
MCP2Lambda
Run any AWS Lambda function as a Large Language Model (LLM) tool without code changes using Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Stars: 57
MCP2Lambda is a server that acts as a bridge between MCP clients and AWS Lambda functions, allowing generative AI models to access and run Lambda functions as tools. It enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with Lambda functions without code changes, providing access to private resources, AWS services, private networks, and the public internet. The server supports autodiscovery of Lambda functions and their invocation by name with parameters. It standardizes AI model access to external tools using the MCP protocol.
README:
Run any AWS Lambda function as a Large Language Model (LLM) tool without code changes using Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP).
graph LR
A[Model] <--> B[MCP Client]
B <--> C["MCP2Lambda<br>(MCP Server)"]
C <--> D[Lambda Function]
D <--> E[Other AWS Services]
D <--> F[Internet]
D <--> G[VPC]
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#bfb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:4px
style D fill:#fbb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#fbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#dff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style G fill:#ffd,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2pxThis MCP server acts as a bridge between MCP clients and AWS Lambda functions, allowing generative AI models to access and run Lambda functions as tools. This is useful, for example, to access private resources such as internal applications and databases without the need to provide public network access. This approach allows the model to use other AWS services, private networks, and the public internet.
From a security perspective, this approach implements segregation of duties by allowing the model to invoke the Lambda functions but not to access the other AWS services directly. The client only needs AWS credentials to invoke the Lambda functions. The Lambda functions can then interact with other AWS services (using the function role) and access public or private networks.
The MCP server gives access to two tools:
-
The first tool can autodiscover all Lambda functions in your account that match a prefix or an allowed list of names. This tool shares the names of the functions and their descriptions with the model.
-
The second tool allows to invoke those Lambda functions by name passing the required parameters.
No code changes are required. You should change these configurations to improve results:
The gateway supports two different strategies for handling Lambda functions:
-
Pre-Discovery Mode (default: enabled): Registers each Lambda function as an individual tool at startup. This provides a more intuitive interface where each function appears as its own named tool.
-
Generic Mode: Uses two generic tools (
list_lambda_functionsandinvoke_lambda_function) to interact with Lambda functions.
You can control this behavior through:
- Environment variable:
PRE_DISCOVERY=true|false - CLI flag:
--no-pre-discovery(disables pre-discovery mode)
Example:
# Disable pre-discovery mode
export PRE_DISCOVERY=false
python main.py
# Or using CLI flag to disable pre-discovery
python main.py --no-pre-discovery-
To provide the MCP client with the knowledge to use a Lambda function, the description of the Lambda function should indicate what the function does and which parameters it uses. See the sample functions for a quick demo and more details.
-
To help the model use the tools available via AWS Lambda, you can add something like this to your system prompt:
Use the AWS Lambda tools to improve your answers.
MCP2Lambda enables LLMs to interact with AWS Lambda functions as tools, extending their capabilities beyond text generation. This allows models to:
- Access real-time and private data, including data sources in your VPCs
- Execute custom code using a Lambda function as sandbox environment
- Interact with external services and APIs using Lambda functions internet access (and bandwidth)
- Perform specialized calculations or data processing
The server uses the MCP protocol, which standardizes the way AI models can access external tools.
By default, only functions whose name starts with mcp2lambda- will be available to the model.
- Python 3.12 or higher
- AWS account with configured credentials
- AWS Lambda functions (sample functions provided in the repo)
- An application using Amazon Bedrock with the Converse API
- An MCP-compatible client like Claude Desktop
To install MCP2Lambda for Claude Desktop automatically via Smithery:
npx -y @smithery/cli install @danilop/MCP2Lambda --client claude-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/mcp2lambda.git cd mcp2lambda -
Configure AWS credentials. For example, using the AWS CLI:
aws configure
This repository includes three sample Lambda functions that demonstrate different use cases. These functions have basic permissions and can only write to CloudWatch logs.
Retrieves a customer ID based on an email address. This function takes an email parameter and returns the associated customer ID, demonstrating how to build simple lookup tools. The function is hard coded to reply to the [email protected] email address. For example, you can ask the model to get the customer ID for the email [email protected].
Retrieves detailed customer information based on a customer ID. This function returns customer details like name, email, and status, showing how Lambda can provide context-specific data. The function is hard coded to reply to the customer ID returned by the previous function. For example, you can ask the model to "Get the customer status for email [email protected]". This will use both functions to get to the result.
Executes arbitrary Python code within a Lambda sandbox environment. This powerful function allows Claude to write and run Python code to perform calculations, data processing, or other operations not built into the model. For example, you can ask the model to "Calculate the number of prime numbers between 1 and 10, 1 and 100, and so on up to 1M".
The repository includes sample Lambda functions in the sample_functions directory.
-
Install the AWS SAM CLI: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/install-sam-cli.html
-
Deploy the sample functions:
cd sample_functions sam build sam deploy
The sample functions will be deployed with the prefix mcp2lambda-.
MCP2Lambda can also be used with Amazon Bedrock's Converse API, allowing you to use the MCP protocol with any of the models supported by Bedrock.
The mcp_client_bedrock directory contains a client implementation that connects MCP2Lambda to Amazon Bedrock models.
See https://github.com/mikegc-aws/amazon-bedrock-mcp for more information.
- Amazon Bedrock access and permissions to use models like Claude, Mistral, Llama, etc.
- Boto3 configured with appropriate credentials
-
Navigate to the mcp_client_bedrock directory:
cd mcp_client_bedrock -
Install dependencies:
uv pip install -e . -
Run the client:
python main.py
The client is configured to use Anthropic's Claude 3.7 Sonnet by default, but you can modify the model_id in main.py to use other Bedrock models:
# Examples of supported models:
model_id = "us.anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0"
#model_id = "us.amazon.nova-pro-v1:0"You can also customize the system prompt in the same file to change how the model behaves.
-
Start the MCP2Lambda server in one terminal:
cd mcp2lambda uv run main.py -
Run the Bedrock client in another terminal:
cd mcp_client_bedrock python main.py -
Interact with the model through the command-line interface. The model will have access to the Lambda functions deployed earlier.
Add the following to your Claude Desktop configuration file:
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp2lambda": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"<full path to the mcp2lambda directory>",
"run",
"main.py"
]
}
}
}To help the model use tools via AWS Lambda, in your settings profile, you can add to your personal preferences a sentence like:
Use the AWS Lambda tools to improve your answers.
Start the MCP server locally:
cd mcp2lambda
uv run main.pyFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MCP2Lambda
Similar Open Source Tools

MCP2Lambda
MCP2Lambda is a server that acts as a bridge between MCP clients and AWS Lambda functions, allowing generative AI models to access and run Lambda functions as tools. It enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with Lambda functions without code changes, providing access to private resources, AWS services, private networks, and the public internet. The server supports autodiscovery of Lambda functions and their invocation by name with parameters. It standardizes AI model access to external tools using the MCP protocol.
serverless-pdf-chat
The serverless-pdf-chat repository contains a sample application that allows users to ask natural language questions of any PDF document they upload. It leverages serverless services like Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB to provide text generation and analysis capabilities. The application architecture involves uploading a PDF document to an S3 bucket, extracting metadata, converting text to vectors, and using a LangChain to search for information related to user prompts. The application is not intended for production use and serves as a demonstration and educational tool.
open-deep-research
Open Deep Research is an open-source project that serves as a clone of Open AI's Deep Research experiment. It utilizes Firecrawl's extract and search method along with a reasoning model to conduct in-depth research on the web. The project features Firecrawl Search + Extract, real-time data feeding to AI via search, structured data extraction from multiple websites, Next.js App Router for advanced routing, React Server Components and Server Actions for server-side rendering, AI SDK for generating text and structured objects, support for various model providers, styling with Tailwind CSS, data persistence with Vercel Postgres and Blob, and simple and secure authentication with NextAuth.js.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
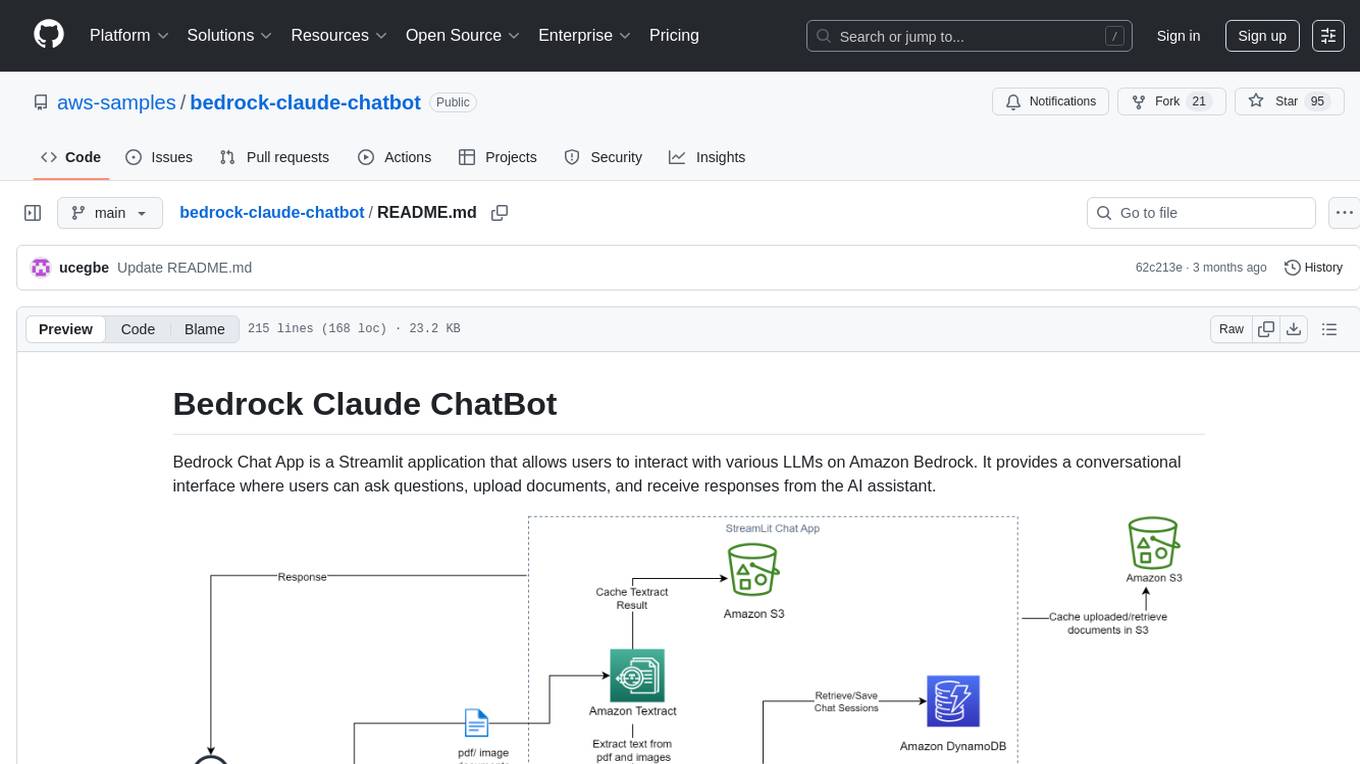
bedrock-claude-chatbot
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.
vulnerability-analysis
The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Vulnerability Analysis for Container Security showcases accelerated analysis on common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) at an enterprise scale, reducing mitigation time from days to seconds. It enables security analysts to determine software package vulnerabilities using large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). The blueprint is designed for security analysts, IT engineers, and AI practitioners in cybersecurity. It requires NVAIE developer license and API keys for vulnerability databases, search engines, and LLM model services. Hardware requirements include L40 GPU for pipeline operation and optional LLM NIM and Embedding NIM. The workflow involves LLM pipeline for CVE impact analysis, utilizing LLM planner, agent, and summarization nodes. The blueprint uses NVIDIA NIM microservices and Morpheus Cybersecurity AI SDK for vulnerability analysis.
honcho
Honcho is a platform for creating personalized AI agents and LLM powered applications for end users. The repository is a monorepo containing the server/API for managing database interactions and storing application state, along with a Python SDK. It utilizes FastAPI for user context management and Poetry for dependency management. The API can be run using Docker or manually by setting environment variables. The client SDK can be installed using pip or Poetry. The project is open source and welcomes contributions, following a fork and PR workflow. Honcho is licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.
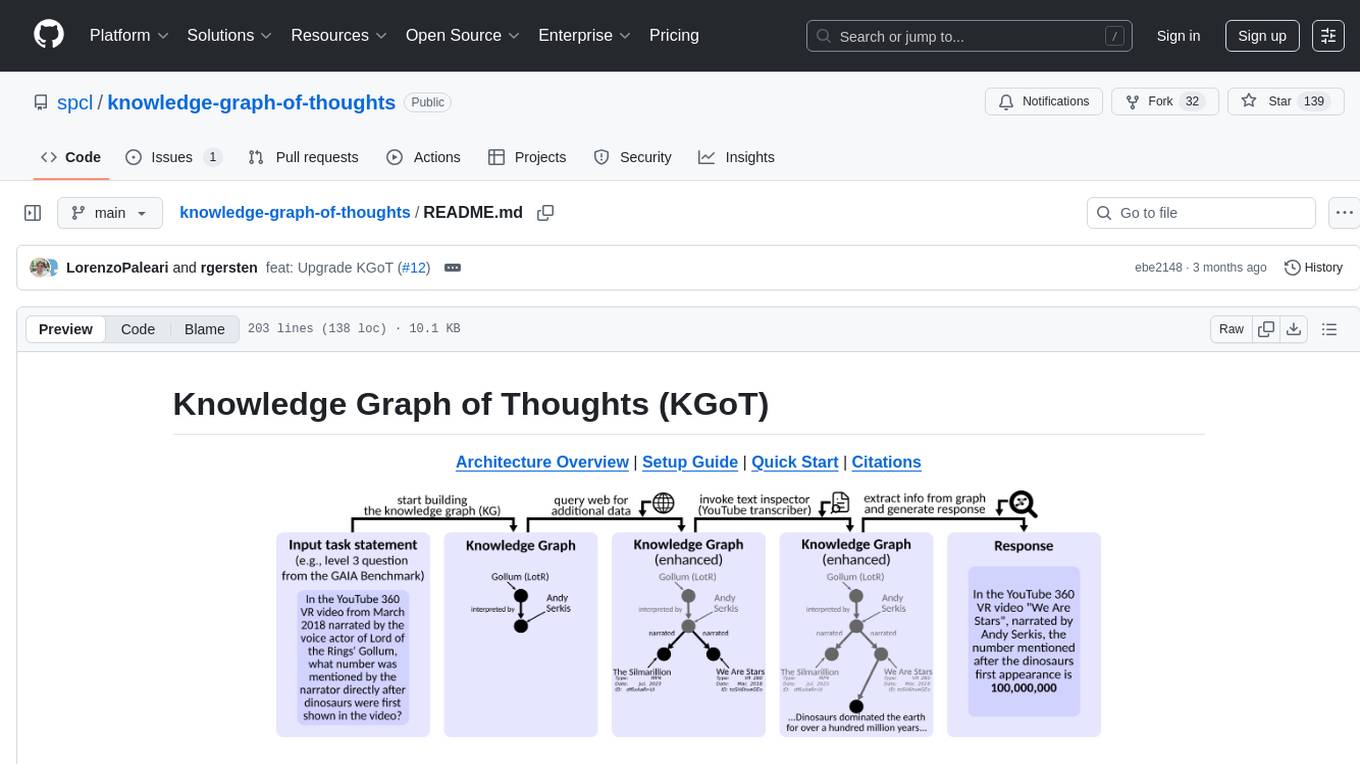
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
aws-ai-stack
AWS AI Stack is a full-stack boilerplate project designed for building serverless AI applications on AWS. It provides a trusted AWS foundation for AI apps with access to powerful LLM models via Bedrock. The architecture is serverless, ensuring cost-efficiency by only paying for usage. The project includes features like AI Chat & Streaming Responses, Multiple AI Models & Data Privacy, Custom Domain Names, API & Event-Driven architecture, Built-In Authentication, Multi-Environment support, and CI/CD with Github Actions. Users can easily create AI Chat bots, authentication services, business logic, and async workers using AWS Lambda, API Gateway, DynamoDB, and EventBridge.
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.
safety-tooling
This repository, safety-tooling, is designed to be shared across various AI Safety projects. It provides an LLM API with a common interface for OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google models. The aim is to facilitate collaboration among AI Safety researchers, especially those with limited software engineering backgrounds, by offering a platform for contributing to a larger codebase. The repo can be used as a git submodule for easy collaboration and updates. It also supports pip installation for convenience. The repository includes features for installation, secrets management, linting, formatting, Redis configuration, testing, dependency management, inference, finetuning, API usage tracking, and various utilities for data processing and experimentation.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
PolyMind
PolyMind is a multimodal, function calling powered LLM webui designed for various tasks such as internet searching, image generation, port scanning, Wolfram Alpha integration, Python interpretation, and semantic search. It offers a plugin system for adding extra functions and supports different models and endpoints. The tool allows users to interact via function calling and provides features like image input, image generation, and text file search. The application's configuration is stored in a `config.json` file with options for backend selection, compatibility mode, IP address settings, API key, and enabled features.
generative-ai-sagemaker-cdk-demo
This repository showcases how to deploy generative AI models from Amazon SageMaker JumpStart using the AWS CDK. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content and ideas, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. The repository provides a detailed guide on deploying image and text generative AI models, utilizing pre-trained models from SageMaker JumpStart. The web application is built on Streamlit and hosted on Amazon ECS with Fargate. It interacts with the SageMaker model endpoints through Lambda functions and Amazon API Gateway. The repository also includes instructions on setting up the AWS CDK application, deploying the stacks, using the models, and viewing the deployed resources on the AWS Management Console.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
For similar tasks

MCP2Lambda
MCP2Lambda is a server that acts as a bridge between MCP clients and AWS Lambda functions, allowing generative AI models to access and run Lambda functions as tools. It enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with Lambda functions without code changes, providing access to private resources, AWS services, private networks, and the public internet. The server supports autodiscovery of Lambda functions and their invocation by name with parameters. It standardizes AI model access to external tools using the MCP protocol.
appwrite
Appwrite is a best-in-class, developer-first platform that provides everything needed to create scalable, stable, and production-ready software quickly. It is an end-to-end platform for building Web, Mobile, Native, or Backend apps, packaged as Docker microservices. Appwrite abstracts the complexity of building modern apps and allows users to build secure, full-stack applications faster. It offers features like user authentication, database management, storage, file management, image manipulation, Cloud Functions, messaging, and more services.
arcade-ai
Arcade AI is a developer-focused tooling and API platform designed to enhance the capabilities of LLM applications and agents. It simplifies the process of connecting agentic applications with user data and services, allowing developers to concentrate on building their applications. The platform offers prebuilt toolkits for interacting with various services, supports multiple authentication providers, and provides access to different language models. Users can also create custom toolkits and evaluate their tools using Arcade AI. Contributions are welcome, and self-hosting is possible with the provided documentation.
M.I.L.E.S
M.I.L.E.S. (Machine Intelligent Language Enabled System) is a voice assistant powered by GPT-4 Turbo, offering a range of capabilities beyond existing assistants. With its advanced language understanding, M.I.L.E.S. provides accurate and efficient responses to user queries. It seamlessly integrates with smart home devices, Spotify, and offers real-time weather information. Additionally, M.I.L.E.S. possesses persistent memory, a built-in calculator, and multi-tasking abilities. Its realistic voice, accurate wake word detection, and internet browsing capabilities enhance the user experience. M.I.L.E.S. prioritizes user privacy by processing data locally, encrypting sensitive information, and adhering to strict data retention policies.
letmedoit
LetMeDoIt AI is a virtual assistant designed to revolutionize the way you work. It goes beyond being a mere chatbot by offering a unique and powerful capability - the ability to execute commands and perform computing tasks on your behalf. With LetMeDoIt AI, you can access OpenAI ChatGPT-4, Google Gemini Pro, and Microsoft AutoGen, local LLMs, all in one place, to enhance your productivity.
awesome-tool-llm
This repository focuses on exploring tools that enhance the performance of language models for various tasks. It provides a structured list of literature relevant to tool-augmented language models, covering topics such as tool basics, tool use paradigm, scenarios, advanced methods, and evaluation. The repository includes papers, preprints, and books that discuss the use of tools in conjunction with language models for tasks like reasoning, question answering, mathematical calculations, accessing knowledge, interacting with the world, and handling non-textual modalities.

MAVIS
MAVIS (Math Visual Intelligent System) is an AI-driven application that allows users to analyze visual data such as images and generate interactive answers based on them. It can perform complex mathematical calculations, solve programming tasks, and create professional graphics. MAVIS supports Python for coding and frameworks like Matplotlib, Plotly, Seaborn, Altair, NumPy, Math, SymPy, and Pandas. It is designed to make projects more efficient and professional.
agentmark
AgentMark is a tool designed to make it easy for developers to develop, test, and evaluate AI Agents. It combines Markdown syntax with JSX components to create reliable Agents. The tool seamlessly integrates with SDKs, offering comprehensive tooling such as full type safety, unified prompt configuration, syntax highlighting, loops and conditionals, custom SDK adapters, and support for text, object, image, and speech generation across multiple model providers.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.