phoenix
AI Observability & Evaluation
Stars: 8509

Phoenix is a tool that provides MLOps and LLMOps insights at lightning speed with zero-config observability. It offers a notebook-first experience for monitoring models and LLM Applications by providing LLM Traces, LLM Evals, Embedding Analysis, RAG Analysis, and Structured Data Analysis. Users can trace through the execution of LLM Applications, evaluate generative models, explore embedding point-clouds, visualize generative application's search and retrieval process, and statistically analyze structured data. Phoenix is designed to help users troubleshoot problems related to retrieval, tool execution, relevance, toxicity, drift, and performance degradation.
README:
Phoenix is an open-source AI observability platform designed for experimentation, evaluation, and troubleshooting. It provides:
- Tracing - Trace your LLM application's runtime using OpenTelemetry-based instrumentation.
- Evaluation - Leverage LLMs to benchmark your application's performance using response and retrieval evals.
- Datasets - Create versioned datasets of examples for experimentation, evaluation, and fine-tuning.
- Experiments - Track and evaluate changes to prompts, LLMs, and retrieval.
- Playground- Optimize prompts, compare models, adjust parameters, and replay traced LLM calls.
- Prompt Management- Manage and test prompt changes systematically using version control, tagging, and experimentation.
Phoenix is vendor and language agnostic with out-of-the-box support for popular frameworks (🦙LlamaIndex, 🦜⛓LangChain, Haystack, 🧩DSPy, 🤗smolagents) and LLM providers (OpenAI, Bedrock, MistralAI, VertexAI, LiteLLM, Google GenAI and more). For details on auto-instrumentation, check out the OpenInference project.
Phoenix runs practically anywhere, including your local machine, a Jupyter notebook, a containerized deployment, or in the cloud.
Install Phoenix via pip or conda
pip install arize-phoenixPhoenix container images are available via Docker Hub and can be deployed using Docker or Kubernetes. Arize AI also provides cloud instances at app.phoenix.arize.com.
The arize-phoenix package includes the entire Phoenix platfom. However if you have deployed the Phoenix platform, there are light-weight Python sub-packages and TypeScript packages that can be used in conjunction with the platfrom.
| Package | Version & Docs | Description |
|---|---|---|
| arize-phoenix-otel |
 
|
Provides a lightweight wrapper around OpenTelemetry primitives with Phoenix-aware defaults |
| arize-phoenix-client |
 
|
Lightweight client for interacting with the Phoenix server via its OpenAPI REST interface |
| arize-phoenix-evals |
 
|
Tooling to evaluate LLM applications including RAG relevance, answer relevance, and more |
| Package | Version & Docs | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @arizeai/phoenix-otel |
 
|
Provides a lightweight wrapper around OpenTelemetry primitives with Phoenix-aware defaults |
| @arizeai/phoenix-client |
 
|
Client for the Arize Phoenix API |
| @arizeai/phoenix-evals |
 
|
TypeScript evaluation library for LLM applications (alpha release) |
| @arizeai/phoenix-mcp |
 
|
MCP server implementation for Arize Phoenix providing unified interface to Phoenix's capabilities |
| @arizeai/phoenix-cli |
 
|
CLI for fetching traces, datasets, and experiments for use with Claude Code, Cursor, and other coding agents |
Phoenix is built on top of OpenTelemetry and is vendor, language, and framework agnostic. For details about tracing integrations and example applications, see the OpenInference project.
Python Integrations
| Integration | Package | Version Badge |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | openinference-instrumentation-openai |
 |
| OpenAI Agents | openinference-instrumentation-openai-agents |
 |
| LlamaIndex | openinference-instrumentation-llama-index |
 |
| DSPy | openinference-instrumentation-dspy |
 |
| AWS Bedrock | openinference-instrumentation-bedrock |
 |
| LangChain | openinference-instrumentation-langchain |
 |
| MistralAI | openinference-instrumentation-mistralai |
 |
| Google GenAI | openinference-instrumentation-google-genai |
 |
| Google ADK | openinference-instrumentation-google-adk |
 |
| Guardrails | openinference-instrumentation-guardrails |
 |
| VertexAI | openinference-instrumentation-vertexai |
 |
| CrewAI | openinference-instrumentation-crewai |
 |
| Haystack | openinference-instrumentation-haystack |
 |
| LiteLLM | openinference-instrumentation-litellm |
 |
| Groq | openinference-instrumentation-groq |
 |
| Instructor | openinference-instrumentation-instructor |
 |
| Anthropic | openinference-instrumentation-anthropic |
 |
| Smolagents | openinference-instrumentation-smolagents |
 |
| Agno | openinference-instrumentation-agno |
 |
| MCP | openinference-instrumentation-mcp |
 |
| Pydantic AI | openinference-instrumentation-pydantic-ai |
 |
| Autogen AgentChat | openinference-instrumentation-autogen-agentchat |
 |
| Portkey | openinference-instrumentation-portkey |
 |
Normalize and convert data across other instrumentation libraries by adding span processors that unify data.
| Package | Description | Version |
|---|---|---|
openinference-instrumentation-openlit |
OpenInference Span Processor for OpenLIT traces. |  |
openinference-instrumentation-openllmetry |
OpenInference Span Processor for OpenLLMetry (Traceloop) traces. |  |
| Integration | Package | Version Badge |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | @arizeai/openinference-instrumentation-openai |
 |
| LangChain.js | @arizeai/openinference-instrumentation-langchain |
 |
| Vercel AI SDK | @arizeai/openinference-vercel |
 |
| BeeAI | @arizeai/openinference-instrumentation-beeai |
 |
| Mastra | @mastra/arize |
 |
| Integration | Package | Version Badge |
|---|---|---|
| LangChain4j | openinference-instrumentation-langchain4j |
 |
| SpringAI | openinference-instrumentation-springAI |
 |
| Platform | Description | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| BeeAI | AI agent framework with built-in observability | Integration Guide |
| Dify | Open-source LLM app development platform | Integration Guide |
| Envoy AI Gateway | AI Gateway built on Envoy Proxy for AI workloads | Integration Guide |
| LangFlow | Visual framework for building multi-agent and RAG applications | Integration Guide |
| LiteLLM Proxy | Proxy server for LLMs | Integration Guide |
We take data security and privacy very seriously. For more details, see our Security and Privacy documentation.
By default, Phoenix collects basic web analytics (e.g., page views, UI interactions) to help us understand how Phoenix is used and improve the product. None of your trace data, evaluation results, or any sensitive information is ever collected.
You can opt-out of telemetry by setting the environment variable: PHOENIX_TELEMETRY_ENABLED=false
Join our community to connect with thousands of AI builders.
- 🌍 Join our Slack community.
- 📚 Read our documentation.
- 💡 Ask questions and provide feedback in the #phoenix-support channel.
- 🌟 Leave a star on our GitHub.
- 🐞 Report bugs with GitHub Issues.
- 𝕏 Follow us on 𝕏.
- 🗺️ Check out our roadmap to see where we're heading next.
- 🧑🏫 Deep dive into everything Agents and LLM Evaluations on Arize's Learning Hubs.
See the migration guide for a list of breaking changes.
Copyright 2025 Arize AI, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Portions of this code are patent protected by one or more U.S. Patents. See the IP_NOTICE.
This software is licensed under the terms of the Elastic License 2.0 (ELv2). See LICENSE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for phoenix
Similar Open Source Tools

phoenix
Phoenix is a tool that provides MLOps and LLMOps insights at lightning speed with zero-config observability. It offers a notebook-first experience for monitoring models and LLM Applications by providing LLM Traces, LLM Evals, Embedding Analysis, RAG Analysis, and Structured Data Analysis. Users can trace through the execution of LLM Applications, evaluate generative models, explore embedding point-clouds, visualize generative application's search and retrieval process, and statistically analyze structured data. Phoenix is designed to help users troubleshoot problems related to retrieval, tool execution, relevance, toxicity, drift, and performance degradation.

oumi
Oumi is an open-source platform for building state-of-the-art foundation models, offering tools for data preparation, training, evaluation, and deployment. It supports training and fine-tuning models with various parameters, working with text and multimodal models, synthesizing and curating training data, deploying models efficiently, evaluating models comprehensively, and running on different platforms. Oumi provides a consistent API, reliability, and flexibility for research purposes.
langfuse
Langfuse is a powerful tool that helps you develop, monitor, and test your LLM applications. With Langfuse, you can: * **Develop:** Instrument your app and start ingesting traces to Langfuse, inspect and debug complex logs, and manage, version, and deploy prompts from within Langfuse. * **Monitor:** Track metrics (cost, latency, quality) and gain insights from dashboards & data exports, collect and calculate scores for your LLM completions, run model-based evaluations, collect user feedback, and manually score observations in Langfuse. * **Test:** Track and test app behaviour before deploying a new version, test expected in and output pairs and benchmark performance before deploying, and track versions and releases in your application. Langfuse is easy to get started with and offers a generous free tier. You can sign up for Langfuse Cloud or deploy Langfuse locally or on your own infrastructure. Langfuse also offers a variety of integrations to make it easy to connect to your LLM applications.

composio
Composio is a production-ready toolset for AI agents that enables users to integrate AI agents with various agentic tools effortlessly. It provides support for over 100 tools across different categories, including popular softwares like GitHub, Notion, Linear, Gmail, Slack, and more. Composio ensures managed authorization with support for six different authentication protocols, offering better agentic accuracy and ease of use. Users can easily extend Composio with additional tools, frameworks, and authorization protocols. The toolset is designed to be embeddable and pluggable, allowing for seamless integration and consistent user experience.
helicone
Helicone is an open-source observability platform designed for Language Learning Models (LLMs). It logs requests to OpenAI in a user-friendly UI, offers caching, rate limits, and retries, tracks costs and latencies, provides a playground for iterating on prompts and chat conversations, supports collaboration, and will soon have APIs for feedback and evaluation. The platform is deployed on Cloudflare and consists of services like Web (NextJs), Worker (Cloudflare Workers), Jawn (Express), Supabase, and ClickHouse. Users can interact with Helicone locally by setting up the required services and environment variables. The platform encourages contributions and provides resources for learning, documentation, and integrations.
awesome-llm-webapps
This repository is a curated list of open-source, actively maintained web applications that leverage large language models (LLMs) for various use cases, including chatbots, natural language interfaces, assistants, and question answering systems. The projects are evaluated based on key criteria such as licensing, maintenance status, complexity, and features, to help users select the most suitable starting point for their LLM-based applications. The repository welcomes contributions and encourages users to submit projects that meet the criteria or suggest improvements to the existing list.
awesome-LangGraph
Awesome LangGraph is a curated list of projects, resources, and tools for building stateful, multi-actor applications with LangGraph. It provides valuable resources for developers at all stages of development, from beginners to those building production-ready systems. The repository covers core ecosystem components, LangChain ecosystem, LangGraph platform, official resources, starter templates, pre-built agents, example applications, development tools, community projects, AI assistants, content & media, knowledge & retrieval, finance & business, sustainability, learning resources, companies using LangGraph, contributing guidelines, and acknowledgments.
swift
SWIFT (Scalable lightWeight Infrastructure for Fine-Tuning) supports training, inference, evaluation and deployment of nearly **200 LLMs and MLLMs** (multimodal large models). Developers can directly apply our framework to their own research and production environments to realize the complete workflow from model training and evaluation to application. In addition to supporting the lightweight training solutions provided by [PEFT](https://github.com/huggingface/peft), we also provide a complete **Adapters library** to support the latest training techniques such as NEFTune, LoRA+, LLaMA-PRO, etc. This adapter library can be used directly in your own custom workflow without our training scripts. To facilitate use by users unfamiliar with deep learning, we provide a Gradio web-ui for controlling training and inference, as well as accompanying deep learning courses and best practices for beginners. Additionally, we are expanding capabilities for other modalities. Currently, we support full-parameter training and LoRA training for AnimateDiff.
PocketFlow
Pocket Flow is a 100-line minimalist LLM framework designed for (Multi-)Agents, Workflow, RAG, etc. It provides a core abstraction for LLM projects by focusing on computation and communication through a graph structure and shared store. The framework aims to support the development of LLM Agents, such as Cursor AI, by offering a minimal and low-level approach that is well-suited for understanding and usage. Users can install Pocket Flow via pip or by copying the source code, and detailed documentation is available on the project website.
Hands-On-Large-Language-Models-CN
Hands-On Large Language Models CN(ZH) is a Chinese version of the book 'Hands-On Large Language Models' by Jay Alammar and Maarten Grootendorst. It provides detailed code annotations and additional insights, offers Notebook versions suitable for Chinese network environments, utilizes openbayes for free GPU access, allows convenient environment setup with vscode, and includes accompanying Chinese language videos on platforms like Bilibili and YouTube. The book covers various chapters on topics like Tokens and Embeddings, Transformer LLMs, Text Classification, Text Clustering, Prompt Engineering, Text Generation, Semantic Search, Multimodal LLMs, Text Embedding Models, Fine-tuning Models, and more.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.
ipex-llm
IPEX-LLM is a PyTorch library for running Large Language Models (LLMs) on Intel CPUs and GPUs with very low latency. It provides seamless integration with various LLM frameworks and tools, including llama.cpp, ollama, Text-Generation-WebUI, HuggingFace transformers, and more. IPEX-LLM has been optimized and verified on over 50 LLM models, including LLaMA, Mistral, Mixtral, Gemma, LLaVA, Whisper, ChatGLM, Baichuan, Qwen, and RWKV. It supports a range of low-bit inference formats, including INT4, FP8, FP4, INT8, INT2, FP16, and BF16, as well as finetuning capabilities for LoRA, QLoRA, DPO, QA-LoRA, and ReLoRA. IPEX-LLM is actively maintained and updated with new features and optimizations, making it a valuable tool for researchers, developers, and anyone interested in exploring and utilizing LLMs.
ipex-llm
The `ipex-llm` repository is an LLM acceleration library designed for Intel GPU, NPU, and CPU. It provides seamless integration with various models and tools like llama.cpp, Ollama, HuggingFace transformers, LangChain, LlamaIndex, vLLM, Text-Generation-WebUI, DeepSpeed-AutoTP, FastChat, Axolotl, and more. The library offers optimizations for over 70 models, XPU acceleration, and support for low-bit (FP8/FP6/FP4/INT4) operations. Users can run different models on Intel GPUs, NPU, and CPUs with support for various features like finetuning, inference, serving, and benchmarking.
ai-dev-kit
The AI Dev Kit is a comprehensive toolkit designed to enhance AI-driven development on Databricks. It provides trusted sources for AI coding assistants like Claude Code and Cursor to build faster and smarter on Databricks. The kit includes features such as Spark Declarative Pipelines, Databricks Jobs, AI/BI Dashboards, Unity Catalog, Genie Spaces, Knowledge Assistants, MLflow Experiments, Model Serving, Databricks Apps, and more. Users can choose from different adventures like installing the kit, using the visual builder app, teaching AI assistants Databricks patterns, executing Databricks actions, or building custom integrations with the core library. The kit also includes components like databricks-tools-core, databricks-mcp-server, databricks-skills, databricks-builder-app, and ai-dev-project.
UMOE-Scaling-Unified-Multimodal-LLMs
Uni-MoE is a MoE-based unified multimodal model that can handle diverse modalities including audio, speech, image, text, and video. The project focuses on scaling Unified Multimodal LLMs with a Mixture of Experts framework. It offers enhanced functionality for training across multiple nodes and GPUs, as well as parallel processing at both the expert and modality levels. The model architecture involves three training stages: building connectors for multimodal understanding, developing modality-specific experts, and incorporating multiple trained experts into LLMs using the LoRA technique on mixed multimodal data. The tool provides instructions for installation, weights organization, inference, training, and evaluation on various datasets.
For similar tasks

phoenix
Phoenix is a tool that provides MLOps and LLMOps insights at lightning speed with zero-config observability. It offers a notebook-first experience for monitoring models and LLM Applications by providing LLM Traces, LLM Evals, Embedding Analysis, RAG Analysis, and Structured Data Analysis. Users can trace through the execution of LLM Applications, evaluate generative models, explore embedding point-clouds, visualize generative application's search and retrieval process, and statistically analyze structured data. Phoenix is designed to help users troubleshoot problems related to retrieval, tool execution, relevance, toxicity, drift, and performance degradation.
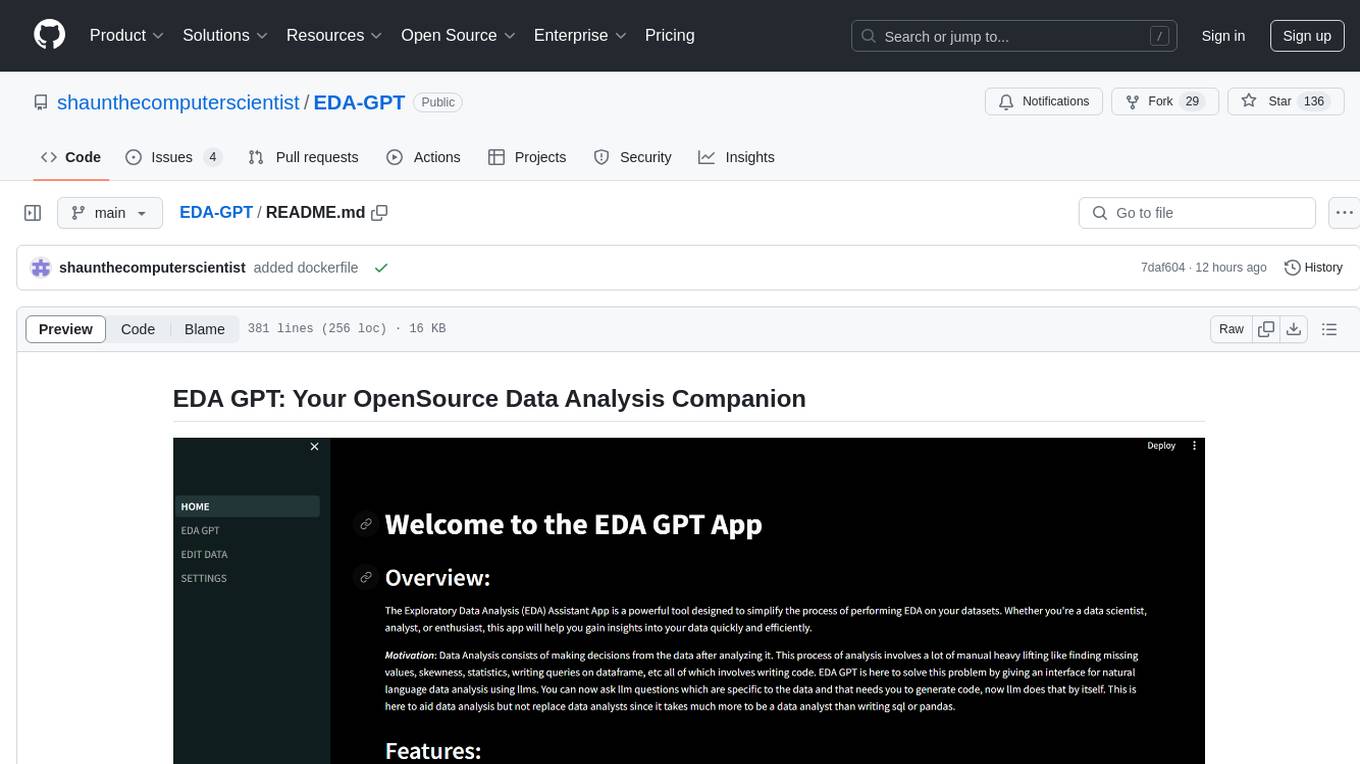
EDA-GPT
EDA GPT is an open-source data analysis companion that offers a comprehensive solution for structured and unstructured data analysis. It streamlines the data analysis process, empowering users to explore, visualize, and gain insights from their data. EDA GPT supports analyzing structured data in various formats like CSV, XLSX, and SQLite, generating graphs, and conducting in-depth analysis of unstructured data such as PDFs and images. It provides a user-friendly interface, powerful features, and capabilities like comparing performance with other tools, analyzing large language models, multimodal search, data cleaning, and editing. The tool is optimized for maximal parallel processing, searching internet and documents, and creating analysis reports from structured and unstructured data.
intro-llm-rag
This repository serves as a comprehensive guide for technical teams interested in developing conversational AI solutions using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques. It covers theoretical knowledge and practical code implementations, making it suitable for individuals with a basic technical background. The content includes information on large language models (LLMs), transformers, prompt engineering, embeddings, vector stores, and various other key concepts related to conversational AI. The repository also provides hands-on examples for two different use cases, along with implementation details and performance analysis.
vertex-ai-samples
The Google Cloud Vertex AI sample repository contains notebooks and community content that demonstrate how to develop and manage ML workflows using Google Cloud Vertex AI.
AI-Horde
The AI Horde is an enterprise-level ML-Ops crowdsourced distributed inference cluster for AI Models. This middleware can support both Image and Text generation. It is infinitely scalable and supports seamless drop-in/drop-out of compute resources. The Public version allows people without a powerful GPU to use Stable Diffusion or Large Language Models like Pygmalion/Llama by relying on spare/idle resources provided by the community and also allows non-python clients, such as games and apps, to use AI-provided generations.
truss
Truss is a tool that simplifies the process of serving AI/ML models in production. It provides a consistent and easy-to-use interface for packaging, testing, and deploying models, regardless of the framework they were created with. Truss also includes a live reload server for fast feedback during development, and a batteries-included model serving environment that eliminates the need for Docker and Kubernetes configuration.

cyclops
Cyclops is a toolkit for facilitating research and deployment of ML models for healthcare. It provides a few high-level APIs namely: data - Create datasets for training, inference and evaluation. We use the popular 🤗 datasets to efficiently load and slice different modalities of data models - Use common model implementations using scikit-learn and PyTorch tasks - Use common ML task formulations such as binary classification or multi-label classification on tabular, time-series and image data evaluate - Evaluate models on clinical prediction tasks monitor - Detect dataset shift relevant for clinical use cases report - Create model report cards for clinical ML models
vertex-ai-mlops
Vertex AI is a platform for end-to-end model development. It consist of core components that make the processes of MLOps possible for design patterns of all types.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.