awesome-air-quality
An awesome list of air quality resources.
Stars: 56
The 'awesome-air-quality' repository is a curated list of software libraries, tools, and resources related to air quality data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. It includes libraries in various programming languages such as Python, Java, R, and C#, as well as hardware drivers and software for gas sensors and particulate matter sensors. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools for working with air quality data from different sources and for different purposes.
README:
Please read our contributing guidelines and open a pull-request.
-
C#
- openair - National air quality data acquisition library (Chinese)
-
Java
- NAPSDataAnalysis - Canadian National Air Pollution Surveillance Program (NAPS) data downloader, importer, extractor, analysis, and visualization toolbox.
-
NodeJS
- openaq - A JS client for the OpenAQ API
-
Python
- airbase - An easy downloader for the AirBase air quality data.
- atmospy - visualization and analysis tools for air quality data in python
- py-openaq - python wrapper for the OpenAQ API
- py-quantaq - A python wrapper for the QuantAQ RESTful API
- py-opcsim - Python library to simulate OPCs and Nephlometers under different conditions
- py-smps - Python library for the analysis and visualization of data from a Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer (SMPS) and other similar instruments (SEMS, OPC's).
- python-aqi - A library to convert between AQI value and pollutant concentration (µg/m³ or ppm)
- The QuantAQ CLI - QuantAQ command line interface
- quantpy - Provides tools for visually evaluating low-cost air quality sensors
- sensortoolkit - Air Sensor Data Analysis Library
-
R
- AirBeamR - An interactive data tool to visualize and work with AirBeam, OpenAQ, and PurpleAir data
- AirMonitor - Utilities for working with air quality monitoring data CRAN
- AirSensor - Utilities for working with data from PurpleAir sensorsCRAN
- AMET - Code base for the U.S. EPA’s Atmospheric Model Evaluation Tool (AMET).
- beethoven - BEETHOVEN is: Building an Extensible, rEproducible, Test-driven, Harmonized, Open-source, Versioned, ENsemble model for air quality.
- CMAQ - Code for U.S. EPA’s Community Multiscale Air Quality Model (CMAQ) which helps in conducting air quality model simulations.
- openair - Tools to analyse, interpret and understand air pollution data. Data are typically hourly time series and both monitoring data and dispersion model output can be analysed. Many functions can also be applied to other data, including meteorological and traffic data. CRAN
- openairmaps - mapping functions to support openair CRAN
- Purple Air Data Merger - Merges and corrects Purple Air SD Card Data
- qualR - This is the qualR package, it will help you bring São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro air quality data to your R session 🇧🇷.
- quantr - Provides tools for visually evaluating low-cost air quality sensors
- RAQSAPI - A R extension to Retrieve EPA Air Quality System Data via the AQS Data Mart API.
- rmweather - Tools to Conduct Meteorological Normalisation on Air Quality Data.
- rPollution - R functions to work with air pollution data
- r-quantaq - The official R wrapper for the QuantAQ API
- saqgetr - Import Air Quality Monitoring Data in a Fast and Easy Way
- sensortoolkit - _A collection of R scripts for managing an air quality sensor network
- biteSizedAQ - A collection of bite sized projects aimed at democratizing access to air quality data, pipelines and insights in a manner that is free, open, accessible and easy to understand. Air pollution can feel like a giant overwhelming issue and it is, but by consistently taking bite-sized smart steps, we can collectively make significant progress in tackling it!
-
Rust
- openaq-client - Unofficial Open Air Quality API Client written in Rust crate
-
C
-
C++
- Nova Fitness SDS dust sensors arduino library
- PMS - Arduino library for Plantower PMS x003 family sensors.
- Sensirion SPS30 driver for ESP32, SODAQ, MEGA2560, UNO, ESP8266, Particle-photon on UART OR I2C coummunication
- Arduino library for Sensirion SCD4x sensors
- Embedded UART Driver for Sensirion Particulate Matter Sensors
-
Python
- bme680-python - Python library for the BME680 gas, temperature, humidity and pressure sensor.
- py-licor - Python logging software for the Licor 840 CO2/H2O analyzer
- Software to read out Sensirion SCD30 CO₂ Sensor values over I2C on Raspberry Pi
- Sentinair - A flexible tool for data acquisition from heterogeneous low-cost gas sensors and other devices
-
Rust
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for awesome-air-quality
Similar Open Source Tools

awesome-air-quality
The 'awesome-air-quality' repository is a curated list of software libraries, tools, and resources related to air quality data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. It includes libraries in various programming languages such as Python, Java, R, and C#, as well as hardware drivers and software for gas sensors and particulate matter sensors. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools for working with air quality data from different sources and for different purposes.
awesome-mlops
Awesome MLOps is a curated list of tools related to Machine Learning Operations, covering areas such as AutoML, CI/CD for Machine Learning, Data Cataloging, Data Enrichment, Data Exploration, Data Management, Data Processing, Data Validation, Data Visualization, Drift Detection, Feature Engineering, Feature Store, Hyperparameter Tuning, Knowledge Sharing, Machine Learning Platforms, Model Fairness and Privacy, Model Interpretability, Model Lifecycle, Model Serving, Model Testing & Validation, Optimization Tools, Simplification Tools, Visual Analysis and Debugging, and Workflow Tools. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of tools and resources for individuals and teams working in the field of MLOps.
doris
Doris is a lightweight and user-friendly data visualization tool designed for quick and easy exploration of datasets. It provides a simple interface for users to upload their data and generate interactive visualizations without the need for coding. With Doris, users can easily create charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze and present their data in a visually appealing way. The tool supports various data formats and offers customization options to tailor visualizations to specific needs. Whether you are a data analyst, researcher, or student, Doris simplifies the process of data exploration and presentation.

Bodo
Bodo is a high-performance Python compute engine designed for large-scale data processing and AI workloads. It utilizes an auto-parallelizing just-in-time compiler to optimize Python programs, making them 20x to 240x faster compared to alternatives. Bodo seamlessly integrates with native Python APIs like Pandas and NumPy, eliminates runtime overheads using MPI for distributed execution, and provides exceptional performance and scalability for data workloads. It is easy to use, interoperable with the Python ecosystem, and integrates with modern data platforms like Apache Iceberg and Snowflake. Bodo focuses on data-intensive and computationally heavy workloads in data engineering, data science, and AI/ML, offering automatic optimization and parallelization, linear scalability, advanced I/O support, and a high-performance SQL engine.

deepflow
DeepFlow is an open-source project that provides deep observability for complex cloud-native and AI applications. It offers Zero Code data collection with eBPF for metrics, distributed tracing, request logs, and function profiling. DeepFlow is integrated with SmartEncoding to achieve Full Stack correlation and efficient access to all observability data. With DeepFlow, cloud-native and AI applications automatically gain deep observability, removing the burden of developers continually instrumenting code and providing monitoring and diagnostic capabilities covering everything from code to infrastructure for DevOps/SRE teams.

ReaLHF
ReaLHF is a distributed system designed for efficient RLHF training with Large Language Models (LLMs). It introduces a novel approach called parameter reallocation to dynamically redistribute LLM parameters across the cluster, optimizing allocations and parallelism for each computation workload. ReaL minimizes redundant communication while maximizing GPU utilization, achieving significantly higher Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) training throughput compared to other systems. It supports large-scale training with various parallelism strategies and enables memory-efficient training with parameter and optimizer offloading. The system seamlessly integrates with HuggingFace checkpoints and inference frameworks, allowing for easy launching of local or distributed experiments. ReaLHF offers flexibility through versatile configuration customization and supports various RLHF algorithms, including DPO, PPO, RAFT, and more, while allowing the addition of custom algorithms for high efficiency.
awesome-openvino
Awesome OpenVINO is a curated list of AI projects based on the OpenVINO toolkit, offering a rich assortment of projects, libraries, and tutorials covering various topics like model optimization, deployment, and real-world applications across industries. It serves as a valuable resource continuously updated to maximize the potential of OpenVINO in projects, featuring projects like Stable Diffusion web UI, Visioncom, FastSD CPU, OpenVINO AI Plugins for GIMP, and more.
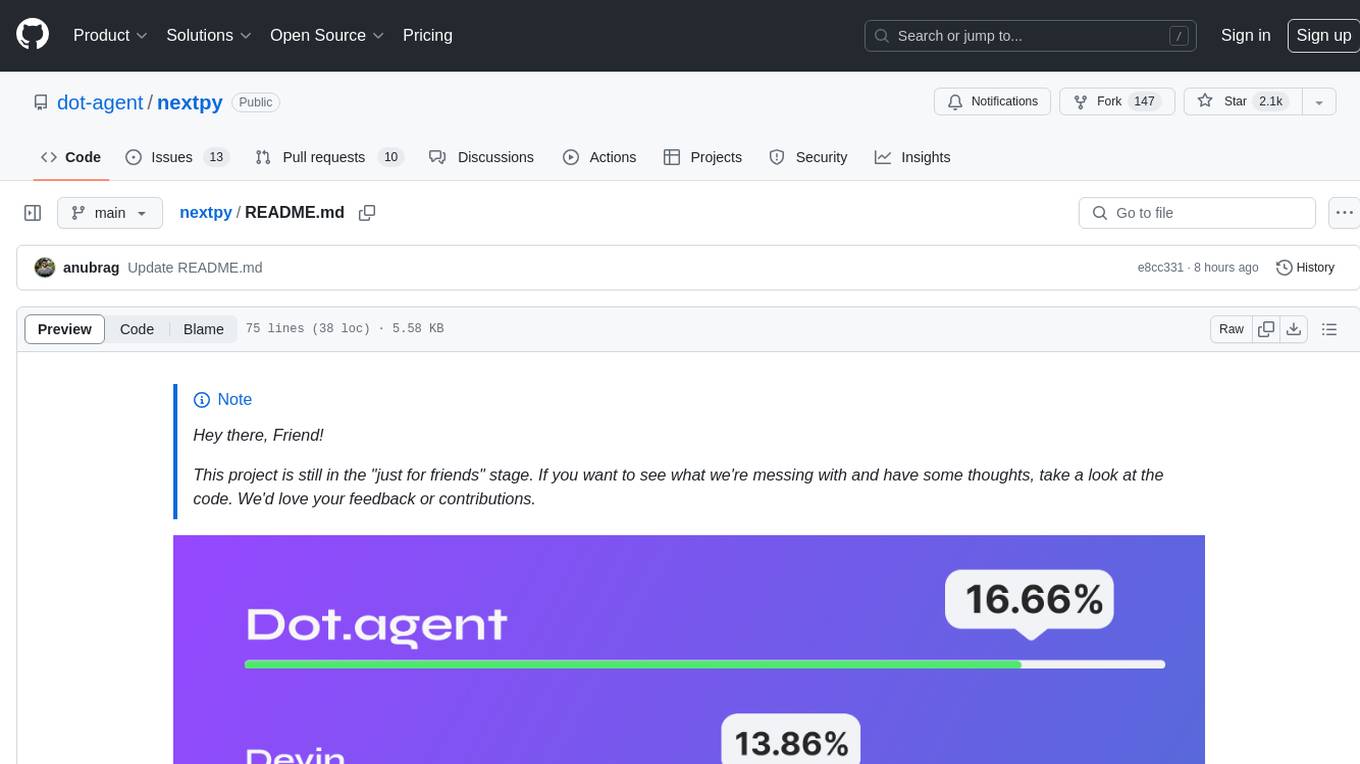
nextpy
Nextpy is a cutting-edge software development framework optimized for AI-based code generation. It provides guardrails for defining AI system boundaries, structured outputs for prompt engineering, a powerful prompt engine for efficient processing, better AI generations with precise output control, modularity for multiplatform and extensible usage, developer-first approach for transferable knowledge, and containerized & scalable deployment options. It offers 4-10x faster performance compared to Streamlit apps, with a focus on cooperation within the open-source community and integration of key components from various projects.
geoai
geoai is a Python package designed for utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the context of geospatial data. It allows users to visualize various types of geospatial data such as vector, raster, and LiDAR data. Additionally, the package offers functionalities for segmenting remote sensing imagery using the Segment Anything Model and classifying remote sensing imagery with deep learning models. With a focus on geospatial AI applications, geoai provides a versatile tool for processing and analyzing spatial data with the power of AI.

vulcan-sql
VulcanSQL is an Analytical Data API Framework for AI agents and data apps. It aims to help data professionals deliver RESTful APIs from databases, data warehouses or data lakes much easier and secure. It turns your SQL into APIs in no time!
dagger
Dagger is an open-source runtime for composable workflows, ideal for systems requiring repeatability, modularity, observability, and cross-platform support. It features a reproducible execution engine, a universal type system, a powerful data layer, native SDKs for multiple languages, an open ecosystem, an interactive command-line environment, batteries-included observability, and seamless integration with various platforms and frameworks. It also offers LLM augmentation for connecting to LLM endpoints. Dagger is suitable for AI agents and CI/CD workflows.
cube
Cube is a semantic layer for building data applications, helping data engineers and application developers access data from modern data stores, organize it into consistent definitions, and deliver it to every application. It works with SQL-enabled data sources, providing sub-second latency and high concurrency for API requests. Cube addresses SQL code organization, performance, and access control issues in data applications, enabling efficient data modeling, access control, and performance optimizations for various tools like embedded analytics, dashboarding, reporting, and data notebooks.

RAGFoundry
RAG Foundry is a library designed to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by fine-tuning models on RAG-augmented datasets. It helps create training data, train models using parameter-efficient finetuning (PEFT), and measure performance using RAG-specific metrics. The library is modular, customizable using configuration files, and facilitates prototyping with various RAG settings and configurations for tasks like data processing, retrieval, training, inference, and evaluation.
aihwkit
The IBM Analog Hardware Acceleration Kit is an open-source Python toolkit for exploring and using the capabilities of in-memory computing devices in the context of artificial intelligence. It consists of two main components: Pytorch integration and Analog devices simulator. The Pytorch integration provides a series of primitives and features that allow using the toolkit within PyTorch, including analog neural network modules, analog training using torch training workflow, and analog inference using torch inference workflow. The Analog devices simulator is a high-performant (CUDA-capable) C++ simulator that allows for simulating a wide range of analog devices and crossbar configurations by using abstract functional models of material characteristics with adjustable parameters. Along with the two main components, the toolkit includes other functionalities such as a library of device presets, a module for executing high-level use cases, a utility to automatically convert a downloaded model to its equivalent Analog model, and integration with the AIHW Composer platform. The toolkit is currently in beta and under active development, and users are advised to be mindful of potential issues and keep an eye for improvements, new features, and bug fixes in upcoming versions.

RAG-FiT
RAG-FiT is a library designed to improve Language Models' ability to use external information by fine-tuning models on specially created RAG-augmented datasets. The library assists in creating training data, training models using parameter-efficient finetuning (PEFT), and evaluating performance using RAG-specific metrics. It is modular, customizable via configuration files, and facilitates fast prototyping and experimentation with various RAG settings and configurations.
For similar tasks

awesome-air-quality
The 'awesome-air-quality' repository is a curated list of software libraries, tools, and resources related to air quality data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. It includes libraries in various programming languages such as Python, Java, R, and C#, as well as hardware drivers and software for gas sensors and particulate matter sensors. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools for working with air quality data from different sources and for different purposes.
For similar jobs

awesome-air-quality
The 'awesome-air-quality' repository is a curated list of software libraries, tools, and resources related to air quality data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. It includes libraries in various programming languages such as Python, Java, R, and C#, as well as hardware drivers and software for gas sensors and particulate matter sensors. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of tools for working with air quality data from different sources and for different purposes.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.