iris-llm
IRIS: Demonstrator for use of LLMs in python (outdated)
Stars: 62
iris-llm is a personal project aimed at creating an Intelligent Residential Integration System (IRIS) with a voice interface to local language models or GPT. It provides options for chat engines, text-to-speech engines, speech-to-text engines, feedback sounds, and push-to-talk or wake word features. The tool is still in early development and serves as a tutorial for Python coders interested in working with language models.
README:
This is not fully functional yet, in that it is not capable of anything other than chatting - it can't control your devices. I haven't worked on it in months and I may never finish it. It is useful as a tutorial if you're a python coder who wants to learn how to use local language models etc., although as it goes further out of date it becomes less relevant. Maybe I will return to it one day when I have some time. If you're here to learn, remember to check out the prototypes branch where the step-by-step stuff is.
The original idea for IRIS was "IRIS: Intelligent Residential Integration System - a mind for your home!". I still want a Jarvis... but I never made much progress after getting the voice-to-voice LLM chat working. It's pretty well put together and there's useful info in the prototypes branch. But no, it's not going to control your home! Here's the original readme anyway...
This is a personal project, but maybe there'll be something that helps someone. It's very early in its development at the moment, but if you know a bit about python you should be able to get it running, and it'll present a voice interface to your local language models (or even GPT if you choose that option).
If you want to understand how the voice-to-voice stuff works in detail, check out the prototypes branch.
There are a few options for which chat engine, which text-to-speech model etc. it'll use. Run 'python configure.py' to configure it. In default configuration it'll use all offline models.
Note: I'm sorry I haven't frozen a fresh venv into a requirements.txt for you yet so you'll have to just work through figuring out which dependencies you need to pip install. I'll get around to it soon.
IRIS can use Oobabooga (https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui) via its API. This is a convenient way to access local LLM models because it has a nice interface for setting up your model and your character, has wide compatibility with different model types, and works really well.
You need to have Oobabooga fully set up and working with your favourite model, plus a character named "Iris" that works in Oobabooga in chat mode.
I set my CMD_FLAGS (in Oobabooga's webui.py) to '--auto-device --api --chat --xformers --model-menu --model_type gptj' (for gptq models - I also make sure to save working settings in the Oobabooga web ui for the model before I try to use it via IRIS). Most important is to enable the API with --api. Basically make sure Oobabooga is working with your model, and running with the API listening on port 5000
Alternatively, IRIS can use GPT as its chat engine. For this you'll need an OpenAI API key of your own, and beware that this version uses online services and so is not private.
Put your OpenAI API key in your environment variables as OPEN_AI_API_KEY
By default the GPT mode uses GPT-3 (text-davinci-002)
This probably works with other openai API compatible hosts like koboldcpp and would probably be my go to now.
This voice engine doesn't sound quite as good as some others but it's all local, is fast, and is really good at figuring out how to pronounce the sentence in a naural way (for example, it knows the difference between "St Peters" and "Peter St.", and it can pronounce numbers). I've only tested it on Windows - if you're on Linux you may need to tweak some of the settings in the module.
Google's voice is a bit slow but it sounds good. If you don't mind sharing your conversation with the internet!
A local model that works reasonably well and protects your privacy by not sending your audio sample to the internet.
Google's STT is pretty good, but it's not private.
IRIS will give you some audio cues so that you know what's going on - especially useful if you're not near your screen.
Choose this option to disable the bleeps and bloops.
IRIS won't listen to the mic until you press space each time. The library I used in this module is Windows specific, sorry!
IRIS has a 'hey siri' type feature. Say "Iris, pay attention" to make IRIS wake up from idle. Then you only need to say "Iris" or "Hey Iris" in order for it to start listening. To put IRIS back into idle mode, say "Iris, stop paying attention".
One of the problems with the wakeword system is that it might be interpreting some long sentence it's heard while you're trying to say the wakeword, and you just have to wait silently until it's ready. It can be tricky to know when it's ready, which is why it outputs ':' and '.' during the "waiting for wakeword" phase. ':' means it's ready to listen. If you see a '.', that means it's picked up some audio and you'll have to wait for the next ':' before you can say the wakeword. I tried using audio prompts for this, but it was too annoying. This is one of the reasons I prefer to use a push-to-talk (really a mute mic) button on my bluetooth speaker.
Regardless of whether you're using other online options, IRIS always uses offline models to listen for the wake word, so it's not sending all your audio to the internet all the time!
IRIS won't wait at all, and will always listen when it's your turn to talk. This works well if your microphone has a mute or push-to-talk button on it.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for iris-llm
Similar Open Source Tools

iris-llm
iris-llm is a personal project aimed at creating an Intelligent Residential Integration System (IRIS) with a voice interface to local language models or GPT. It provides options for chat engines, text-to-speech engines, speech-to-text engines, feedback sounds, and push-to-talk or wake word features. The tool is still in early development and serves as a tutorial for Python coders interested in working with language models.
aitools_client
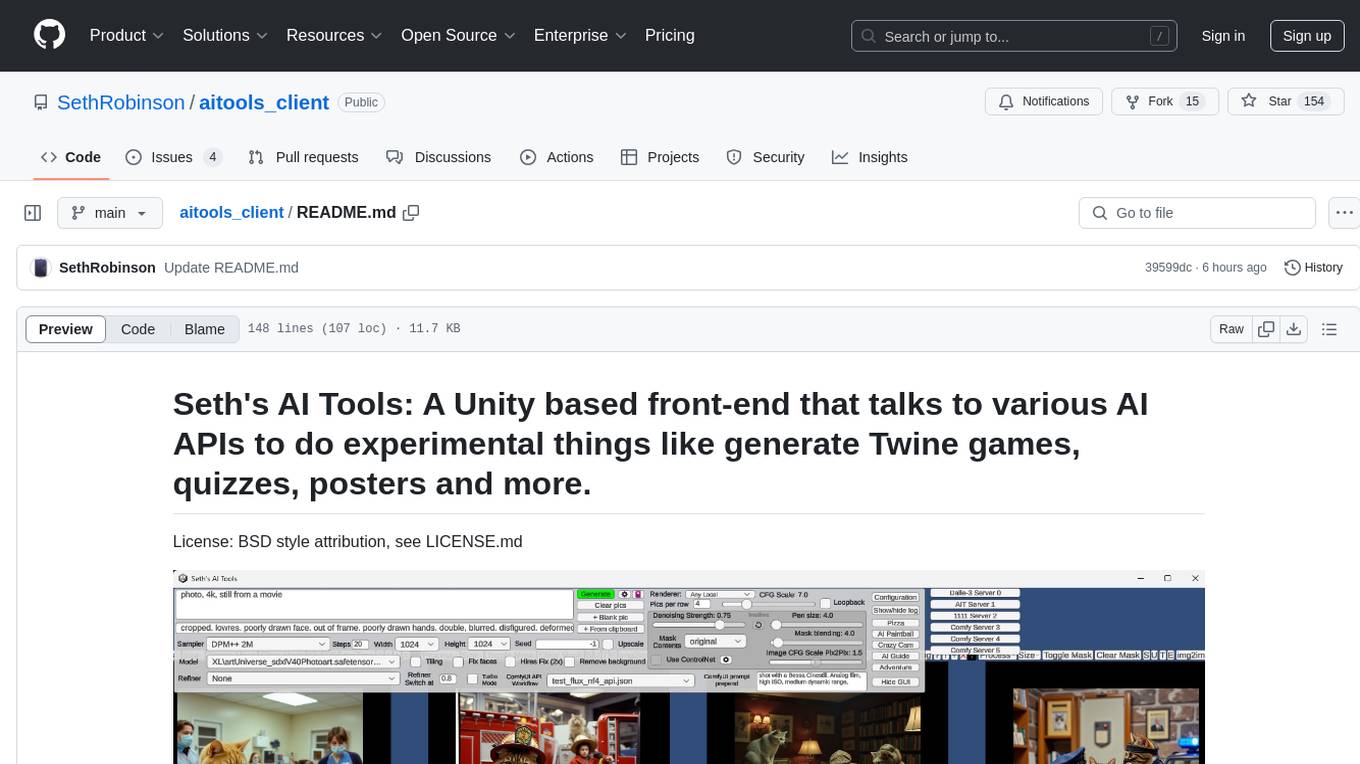
Seth's AI Tools is a Unity-based front-end that interfaces with various AI APIs to perform tasks such as generating Twine games, quizzes, posters, and more. The tool is a native Windows application that supports features like live update integration with image editors, text-to-image conversion, image processing, mask painting, and more. It allows users to connect to multiple servers for fast generation using GPUs and offers a neat workflow for evolving images in real-time. The tool respects user privacy by operating locally and includes built-in games and apps to test AI/SD capabilities. Additionally, it features an AI Guide for creating motivational posters and illustrated stories, as well as an Adventure mode with presets for generating web quizzes and Twine game projects.
WeeaBlind
Weeablind is a program that uses modern AI speech synthesis, diarization, language identification, and voice cloning to dub multi-lingual media and anime. It aims to create a pleasant alternative for folks facing accessibility hurdles such as blindness, dyslexia, learning disabilities, or simply those that don't enjoy reading subtitles. The program relies on state-of-the-art technologies such as ffmpeg, pydub, Coqui TTS, speechbrain, and pyannote.audio to analyze and synthesize speech that stays in-line with the source video file. Users have the option of dubbing every subtitle in the video, setting the start and end times, dubbing only foreign-language content, or full-blown multi-speaker dubbing with speaking rate and volume matching.

local-chat
LocalChat is a simple, easy-to-set-up, and open-source local AI chat tool that allows users to interact with generative language models on their own computers without transmitting data to a cloud server. It provides a chat-like interface for users to experience ChatGPT-like behavior locally, ensuring GDPR compliance and data privacy. Users can download LocalChat for macOS, Windows, or Linux to chat with open-weight generative language models.
llm_engineering
LLM Engineering is an 8-week course designed to help learners master AI and LLMs through a series of projects that gradually increase in complexity. The course covers setting up the environment, working with APIs, using Google Colab for GPU processing, and building an autonomous Agentic AI solution. Learners are encouraged to actively participate, run code cells, tweak code, and share their progress with the community. The emphasis is on practical, educational projects that teach valuable business skills.
kobold_assistant
Kobold-Assistant is a fully offline voice assistant interface to KoboldAI's large language model API. It can work online with the KoboldAI horde and online speech-to-text and text-to-speech models. The assistant, called Jenny by default, uses the latest coqui 'jenny' text to speech model and openAI's whisper speech recognition. Users can customize the assistant name, speech-to-text model, text-to-speech model, and prompts through configuration. The tool requires system packages like GCC, portaudio development libraries, and ffmpeg, along with Python >=3.7, <3.11, and runs on Ubuntu/Debian systems. Users can interact with the assistant through commands like 'serve' and 'list-mics'.
yet-another-applied-llm-benchmark
Yet Another Applied LLM Benchmark is a collection of diverse tests designed to evaluate the capabilities of language models in performing real-world tasks. The benchmark includes tests such as converting code, decompiling bytecode, explaining minified JavaScript, identifying encoding formats, writing parsers, and generating SQL queries. It features a dataflow domain-specific language for easily adding new tests and has nearly 100 tests based on actual scenarios encountered when working with language models. The benchmark aims to assess whether models can effectively handle tasks that users genuinely care about.
bidirectional_streaming_ai_voice
This repository contains Python scripts that enable two-way voice conversations with Anthropic Claude, utilizing ElevenLabs for text-to-speech, Faster-Whisper for speech-to-text, and Pygame for audio playback. The tool operates by transcribing human audio using Faster-Whisper, sending the transcription to Anthropic Claude for response generation, and converting the LLM's response into audio using ElevenLabs. The audio is then played back through Pygame, allowing for a seamless and interactive conversation between the user and the AI. The repository includes variations of the main script to support different operating systems and configurations, such as using CPU transcription on Linux or employing the AssemblyAI API instead of Faster-Whisper.
discourse-chatbot
The discourse-chatbot is an original AI chatbot for Discourse forums that allows users to converse with the bot in posts or chat channels. Users can customize the character of the bot, enable RAG mode for expert answers, search Wikipedia, news, and Google, provide market data, perform accurate math calculations, and experiment with vision support. The bot uses cutting-edge Open AI API and supports Azure and proxy server connections. It includes a quota system for access management and can be used in RAG mode or basic bot mode. The setup involves creating embeddings to make the bot aware of forum content and setting up bot access permissions based on trust levels. Users must obtain an API token from Open AI and configure group quotas to interact with the bot. The plugin is extensible to support other cloud bots and content search beyond the provided set.
AnnA_Anki_neuronal_Appendix
AnnA is a Python script designed to create filtered decks in optimal review order for Anki flashcards. It uses Machine Learning / AI to ensure semantically linked cards are reviewed far apart. The script helps users manage their daily reviews by creating special filtered decks that prioritize reviewing cards that are most different from the rest. It also allows users to reduce the number of daily reviews while increasing retention and automatically identifies semantic neighbors for each note.
ai-agents-masterclass
AI Agents Masterclass is a repository dedicated to teaching developers how to use AI agents to transform businesses and create powerful software. It provides weekly videos with accompanying code folders, guiding users on setting up Python environments, using environment variables, and installing necessary packages to run the code. The focus is on Large Language Models that can interact with the outside world to perform tasks like drafting emails, booking appointments, and managing tasks, enabling users to create innovative applications with minimal coding effort.
coding-with-ai
Coding-with-ai is a curated collection of techniques and best practices for utilizing AI coding tools to achieve transformative results in coding projects. It bridges the gap between AI coding demos and daily coding reality by providing insights into specific patterns like memory files, test-driven regeneration, and parallel AI sessions. The repository offers guidance on setting up memory files, writing detailed specs, drafting solutions before using assistants, getting multiple options, choosing stable libraries, and triggering careful planning. It also covers UI prototyping, coding practices, debugging strategies, testing methodologies, and cross-stage techniques for efficient coding with AI tools.
wingman-ai
Wingman AI allows you to use your voice to talk to various AI providers and LLMs, process your conversations, and ultimately trigger actions such as pressing buttons or reading answers. Our _Wingmen_ are like characters and your interface to this world, and you can easily control their behavior and characteristics, even if you're not a developer. AI is complex and it scares people. It's also **not just ChatGPT**. We want to make it as easy as possible for you to get started. That's what _Wingman AI_ is all about. It's a **framework** that allows you to build your own Wingmen and use them in your games and programs. The idea is simple, but the possibilities are endless. For example, you could: * **Role play** with an AI while playing for more immersion. Have air traffic control (ATC) in _Star Citizen_ or _Flight Simulator_. Talk to Shadowheart in Baldur's Gate 3 and have her respond in her own (cloned) voice. * Get live data such as trade information, build guides, or wiki content and have it read to you in-game by a _character_ and voice you control. * Execute keystrokes in games/applications and create complex macros. Trigger them in natural conversations with **no need for exact phrases.** The AI understands the context of your dialog and is quite _smart_ in recognizing your intent. Say _"It's raining! I can't see a thing!"_ and have it trigger a command you simply named _WipeVisors_. * Automate tasks on your computer * improve accessibility * ... and much more
lumentis
Lumentis is a tool that allows users to generate beautiful and comprehensive documentation from meeting transcripts and large documents with a single command. It reads transcripts, asks questions to understand themes and audience, generates an outline, and creates detailed pages with visual variety and styles. Users can switch models for different tasks, control the process, and deploy the generated docs to Vercel. The tool is designed to be open, clean, fast, and easy to use, with upcoming features including folders, PDFs, auto-transcription, website scraping, scientific papers handling, summarization, and continuous updates.
Aimmy
Aimmy is a universal AI-Based Aim Alignment Mechanism developed by BabyHamsta, MarsQQ & Taylor to make gaming more accessible for users who have difficulty aiming. It utilizes DirectML, ONNX, and YOLOV8 for player detection, offering high accuracy and fast performance. Aimmy features an easy-to-use UI, extensive customizability, and is free of ads and paywalls. It is designed for gamers facing challenges like physical or mental disabilities, poor hand-eye coordination, or aiming difficulties due to environmental factors. Aimmy provides various features like AI detection, customizability, anti-recoil system, mouse movement methods, hotswappability, and a model/configuration store with repository support.
For similar tasks

iris-llm
iris-llm is a personal project aimed at creating an Intelligent Residential Integration System (IRIS) with a voice interface to local language models or GPT. It provides options for chat engines, text-to-speech engines, speech-to-text engines, feedback sounds, and push-to-talk or wake word features. The tool is still in early development and serves as a tutorial for Python coders interested in working with language models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.