base classes for building Generators, Actions, Tasks, and Agents to create AI-powered applications in Ruby. It supports various AI models and providers, such as OpenAI, Gemini, and Claude. Generators generate specific outputs, Actions perform operations, Agents are autonomous entities for tasks or monitoring, and Triggers decide when Agents are activated. The framework offers sample Generators and usage examples for building AI applications.
foyle
Foyle is a project focused on building agents to assist software developers in deploying and operating software. It aims to improve agent performance by collecting human feedback on agent suggestions and human examples of reasoning traces. Foyle utilizes a literate environment using vscode notebooks to interact with infrastructure, capturing prompts, AI-provided answers, and user corrections. The goal is to continuously retrain AI to enhance performance. Additionally, Foyle emphasizes the importance of reasoning traces for training agents to work with internal systems, providing a self-documenting process for operations and troubleshooting.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
trackmania_rl_public
This repository contains the reinforcement learning training code for Trackmania AI with Reinforcement Learning. It is a research work-in-progress project that aims to apply reinforcement learning principles to play Trackmania. The code is constantly evolving and may not be clean or easily usable. The training hyperparameters are intentionally changed in the public repository to encourage understanding of reinforcement learning principles. The project may not receive active support for setup or usage at the moment.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
chat-with-code
Chat-with-code is a codebase chatbot that enables users to interact with their codebase using the OpenAI Language Model. It provides a user-friendly chat interface where users can ask questions and interact with their code. The tool clones, chunks, and embeds the codebase, allowing for natural language interactions. It is designed to assist users in exploring and understanding their codebase more intuitively.

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.

GlaDOS
This project aims to create a real-life version of GLaDOS, an aware, interactive, and embodied AI entity. It involves training a voice generator, developing a 'Personality Core,' implementing a memory system, providing vision capabilities, creating 3D-printable parts, and designing an animatronics system. The software architecture focuses on low-latency voice interactions, utilizing a circular buffer for data recording, text streaming for quick transcription, and a text-to-speech system. The project also emphasizes minimal dependencies for running on constrained hardware. The hardware system includes servo- and stepper-motors, 3D-printable parts for GLaDOS's body, animations for expression, and a vision system for tracking and interaction. Installation instructions cover setting up the TTS engine, required Python packages, compiling llama.cpp, installing an inference backend, and voice recognition setup. GLaDOS can be run using 'python glados.py' and tested using 'demo.ipynb'.
fuji-web
Fuji-Web is an intelligent AI partner designed for full browser automation. It autonomously navigates websites and performs tasks on behalf of the user while providing explanations for each action step. Users can easily install the extension in their browser, access the Fuji icon to input tasks, and interact with the tool to streamline web browsing tasks. The tool aims to enhance user productivity by automating repetitive web actions and providing a seamless browsing experience.
GLaDOS
GLaDOS Personality Core is a project dedicated to building a real-life version of GLaDOS, an aware, interactive, and embodied AI system. The project aims to train GLaDOS voice generator, create a 'Personality Core,' develop medium- and long-term memory, provide vision capabilities, design 3D-printable parts, and build an animatronics system. The software architecture focuses on low-latency voice interactions and minimal dependencies. The hardware system includes servo- and stepper-motors, 3D printable parts for GLaDOS's body, animations for expression, and a vision system for tracking and interaction. Installation instructions involve setting up a local LLM server, installing drivers, and running GLaDOS on different operating systems.
godot_rl_agents
Godot RL Agents is an open-source package that facilitates the integration of Machine Learning algorithms with games created in the Godot Engine. It provides interfaces for popular RL frameworks, support for memory-based agents, 2D and 3D games, AI sensors, and is licensed under MIT. Users can train agents in the Godot editor, create custom environments, export trained agents in ONNX format, and utilize advanced features like different RL training frameworks.
trinityX
TrinityX is an open-source HPC, AI, and cloud platform designed to provide all services required in a modern system, with full customization options. It includes default services like Luna node provisioner, OpenLDAP, SLURM or OpenPBS, Prometheus, Grafana, OpenOndemand, and more. TrinityX also sets up NFS-shared directories, OpenHPC applications, environment modules, HA, and more. Users can install TrinityX on Enterprise Linux, configure network interfaces, set up passwordless authentication, and customize the installation using Ansible playbooks. The platform supports HA, OpenHPC integration, and provides detailed documentation for users to contribute to the project.
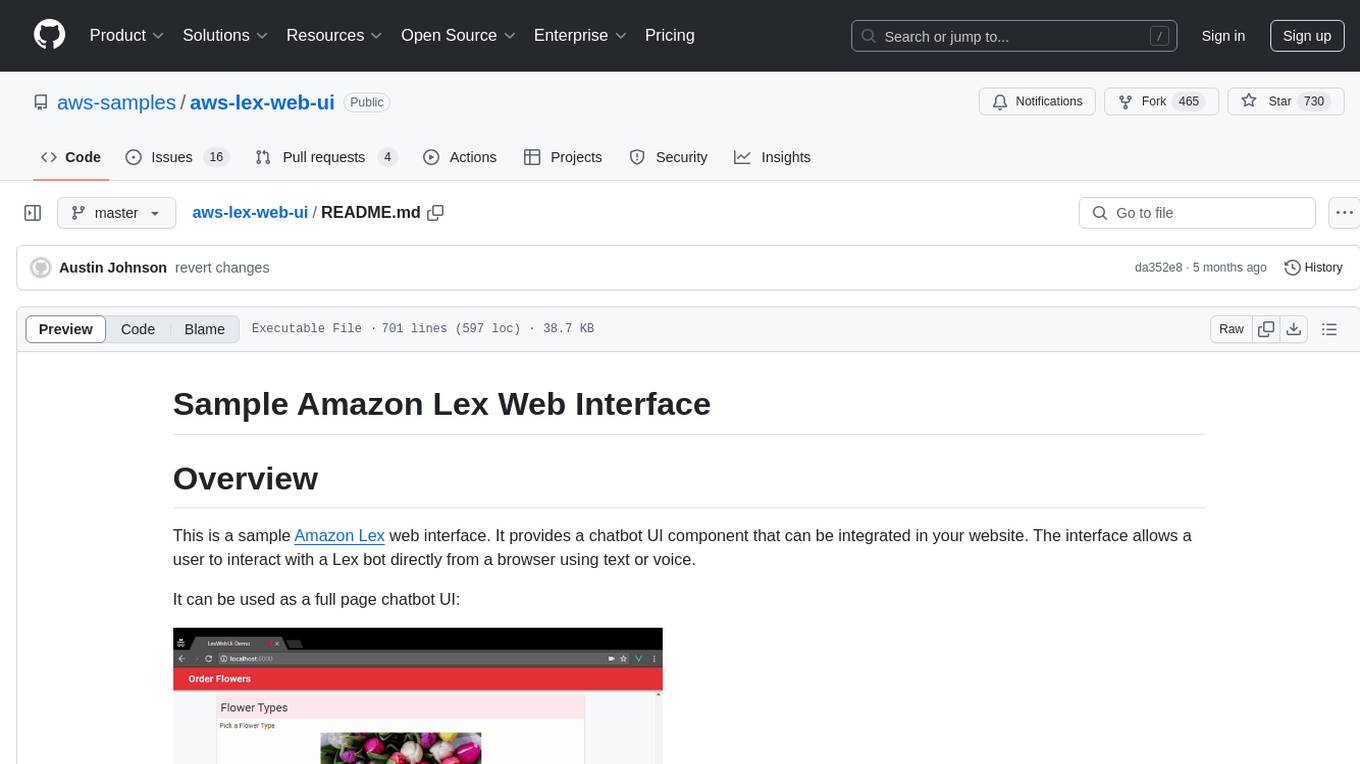
aws-lex-web-ui
The AWS Lex Web UI is a sample Amazon Lex web interface that provides a chatbot UI component for integration into websites. It supports voice and text interactions, Lex response cards, and programmable configuration using JavaScript. The interface can be used as a full-page chatbot UI or embedded as a widget. It offers mobile-ready responsive UI, seamless voice-text switching, and interactive messaging support. The project includes CloudFormation templates for easy deployment and customization. Users can modify configurations, integrate the UI into existing sites, and deploy using various methods like CloudFormation, pre-built libraries, or npm installation.
For similar tasks

CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
This repository provides a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing users to enhance code suggestions using chat models. It supports different suggestion services and strategies for generating code suggestions. Users can customize prompt formats and utilize local models for code completion.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.