
spear
SPEAR: A Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research
Stars: 225
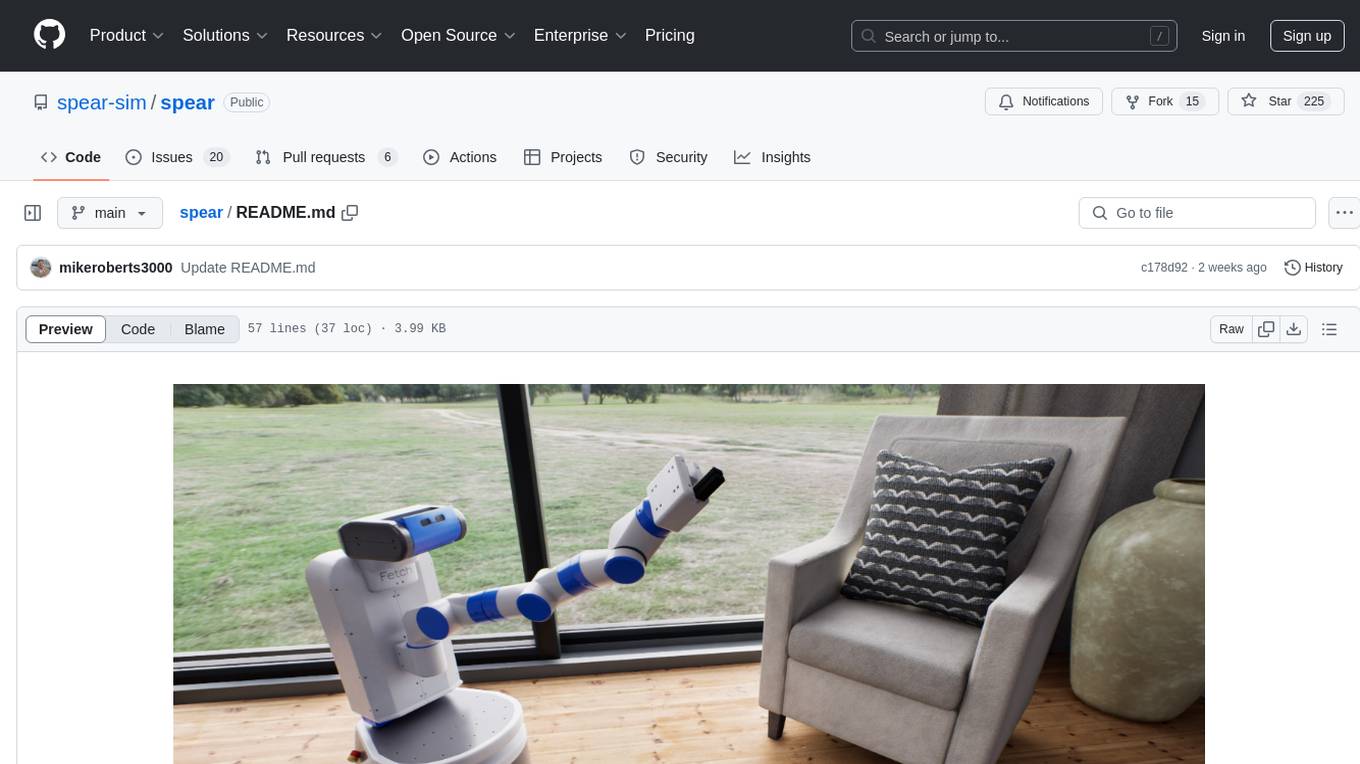
SPEAR is a Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research that addresses limitations in existing simulators by offering 300 unique virtual indoor environments with detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and unique floor plans. It provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interaction via Python, released under an MIT License. The simulator was developed with support from the Intelligent Systems Lab at Intel and Kujiale.
README:
Interactive simulators are becoming powerful tools for training embodied agents, but existing simulators suffer from limited content diversity, physical interactivity, and visual fidelity. We address these limitations by introducing SPEAR: A Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research. To create our simulator, we worked closely with a team of professional artists for over a year to construct 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each of our environments features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout designed by a professional artist, i.e., we do not rely on remixing existing layouts to create additional content. Our environments are implemented as Unreal Engine assets, and we provide an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.
The SPEAR code is released under an MIT License, and the SPEAR assets are released under various licenses that permit academic use.
If you find SPEAR useful in your research, please cite this repository as follows:
@misc{spear,
author = {Mike Roberts AND Rachith Prakash AND Renhan Wang AND Quentin Leboutet AND
Stephan R. Richter AND Stefan Leutenegger AND Rui Tang AND Matthias
M{\"u}ller AND German Ros AND Vladlen Koltun},
title = {{SPEAR}: {A} Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research},
howpublished = {\url{http://github.com/spear-sim/spear}}
}
Minimum and recommended system specifications for the Unreal Engine are given here.
See our latest release notes for download links. The easiest way to start working with SPEAR is to download a precompiled binary for your platform. Our precompiled binaries come pre-packaged with the scene pictured above. You can start interactively navigating around this scene with the keyboard and mouse simply by running the downloaded binary with no additional arguments.
- Our Getting Started tutorial explains how to interact with multiple scenes and our Python interface.
- Our Building SpearSim tutorial explains how to build from source.
- Our Importing and Exporting Assets tutorial explains how to import and export assets.
- Our Coding Guidelines document describes our coding standard.
- Our Contribution Guidelines document contains information on how to contribute effectively.
- The code in this repository is licensed under an MIT License.
- The licenses for all of our third-party code dependencies are given here.
- The
apartment,debug, andwarehousescenes are licensed under a CC0 License. - The OpenBot and Fetch assets in this repository are licensed under a CC0 License.
- The license for the
kujialescenes is given here. - The license for the
StarterContentassets referenced in thedebugscenes is given here.
From 2021 to 2024, SPEAR was developed with generous support from the Intelligent Systems Lab at Intel and Kujiale. Beginning in 2024, SPEAR is being developed by an independent consortium with generous support from Kujiale.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for spear
Similar Open Source Tools

spear
SPEAR is a Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research that addresses limitations in existing simulators by offering 300 unique virtual indoor environments with detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and unique floor plans. It provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interaction via Python, released under an MIT License. The simulator was developed with support from the Intelligent Systems Lab at Intel and Kujiale.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.
ModernBERT
ModernBERT is a repository focused on modernizing BERT through architecture changes and scaling. It introduces FlexBERT, a modular approach to encoder building blocks, and heavily relies on .yaml configuration files to build models. The codebase builds upon MosaicBERT and incorporates Flash Attention 2. The repository is used for pre-training and GLUE evaluations, with a focus on reproducibility and documentation. It provides a collaboration between Answer.AI, LightOn, and friends.
gen-cv
This repository is a rich resource offering examples of synthetic image generation, manipulation, and reasoning using Azure Machine Learning, Computer Vision, OpenAI, and open-source frameworks like Stable Diffusion. It provides practical insights into image processing applications, including content generation, video analysis, avatar creation, and image manipulation with various tools and APIs.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
AI4U
AI4U is a tool that provides a framework for modeling virtual reality and game environments. It offers an alternative approach to modeling Non-Player Characters (NPCs) in Godot Game Engine. AI4U defines an agent living in an environment and interacting with it through sensors and actuators. Sensors provide data to the agent's brain, while actuators send actions from the agent to the environment. The brain processes the sensor data and makes decisions (selects an action by time). AI4U can also be used in other situations, such as modeling environments for artificial intelligence experiments.
motleycrew
Motleycrew is an ultimate framework for building multi-agent AI systems, allowing users to mix and match AI agents and tools from popular frameworks, design advanced workflows, and leverage dynamic knowledge graphs with simplicity and elegance. It acts as a conductor orchestrating a symphony of AI agents and tools, providing building blocks for creating AI systems and enabling users to focus on high-level design while taking care of the rest. The framework offers integration with various tools, flexibility in providing agents with tools or other agents, advanced flow design capabilities, and built-in observability and caching features.
xef
xef.ai is a one-stop library designed to bring the power of modern AI to applications and services. It offers integration with Large Language Models (LLM), image generation, and other AI services. The library is packaged in two layers: core libraries for basic AI services integration and integrations with other libraries. xef.ai aims to simplify the transition to modern AI for developers by providing an idiomatic interface, currently supporting Kotlin. Inspired by LangChain and Hugging Face, xef.ai may transmit source code and user input data to third-party services, so users should review privacy policies and take precautions. Libraries are available in Maven Central under the `com.xebia` group, with `xef-core` as the core library. Developers can add these libraries to their projects and explore examples to understand usage.
serena
Serena is a powerful coding agent that integrates with existing LLMs to provide essential semantic code retrieval and editing tools. It is free to use and does not require API keys or subscriptions. Serena can be used for coding tasks such as analyzing, planning, and editing code directly on your codebase. It supports various programming languages and offers semantic code analysis capabilities through language servers. Serena can be integrated with different LLMs using the model context protocol (MCP) or Agno framework. The tool provides a range of functionalities for code retrieval, editing, and execution, making it a versatile coding assistant for developers.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
dbrx
DBRX is a large language model trained by Databricks and made available under an open license. It is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 132B total parameters and 36B live parameters, using 16 experts, of which 4 are active during training or inference. DBRX was pre-trained for 12T tokens of text and has a context length of 32K tokens. The model is available in two versions: a base model and an Instruct model, which is finetuned for instruction following. DBRX can be used for a variety of tasks, including text generation, question answering, summarization, and translation.
Robyn
Robyn is an experimental, semi-automated and open-sourced Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) package from Meta Marketing Science. It uses various machine learning techniques to define media channel efficiency and effectivity, explore adstock rates and saturation curves. Built for granular datasets with many independent variables, especially suitable for digital and direct response advertisers with rich data sources. Aiming to democratize MMM, make it accessible for advertisers of all sizes, and contribute to the measurement landscape.

NaLLM
The NaLLM project repository explores the synergies between Neo4j and Large Language Models (LLMs) through three primary use cases: Natural Language Interface to a Knowledge Graph, Creating a Knowledge Graph from Unstructured Data, and Generating a Report using static and LLM data. The repository contains backend and frontend code organized for easy navigation. It includes blog posts, a demo database, instructions for running demos, and guidelines for contributing. The project aims to showcase the potential of Neo4j and LLMs in various applications.
EasyLM
EasyLM is a one-stop solution for pre-training, fine-tuning, evaluating, and serving large language models in JAX/Flax. It simplifies the process by leveraging JAX's pjit functionality to scale up training to multiple TPU/GPU accelerators. Built on top of Huggingface's transformers and datasets, EasyLM offers an easy-to-use and customizable codebase for training large language models without the complexity found in other frameworks. It supports sharding model weights and training data across multiple accelerators, enabling multi-TPU/GPU training on a single host or across multiple hosts on Google Cloud TPU Pods. EasyLM currently supports models like LLaMA, LLaMA 2, and LLaMA 3.
SuperKnowa
SuperKnowa is a fast framework to build Enterprise RAG (Retriever Augmented Generation) Pipelines at Scale, powered by watsonx. It accelerates Enterprise Generative AI applications to get prod-ready solutions quickly on private data. The framework provides pluggable components for tackling various Generative AI use cases using Large Language Models (LLMs), allowing users to assemble building blocks to address challenges in AI-driven text generation. SuperKnowa is battle-tested from 1M to 200M private knowledge base & scaled to billions of retriever tokens.
morphik-core
Morphik is an AI-native toolset designed to help developers integrate context into their AI applications by providing tools to store, represent, and search unstructured data. It offers features such as multimodal search, fast metadata extraction, and integrations with existing tools. Morphik aims to address the challenges of traditional AI approaches that struggle with visually rich documents and provide a more comprehensive solution for understanding and processing complex data.
For similar tasks
stable-diffusion.cpp
The stable-diffusion.cpp repository provides an implementation for inferring stable diffusion in pure C/C++. It offers features such as support for different versions of stable diffusion, lightweight and dependency-free implementation, various quantization support, memory-efficient CPU inference, GPU acceleration, and more. Users can download the built executable program or build it manually. The repository also includes instructions for downloading weights, building from scratch, using different acceleration methods, running the tool, converting weights, and utilizing various features like Flash Attention, ESRGAN upscaling, PhotoMaker support, and more. Additionally, it mentions future TODOs and provides information on memory requirements, bindings, UIs, contributors, and references.
FileKitty
FileKitty is a simple file selection and concatenation tool that allows users to select files from a directory, concatenate them into a single file, save the concatenated file, and copy files to the clipboard. It is useful for concatenating files for use in a single file format and pasting file contents into an LLM to provide context to a prompt. The tool is built using Poetry to manage dependencies and build the app.
ppl.llm.kernel.cuda
ppl.llm.kernel.cuda is a primitive cuda kernel library for ppl.nn.llm system, designed for Ampere and Hopper architectures. It requires Linux running on x86_64 or arm64 CPUs with specific versions of GCC, CMake, Git, and CUDA Toolkit. Users can follow the provided Quick Start guide to install prerequisites, clone the source code, and build from source. The project is distributed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.

spear
SPEAR is a Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research that addresses limitations in existing simulators by offering 300 unique virtual indoor environments with detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and unique floor plans. It provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interaction via Python, released under an MIT License. The simulator was developed with support from the Intelligent Systems Lab at Intel and Kujiale.
vox-deorum
Vox Deorum is a tool that enhances the Civilization V gaming experience by incorporating AI-enhanced opponents powered by GPT, Claude, and other large language models. It allows players to interact with AI players using language models, review gameplay sessions with the Vox Deorum Replayer, and play with local models. The tool's architecture involves components like Community Patch DLL, Bridge Service, MCP Server, Vox Agents, and Lua integration scripts for Civ 5 Mod. Developers can build from source using Node.js, Python 3.x, Visual Studio Build Tools, and Git with LFS. The tool is designed to run on Windows 10/11 and requires an API key from a preferred LLM provider.
AgentGym
AgentGym is a framework designed to help the AI community evaluate and develop generally-capable Large Language Model-based agents. It features diverse interactive environments and tasks with real-time feedback and concurrency. The platform supports 14 environments across various domains like web navigating, text games, house-holding tasks, digital games, and more. AgentGym includes a trajectory set (AgentTraj) and a benchmark suite (AgentEval) to facilitate agent exploration and evaluation. The framework allows for agent self-evolution beyond existing data, showcasing comparable results to state-of-the-art models.
Everything-LLMs-And-Robotics
The Everything-LLMs-And-Robotics repository is the world's largest GitHub repository focusing on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Robotics. It provides educational resources, research papers, project demos, and Twitter threads related to LLMs, Robotics, and their combination. The repository covers topics such as reasoning, planning, manipulation, instructions and navigation, simulation frameworks, perception, and more, showcasing the latest advancements in the field.
anthrax-ai
AnthraxAI is a Vulkan-based game engine that allows users to create and develop 3D games. The engine provides features such as scene selection, camera movement, object manipulation, debugging tools, audio playback, and real-time shader code updates. Users can build and configure the project using CMake and compile shaders using the glslc compiler. The engine supports building on both Linux and Windows platforms, with specific dependencies for each. Visual Studio Code integration is available for building and debugging the project, with instructions provided in the readme for setting up the workspace and required extensions.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.