
torchtitan
A PyTorch native platform for training generative AI models
Stars: 5057
Torchtitan is a PyTorch native platform designed for rapid experimentation and large-scale training of generative AI models. It provides a flexible foundation for developers to build upon with extension points for creating custom extensions. The tool showcases PyTorch's latest distributed training features and supports pretraining Llama 3.1 LLMs of various sizes. It offers key features like multi-dimensional parallelisms, FSDP2 with per-parameter sharding, Tensor Parallel, Pipeline Parallel, and more. Users can contribute to the tool through the experiments folder and core contributions guidelines. Installation can be done from source, nightly builds, or stable releases. The tool also supports training Llama 3.1 models and provides guidance on starting a training run and multi-node training. Citation information is available for referencing the tool in academic work, and the source code is under a BSD 3 license.
README:
torchtitan is under extensive development. To use the latest features of torchtitan, we recommend using the most recent PyTorch nightly.
- [2025/11] AMD released an optimized fork of
torchtitanfor AMD GPUs. - [2025/10] We released
torchtitanv0.2.0. - [2025/10] SkyPilot now supports
torchtitan! See the tutorial here. - [2025/07] We published instructions on how to add a model to
torchtitan. - [2025/04] Our paper was accepted by ICLR 2025.
- [2024/12] GPU MODE lecture on torchtitan.
- [2024/07] Presentation at PyTorch Conference 2024.
torchtitan is a PyTorch native platform designed for rapid experimentation and large-scale training of generative AI models. As a minimal clean-room implementation of PyTorch native scaling techniques, torchtitan provides a flexible foundation for developers to build upon. With torchtitan extension points, one can easily create custom extensions tailored to specific needs.
Our mission is to accelerate innovation in the field of generative AI by empowering researchers and developers to explore new modeling architectures and infrastructure techniques.
The Guiding Principles when building torchtitan
- Designed to be easy to understand, use and extend for different training purposes.
- Minimal changes to the model code when applying multi-dimensional parallelism.
- Bias towards a clean, minimal codebase while providing basic reusable / swappable components.
torchtitan has been showcasing PyTorch's latest distributed training features, via support for pretraining Llama 3.1 LLMs of various sizes.
We look forward to your contributions!
- To accelerate contributions to and innovations around torchtitan, we host an
experimentsfolder. New ideas should start there. To contribute, follow theexperiments guidelines. - For fixes and contributions to core, follow these
guidelines.
- Multi-dimensional composable parallelisms
- FSDP2 with per-parameter sharding
- Tensor Parallel (including async TP)
- Pipeline Parallel
- Context Parallel
- Meta device initialization
- Selective (layer or operator) and full activation checkpointing
-
Distributed checkpointing (including async checkpointing)
-
Interoperable checkpoints which can be loaded directly into
torchtunefor fine-tuning
-
Interoperable checkpoints which can be loaded directly into
-
torch.compilesupport - Float8 support (how-to)
- MXFP8 training for dense and MoE models on Blackwell GPUs.
- DDP and HSDP
- TorchFT integration
- Checkpointable data-loading, with the C4 dataset pre-configured (144M entries) and support for custom datasets
- Gradient accumulation, enabled by giving an additional
--training.global_batch_sizeargument in configuration - Flexible learning rate scheduler (warmup-stable-decay)
- Loss, GPU memory, throughput (tokens/sec), TFLOPs, and MFU displayed and logged via Tensorboard or Weights & Biases
- Debugging tools including CPU/GPU profiling, memory profiling, Flight Recorder, etc.
- All options easily configured via toml files
-
Helper scripts to
- download tokenizers from Hugging Face
- convert original Llama 3 checkpoints into the expected DCP format
- estimate FSDP/HSDP memory usage without materializing the model
- run distributed inference with Tensor Parallel
We report performance on up to 512 GPUs, and verify loss converging correctness of various techniques.
You may want to see how the model is defined or how parallelism techniques are applied. For a guided tour, see these files first:
- torchtitan/train.py - the main training loop and high-level setup code
- torchtitan/models/llama3/model/model.py - the Llama 3.1 model definition
-
torchtitan/models/llama3/infra/parallelize.py - helpers for applying Data Parallel, Tensor Parallel, activation checkpointing, and
torch.compileto the model - torchtitan/models/llama3/infra/pipeline.py - helpers for applying Pipeline Parallel to the model
- torchtitan/components/checkpoint.py - utils for saving/loading distributed checkpoints
- torchtitan/components/quantization/float8.py - utils for applying Float8 techniques
One can directly run the source code, or install torchtitan from a nightly build, or a stable release.
This method requires the nightly build of PyTorch, or the latest PyTorch built from source.
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/torchtitan
cd torchtitan
pip install -r requirements.txtThis method requires the nightly build of PyTorch. You can replace cu126 with another version of cuda (e.g. cu128) or an AMD GPU (e.g. rocm6.3).
pip3 install --pre torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu126 --force-reinstall
pip install --pre torchtitan --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu126One can install the latest stable release of torchtitan via pip or conda.
pip install torchtitanconda install conda-forge::torchtitanNote that each stable release pins the nightly versions of torch and torchao. Please see release.md for more details.
torchtitan currently supports training Llama 3.1 (8B, 70B, 405B) out of the box. To get started training these models, we need to download the tokenizer. Follow the instructions on the official meta-llama repository to ensure you have access to the Llama model weights.
Once you have confirmed access, you can run the following command to download the Llama 3.1 tokenizer to your local machine.
# Get your HF token from https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
# Llama 3.1 tokenizer
python scripts/download_hf_assets.py --repo_id meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B --assets tokenizer --hf_token=...Llama 3 8B model locally on 8 GPUs
CONFIG_FILE="./torchtitan/models/llama3/train_configs/llama3_8b.toml" ./run_train.shFor training on ParallelCluster/Slurm type configurations, you can use the multinode_trainer.slurm file to submit your sbatch job.
To get started adjust the number of nodes and GPUs
#SBATCH --ntasks=2
#SBATCH --nodes=2
Then start a run where nnodes is your total node count, matching the sbatch node count above.
srun torchrun --nnodes 2
If your gpu count per node is not 8, adjust --nproc_per_node in the torchrun command and #SBATCH --gpus-per-task in the SBATCH command section.
We provide a detailed look into the parallelisms and optimizations available in torchtitan, along with summary advice on when to use various techniques.
TorchTitan: One-stop PyTorch native solution for production ready LLM pre-training
@inproceedings{
liang2025torchtitan,
title={TorchTitan: One-stop PyTorch native solution for production ready {LLM} pretraining},
author={Wanchao Liang and Tianyu Liu and Less Wright and Will Constable and Andrew Gu and Chien-Chin Huang and Iris Zhang and Wei Feng and Howard Huang and Junjie Wang and Sanket Purandare and Gokul Nadathur and Stratos Idreos},
booktitle={The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2025},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=SFN6Wm7YBI}
}
Source code is made available under a BSD 3 license, however you may have other legal obligations that govern your use of other content linked in this repository, such as the license or terms of service for third-party data and models.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for torchtitan
Similar Open Source Tools
For similar tasks
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.

DocsGPT
DocsGPT is an open-source documentation assistant powered by GPT models. It simplifies the process of searching for information in project documentation by allowing developers to ask questions and receive accurate answers. With DocsGPT, users can say goodbye to manual searches and quickly find the information they need. The tool aims to revolutionize project documentation experiences and offers features like live previews, Discord community, guides, and contribution opportunities. It consists of a Flask app, Chrome extension, similarity search index creation script, and a frontend built with Vite and React. Users can quickly get started with DocsGPT by following the provided setup instructions and can contribute to its development by following the guidelines in the CONTRIBUTING.md file. The project follows a Code of Conduct to ensure a harassment-free community environment for all participants. DocsGPT is licensed under MIT and is built with LangChain.
Ollamac
Ollamac is a macOS app designed for interacting with Ollama models. It is optimized for macOS, allowing users to easily use any model from the Ollama library. The app features a user-friendly interface, chat archive for saving interactions, and real-time communication using HTTP streaming technology. Ollamac is open-source, enabling users to contribute to its development and enhance its capabilities. It requires macOS 14 or later and the Ollama system to be installed on the user's Mac with at least one Ollama model downloaded.
npi
NPi is an open-source platform providing Tool-use APIs to empower AI agents with the ability to take action in the virtual world. It is currently under active development, and the APIs are subject to change in future releases. NPi offers a command line tool for installation and setup, along with a GitHub app for easy access to repositories. The platform also includes a Python SDK and examples like Calendar Negotiator and Twitter Crawler. Join the NPi community on Discord to contribute to the development and explore the roadmap for future enhancements.
ain
DeFiChain is a blockchain platform dedicated to enabling decentralized finance with Bitcoin-grade security, strength, and immutability. It offers fast, intelligent, and transparent financial services accessible to everyone. DeFiChain has made significant modifications from Bitcoin Core, including moving to Proof-of-Stake, introducing a masternode model, supporting a community fund, anchoring to the Bitcoin blockchain, and enhancing decentralized financial transaction and opcode support. The platform is under active development with regular releases and contributions are welcomed.
doc-comments-ai
doc-comments-ai is a tool designed to automatically generate code documentation using language models. It allows users to easily create documentation comment blocks for methods in various programming languages such as Python, Typescript, Javascript, Java, Rust, and more. The tool supports both OpenAI and local LLMs, ensuring data privacy and security. Users can generate documentation comments for methods in files, inline comments in method bodies, and choose from different models like GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4, and Azure OpenAI. Additionally, the tool provides support for Treesitter integration and offers guidance on selecting the appropriate model for comprehensive documentation needs.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
ansible-power-aix
The IBM Power Systems AIX Collection provides modules to manage configurations and deployments of Power AIX systems, enabling workloads on Power platforms as part of an enterprise automation strategy through the Ansible ecosystem. It includes example best practices, requirements for AIX versions, Ansible, and Python, along with resources for documentation and contribution.
For similar jobs
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
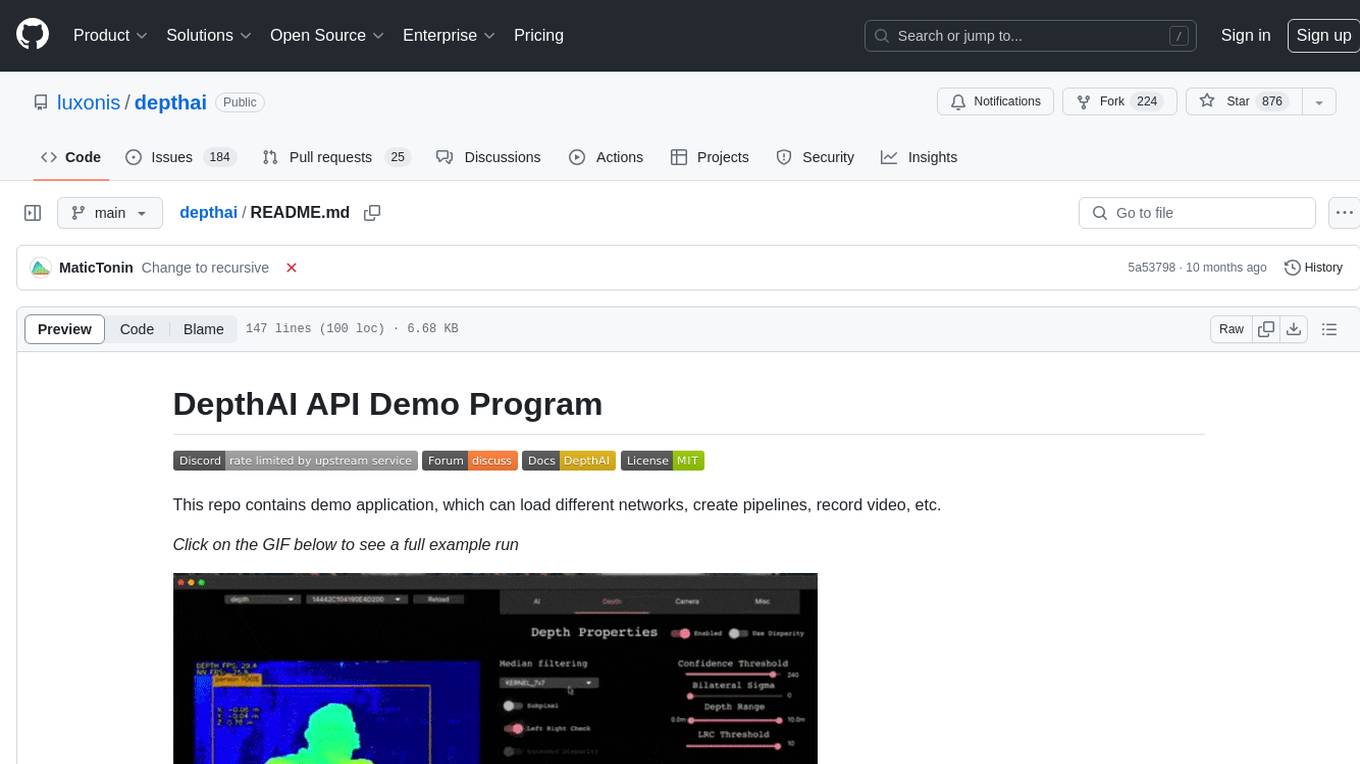
depthai
This repository contains a demo application for DepthAI, a tool that can load different networks, create pipelines, record video, and more. It provides documentation for installation and usage, including running programs through Docker. Users can explore DepthAI features via command line arguments or a clickable QT interface. Supported models include various AI models for tasks like face detection, human pose estimation, and object detection. The tool collects anonymous usage statistics by default, which can be disabled. Users can report issues to the development team for support and troubleshooting.





