guardrails
Adding guardrails to large language models.
Stars: 6410

Guardrails is a Python framework that helps build reliable AI applications by performing two key functions: 1. Guardrails runs Input/Output Guards in your application that detect, quantify and mitigate the presence of specific types of risks. To look at the full suite of risks, check out Guardrails Hub. 2. Guardrails help you generate structured data from LLMs.
README:
- [Feb 12, 2025] We just launched Guardrails Index -- the first of its kind benchmark comparing the performance and latency of 24 guardrails across 6 most common categories! Check out the index at index.guardrailsai.com
Guardrails is a Python framework that helps build reliable AI applications by performing two key functions:
- Guardrails runs Input/Output Guards in your application that detect, quantify and mitigate the presence of specific types of risks. To look at the full suite of risks, check out Guardrails Hub.
- Guardrails help you generate structured data from LLMs.
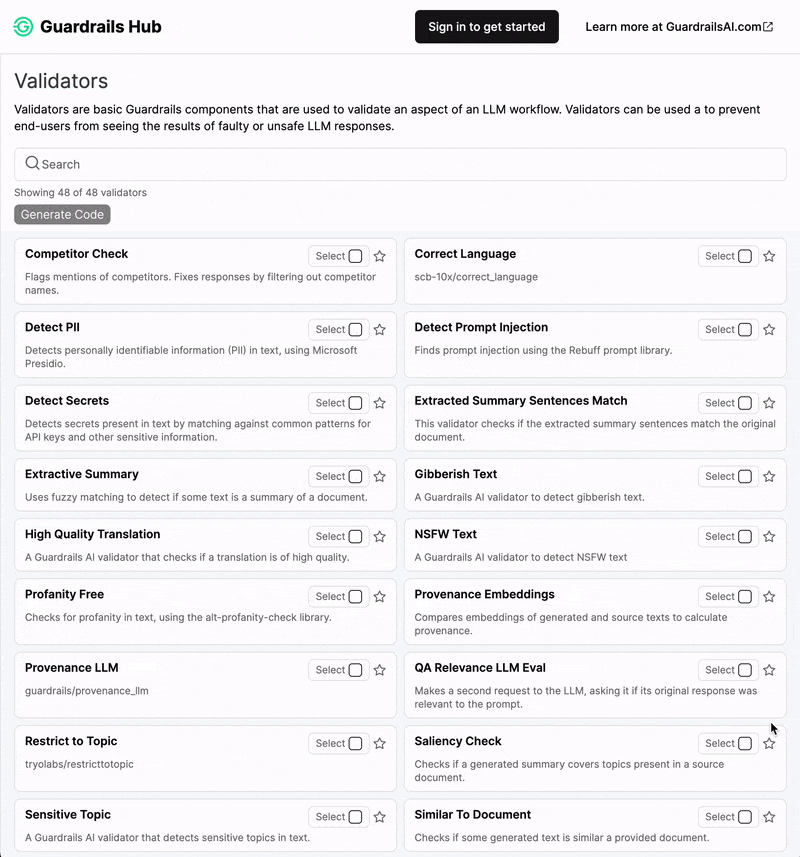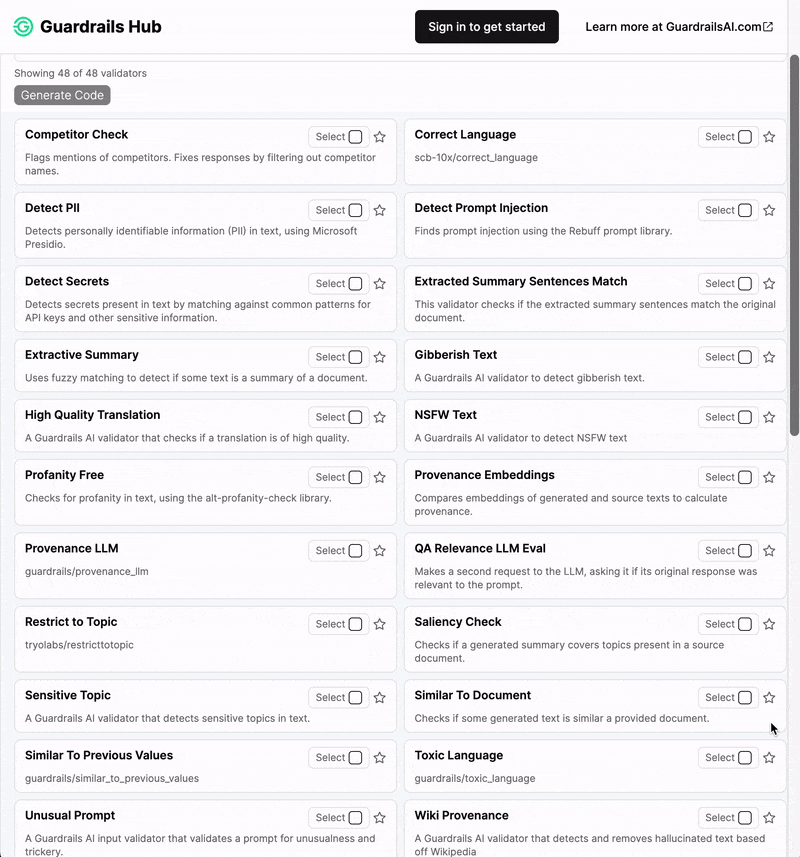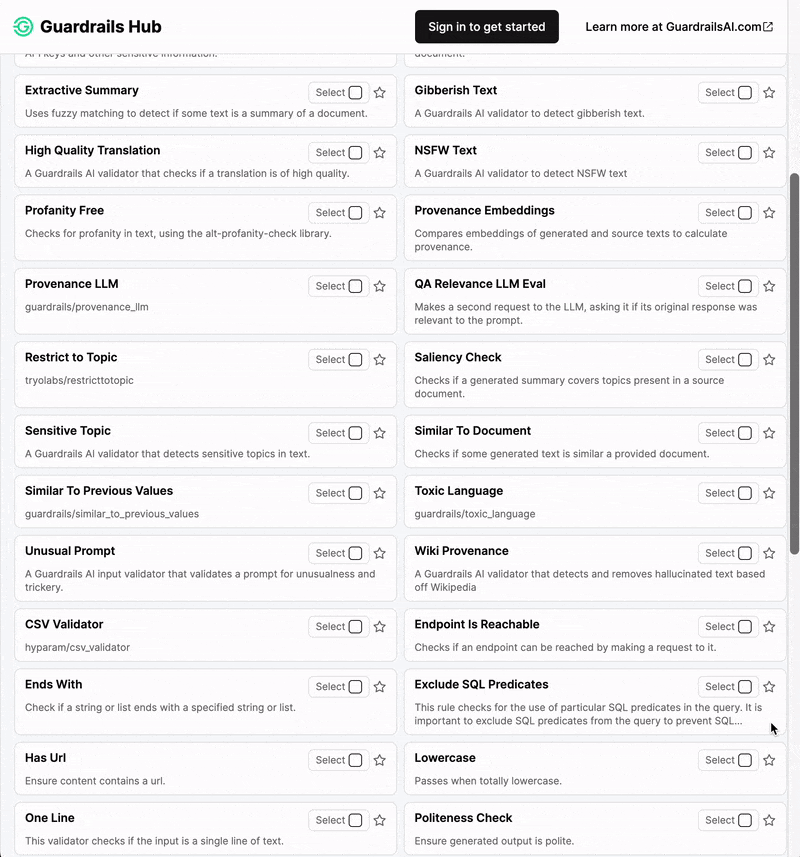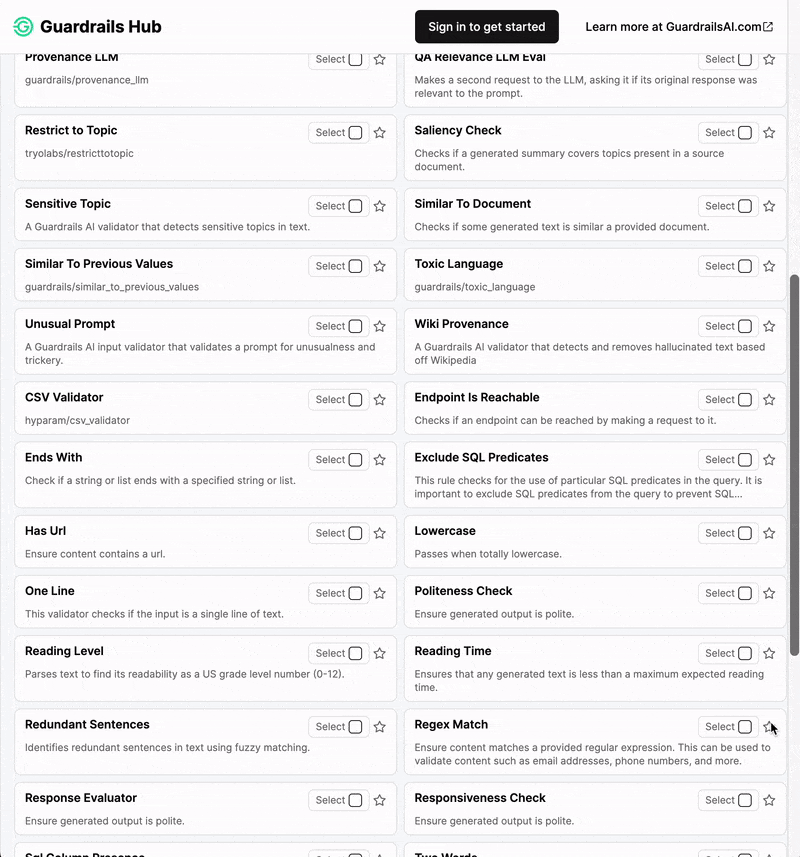
Guardrails Hub is a collection of pre-built measures of specific types of risks (called 'validators'). Multiple validators can be combined together into Input and Output Guards that intercept the inputs and outputs of LLMs. Visit Guardrails Hub to see the full list of validators and their documentation.
pip install guardrails-ai-
Download and configure the Guardrails Hub CLI.
pip install guardrails-ai guardrails configure
-
Install a guardrail from Guardrails Hub.
guardrails hub install hub://guardrails/regex_match
-
Create a Guard from the installed guardrail.
from guardrails import Guard, OnFailAction from guardrails.hub import RegexMatch guard = Guard().use( RegexMatch, regex="\(?\d{3}\)?-? *\d{3}-? *-?\d{4}", on_fail=OnFailAction.EXCEPTION ) guard.validate("123-456-7890") # Guardrail passes try: guard.validate("1234-789-0000") # Guardrail fails except Exception as e: print(e)
Output:
Validation failed for field with errors: Result must match \(?\d{3}\)?-? *\d{3}-? *-?\d{4} -
Run multiple guardrails within a Guard. First, install the necessary guardrails from Guardrails Hub.
guardrails hub install hub://guardrails/competitor_check guardrails hub install hub://guardrails/toxic_language
Then, create a Guard from the installed guardrails.
from guardrails import Guard, OnFailAction from guardrails.hub import CompetitorCheck, ToxicLanguage guard = Guard().use( CompetitorCheck(["Apple", "Microsoft", "Google"], on_fail=OnFailAction.EXCEPTION), ToxicLanguage(threshold=0.5, validation_method="sentence", on_fail=OnFailAction.EXCEPTION) ) guard.validate( """An apple a day keeps a doctor away. This is good advice for keeping your health.""" ) # Both the guardrails pass try: guard.validate( """Shut the hell up! Apple just released a new iPhone.""" ) # Both the guardrails fail except Exception as e: print(e)
Output:
Validation failed for field with errors: Found the following competitors: [['Apple']]. Please avoid naming those competitors next time, The following sentences in your response were found to be toxic: - Shut the hell up!
Let's go through an example where we ask an LLM to generate fake pet names. To do this, we'll create a Pydantic BaseModel that represents the structure of the output we want.
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class Pet(BaseModel):
pet_type: str = Field(description="Species of pet")
name: str = Field(description="a unique pet name")Now, create a Guard from the Pet class. The Guard can be used to call the LLM in a manner so that the output is formatted to the Pet class. Under the hood, this is done by either of two methods:
- Function calling: For LLMs that support function calling, we generate structured data using the function call syntax.
- Prompt optimization: For LLMs that don't support function calling, we add the schema of the expected output to the prompt so that the LLM can generate structured data.
from guardrails import Guard
import openai
prompt = """
What kind of pet should I get and what should I name it?
${gr.complete_json_suffix_v2}
"""
guard = Guard.for_pydantic(output_class=Pet, prompt=prompt)
raw_output, validated_output, *rest = guard(
llm_api=openai.completions.create,
engine="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct"
)
print(validated_output)This prints:
{
"pet_type": "dog",
"name": "Buddy
}
Guardrails can be set up as a standalone service served by Flask with guardrails start, allowing you to interact with it via a REST API. This approach simplifies development and deployment of Guardrails-powered applications.
- Install:
pip install "guardrails-ai" - Configure:
guardrails configure - Create a config:
guardrails create --validators=hub://guardrails/two_words --guard-name=two-word-guard - Start the dev server:
guardrails start --config=./config.py - Interact with the dev server via the snippets below
# with the guardrails client
import guardrails as gr
gr.settings.use_server = True
guard = gr.Guard(name='two-word-guard')
guard.validate('this is more than two words')
# or with the openai sdk
import openai
openai.base_url = "http://localhost:8000/guards/two-word-guard/openai/v1/"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "youropenaikey"
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "tell me about an apple with 3 words exactly",
},
]
completion = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=messages,
)
For production deployments, we recommend using Docker with Gunicorn as the WSGI server for improved performance and scalability.
You can reach out to us on Discord or Twitter.
Yes, Guardrails can be used with proprietary and open-source LLMs. Check out this guide on how to use Guardrails with any LLM.
Yes, you can create your own validators and contribute them to Guardrails Hub. Check out this guide on how to create your own validators.
Guardrails can be used with Python and JavaScript. Check out the docs on how to use Guardrails from JavaScript. We are working on adding support for other languages. If you would like to contribute to Guardrails, please reach out to us on Discord or Twitter.
We welcome contributions to Guardrails!
Get started by checking out Github issues and check out the Contributing Guide. Feel free to open an issue, or reach out if you would like to add to the project!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for guardrails
Similar Open Source Tools

guardrails
Guardrails is a Python framework that helps build reliable AI applications by performing two key functions: 1. Guardrails runs Input/Output Guards in your application that detect, quantify and mitigate the presence of specific types of risks. To look at the full suite of risks, check out Guardrails Hub. 2. Guardrails help you generate structured data from LLMs.
web-llm
WebLLM is a modular and customizable javascript package that directly brings language model chats directly onto web browsers with hardware acceleration. Everything runs inside the browser with no server support and is accelerated with WebGPU. WebLLM is fully compatible with OpenAI API. That is, you can use the same OpenAI API on any open source models locally, with functionalities including json-mode, function-calling, streaming, etc. We can bring a lot of fun opportunities to build AI assistants for everyone and enable privacy while enjoying GPU acceleration.
quivr
Quivr is a personal assistant powered by Generative AI, designed to be a second brain for users. It offers fast and efficient access to data, ensuring security and compatibility with various file formats. Quivr is open source and free to use, allowing users to share their brains publicly or keep them private. The marketplace feature enables users to share and utilize brains created by others, boosting productivity. Quivr's offline mode provides anytime, anywhere access to data. Key features include speed, security, OS compatibility, file compatibility, open source nature, public/private sharing options, a marketplace, and offline mode.
openorch
OpenOrch is a daemon that transforms servers into a powerful development environment, running AI models, containers, and microservices. It serves as a blend of Kubernetes and a language-agnostic backend framework for building applications on fixed-resource setups. Users can deploy AI models and build microservices, managing applications while retaining control over infrastructure and data.
otto-m8
otto-m8 is a flowchart based automation platform designed to run deep learning workloads with minimal to no code. It provides a user-friendly interface to spin up a wide range of AI models, including traditional deep learning models and large language models. The tool deploys Docker containers of workflows as APIs for integration with existing workflows, building AI chatbots, or standalone applications. Otto-m8 operates on an Input, Process, Output paradigm, simplifying the process of running AI models into a flowchart-like UI.

1backend
1Backend is a flexible and scalable platform designed for running AI models on private servers and handling high-concurrency workloads. It provides a ChatGPT-like interface for users and a network-accessible API for machines, serving as a general-purpose backend framework. The platform offers on-premise ChatGPT alternatives, a microservices-first web framework, out-of-the-box services like file uploads and user management, infrastructure simplification acting as a container orchestrator, reverse proxy, multi-database support with its own ORM, and AI integration with platforms like LlamaCpp and StableDiffusion.
kwaak
Kwaak is a tool that allows users to run a team of autonomous AI agents locally from their own machine. It enables users to write code, improve test coverage, update documentation, and enhance code quality while focusing on building innovative projects. Kwaak is designed to run multiple agents in parallel, interact with codebases, answer questions about code, find examples, write and execute code, create pull requests, and more. It is free and open-source, allowing users to bring their own API keys or models via Ollama. Kwaak is part of the bosun.ai project, aiming to be a platform for autonomous code improvement.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.
hydraai
Generate React components on-the-fly at runtime using AI. Register your components, and let Hydra choose when to show them in your App. Hydra development is still early, and patterns for different types of components and apps are still being developed. Join the discord to chat with the developers. Expects to be used in a NextJS project. Components that have function props do not work.

Fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework designed to augment humans using AI by organizing prompts by real-world tasks. It addresses the integration problem of AI by creating and organizing prompts for various tasks. Users can create, collect, and organize AI solutions in a single place for use in their favorite tools. Fabric also serves as a command-line interface for those focused on the terminal. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities, including support for multiple AI providers, internationalization, speech-to-text, AI reasoning, model management, web search, text-to-speech, desktop notifications, and more. The project aims to help humans flourish by leveraging AI technology to solve human problems and enhance creativity.
langroid
Langroid is a Python framework that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It uses a multi-agent paradigm inspired by the Actor Framework, where you set up Agents, equip them with optional components (LLM, vector-store and tools/functions), assign them tasks, and have them collaboratively solve a problem by exchanging messages. Langroid is a fresh take on LLM app-development, where considerable thought has gone into simplifying the developer experience; it does not use Langchain.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework for augmenting humans using AI. It provides a structured approach to breaking down problems into individual components and applying AI to them one at a time. Fabric includes a collection of pre-defined Patterns (prompts) that can be used for a variety of tasks, such as extracting the most interesting parts of YouTube videos and podcasts, writing essays, summarizing academic papers, creating AI art prompts, and more. Users can also create their own custom Patterns. Fabric is designed to be easy to use, with a command-line interface and a variety of helper apps. It is also extensible, allowing users to integrate it with their own AI applications and infrastructure.
simpleAI
SimpleAI is a self-hosted alternative to the not-so-open AI API, focused on replicating main endpoints for LLM such as text completion, chat, edits, and embeddings. It allows quick experimentation with different models, creating benchmarks, and handling specific use cases without relying on external services. Users can integrate and declare models through gRPC, query endpoints using Swagger UI or API, and resolve common issues like CORS with FastAPI middleware. The project is open for contributions and welcomes PRs, issues, documentation, and more.
bia-bob
BIA `bob` is a Jupyter-based assistant for interacting with data using large language models to generate Python code. It can utilize OpenAI's chatGPT, Google's Gemini, Helmholtz' blablador, and Ollama. Users need respective accounts to access these services. Bob can assist in code generation, bug fixing, code documentation, GPU-acceleration, and offers a no-code custom Jupyter Kernel. It provides example notebooks for various tasks like bio-image analysis, model selection, and bug fixing. Installation is recommended via conda/mamba environment. Custom endpoints like blablador and ollama can be used. Google Cloud AI API integration is also supported. The tool is extensible for Python libraries to enhance Bob's functionality.
For similar tasks

guardrails
Guardrails is a Python framework that helps build reliable AI applications by performing two key functions: 1. Guardrails runs Input/Output Guards in your application that detect, quantify and mitigate the presence of specific types of risks. To look at the full suite of risks, check out Guardrails Hub. 2. Guardrails help you generate structured data from LLMs.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.