aim
Aim 💫 — An easy-to-use & supercharged open-source experiment tracker.
Stars: 5400

Aim is an open-source, self-hosted ML experiment tracking tool designed to handle 10,000s of training runs. Aim provides a performant and beautiful UI for exploring and comparing training runs. Additionally, its SDK enables programmatic access to tracked metadata — perfect for automations and Jupyter Notebook analysis. **Aim's mission is to democratize AI dev tools 🎯**
README:
| Drop a star to support Aim ⭐ |
Join Aim discord community

|
 Aim logs your training runs and any AI Metadata, enables a beautiful UI to compare, observe them and an API to query them programmatically.
Aim logs your training runs and any AI Metadata, enables a beautiful UI to compare, observe them and an API to query them programmatically.
AimStack offers enterprise support that's beyond core Aim. Contact via [email protected] e-mail.
About • Demos • Ecosystem • Quick Start • Examples • Documentation • Community • Blog
Aim is an open-source, self-hosted ML experiment tracking tool designed to handle 10,000s of training runs.
Aim provides a performant and beautiful UI for exploring and comparing training runs. Additionally, its SDK enables programmatic access to tracked metadata — perfect for automations and Jupyter Notebook analysis.
Aim's mission is to democratize AI dev tools 🎯
| Log Metadata Across Your ML Pipeline 💾 | Visualize & Compare Metadata via UI 📊 |
|---|---|
|
|
| Run ML Trainings Effectively ⚡ | Organize Your Experiments 🗂️ |
|
|
Check out live Aim demos NOW to see it in action.
| Machine translation experiments | lightweight-GAN experiments |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Training logs of a neural translation model(from WMT'19 competition). | Training logs of 'lightweight' GAN, proposed in ICLR 2021. |
| FastSpeech 2 experiments | Simple MNIST |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Training logs of Microsoft's "FastSpeech 2: Fast and High-Quality End-to-End Text to Speech". | Simple MNIST training logs. |
Aim is not just an experiment tracker. It's a groundwork for an ecosystem. Check out the two most famous Aim-based tools.
| aimlflow | Aim-spaCy |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Exploring MLflow experiments with a powerful UI | an Aim-based spaCy experiment tracker |
Follow the steps below to get started with Aim.
pip3 install aimfrom aim import Run
# Initialize a new run
run = Run()
# Log run parameters
run["hparams"] = {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"batch_size": 32,
}
# Log metrics
for i in range(10):
run.track(i, name='loss', step=i, context={ "subset":"train" })
run.track(i, name='acc', step=i, context={ "subset":"train" })See the full list of supported trackable objects(e.g. images, text, etc) here.
aim upMigrate from other tools
Aim has built-in converters to easily migrate logs from other tools. These migrations cover the most common usage scenarios. In case of custom and complex scenarios you can use Aim SDK to implement your own conversion script.
Integrate Aim into an existing project
Aim easily integrates with a wide range of ML frameworks, providing built-in callbacks for most of them.
- Integration with Pytorch Ignite
- Integration with Pytorch Lightning
- Integration with Hugging Face
- Integration with Keras & tf.Keras
- Integration with Keras Tuner
- Integration with XGboost
- Integration with CatBoost
- Integration with LightGBM
- Integration with fastai
- Integration with MXNet
- Integration with Optuna
- Integration with PaddlePaddle
- Integration with Stable-Baselines3
- Integration with Acme
- Integration with Prophet
Query runs programmatically via SDK
Aim Python SDK empowers you to query and access any piece of tracked metadata with ease.
from aim import Repo
my_repo = Repo('/path/to/aim/repo')
query = "metric.name == 'loss'" # Example query
# Get collection of metrics
for run_metrics_collection in my_repo.query_metrics(query).iter_runs():
for metric in run_metrics_collection:
# Get run params
params = metric.run[...]
# Get metric values
steps, metric_values = metric.values.sparse_numpy()Set up a centralized tracking server
Aim remote tracking server allows running experiments in a multi-host environment and collect tracked data in a centralized location.
See the docs on how to set up the remote server.
Deploy Aim on kubernetes
- The official Aim docker image: https://hub.docker.com/r/aimstack/aim
- A guide on how to deploy Aim on kubernetes: https://aimstack.readthedocs.io/en/latest/using/k8s_deployment.html
Read the full documentation on aimstack.readthedocs.io 📖
TensorBoard vs Aim
Training run comparison
Order of magnitude faster training run comparison with Aim
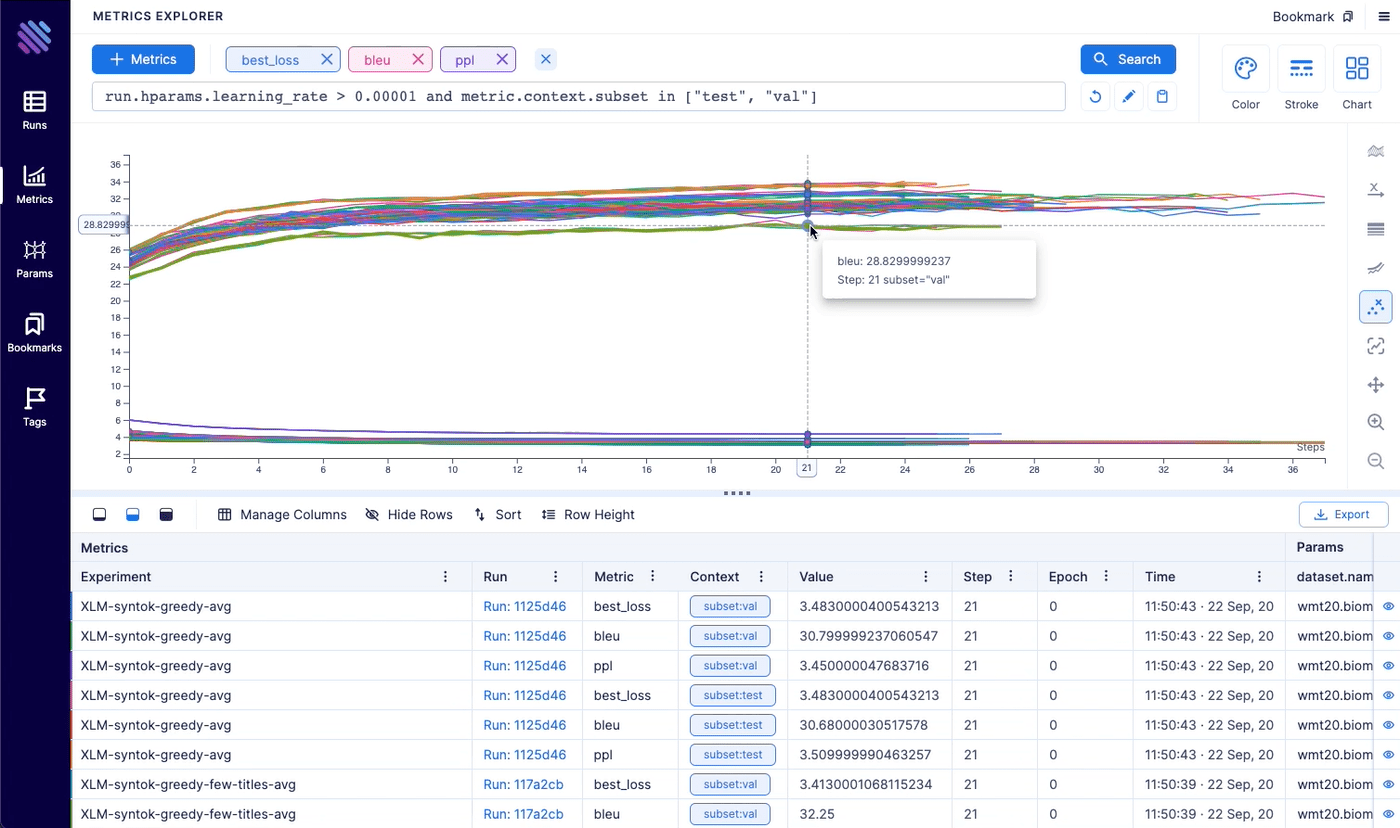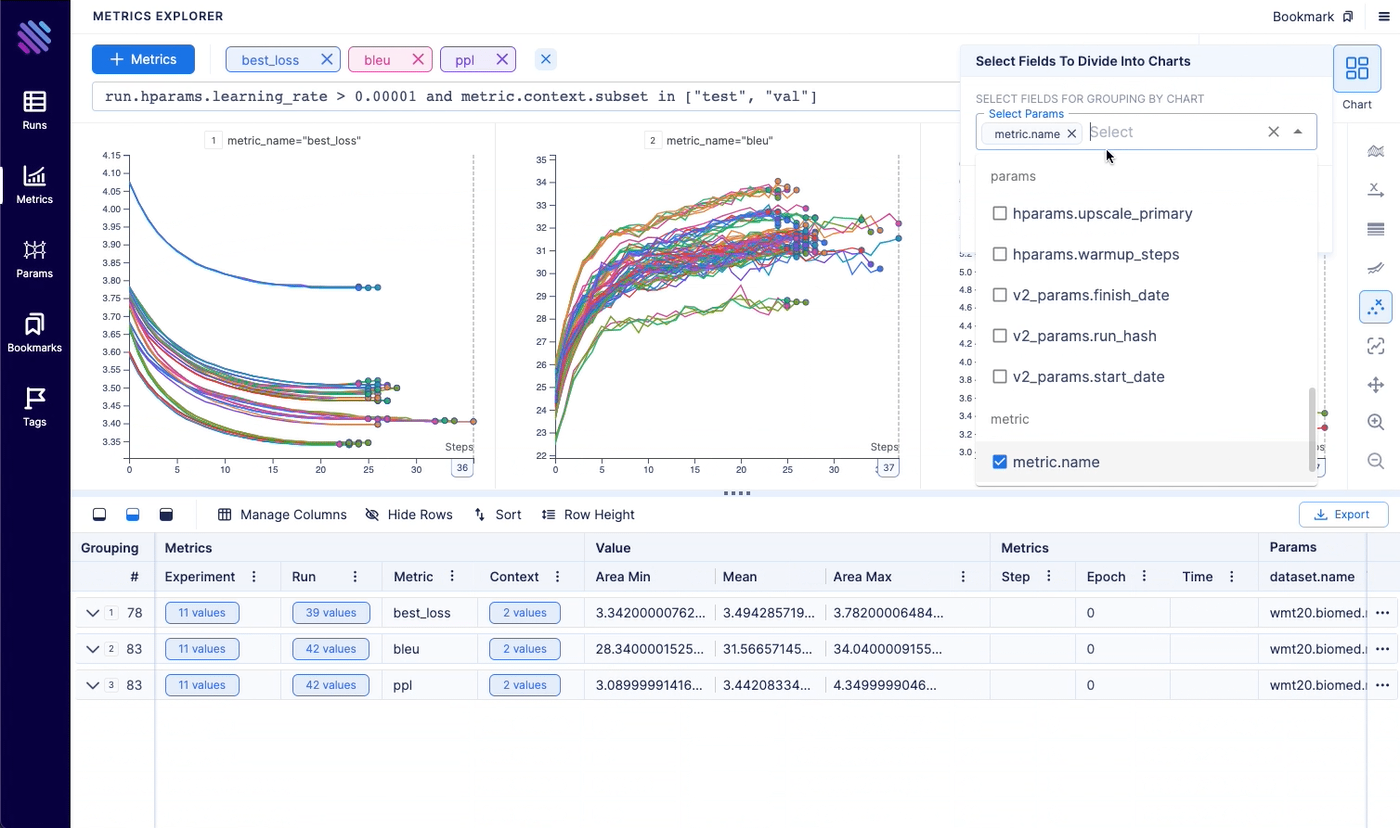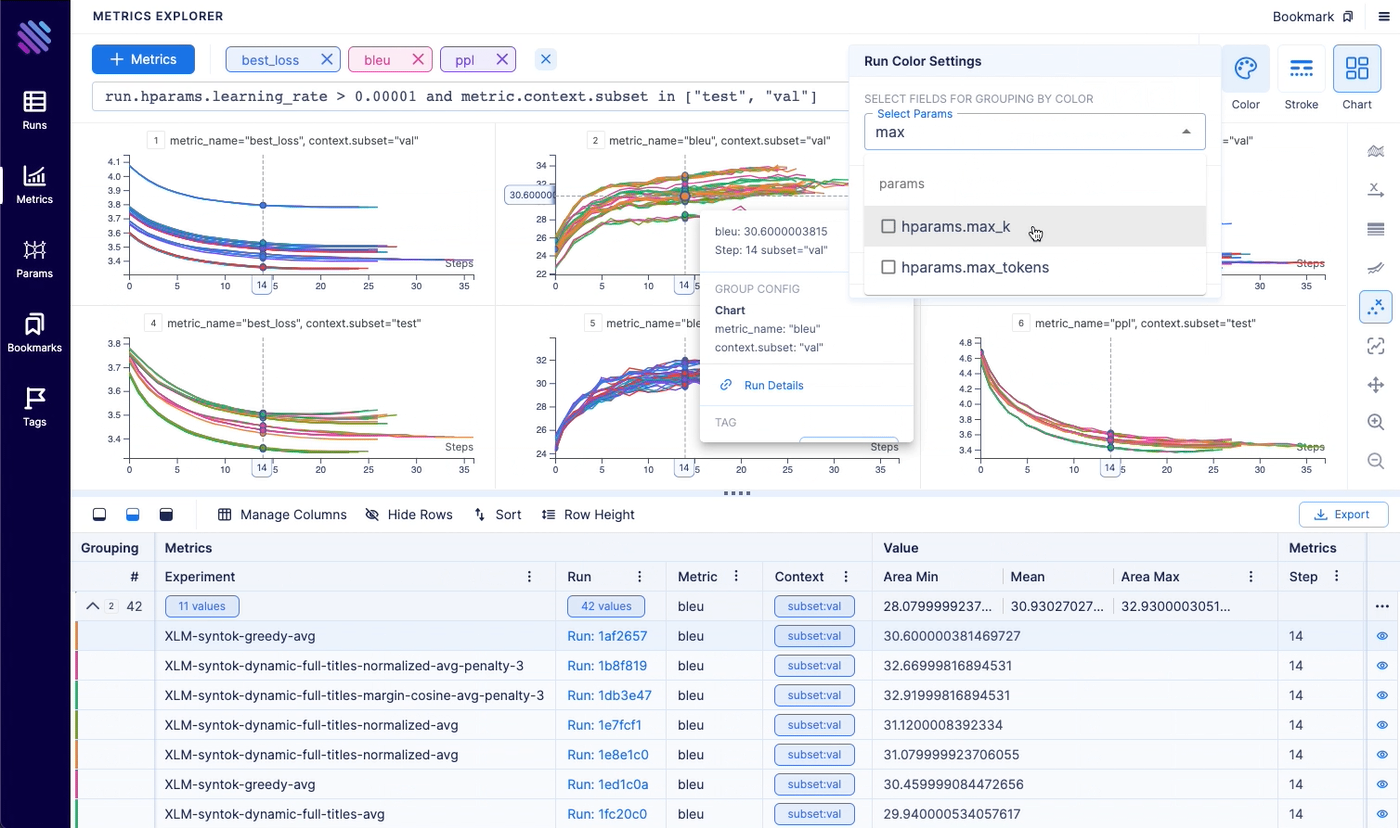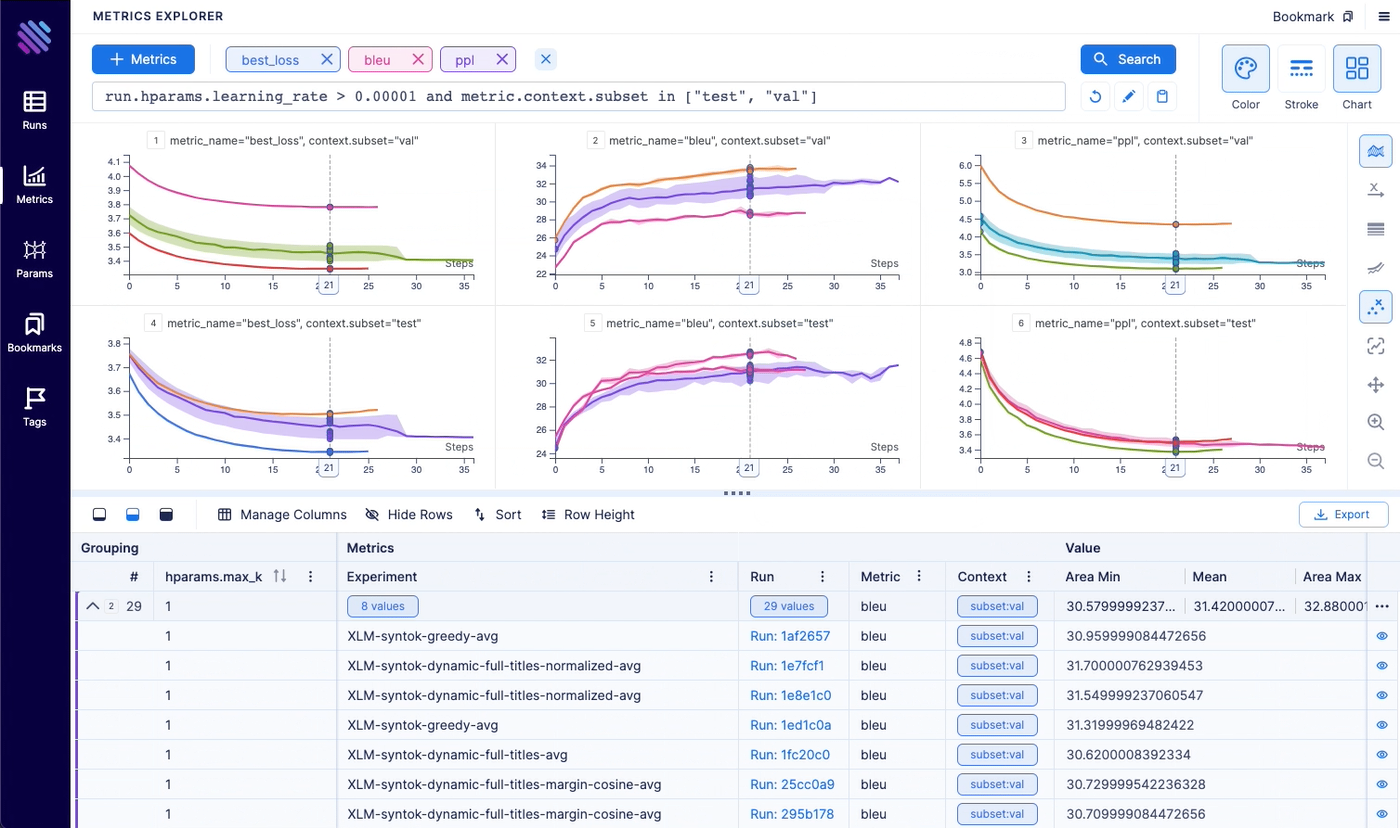
- The tracked params are first class citizens at Aim. You can search, group, aggregate via params - deeply explore all the tracked data (metrics, params, images) on the UI.
- With tensorboard the users are forced to record those parameters in the training run name to be able to search and compare. This causes a super-tedius comparison experience and usability issues on the UI when there are many experiments and params. TensorBoard doesn't have features to group, aggregate the metrics
Scalability
- Aim is built to handle 1000s of training runs - both on the backend and on the UI.
- TensorBoard becomes really slow and hard to use when a few hundred training runs are queried / compared.
Beloved TB visualizations to be added on Aim
- Embedding projector.
- Neural network visualization.
MLflow vs Aim
MLFlow is an end-to-end ML Lifecycle tool. Aim is focused on training tracking. The main differences of Aim and MLflow are around the UI scalability and run comparison features.
Aim and MLflow are a perfect match - check out the aimlflow - the tool that enables Aim superpowers on Mlflow.
Run comparison
- Aim treats tracked parameters as first-class citizens. Users can query runs, metrics, images and filter using the params.
- MLFlow does have a search by tracked config, but there are no grouping, aggregation, subplotting by hyparparams and other comparison features available.
UI Scalability
- Aim UI can handle several thousands of metrics at the same time smoothly with 1000s of steps. It may get shaky when you explore 1000s of metrics with 10000s of steps each. But we are constantly optimizing!
- MLflow UI becomes slow to use when there are a few hundreds of runs.
Weights and Biases vs Aim
Hosted vs self-hosted
- Weights and Biases is a hosted closed-source MLOps platform.
- Aim is self-hosted, free and open-source experiment tracking tool.
The Aim product roadmap ❇️
- The
Backlogcontains the issues we are going to choose from and prioritize weekly - The issues are mainly prioritized by the highly-requested features
The high-level features we are going to work on the next few months:
In progress
- [ ] Aim SDK low-level interface
- [ ] Dashboards – customizable layouts with embedded explorers
- [ ] Ergonomic UI kit
- [ ] Text Explorer
Next-up
Aim UI
- Runs management
- Runs explorer – query and visualize runs data(images, audio, distributions, ...) in a central dashboard
- Explorers
- Distributions Explorer
SDK and Storage
- Scalability
- Smooth UI and SDK experience with over 10.000 runs
- Runs management
- CLI commands
- Reporting - runs summary and run details in a CLI compatible format
- Manipulations – copy, move, delete runs, params and sequences
- CLI commands
- Cloud storage support – store runs blob(e.g. images) data on the cloud
- Artifact storage – store files, model checkpoints, and beyond
Integrations
- ML Frameworks:
- Shortlist: scikit-learn
- Resource management tools
- Shortlist: Kubeflow, Slurm
- Workflow orchestration tools
Done
- [x] Live updates (Shipped: Oct 18 2021)
- [x] Images tracking and visualization (Start: Oct 18 2021, Shipped: Nov 19 2021)
- [x] Distributions tracking and visualization (Start: Nov 10 2021, Shipped: Dec 3 2021)
- [x] Jupyter integration (Start: Nov 18 2021, Shipped: Dec 3 2021)
- [x] Audio tracking and visualization (Start: Dec 6 2021, Shipped: Dec 17 2021)
- [x] Transcripts tracking and visualization (Start: Dec 6 2021, Shipped: Dec 17 2021)
- [x] Plotly integration (Start: Dec 1 2021, Shipped: Dec 17 2021)
- [x] Colab integration (Start: Nov 18 2021, Shipped: Dec 17 2021)
- [x] Centralized tracking server (Start: Oct 18 2021, Shipped: Jan 22 2022)
- [x] Tensorboard adaptor - visualize TensorBoard logs with Aim (Start: Dec 17 2021, Shipped: Feb 3 2022)
- [x] Track git info, env vars, CLI arguments, dependencies (Start: Jan 17 2022, Shipped: Feb 3 2022)
- [x] MLFlow adaptor (visualize MLflow logs with Aim) (Start: Feb 14 2022, Shipped: Feb 22 2022)
- [x] Activeloop Hub integration (Start: Feb 14 2022, Shipped: Feb 22 2022)
- [x] PyTorch-Ignite integration (Start: Feb 14 2022, Shipped: Feb 22 2022)
- [x] Run summary and overview info(system params, CLI args, git info, ...) (Start: Feb 14 2022, Shipped: Mar 9 2022)
- [x] Add DVC related metadata into aim run (Start: Mar 7 2022, Shipped: Mar 26 2022)
- [x] Ability to attach notes to Run from UI (Start: Mar 7 2022, Shipped: Apr 29 2022)
- [x] Fairseq integration (Start: Mar 27 2022, Shipped: Mar 29 2022)
- [x] LightGBM integration (Start: Apr 14 2022, Shipped: May 17 2022)
- [x] CatBoost integration (Start: Apr 20 2022, Shipped: May 17 2022)
- [x] Run execution details(display stdout/stderr logs) (Start: Apr 25 2022, Shipped: May 17 2022)
- [x] Long sequences(up to 5M of steps) support (Start: Apr 25 2022, Shipped: Jun 22 2022)
- [x] Figures Explorer (Start: Mar 1 2022, Shipped: Aug 21 2022)
- [x] Notify on stuck runs (Start: Jul 22 2022, Shipped: Aug 21 2022)
- [x] Integration with KerasTuner (Start: Aug 10 2022, Shipped: Aug 21 2022)
- [x] Integration with WandB (Start: Aug 15 2022, Shipped: Aug 21 2022)
- [x] Stable remote tracking server (Start: Jun 15 2022, Shipped: Aug 21 2022)
- [x] Integration with fast.ai (Start: Aug 22 2022, Shipped: Oct 6 2022)
- [x] Integration with MXNet (Start: Sep 20 2022, Shipped: Oct 6 2022)
- [x] Project overview page (Start: Sep 1 2022, Shipped: Oct 6 2022)
- [x] Remote tracking server scaling (Start: Sep 11 2022, Shipped: Nov 26 2022)
- [x] Integration with PaddlePaddle (Start: Oct 2 2022, Shipped: Nov 26 2022)
- [x] Integration with Optuna (Start: Oct 2 2022, Shipped: Nov 26 2022)
- [x] Audios Explorer (Start: Oct 30 2022, Shipped: Nov 26 2022)
- [x] Experiment page (Start: Nov 9 2022, Shipped: Nov 26 2022)
- [x] HuggingFace datasets (Start: Dec 29 2022, Feb 3 2023)
Add Aim badge to your README, if you've enjoyed using Aim in your work:
[](https://github.com/aimhubio/aim)
In case you've found Aim helpful in your research journey, we'd be thrilled if you could acknowledge Aim's contribution:
@software{Arakelyan_Aim_2020,
author = {Arakelyan, Gor and Soghomonyan, Gevorg and {The Aim team}},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.6536395},
license = {Apache-2.0},
month = {6},
title = {{Aim}},
url = {https://github.com/aimhubio/aim},
version = {3.9.3},
year = {2020}
}Considering contibuting to Aim? To get started, please take a moment to read the CONTRIBUTING.md guide.
Join Aim contributors by submitting your first pull request. Happy coding! 😊
Made with contrib.rocks.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aim
Similar Open Source Tools

aim
Aim is an open-source, self-hosted ML experiment tracking tool designed to handle 10,000s of training runs. Aim provides a performant and beautiful UI for exploring and comparing training runs. Additionally, its SDK enables programmatic access to tracked metadata — perfect for automations and Jupyter Notebook analysis. **Aim's mission is to democratize AI dev tools 🎯**

feast
Feast is an open source feature store for machine learning, providing a fast path to manage infrastructure for productionizing analytic data. It allows ML platform teams to make features consistently available, avoid data leakage, and decouple ML from data infrastructure. Feast abstracts feature storage from retrieval, ensuring portability across different model training and serving scenarios.
SuperAGI
SuperAGI is an open-source framework designed to build, manage, and run autonomous AI agents. It enables developers to create production-ready and scalable agents, extend agent capabilities with toolkits, and interact with agents through a graphical user interface. The framework allows users to connect to multiple Vector DBs, optimize token usage, store agent memory, utilize custom fine-tuned models, and automate tasks with predefined steps. SuperAGI also provides a marketplace for toolkits that enable agents to interact with external systems and third-party plugins.
ailoy
Ailoy is a lightweight library for building AI applications such as agent systems or RAG pipelines with ease. It enables AI features effortlessly, supporting AI models locally or via cloud APIs, multi-turn conversation, system message customization, reasoning-based workflows, tool calling capabilities, and built-in vector store support. It also supports running native-equivalent functionality in web browsers using WASM. The library is in early development stages and provides examples in the `examples` directory for inspiration on building applications with Agents.
L3AGI
L3AGI is an open-source tool that enables AI Assistants to collaborate together as effectively as human teams. It provides a robust set of functionalities that empower users to design, supervise, and execute both autonomous AI Assistants and Teams of Assistants. Key features include the ability to create and manage Teams of AI Assistants, design and oversee standalone AI Assistants, equip AI Assistants with the ability to retain and recall information, connect AI Assistants to an array of data sources for efficient information retrieval and processing, and employ curated sets of tools for specific tasks. L3AGI also offers a user-friendly interface, APIs for integration with other systems, and a vibrant community for support and collaboration.
netsaur
Netsaur is a powerful machine learning library for Deno, offering a lightweight and easy-to-use neural network solution. It is blazingly fast and efficient, providing a simple API for creating and training neural networks. Netsaur can run on both CPU and GPU, making it suitable for serverless environments. With Netsaur, users can quickly build and deploy machine learning models for various applications with minimal dependencies. This library is perfect for both beginners and experienced machine learning practitioners.

VideoRefer
VideoRefer Suite is a tool designed to enhance the fine-grained spatial-temporal understanding capabilities of Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs). It consists of three primary components: Model (VideoRefer) for perceiving, reasoning, and retrieval for user-defined regions at any specified timestamps, Dataset (VideoRefer-700K) for high-quality object-level video instruction data, and Benchmark (VideoRefer-Bench) to evaluate object-level video understanding capabilities. The tool can understand any object within a video.
kan-gpt
The KAN-GPT repository is a PyTorch implementation of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs) using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for language modeling. It provides a model for generating text based on prompts, with a focus on improving performance compared to traditional MLP-GPT models. The repository includes scripts for training the model, downloading datasets, and evaluating model performance. Development tasks include integrating with other libraries, testing, and documentation.
ChatGPT-Next-Web
ChatGPT Next Web is a well-designed cross-platform ChatGPT web UI tool that supports Claude, GPT4, and Gemini Pro models. It allows users to deploy their private ChatGPT applications with ease. The tool offers features like one-click deployment, compact client for Linux/Windows/MacOS, compatibility with self-deployed LLMs, privacy-first approach with local data storage, markdown support, responsive design, fast loading speed, prompt templates, awesome prompts, chat history compression, multilingual support, and more.
intlayer
Intlayer is an open-source, flexible i18n toolkit with AI-powered translation and CMS capabilities. It is a modern i18n solution for web and mobile apps, framework-agnostic, and includes features like per-locale content files, TypeScript autocompletion, tree-shakable dictionaries, and CI/CD integration. With Intlayer, internationalization becomes faster, cleaner, and smarter, offering benefits such as cross-framework support, JavaScript-powered content management, simplified setup, enhanced routing, AI-powered translation, and more.
evalplus
EvalPlus is a rigorous evaluation framework for LLM4Code, providing HumanEval+ and MBPP+ tests to evaluate large language models on code generation tasks. It offers precise evaluation and ranking, coding rigorousness analysis, and pre-generated code samples. Users can use EvalPlus to generate code solutions, post-process code, and evaluate code quality. The tool includes tools for code generation and test input generation using various backends.
gitmesh
GitMesh is an AI-powered Git collaboration network designed to address contributor dropout in open source projects. It offers real-time branch-level insights, intelligent contributor-task matching, and automated workflows. The platform transforms complex codebases into clear contribution journeys, fostering engagement through gamified rewards and integration with open source support programs. GitMesh's mascot, Meshy/Mesh Wolf, symbolizes agility, resilience, and teamwork, reflecting the platform's ethos of efficiency and power through collaboration.
sfdx-hardis
sfdx-hardis is a toolbox for Salesforce DX, developed by Cloudity, that simplifies tasks which would otherwise take minutes or hours to complete manually. It enables users to define complete CI/CD pipelines for Salesforce projects, backup metadata, and monitor any Salesforce org. The tool offers a wide range of commands that can be accessed via the command line interface or through a Visual Studio Code extension. Additionally, sfdx-hardis provides Docker images for easy integration into CI workflows. The tool is designed to be natively compliant with various platforms and tools, making it a versatile solution for Salesforce developers.
GPULlama3.java
GPULlama3.java powered by TornadoVM is a Java-native implementation of Llama3 that automatically compiles and executes Java code on GPUs via TornadoVM. It supports Llama3, Mistral, Qwen2.5, Qwen3, and Phi3 models in the GGUF format. The repository aims to provide GPU acceleration for Java code, enabling faster execution and high-performance access to off-heap memory. It offers features like interactive and instruction modes, flexible backend switching between OpenCL and PTX, and cross-platform compatibility with NVIDIA, Intel, and Apple GPUs.
chatllm.cpp
ChatLLM.cpp is a pure C++ implementation tool for real-time chatting with RAG on your computer. It supports inference of various models ranging from less than 1B to more than 300B. The tool provides accelerated memory-efficient CPU inference with quantization, optimized KV cache, and parallel computing. It allows streaming generation with a typewriter effect and continuous chatting with virtually unlimited content length. ChatLLM.cpp also offers features like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), LoRA, Python/JavaScript/C bindings, web demo, and more possibilities. Users can clone the repository, quantize models, build the project using make or CMake, and run quantized models for interactive chatting.
llama-api-server
This project aims to create a RESTful API server compatible with the OpenAI API using open-source backends like llama/llama2. With this project, various GPT tools/frameworks can be compatible with your own model. Key features include: - **Compatibility with OpenAI API**: The API server follows the OpenAI API structure, allowing seamless integration with existing tools and frameworks. - **Support for Multiple Backends**: The server supports both llama.cpp and pyllama backends, providing flexibility in model selection. - **Customization Options**: Users can configure model parameters such as temperature, top_p, and top_k to fine-tune the model's behavior. - **Batch Processing**: The API supports batch processing for embeddings, enabling efficient handling of multiple inputs. - **Token Authentication**: The server utilizes token authentication to secure access to the API. This tool is particularly useful for developers and researchers who want to integrate large language models into their applications or explore custom models without relying on proprietary APIs.
For similar tasks

aim
Aim is an open-source, self-hosted ML experiment tracking tool designed to handle 10,000s of training runs. Aim provides a performant and beautiful UI for exploring and comparing training runs. Additionally, its SDK enables programmatic access to tracked metadata — perfect for automations and Jupyter Notebook analysis. **Aim's mission is to democratize AI dev tools 🎯**
For similar jobs

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.