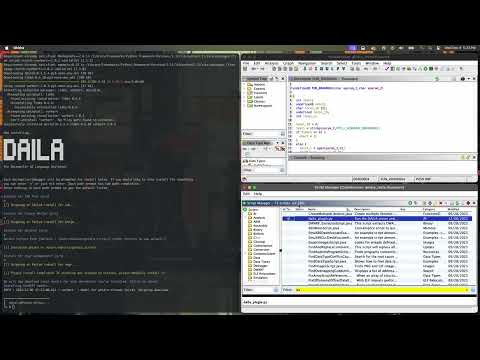
DAILA
A decompiler-agnostic plugin for interacting with AI in your decompiler. GPT-4, Claude, and local models supported!
Stars: 600
DAILA is a unified interface for AI systems in decompilers, supporting various decompilers and AI systems. It allows users to utilize local and remote LLMs, like ChatGPT and Claude, and local models such as VarBERT. DAILA can be used as a decompiler plugin with GUI or as a scripting library. It also provides a Docker container for offline installations and supports tasks like summarizing functions and renaming variables in decompilation.
README:
The Decompiler Artificial Intelligence Language Assistant (DAILA) is a unified interface for AI systems to be used in decompilers. Using DAILA, you can utilize various AI systems, like local and remote LLMs, all in the same scripting and GUI interfaces across many decompilers. DAILA was featured in the keynote talk at HITCON CMT 2023.
Join our discord below for more online help (hosted on the BinSync server):
DAILA interacts with the decompiler abstractly through the LibBS library. This allows DAILA to support the following decompilers:
- IDA Pro: >= 8.4
- Ghidra: >= 11.1
- Binary Ninja: >= 2.4
- angr-management: >= 9.0
DAILA supports any LLM supported in LiteLLM, such as:
- ChatGPT
- Claude
- Llama2
- Gemini
- and more...
DAILA also supports local models of different types, like VarBERT, a local model for renaming variables in decompilation published in S&P 2024.
Install our library backend through pip and our decompiler plugin through our installer:
pip3 install dailalib && daila --install This is the light mode. If you want to use VarBERT, you must install the full version:
pip3 install 'dailalib[full]' && daila --install This will also download the VarBERT models for you through the VarBERT API. If you happen to be installing DAILA on a machine that won't have internet access, like a secure network, you can use our Docker image in the Docker Container section.
You need to do a few extra steps to get Ghidra working. Next, enable the DAILA plugin:
- Start Ghidra and open a binary
- Goto the
Windows > Script Managermenu - Search for
dailaand enable the script
You must have python3 in your path for the Ghidra version to work. We quite literally call it from inside Python 2.
You may also need to enable the $USER_HOME/ghidra_scripts as a valid scripts path in Ghidra.
If the above fails, you will need to manually install.
To manually install, first pip3 install dailalib on the repo, then copy the daila_plugin.py file to your decompiler's plugin directory.
DAILA is designed to be used in two ways:
- As a decompiler plugin with a GUI
- As a scripting library in your decompiler
With the exception of Ghidra (see below), when you start your decompiler you will have a new context menu which you can access when you right-click anywhere in a function:
If you are using Ghidra, go to Tools->DAILA->Start DAILA Backend to start the backend server.
After you've done this, you can use the context menu as shown above.
You can use DAILA in your own scripts by importing the dailalib package.
Here is an example using the OpenAI API:
from dailalib import LiteLLMAIAPI
from libbs.api import DecompilerInterface
deci = DecompilerInterface.discover()
ai_api = LiteLLMAIAPI(decompiler_interface=deci)
for function in deci.functions:
summary = ai_api.summarize_function(function)If you are attempting to install DAILA for a one-shot install that will not use the internet after install, like on a secure network, you can use our Docker container.
You should either build the container yourself, save the image to a tarball, and then load it on the target machine, or you can use our pre-built image.
You can build the container yourself by running docker build -t daila . in the root of this repo.
You can also download our pre-built image by running docker pull binsync/daila:latest (the image is for x86_64 Linux).
The container contains DAILA and a copy of Ghidra.
Now you need to foward X11 to the container so that you can see the GUI. To do this, you need to run the container with the following flags:
docker run -it --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix binsync/daila:latestIn the container, you can launch ghidra from /tools/ghidra_10.4_PUBLIC/ghidraRun.
Now follow the Ghidra Extra Steps to enable the DAILA plugin and you're good to go!
DAILA supports the LiteLLM API, which in turn supports various backends like OpenAI.
To use a commercial LLM API, you must provide your own API key.
As an example, to use the OpenAI API, you must have an OpenAI API key.
If your decompiler does not have access to the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable, then you must use the decompiler option from
DAILA to set the API key.
In Settings, you can also add/use any OpenAI-based LLM endpoint, like using Llama2.
Currently, DAILA supports the following prompts:
- Summarize a function
- Rename variables
- Rename function
- Identify the source of a function
- Find potential vulnerabilities in a function
- Summarize the man page of a library call
- Free prompting... just type in your own prompt!
VarBERT is a local BERT model from the S&P 2024 paper ""Len or index or count, anything but v1": Predicting Variable Names in Decompilation Output with Transfer Learning". VarBERT is for renaming variables (both stack, register, and arguments) in decompilation. To understand how to use VarBERT as a library, please see the VarBERT API documentation. Using it in DAILA is a simple as using the GUI context-menu when clicking on a function.
You can find a demo of VarBERT running inside DAILA below:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for DAILA
Similar Open Source Tools

DAILA
DAILA is a unified interface for AI systems in decompilers, supporting various decompilers and AI systems. It allows users to utilize local and remote LLMs, like ChatGPT and Claude, and local models such as VarBERT. DAILA can be used as a decompiler plugin with GUI or as a scripting library. It also provides a Docker container for offline installations and supports tasks like summarizing functions and renaming variables in decompilation.
ai-manus
AI Manus is a general-purpose AI Agent system that supports running various tools and operations in a sandbox environment. It offers deployment with minimal dependencies, supports multiple tools like Terminal, Browser, File, Web Search, and messaging tools, allocates separate sandboxes for tasks, manages session history, supports stopping and interrupting conversations, file upload and download, and is multilingual. The system also provides user login and authentication. The project primarily relies on Docker for development and deployment, with model capability requirements and recommended Deepseek and GPT models.
generator
ctx is a tool designed to automatically generate organized context files from code files, GitHub repositories, Git commits, web pages, and plain text. It aims to efficiently provide necessary context to AI language models like ChatGPT and Claude, enabling users to streamline code refactoring, multiple iteration development, documentation generation, and seamless AI integration. With ctx, users can create structured markdown documents, save context files, and serve context through an MCP server for real-time assistance. The tool simplifies the process of sharing project information with AI assistants, making AI conversations smarter and easier.
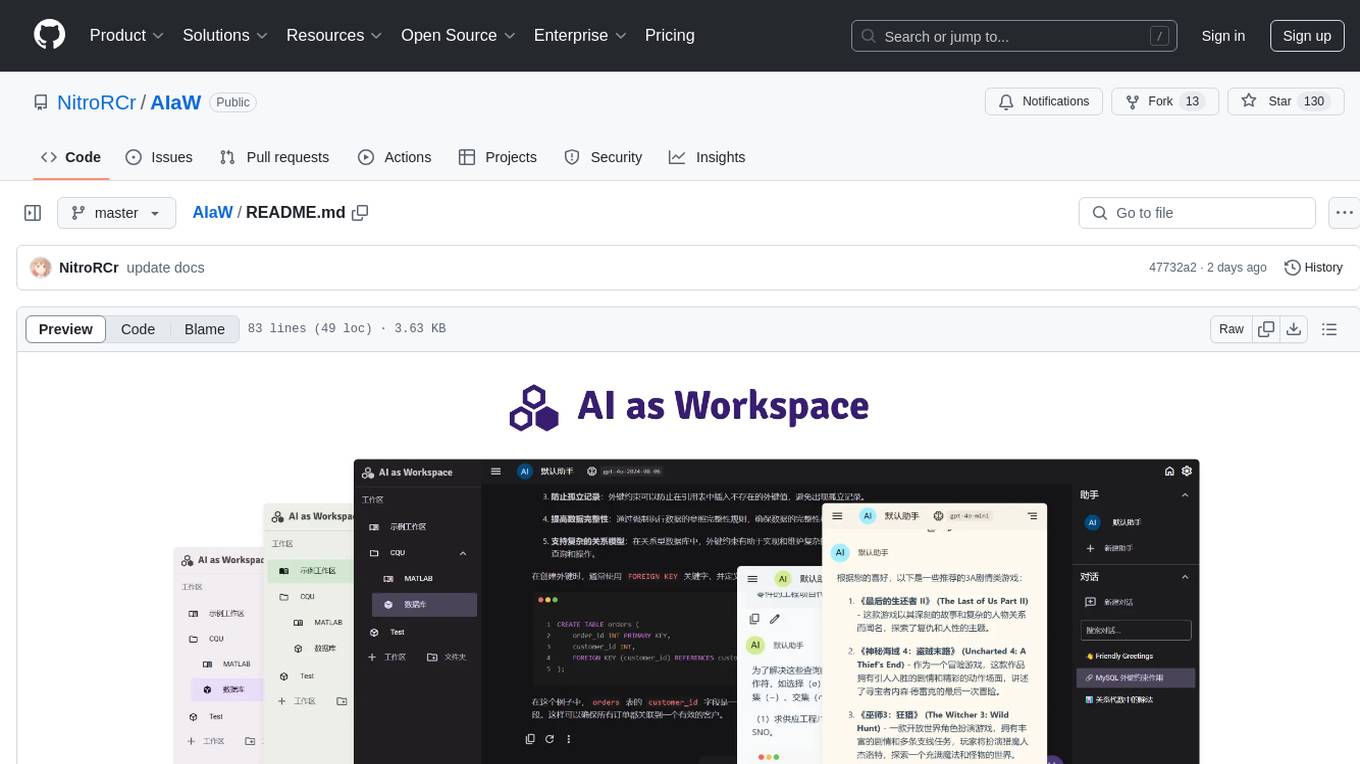
AIaW
AIaW is a next-generation LLM client with full functionality, lightweight, and extensible. It supports various basic functions such as streaming transfer, image uploading, and latex formulas. The tool is cross-platform with a responsive interface design. It supports multiple service providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Users can modify questions, regenerate in a forked manner, and visualize conversations in a tree structure. Additionally, it offers features like file parsing, video parsing, plugin system, assistant market, local storage with real-time cloud sync, and customizable interface themes. Users can create multiple workspaces, use dynamic prompt word variables, extend plugins, and benefit from detailed design elements like real-time content preview, optimized code pasting, and support for various file types.
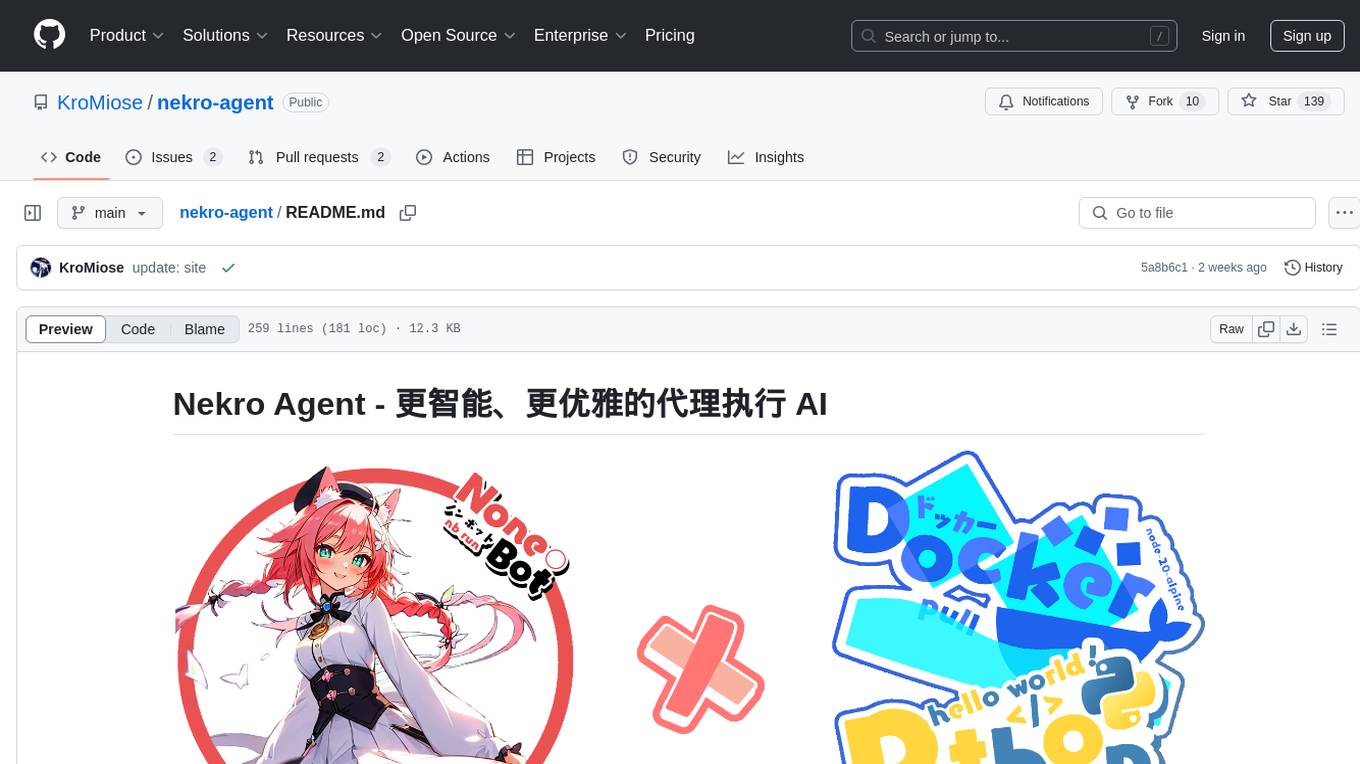
nekro-agent
Nekro Agent is an AI chat plugin and proxy execution bot that is highly scalable, offers high freedom, and has minimal deployment requirements. It features context-aware chat for group/private chats, custom character settings, sandboxed execution environment, interactive image resource handling, customizable extension development interface, easy deployment with docker-compose, integration with Stable Diffusion for AI drawing capabilities, support for various file types interaction, hot configuration updates and command control, native multimodal understanding, visual application management control panel, CoT (Chain of Thought) support, self-triggered timers and holiday greetings, event notification understanding, and more. It allows for third-party extensions and AI-generated extensions, and includes features like automatic context trigger based on LLM, and a variety of basic commands for bot administrators.
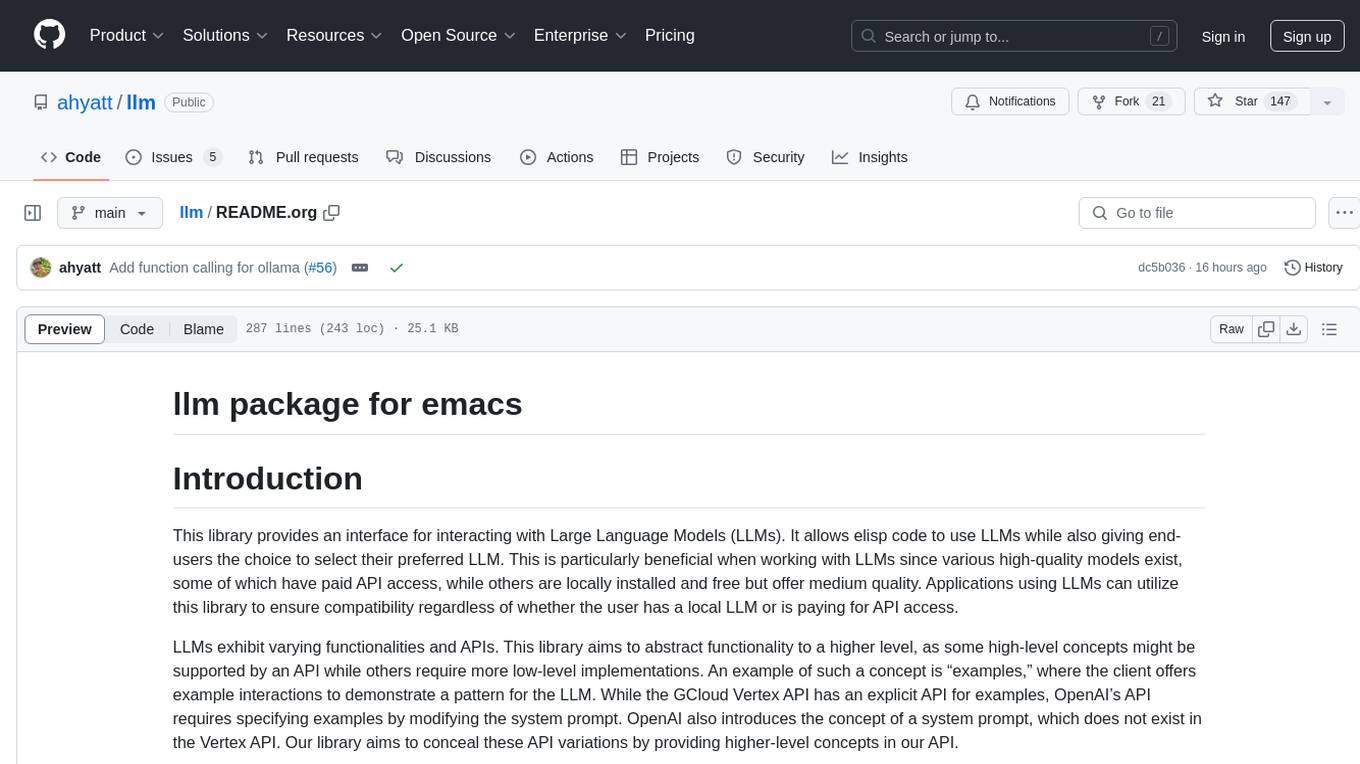
llm
The 'llm' package for Emacs provides an interface for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It abstracts functionality to a higher level, concealing API variations and ensuring compatibility with various LLMs. Users can set up providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Vertex, Claude, Ollama, GPT4All, and a fake client for testing. The package allows for chat interactions, embeddings, token counting, and function calling. It also offers advanced prompt creation and logging capabilities. Users can handle conversations, create prompts with placeholders, and contribute by creating providers.
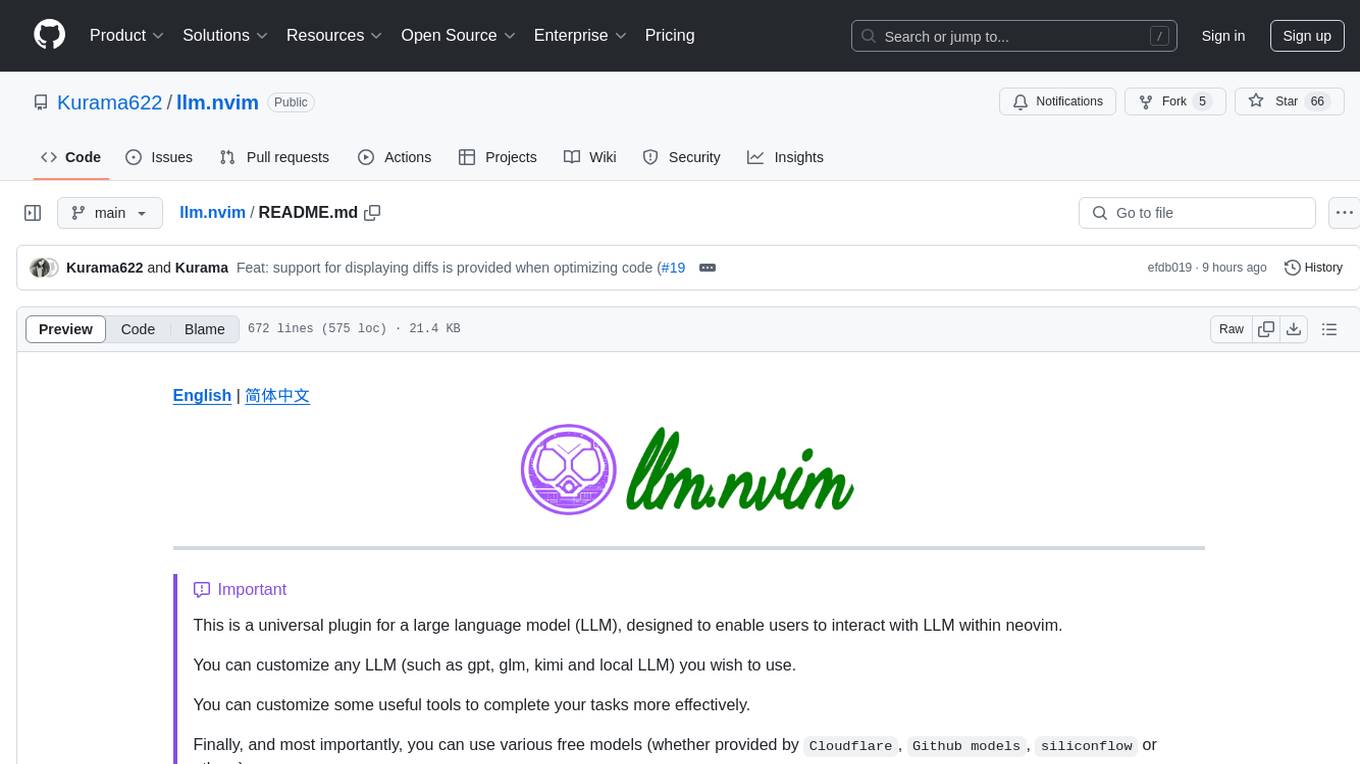
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.

traceroot
TraceRoot is a tool that helps engineers debug production issues 10× faster using AI-powered analysis of traces, logs, and code context. It accelerates the debugging process with AI-powered insights, integrates seamlessly into the development workflow, provides real-time trace and log analysis, code context understanding, and intelligent assistance. Features include ease of use, LLM flexibility, distributed services, AI debugging interface, and integration support. Users can get started with TraceRoot Cloud for a 7-day trial or self-host the tool. SDKs are available for Python and JavaScript/TypeScript.
simple-ai
Simple AI is a lightweight Python library for implementing basic artificial intelligence algorithms. It provides easy-to-use functions and classes for tasks such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. With Simple AI, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI solutions without the complexity of larger frameworks.
odoo-llm
This repository provides a comprehensive framework for integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into Odoo. It enables seamless interaction with AI providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Ollama, and Replicate for chat completions, text embeddings, and more within the Odoo environment. The architecture includes external AI clients connecting via `llm_mcp_server` and Odoo AI Chat with built-in chat interface. The core module `llm` offers provider abstraction, model management, and security, along with tools for CRUD operations and domain-specific tool packs. Various AI providers, infrastructure components, and domain-specific tools are available for different tasks such as content generation, knowledge base management, and AI assistants creation.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
llms
llms.py is a lightweight CLI, API, and ChatGPT-like alternative to Open WebUI for accessing multiple LLMs. It operates entirely offline, ensuring all data is kept private in browser storage. The tool provides a convenient way to interact with various LLM models without the need for an internet connection, prioritizing user privacy and data security.
GraphLLM
GraphLLM is a graph-based framework designed to process data using LLMs. It offers a set of tools including a web scraper, PDF parser, YouTube subtitles downloader, Python sandbox, and TTS engine. The framework provides a GUI for building and debugging graphs with advanced features like loops, conditionals, parallel execution, streaming of results, hierarchical graphs, external tool integration, and dynamic scheduling. GraphLLM is a low-level framework that gives users full control over the raw prompt and output of models, with a steeper learning curve. It is tested with llama70b and qwen 32b, under heavy development with breaking changes expected.
open-ai
Open AI is a powerful tool for artificial intelligence research and development. It provides a wide range of machine learning models and algorithms, making it easier for developers to create innovative AI applications. With Open AI, users can explore cutting-edge technologies such as natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation to support users in building and deploying AI solutions. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, Open AI offers the tools and resources you need to accelerate your AI projects and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence.

hyper-mcp
hyper-mcp is a fast and secure MCP server that enables adding AI capabilities to applications through WebAssembly plugins. It supports writing plugins in various languages, distributing them via standard OCI registries, and running them in resource-constrained environments. The tool offers sandboxing with WASM for limiting access, cross-platform compatibility, and deployment flexibility. Security features include sandboxed plugins, memory-safe execution, secure plugin distribution, and fine-grained access control. Users can configure the tool for global or project-specific use, start the server with different transport options, and utilize available plugins for tasks like time calculations, QR code generation, hash generation, IP retrieval, and webpage fetching.
llama.ui
llama.ui is an open-source desktop application that provides a beautiful, user-friendly interface for interacting with large language models powered by llama.cpp. It is designed for simplicity and privacy, allowing users to chat with powerful quantized models on their local machine without the need for cloud services. The project offers multi-provider support, conversation management with indexedDB storage, rich UI components including markdown rendering and file attachments, advanced features like PWA support and customizable generation parameters, and is privacy-focused with all data stored locally in the browser.
For similar tasks

DAILA
DAILA is a unified interface for AI systems in decompilers, supporting various decompilers and AI systems. It allows users to utilize local and remote LLMs, like ChatGPT and Claude, and local models such as VarBERT. DAILA can be used as a decompiler plugin with GUI or as a scripting library. It also provides a Docker container for offline installations and supports tasks like summarizing functions and renaming variables in decompilation.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
binary_ninja_mcp
This repository contains a Binary Ninja plugin, MCP server, and bridge that enables seamless integration of Binary Ninja's capabilities with your favorite LLM client. It provides real-time integration, AI assistance for reverse engineering, multi-binary support, and various MCP tools for tasks like decompiling functions, getting IL code, managing comments, renaming variables, and more.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.