
Prompt_Engineering
This repository offers a comprehensive collection of tutorials and implementations for Prompt Engineering techniques, ranging from fundamental concepts to advanced strategies. It serves as an essential resource for mastering the art of effectively communicating with and leveraging large language models in AI applications.
Stars: 7100
Prompt Engineering Techniques is a comprehensive repository for learning, building, and sharing prompt engineering techniques, from basic concepts to advanced strategies for leveraging large language models. It provides step-by-step tutorials, practical implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative prompt engineering techniques. The repository covers fundamental concepts, core techniques, advanced strategies, optimization and refinement, specialized applications, and advanced applications in prompt engineering.
README:
🌟 Support This Project: Your sponsorship fuels innovation in prompt engineering development. Become a sponsor to help maintain and expand this valuable resource!
Welcome to one of the most extensive and dynamic collections of Prompt Engineering tutorials and implementations available today. This repository serves as a comprehensive resource for learning, building, and sharing prompt engineering techniques, ranging from basic concepts to advanced strategies for leveraging large language models.
| 🚀 Cutting-edge Updates |
💡 Expert Insights |
🎯 Top 0.1% Content |
Join over 50,000 AI enthusiasts getting unique cutting-edge insights and free tutorials! Plus, subscribers get exclusive early access and special discounts to our upcoming RAG Techniques course!
Prompt engineering is at the forefront of artificial intelligence, revolutionizing the way we interact with and leverage AI technologies. This repository is designed to guide you through the development journey, from basic prompt structures to advanced, cutting-edge techniques.
Our goal is to provide a valuable resource for everyone - from beginners taking their first steps in AI to seasoned practitioners pushing the boundaries of what's possible. By offering a range of examples from foundational to complex, we aim to facilitate learning, experimentation, and innovation in the rapidly evolving field of prompt engineering.
Furthermore, this repository serves as a platform for showcasing innovative prompt engineering techniques. Whether you've developed a novel approach or found an innovative application for existing techniques, we encourage you to share your work with the community.
This repository contains 22 hands-on Jupyter Notebook tutorials covering key prompt engineering techniques. If you want to go deeper with full explanations, intuitive insights, and structured exercises, check out the expanded version in book format:
📚 Prompt Engineering from Zero to Hero
- 📖 All 22 techniques from this repo, fully explained in depth
- 🧠 Step-by-step breakdowns of key concepts & best practices
- 🏋️ Hands-on exercises to sharpen your skills
- 🎯 Designed for learners who want a structured, guided approach
- 📄 Instant access on any device – computer, tablet, or phone
Available on:
- 📕 Amazon Kindle — $9.99
- 📗 Amazon Paperback — $24.99
- 📄 Gumroad (PDF) — Full PDF version
💡 Subscribers to the DiamantAI newsletter receive an exclusive 33% (!) discount on the book.
🚀 Level up with my Agents Towards Production repository. It delivers horizontal, code-first tutorials that cover every tool and step in the lifecycle of building production-grade GenAI agents, guiding you from spark to scale with proven patterns and reusable blueprints for real-world launches, making it the smartest place to start if you're serious about shipping agents to production.
📚 Explore my comprehensive guide on RAG techniques to learn how to enhance AI systems with external knowledge retrieval, complementing language model capabilities with rich, up-to-date information.
🤖 Dive into my GenAI Agents Repository for a wide range of AI agent implementations and tutorials, from simple conversational bots to complex, multi-agent systems for various applications.
This repository grows stronger with your contributions! Join our vibrant Discord community — the central hub for shaping and advancing this project together 🤝
Whether you're a novice eager to learn or an expert ready to share your knowledge, your insights can shape the future of prompt engineering. Join us to propose ideas, get feedback, and collaborate on innovative implementations. For contribution guidelines, please refer to our CONTRIBUTING.md file. Let's advance prompt engineering technology together!
🔗 For discussions on GenAI, or to explore knowledge-sharing opportunities, feel free to connect on LinkedIn.
- 🎓 Learn prompt engineering techniques from beginner to advanced levels
- 🧠 Explore a wide range of prompt structures and applications
- 📚 Step-by-step tutorials and comprehensive documentation
- 🛠️ Practical, ready-to-use prompt implementations
- 🌟 Regular updates with the latest advancements in prompt engineering
- 🤝 Share your own prompt engineering creations with the community
Explore our extensive list of prompt engineering techniques, ranging from basic to advanced:
| # | Category | Technique | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🎓 Fundamental Concepts | Introduction to Prompt Engineering | Comprehensive introduction to fundamental concepts of prompt engineering |
| 2 | 🎓 Fundamental Concepts | Basic Prompt Structures | Exploration of single-turn and multi-turn prompt structures |
| 3 | 🎓 Fundamental Concepts | Prompt Templates and Variables | Creating and using prompt templates with variables |
| 4 | 🔧 Core Techniques | Zero-Shot Prompting | Performing tasks without specific examples |
| 5 | 🔧 Core Techniques | Few-Shot Learning | Learning from a small number of examples |
| 6 | 🔧 Core Techniques | Chain of Thought (CoT) | Step-by-step reasoning processes |
| 7 | 🎯 Advanced Strategies | Self-Consistency | Multiple reasoning paths and result aggregation |
| 8 | 🎯 Advanced Strategies | Constrained Generation | Setting up output constraints |
| 9 | 🎯 Advanced Strategies | Role Prompting | Assigning specific roles to AI models |
| 10 | 🚀 Advanced Implementations | Task Decomposition | Breaking down complex tasks |
| 11 | 🚀 Advanced Implementations | Prompt Chaining | Connecting multiple prompts |
| 12 | 🚀 Advanced Implementations | Instruction Engineering | Crafting clear instructions |
| 13 | ⚡ Optimization | Prompt Optimization | A/B testing and refinement |
| 14 | ⚡ Optimization | Handling Ambiguity | Resolving ambiguous prompts |
| 15 | ⚡ Optimization | Length Management | Managing prompt complexity |
| 16 | 🛠️ Specialized Applications | Negative Prompting | Avoiding undesired outputs |
| 17 | 🛠️ Specialized Applications | Prompt Formatting | Various prompt formats |
| 18 | 🛠️ Specialized Applications | Task-Specific Prompts | Prompts for specific tasks |
| 19 | 🌍 Advanced Applications | Multilingual Prompting | Cross-lingual techniques |
| 20 | 🌍 Advanced Applications | Ethical Considerations | Bias avoidance and inclusivity |
| 21 | 🌍 Advanced Applications | Prompt Security | Preventing injections |
| 22 | 🌍 Advanced Applications | Effectiveness Evaluation | Evaluating prompt performance |
-
Introduction to Prompt Engineering
A comprehensive introduction to the fundamental concepts of prompt engineering in the context of AI and language models.
Combines theoretical explanations with practical demonstrations, covering basic concepts, structured prompts, comparative analysis, and problem-solving applications.
-
Explores two fundamental types of prompt structures: single-turn prompts and multi-turn prompts (conversations).
Uses OpenAI's GPT model and LangChain to demonstrate single-turn and multi-turn prompts, prompt templates, and conversation chains.
-
Prompt Templates and Variables
Introduces creating and using prompt templates with variables, focusing on Python and the Jinja2 templating engine.
Covers template creation, variable insertion, conditional content, list processing, and integration with the OpenAI API.
-
Explores zero-shot prompting, allowing language models to perform tasks without specific examples or prior training.
Demonstrates direct task specification, role-based prompting, format specification, and multi-step reasoning using OpenAI and LangChain.
-
Few-Shot Learning and In-Context Learning
Covers Few-Shot Learning and In-Context Learning techniques using OpenAI's GPT models and the LangChain library.
Implements basic and advanced few-shot learning, in-context learning, and best practices for example selection and evaluation.
-
Chain of Thought (CoT) Prompting
Introduces Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting, encouraging AI models to break down complex problems into step-by-step reasoning processes.
Covers basic and advanced CoT techniques, applying them to various problem-solving scenarios and comparing results with standard prompts.
-
Self-Consistency and Multiple Paths of Reasoning
Explores techniques for generating diverse reasoning paths and aggregating results to improve AI-generated answers.
Demonstrates designing diverse reasoning prompts, generating multiple responses, implementing aggregation methods, and applying self-consistency checks.
-
Constrained and Guided Generation
Focuses on techniques to set up constraints for model outputs and implement rule-based generation.
Uses LangChain's PromptTemplate for structured prompts, implements constraints, and explores rule-based generation techniques.
-
Explores assigning specific roles to AI models and crafting effective role descriptions.
Demonstrates creating role-based prompts, assigning roles to AI models, and refining role descriptions for various scenarios.
-
Explores techniques for breaking down complex tasks and chaining subtasks in prompts.
Covers problem analysis, subtask definition, targeted prompt engineering, sequential execution, and result synthesis.
-
Prompt Chaining and Sequencing
Demonstrates how to connect multiple prompts and build logical flows for complex AI-driven tasks.
Explores basic prompt chaining, sequential prompting, dynamic prompt generation, and error handling within prompt chains.
-
Focuses on crafting clear and effective instructions for language models, balancing specificity and generality.
Covers creating and refining instructions, experimenting with different structures, and implementing iterative improvement based on model responses.
-
Prompt Optimization Techniques
Explores advanced techniques for optimizing prompts, focusing on A/B testing and iterative refinement.
Demonstrates A/B testing of prompts, iterative refinement processes, and performance evaluation using relevant metrics.
-
Handling Ambiguity and Improving Clarity
Focuses on identifying and resolving ambiguous prompts and techniques for writing clearer prompts.
Covers analyzing ambiguous prompts, implementing strategies to resolve ambiguity, and exploring techniques for writing clearer prompts.
-
Prompt Length and Complexity Management
Explores techniques for managing prompt length and complexity when working with large language models.
Demonstrates techniques for balancing detail and conciseness, and strategies for handling long contexts including chunking, summarization, and iterative processing.
-
Negative Prompting and Avoiding Undesired Outputs
Explores negative prompting and techniques for avoiding undesired outputs from large language models.
Covers basic negative examples, explicit exclusions, constraint implementation using LangChain, and methods for evaluating and refining negative prompts.
-
Prompt Formatting and Structure
Explores various prompt formats and structural elements, demonstrating their impact on AI model responses.
Demonstrates creating various prompt formats, incorporating structural elements, and comparing responses from different prompt structures.
-
Explores the creation and use of prompts for specific tasks: text summarization, question-answering, code generation, and creative writing.
Covers designing task-specific prompt templates, implementing them using LangChain, executing with sample inputs, and analyzing outputs for each task type.
-
Multilingual and Cross-lingual Prompting
Explores techniques for designing prompts that work effectively across multiple languages and for language translation tasks.
Covers creating multilingual prompts, implementing language detection and adaptation, designing cross-lingual translation prompts, and handling various writing systems and scripts.
-
Ethical Considerations in Prompt Engineering
Explores the ethical dimensions of prompt engineering, focusing on avoiding biases and creating inclusive and fair prompts.
Covers identifying biases in prompts, implementing strategies to create inclusive prompts, and methods to evaluate and improve the ethical quality of AI outputs.
-
Focuses on preventing prompt injections and implementing content filters in prompts for safe and secure AI applications.
Covers techniques for prompt injection prevention, content filtering implementation, and testing the effectiveness of security and safety measures.
-
Evaluating Prompt Effectiveness
Explores methods and techniques for evaluating the effectiveness of prompts in AI language models.
Covers setting up evaluation metrics, implementing manual and automated evaluation techniques, and providing practical examples using OpenAI and LangChain.
To begin exploring and implementing prompt engineering techniques:
- Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/NirDiamant/Prompt_Engineering.git - Navigate to the technique you're interested in:
cd all_prompt_engineering_techniques - Follow the detailed implementation guide in each technique's notebook.
We welcome contributions from the community! If you have a new technique or improvement to suggest:
- Fork the repository
- Create your feature branch:
git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature - Commit your changes:
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature' - Push to the branch:
git push origin feature/AmazingFeature - Open a pull request
This project is licensed under a custom non-commercial license - see the LICENSE file for details.
⭐️ If you find this repository helpful, please consider giving it a star!
Keywords: Prompt Engineering, AI, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, LLM, Language Models, NLP, Conversational AI, Zero-Shot Learning, Few-Shot Learning, Chain of Thought
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Prompt_Engineering
Similar Open Source Tools

Prompt_Engineering
Prompt Engineering Techniques is a comprehensive repository for learning, building, and sharing prompt engineering techniques, from basic concepts to advanced strategies for leveraging large language models. It provides step-by-step tutorials, practical implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative prompt engineering techniques. The repository covers fundamental concepts, core techniques, advanced strategies, optimization and refinement, specialized applications, and advanced applications in prompt engineering.
RAG_Techniques
Advanced RAG Techniques is a comprehensive collection of cutting-edge Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) tutorials aimed at enhancing the accuracy, efficiency, and contextual richness of RAG systems. The repository serves as a hub for state-of-the-art RAG enhancements, comprehensive documentation, practical implementation guidelines, and regular updates with the latest advancements. It covers a wide range of techniques from foundational RAG methods to advanced retrieval methods, iterative and adaptive techniques, evaluation processes, explainability and transparency features, and advanced architectures integrating knowledge graphs and recursive processing.

agentic-context-engine
Agentic Context Engine (ACE) is a framework that enables AI agents to learn from their execution feedback, continuously improving without fine-tuning or training data. It maintains a Skillbook of evolving strategies, extracting patterns from successful tasks and learning from failures transparently in context. ACE offers self-improving agents, better performance on complex tasks, token reduction in browser automation, and preservation of valuable knowledge over time. Users can integrate ACE with popular agent frameworks and benefit from its innovative approach to in-context learning.
slime
Slime is an LLM post-training framework for RL scaling that provides high-performance training and flexible data generation capabilities. It connects Megatron with SGLang for efficient training and enables custom data generation workflows through server-based engines. The framework includes modules for training, rollout, and data buffer management, offering a comprehensive solution for RL scaling.
Advanced-GPTs
Nerority's Advanced GPT Suite is a collection of 33 GPTs that can be controlled with natural language prompts. The suite includes tools for various tasks such as strategic consulting, business analysis, career profile building, content creation, educational purposes, image-based tasks, knowledge engineering, marketing, persona creation, programming, prompt engineering, role-playing, simulations, and task management. Users can access links, usage instructions, and guides for each GPT on their respective pages. The suite is designed for public demonstration and usage, offering features like meta-sequence optimization, AI priming, prompt classification, and optimization. It also provides tools for generating articles, analyzing contracts, visualizing data, distilling knowledge, creating educational content, exploring topics, generating marketing copy, simulating scenarios, managing tasks, and more.
rlhf_thinking_model
This repository is a collection of research notes and resources focusing on training large language models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It includes methodologies, techniques, and state-of-the-art approaches for optimizing preferences and model alignment in LLM training. The purpose is to serve as a reference for researchers and engineers interested in reinforcement learning, large language models, model alignment, and alternative RL-based methods.
BMAD-METHOD
BMAD-METHOD™ is a universal AI agent framework that revolutionizes Agile AI-Driven Development. It offers specialized AI expertise across various domains, including software development, entertainment, creative writing, business strategy, and personal wellness. The framework introduces two key innovations: Agentic Planning, where dedicated agents collaborate to create detailed specifications, and Context-Engineered Development, which ensures complete understanding and guidance for developers. BMAD-METHOD™ simplifies the development process by eliminating planning inconsistency and context loss, providing a seamless workflow for creating AI agents and expanding functionality through expansion packs.

xllm-service
xLLM-service is a service-layer framework developed based on the xLLM inference engine, providing efficient, fault-tolerant, and flexible LLM inference services for clustered deployment. It addresses challenges in enterprise-level service scenarios such as ensuring SLA of online services, improving resource utilization, reacting to changing request loads, resolving performance bottlenecks, and ensuring high reliability of computing instances. With features like unified scheduling, adaptive dynamic allocation, EPD three-stage disaggregation, and fault-tolerant architecture, xLLM-service offers efficient and reliable LLM inference services.
JamAIBase
JamAI Base is an open-source platform integrating SQLite and LanceDB databases with managed memory and RAG capabilities. It offers built-in LLM, vector embeddings, and reranker orchestration accessible through a spreadsheet-like UI and REST API. Users can transform static tables into dynamic entities, facilitate real-time interactions, manage structured data, and simplify chatbot development. The tool focuses on ease of use, scalability, flexibility, declarative paradigm, and innovative RAG techniques, making complex data operations accessible to users with varying technical expertise.
wanwu
Wanwu AI Agent Platform is an enterprise-grade one-stop commercially friendly AI agent development platform designed for business scenarios. It provides enterprises with a safe, efficient, and compliant one-stop AI solution. The platform integrates cutting-edge technologies such as large language models and business process automation to build an AI engineering platform covering model full life-cycle management, MCP, web search, AI agent rapid development, enterprise knowledge base construction, and complex workflow orchestration. It supports modular architecture design, flexible functional expansion, and secondary development, reducing the application threshold of AI technology while ensuring security and privacy protection of enterprise data. It accelerates digital transformation, cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and business innovation for enterprises of all sizes.
long-llms-learning
A repository sharing the panorama of the methodology literature on Transformer architecture upgrades in Large Language Models for handling extensive context windows, with real-time updating the newest published works. It includes a survey on advancing Transformer architecture in long-context large language models, flash-ReRoPE implementation, latest news on data engineering, lightning attention, Kimi AI assistant, chatglm-6b-128k, gpt-4-turbo-preview, benchmarks like InfiniteBench and LongBench, long-LLMs-evals for evaluating methods for enhancing long-context capabilities, and LLMs-learning for learning technologies and applicated tasks about Large Language Models.
Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.

xllm
xLLM is an efficient LLM inference framework optimized for Chinese AI accelerators, enabling enterprise-grade deployment with enhanced efficiency and reduced cost. It adopts a service-engine decoupled inference architecture, achieving breakthrough efficiency through technologies like elastic scheduling, dynamic PD disaggregation, multi-stream parallel computing, graph fusion optimization, and global KV cache management. xLLM supports deployment of mainstream large models on Chinese AI accelerators, empowering enterprises in scenarios like intelligent customer service, risk control, supply chain optimization, ad recommendation, and more.
AI-Engineering.academy
AI Engineering Academy aims to provide a structured learning path for individuals looking to learn Applied AI effectively. The platform offers multiple roadmaps covering topics like Retrieval Augmented Generation, Fine-tuning, and Deployment. Each roadmap equips learners with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in applied GenAI. Additionally, the platform will feature Hands-on End-to-End AI projects in the future.
AI6127
AI6127 is a course focusing on deep neural networks for natural language processing (NLP). It covers core NLP tasks and machine learning models, emphasizing deep learning methods using libraries like Pytorch. The course aims to teach students state-of-the-art techniques for practical NLP problems, including writing, debugging, and training deep neural models. It also explores advancements in NLP such as Transformers and ChatGPT.
beeai-platform
BeeAI is an open-source platform that simplifies the discovery, running, and sharing of AI agents across different frameworks. It addresses challenges such as framework fragmentation, deployment complexity, and discovery issues by providing a standardized platform for individuals and teams to access agents easily. With features like a centralized agent catalog, framework-agnostic interfaces, containerized agents, and consistent user experiences, BeeAI aims to streamline the process of working with AI agents for both developers and teams.
For similar tasks
ai-commits-intellij-plugin
AI Commits is a plugin for IntelliJ-based IDEs and Android Studio that generates commit messages using git diff and OpenAI. It offers features such as generating commit messages from diff using OpenAI API, computing diff only from selected files and lines in the commit dialog, creating custom prompts for commit message generation, using predefined variables and hints to customize prompts, choosing any of the models available in OpenAI API, setting OpenAI network proxy, and setting custom OpenAI compatible API endpoint.
extensionOS
Extension | OS is an open-source browser extension that brings AI directly to users' web browsers, allowing them to access powerful models like LLMs seamlessly. Users can create prompts, fix grammar, and access intelligent assistance without switching tabs. The extension aims to revolutionize online information interaction by integrating AI into everyday browsing experiences. It offers features like Prompt Factory for tailored prompts, seamless LLM model access, secure API key storage, and a Mixture of Agents feature. The extension was developed to empower users to unleash their creativity with custom prompts and enhance their browsing experience with intelligent assistance.
img-prompt
IMGPrompt is an AI prompt editor tailored for image and video generation tools like Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, DALL·E, FLUX, and Sora. It offers a clean interface for viewing and combining prompts with translations in multiple languages. The tool includes features like smart recommendations, translation, random color generation, prompt tagging, interactive editing, categorized tag display, character count, and localization. Users can enhance their creative workflow by simplifying prompt creation and boosting efficiency.
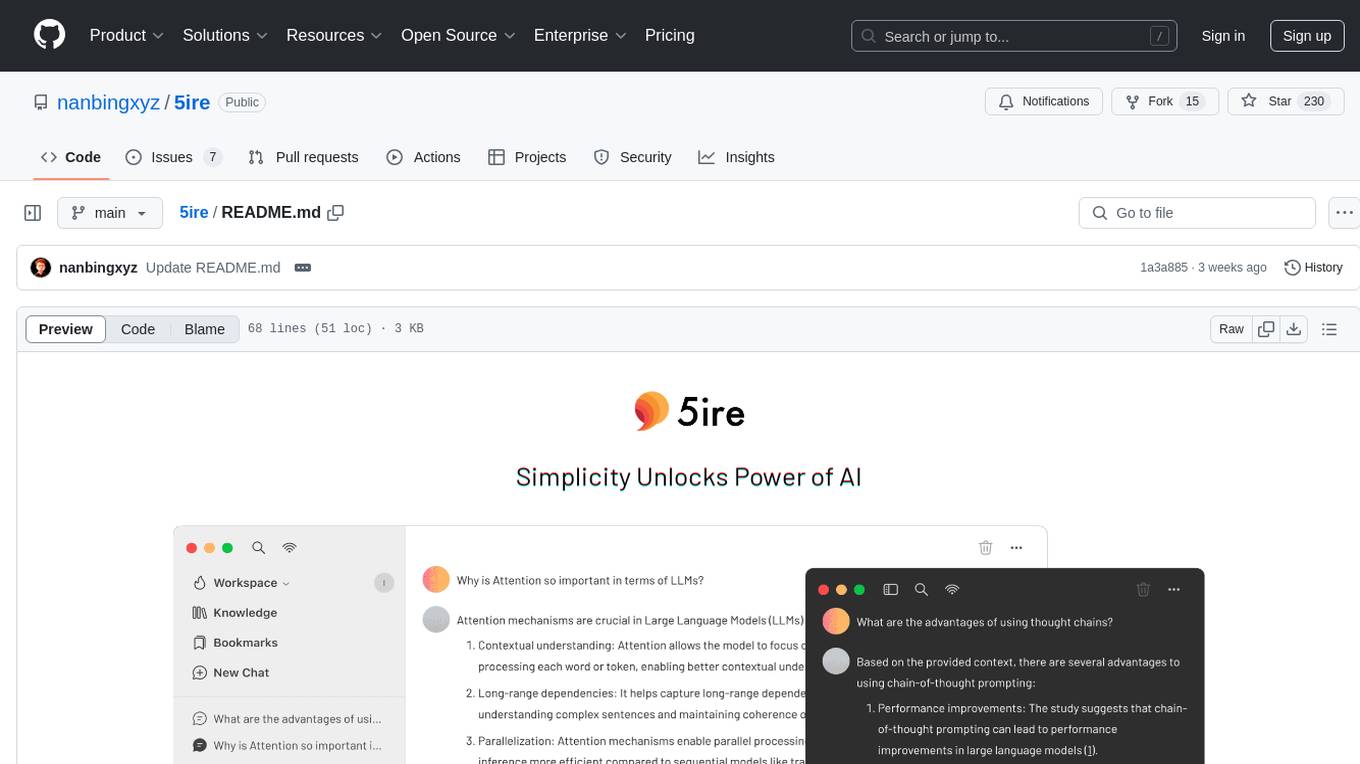
5ire
5ire is a cross-platform desktop client that integrates a local knowledge base for multilingual vectorization, supports parsing and vectorization of various document formats, offers usage analytics to track API spending, provides a prompts library for creating and organizing prompts with variable support, allows bookmarking of conversations, and enables quick keyword searches across conversations. It is licensed under the GNU General Public License version 3.

sidecar
Sidecar is the AI brains of Aide the editor, responsible for creating prompts, interacting with LLM, and ensuring seamless integration of all functionalities. It includes 'tool_box.rs' for handling language-specific smartness, 'symbol/' for smart and independent symbols, 'llm_prompts/' for creating prompts, and 'repomap' for creating a repository map using page rank on code symbols. Users can contribute by submitting bugs, feature requests, reviewing source code changes, and participating in the development workflow.
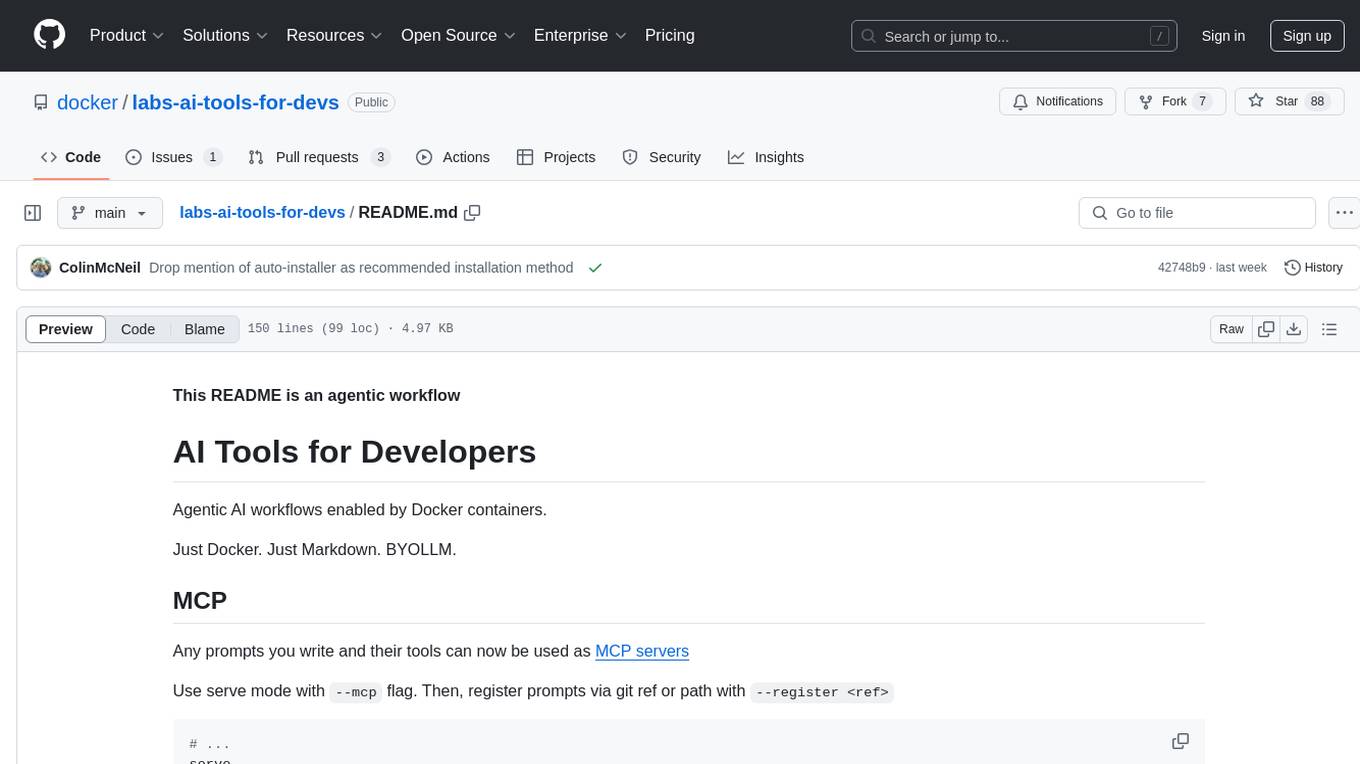
labs-ai-tools-for-devs
This repository provides AI tools for developers through Docker containers, enabling agentic workflows. It allows users to create complex workflows using Dockerized tools and Markdown, leveraging various LLM models. The core features include Dockerized tools, conversation loops, multi-model agents, project-first design, and trackable prompts stored in a git repo.

Prompt_Engineering
Prompt Engineering Techniques is a comprehensive repository for learning, building, and sharing prompt engineering techniques, from basic concepts to advanced strategies for leveraging large language models. It provides step-by-step tutorials, practical implementations, and a platform for showcasing innovative prompt engineering techniques. The repository covers fundamental concepts, core techniques, advanced strategies, optimization and refinement, specialized applications, and advanced applications in prompt engineering.
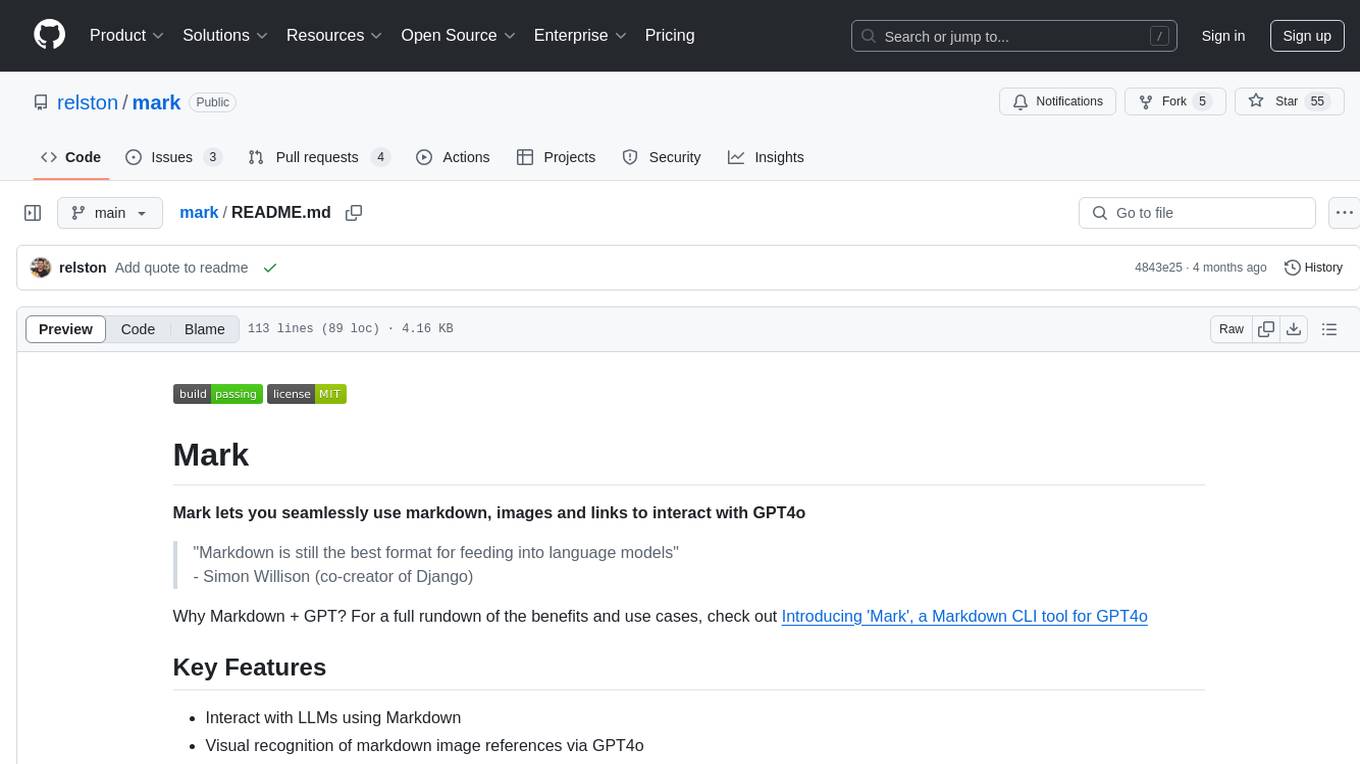
mark
Mark is a CLI tool that allows users to interact with large language models (LLMs) using Markdown format. It enables users to seamlessly integrate GPT responses into Markdown files, supports image recognition, scraping of local and remote links, and image generation. Mark focuses on using Markdown as both a prompt and response medium for LLMs, offering a unique and flexible way to interact with language models for various use cases in development and documentation processes.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.





