
Agent-R1
Agent-R1: Training Powerful LLM Agents with End-to-End Reinforcement Learning
Stars: 1225
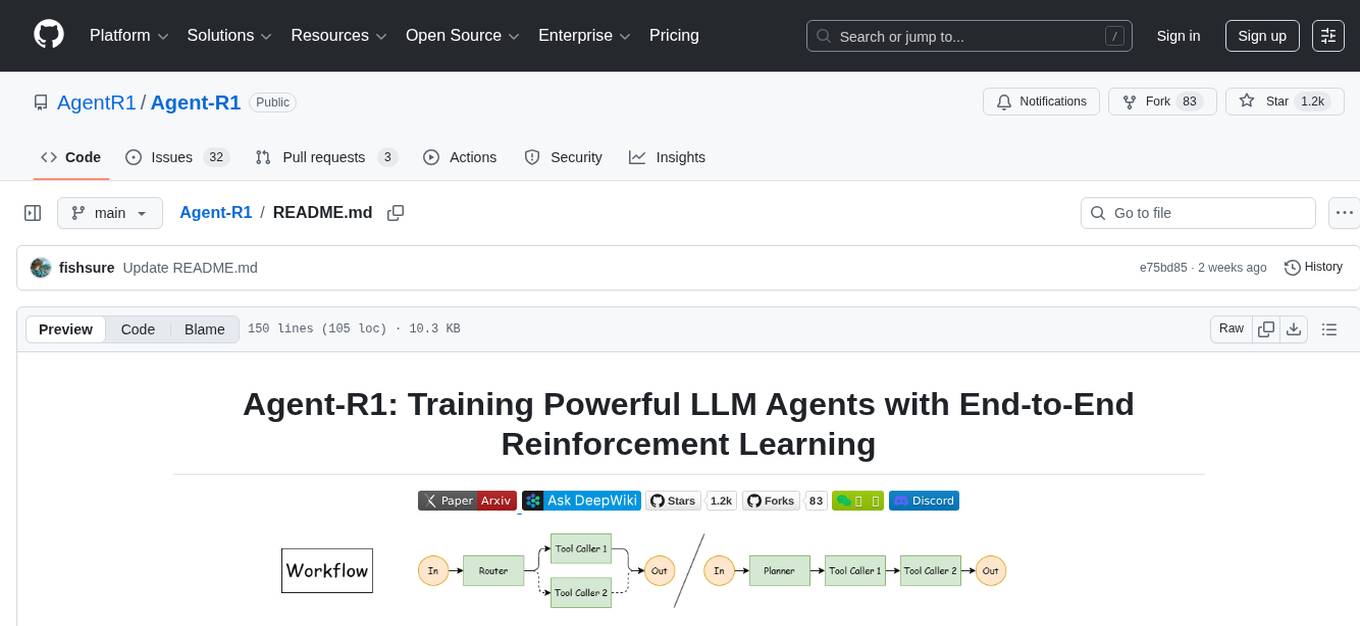
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
README:
Recent Updates
-
[2026.01.10] New Application Released: We are excited to introduce PaperScout, an autonomous agent for academic paper search trained using Agent-R1. It introduces a novel Proximal Sequence Policy Optimization (PSPO) method. Read the paper here.
-
[2025.11.18] Technical Report: We have released the technical report on arXiv. Read the paper here.
-
[2025.05.06] Tool Environment Redesign: Completely redesigned and abstracted tool environments to support more flexible and diverse agent-tool interactions patterns.
-
[2025.05.06] Critical Bug Fixes: Fixed GRPO and Reinforce++ training crash issues that were causing NaN values during training. See issue #30 for details.
-
[2025.05.06] New Tutorials: Added comprehensive tutorials for creating custom tools and tool environments, including the first open-source runnable implementation of ReTool.
Earlier Updates
-
[2025.04.01] Added basic inference scripts and a simple interactive chat interface. You can now easily deploy and interact with your trained models. See inference guide for details.
-
[2025.03.18] Added comprehensive multi-modal support! Agent-R1 now seamlessly integrates with vision-language models (VLMs), enabling agents to process and reason with both text and visual inputs in rich multi-modal environments.
-
[2025.03.18] Refactored our codebase to improve maintainability! We've converted verl from a static folder to a git submodule and separated our custom code extensions. This makes it easier to update
verland understand the project structure.Important: After pulling this update, you'll need to reinitialize your environment. Run
git submodule update --init --recursiveand reinstall verl locally from this directory. -
[2025.03.16] Added support for process rewards! You can now assign rewards for each tool call based on its effectiveness. To balance process rewards with outcome rewards, we implemented reward normalization inspired by PRIME.
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. Our framework employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers need only define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to their unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. We hope our modest contribution can benefit the open-source community, making it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents. For more details on the algorithm, see algorithm doc.
Also check out Awesome-Agent-RL: Our curated collection of papers and resources on unlocking the potential of Agents through Reinforcement Learning.
- Multi-turn Tool Calling: End-to-end reinforcement learning on complete interaction trajectories, allowing agents to learn from sequences of actions
- Multi-tool Coordination: Train agents to effectively coordinate and use multiple tools together to solve complex tasks
- Process Rewards: Assign rewards for each tool call based on its effectiveness, balanced with outcome rewards through normalization
- Custom Tools and Environments: Compatible with mainstream LLM tool calling formats, making it easy to extend with your own tools and scenarios
-
Multiple RL Algorithms: Supports diverse reinforcement learning approaches including
PPO,GRPO, andREINFORCE++ - Multi-modal Support: Compatible with vision-language models (VLMs) and multi-modal reinforcement learning
- Expanded Model Support: Integration with more foundation models beyond the currently supported Qwen
- Additional Use Cases: More example implementations across diverse scenarios and domains
Agent-R1 provides a flexible architecture for creating custom tools and tool environments to suit various agent applications. Our framework is built on two key abstractions:
- BaseTool: Individual tools that agents can use to interact with external systems
- BaseToolEnv: Tool environments that define the state transition function for agent-tool interactions
For detailed guidance on extending Agent-R1, refer to our tutorials:
- Customizing Tools for Multi-hop QA: Learn how to create and customize tools for retrieving information across multiple knowledge sources
- Customizing Tool Environment for ReTool: Understand how to implement tool environments that integrate code execution with LLM reasoning
Additional resources are available in the codebase:
- Example tools:
agent_r1/tool/tools/ - Example environments:
agent_r1/tool/envs/ - Data preprocessing:
examples/data_preprocess/ - Reward functions:
verl/utils/reward_score/
We welcome all forms of feedback! Please raise an issue for bugs, questions, or suggestions. This helps our team address common problems efficiently and builds a more productive community.
Join our community: Connect with other users and our development team in our WeChat group or Discord server.
Student Contributors: Jie Ouyang*, Ruiran Yan*, Yucong Luo*, Zirui Liu, Shuo Yu, Daoyu Wang
Supervisors: Qi Liu, Mingyue Cheng
Affiliation: State Key Laboratory of Cognitive Intelligence, USTC
We extend our gratitude to DeepSeek for providing the DeepSeek-R1 model and inspiring ideas. We are also thankful to the veRL team for their robust infrastructure support. Additionally, we acknowledge the RAGEN team for their groundbreaking discoveries, which significantly influenced our early exploration. Lastly, we deeply appreciate the insightful discussions and contributions from Jie Ouyang, Ruiran Yan, Yucong Luo, Zirui Liu, Shuo Yu and Daoyu Wang.
Agent-R1
@misc{cheng2025agentr1trainingpowerfulllm,
title={Agent-R1: Training Powerful LLM Agents with End-to-End Reinforcement Learning},
author={Mingyue Cheng and Jie Ouyang and Shuo Yu and Ruiran Yan and Yucong Luo and Zirui Liu and Daoyu Wang and Qi Liu and Enhong Chen},
year={2025},
eprint={2511.14460},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.14460},
}TableMind(WSDM 2026)
TableMind is built upon the Agent-R1 framework, leveraging its end-to-end reinforcement learning pipeline to train a specialized tool-augmented agent for structured table reasoning.
@article{jiang2025tablemind,
title={TableMind: An Autonomous Programmatic Agent for Tool-Augmented Table Reasoning},
author={Jiang, Chuang and Cheng, Mingyue and Tao, Xiaoyu and Mao, Qingyang and Ouyang, Jie and Liu, Qi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.06278},
year={2025}
}PaperScout (arXiv 2026)
PaperScout employs the Agent-R1 framework to build an autonomous agent for academic paper search. It introduces Proximal Sequence Policy Optimization (PSPO), a process-aware method designed to align token-level optimization with sequence-level agent interactions.
@misc{pan2026paperscoutautonomousagentacademic,
title={PaperScout: An Autonomous Agent for Academic Paper Search with Process-Aware Sequence-Level Policy Optimization},
author={Tingyue Pan and Jie Ouyang and Mingyue Cheng and Qingchuan Li and Zirui Liu and Mingfan Pan and Shuo Yu and Qi Liu},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.10029},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={[https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.10029](https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.10029)},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Agent-R1
Similar Open Source Tools

Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
AgentForge
AgentForge is a low-code framework tailored for the rapid development, testing, and iteration of AI-powered autonomous agents and Cognitive Architectures. It is compatible with a range of LLM models and offers flexibility to run different models for different agents based on specific needs. The framework is designed for seamless extensibility and database-flexibility, making it an ideal playground for various AI projects. AgentForge is a beta-testing ground and future-proof hub for crafting intelligent, model-agnostic autonomous agents.
beeai-platform
BeeAI is an open-source platform that simplifies the discovery, running, and sharing of AI agents across different frameworks. It addresses challenges such as framework fragmentation, deployment complexity, and discovery issues by providing a standardized platform for individuals and teams to access agents easily. With features like a centralized agent catalog, framework-agnostic interfaces, containerized agents, and consistent user experiences, BeeAI aims to streamline the process of working with AI agents for both developers and teams.
slime
Slime is an LLM post-training framework for RL scaling that provides high-performance training and flexible data generation capabilities. It connects Megatron with SGLang for efficient training and enables custom data generation workflows through server-based engines. The framework includes modules for training, rollout, and data buffer management, offering a comprehensive solution for RL scaling.
MARBLE
MARBLE (Multi-Agent Coordination Backbone with LLM Engine) is a modular framework for developing, testing, and evaluating multi-agent systems leveraging Large Language Models. It provides a structured environment for agents to interact in simulated environments, utilizing cognitive abilities and communication mechanisms for collaborative or competitive tasks. The framework features modular design, multi-agent support, LLM integration, shared memory, flexible environments, metrics and evaluation, industrial coding standards, and Docker support.
heurist-agent-framework
Heurist Agent Framework is a flexible multi-interface AI agent framework that allows processing text and voice messages, generating images and videos, interacting across multiple platforms, fetching and storing information in a knowledge base, accessing external APIs and tools, and composing complex workflows using Mesh Agents. It supports various platforms like Telegram, Discord, Twitter, Farcaster, REST API, and MCP. The framework is built on a modular architecture and provides core components, tools, workflows, and tool integration with MCP support.
BMAD-METHOD
BMAD-METHOD™ is a universal AI agent framework that revolutionizes Agile AI-Driven Development. It offers specialized AI expertise across various domains, including software development, entertainment, creative writing, business strategy, and personal wellness. The framework introduces two key innovations: Agentic Planning, where dedicated agents collaborate to create detailed specifications, and Context-Engineered Development, which ensures complete understanding and guidance for developers. BMAD-METHOD™ simplifies the development process by eliminating planning inconsistency and context loss, providing a seamless workflow for creating AI agents and expanding functionality through expansion packs.
ChatFAQ
ChatFAQ is an open-source comprehensive platform for creating a wide variety of chatbots: generic ones, business-trained, or even capable of redirecting requests to human operators. It includes a specialized NLP/NLG engine based on a RAG architecture and customized chat widgets, ensuring a tailored experience for users and avoiding vendor lock-in.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.

kagent
Kagent is a Kubernetes native framework for building AI agents, designed to be easy to understand and use. It provides a flexible and powerful way to build, deploy, and manage AI agents in Kubernetes. The framework consists of agents, tools, and model configurations defined as Kubernetes custom resources, making them easy to manage and modify. Kagent is extensible, flexible, observable, declarative, testable, and has core components like a controller, UI, engine, and CLI.
koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building and running AI agents entirely in idiomatic Kotlin. It allows users to create agents that interact with tools, handle complex workflows, and communicate with users. Key features include pure Kotlin implementation, MCP integration, embedding capabilities, custom tool creation, ready-to-use components, intelligent history compression, powerful streaming API, persistent agent memory, comprehensive tracing, flexible graph workflows, modular feature system, scalable architecture, and multiplatform support.
memU
MemU is an open-source memory framework designed for AI companions, offering high accuracy, fast retrieval, and cost-effectiveness. It serves as an intelligent 'memory folder' that adapts to various AI companion scenarios. With MemU, users can create AI companions that remember them, learn their preferences, and evolve through interactions. The framework provides advanced retrieval strategies, 24/7 support, and is specialized for AI companions. MemU offers cloud, enterprise, and self-hosting options, with features like memory organization, interconnected knowledge graph, continuous self-improvement, and adaptive forgetting mechanism. It boasts high memory accuracy, fast retrieval, and low cost, making it suitable for building intelligent agents with persistent memory capabilities.
FinRobot
FinRobot is an open-source AI agent platform designed for financial applications using large language models. It transcends the scope of FinGPT, offering a comprehensive solution that integrates a diverse array of AI technologies. The platform's versatility and adaptability cater to the multifaceted needs of the financial industry. FinRobot's ecosystem is organized into four layers, including Financial AI Agents Layer, Financial LLMs Algorithms Layer, LLMOps and DataOps Layers, and Multi-source LLM Foundation Models Layer. The platform's agent workflow involves Perception, Brain, and Action modules to capture, process, and execute financial data and insights. The Smart Scheduler optimizes model diversity and selection for tasks, managed by components like Director Agent, Agent Registration, Agent Adaptor, and Task Manager. The tool provides a structured file organization with subfolders for agents, data sources, and functional modules, along with installation instructions and hands-on tutorials.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
JamAIBase
JamAI Base is an open-source platform integrating SQLite and LanceDB databases with managed memory and RAG capabilities. It offers built-in LLM, vector embeddings, and reranker orchestration accessible through a spreadsheet-like UI and REST API. Users can transform static tables into dynamic entities, facilitate real-time interactions, manage structured data, and simplify chatbot development. The tool focuses on ease of use, scalability, flexibility, declarative paradigm, and innovative RAG techniques, making complex data operations accessible to users with varying technical expertise.
wanwu
Wanwu AI Agent Platform is an enterprise-grade one-stop commercially friendly AI agent development platform designed for business scenarios. It provides enterprises with a safe, efficient, and compliant one-stop AI solution. The platform integrates cutting-edge technologies such as large language models and business process automation to build an AI engineering platform covering model full life-cycle management, MCP, web search, AI agent rapid development, enterprise knowledge base construction, and complex workflow orchestration. It supports modular architecture design, flexible functional expansion, and secondary development, reducing the application threshold of AI technology while ensuring security and privacy protection of enterprise data. It accelerates digital transformation, cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and business innovation for enterprises of all sizes.
For similar tasks
SPAG
This repository contains the implementation of Self-Play of Adversarial Language Game (SPAG) as described in the paper 'Self-playing Adversarial Language Game Enhances LLM Reasoning'. The SPAG involves training Language Models (LLMs) in an adversarial language game called Adversarial Taboo. The repository provides tools for imitation learning, self-play episode collection, and reinforcement learning on game episodes to enhance LLM reasoning abilities. The process involves training models using GPUs, launching imitation learning, conducting self-play episodes, assigning rewards based on outcomes, and learning the SPAG model through reinforcement learning. Continuous improvements on reasoning benchmarks can be observed by repeating the episode-collection and SPAG-learning processes.

Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
crewAI-tools
The crewAI Tools repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents, enabling the creation of custom tools to enhance AI solutions. Tools play a crucial role in improving agent functionality. The guide explains how to equip agents with a range of tools and how to create new tools. Tools are designed to return strings for generating responses. There are two main methods for creating tools: subclassing BaseTool and using the tool decorator. Contributions to the toolset are encouraged, and the development setup includes steps for installing dependencies, activating the virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. Enhance AI agent capabilities with advanced tooling.

Toolio
Toolio is an OpenAI-like HTTP server API implementation that supports structured LLM response generation, making it conform to a JSON schema. It is useful for reliable tool calling and agentic workflows based on schema-driven output. Toolio is based on the MLX framework for Apple Silicon, specifically M1/M2/M3/M4 Macs. It allows users to host MLX-format LLMs for structured output queries and provides a command line client for easier usage of tools. The tool also supports multiple tool calls and the creation of custom tools for specific tasks.
lecca-io
Lecca.io is an AI platform that enables users to configure and deploy Large Language Models (LLMs) with customizable tools and workflows. Users can easily build, customize, and automate AI agents for various tasks. The platform offers features like custom LLM configuration, tool integration, workflow builder, built-in RAG functionalities, and the ability to create custom apps and triggers. Users can also automate LLMs by setting up triggers for autonomous operation. Lecca.io provides documentation for concepts, local development, creating custom apps, adding AI providers, and running Ollama locally. Contributions are welcome, and the platform is distributed under the Apache-2.0 License with Commons Clause, with enterprise features available under a Commercial License.
AI4U
AI4U is a tool that provides a framework for modeling virtual reality and game environments. It offers an alternative approach to modeling Non-Player Characters (NPCs) in Godot Game Engine. AI4U defines an agent living in an environment and interacting with it through sensors and actuators. Sensors provide data to the agent's brain, while actuators send actions from the agent to the environment. The brain processes the sensor data and makes decisions (selects an action by time). AI4U can also be used in other situations, such as modeling environments for artificial intelligence experiments.
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
godot_rl_agents
Godot RL Agents is an open-source package that facilitates the integration of Machine Learning algorithms with games created in the Godot Engine. It provides interfaces for popular RL frameworks, support for memory-based agents, 2D and 3D games, AI sensors, and is licensed under MIT. Users can train agents in the Godot editor, create custom environments, export trained agents in ONNX format, and utilize advanced features like different RL training frameworks.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.






