
22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
Notes and Coding Examples for OOP in Java Class
Stars: 72
The 'Object Oriented Programming in Java' repository provides notes and code examples organized into units to help users understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step. It includes theoretical notes, practical Java examples, setup files for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ IDEA, instructions on setting up Java, running Java programs from the command line, and loading projects in VS Code or IntelliJ IDEA. Users can contribute by opening issues or submitting pull requests. The repository is intended for educational purposes, allowing forking and modification for personal study or classroom use.
README:
Welcome to the Object Oriented Programming in Java repository! This repository contains notes and code examples organized into units, helping you understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step.
The repository is organized into four main folders, each representing a unit of the course:
-
Unit1/
-
NOTES.md– Markdown notes covering fundamental OOP in Java concepts. -
code/– Example Java programs (subfolders).
-
-
Unit2/
NOTES.mdcode/
-
Unit3/
NOTES.mdcode/
-
Unit4/
NOTES.mdcode/
Additionally, you will find:
- .vsode/, .idea/ – Contains setup files for Visual Studio Code (VS Code) and IntelliJ IDEA to help you load and run the Java projects in each of the subfolders.
-
Browse the Notes
Within each unit folder, find theNOTES.mdMarkdown (.md) files. These notes will guide you through the theoretical concepts of each unit. -
Explore the Code Examples
In thecodesubfolder under each unit, you will find practical Java examples illustrating the concepts discussed in the notes. Each example might be in its own subfolder. -
Run and Experiment
Feel free to modify the example code or create your own Java files to practice. Instructions on setting up Java and running the code from the command line are provided below. -
Setup Files
- If you prefer using VS Code, refer to the files in the
setup/vscodedirectory. - If you prefer using IntelliJ IDEA, refer to the files in the
setup/ideadirectory.
- If you prefer using VS Code, refer to the files in the
-
Prerequisites Before you begin, ensure that the following tools are installed on your system:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): Version 11 or higher.
- Git: For version control.
- Gradle: Although we'll use the Gradle Wrapper, having Gradle installed can be helpful.
- Text Editor or IDE: Such as VS Code, IntelliJ IDEA, or Eclipse.
You have two main options for installing the Java Development Kit (JDK): Oracle JDK or OpenJDK. Both will allow you to compile and run Java programs.
OpenJDK is open-source and is typically the easiest to install on Ubuntu:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-21-jdk(You can replace 21 with the version you need, e.g., openjdk-11-jdk.)
If you prefer Oracle’s official JDK:
- Download the
.debpackage from the Oracle Official Website. - Navigate to the directory where the package is saved:
cd /path/to/download - Install the package:
sudo dpkg -i <oracle-jdk-package>.deb
- Verify installation:
You should see the Oracle JDK version displayed.
java -version
After installing Java (whether OpenJDK or Oracle JDK), you can compile and run the example code from the command line. Below is a general step-by-step guide:
-
Open a Terminal: Navigate (
cd) to the directory containing the Java files you want to compile. For instance:cd /path/to/Unit1/code/Example1 -
Compile the Java File(s):
javac Main.java
-
javacis the Java compiler. - This will generate one or more
.classfiles in the same directory.
-
-
Run the Java Program:
java Main
- Make sure Main is the class that contains the
public static void main(String[] args)method.
- Make sure Main is the class that contains the
-
Passing Arguments (Optional):
If your program requires command-line arguments, you can pass them like so:java Main arg1 arg2
- Install the Java Extension Pack from the VS Code Marketplace.
- Copy or clone this repository to your local machine.
- Open the root of this repository with VS Code.
- The extension pack will detect the Java projects, and you can start editing, compiling, and debugging Java code directly within VS Code.
- Install IntelliJ IDEA (Community Edition is sufficient).
- Clone this repository to your local machine.
- From the IntelliJ IDEA Welcome screen, select Open or Import.
- Navigate to this repository’s root folder (or a specific unit’s
codesubfolder) and import it as a Maven/Gradle project if applicable, or simply as a Java project. - IntelliJ will automatically configure the project’s libraries and dependencies.
If you find any issues or want to suggest improvements:
- Open an Issue: Describe the problem or the idea you have.
- Submit a Pull Request: Fork this repository, make changes, and submit a pull request for review.
This repository is intended for educational purposes. Feel free to fork and modify for your personal study or classroom use. If you plan to use it beyond that, please check the specific licensing details or contact the authors of the original work.
Happy Coding!
For any questions or clarifications regarding the course materials, feel free to reach out to me at [email protected] or open an issue in this repository. Enjoy learning Object Oriented Programming in Java!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for 22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
Similar Open Source Tools

22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
The 'Object Oriented Programming in Java' repository provides notes and code examples organized into units to help users understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step. It includes theoretical notes, practical Java examples, setup files for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ IDEA, instructions on setting up Java, running Java programs from the command line, and loading projects in VS Code or IntelliJ IDEA. Users can contribute by opening issues or submitting pull requests. The repository is intended for educational purposes, allowing forking and modification for personal study or classroom use.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
Groqqle
Groqqle 2.1 is a revolutionary, free AI web search and API that instantly returns ORIGINAL content derived from source articles, websites, videos, and even foreign language sources, for ANY target market of ANY reading comprehension level! It combines the power of large language models with advanced web and news search capabilities, offering a user-friendly web interface, a robust API, and now a powerful Groqqle_web_tool for seamless integration into your projects. Developers can instantly incorporate Groqqle into their applications, providing a powerful tool for content generation, research, and analysis across various domains and languages.
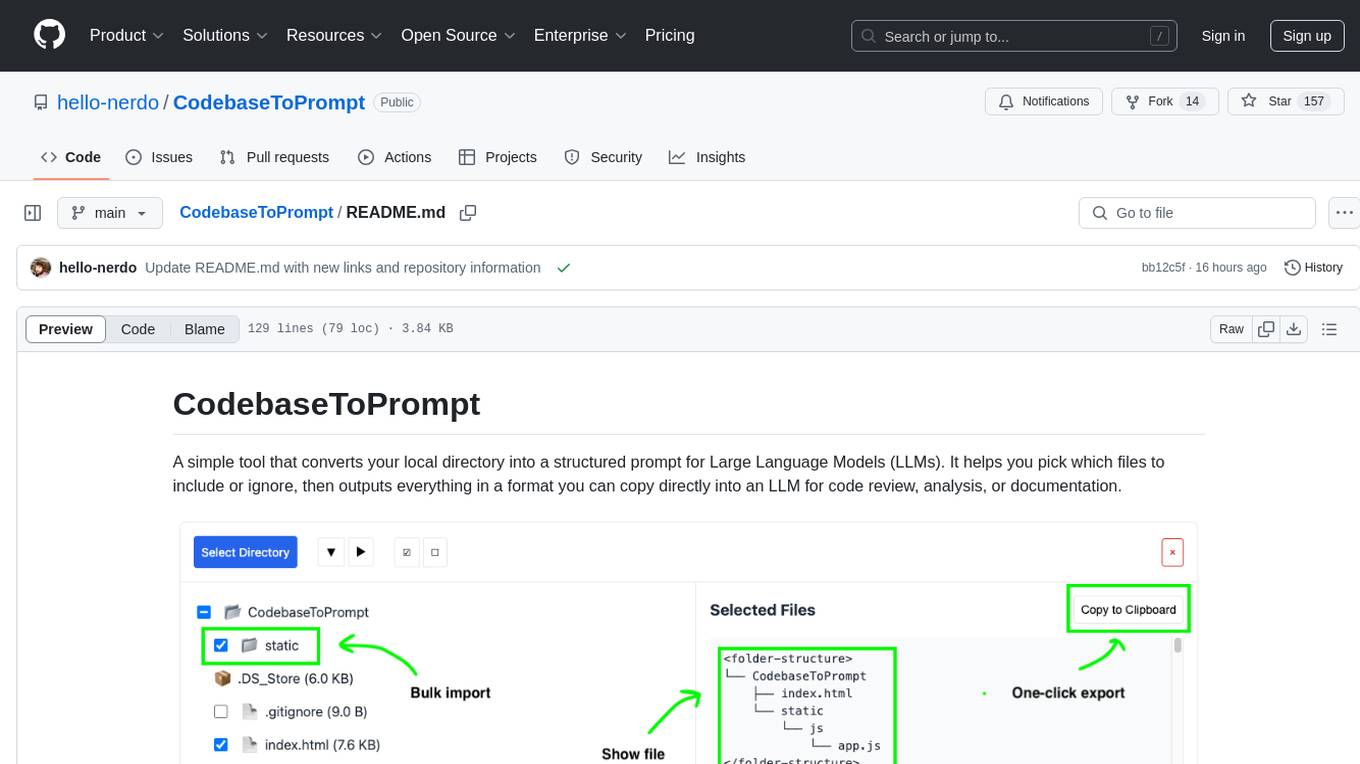
CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in an interactive interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with LLMs, estimates token count, and supports flexible text selection. Users can deploy the tool using Docker for self-contained usage and can contribute to the project by opening issues or submitting pull requests.

swark
Swark is a VS Code extension that automatically generates architecture diagrams from code using large language models (LLMs). It is directly integrated with GitHub Copilot, requires no authentication or API key, and supports all languages. Swark helps users learn new codebases, review AI-generated code, improve documentation, understand legacy code, spot design flaws, and gain test coverage insights. It saves output in a 'swark-output' folder with diagram and log files. Source code is only shared with GitHub Copilot for privacy. The extension settings allow customization for file reading, file extensions, exclusion patterns, and language model selection. Swark is open source under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0.
gitdiagram
GitDiagram is a tool that turns any GitHub repository into an interactive diagram for visualization in seconds. It offers instant visualization, interactivity, fast generation, customization, and API access. The tool utilizes a tech stack including Next.js, FastAPI, PostgreSQL, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Vercel, EC2, GitHub Actions, PostHog, and Api-Analytics. Users can self-host the tool for local development and contribute to its development. GitDiagram is inspired by Gitingest and has future plans to use larger context models, allow user API key input, implement RAG with Mermaid.js docs, and include font-awesome icons in diagrams.
restai
RestAI is an AIaaS (AI as a Service) platform that allows users to create and consume AI agents (projects) using a simple REST API. It supports various types of agents, including RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), RAGSQL (RAG for SQL), inference, vision, and router. RestAI features automatic VRAM management, support for any public LLM supported by LlamaIndex or any local LLM supported by Ollama, a user-friendly API with Swagger documentation, and a frontend for easy access. It also provides evaluation capabilities for RAG agents using deepeval.
pipecat-flows
Pipecat Flows is a framework designed for building structured conversations in AI applications. It allows users to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows, handling state management and LLM interactions. The framework includes a Python module for building conversation flows and a visual editor for designing and exporting flow configurations. Pipecat Flows is suitable for scenarios such as customer service scripts, intake forms, personalized experiences, and complex decision trees.
Zentara-Code
Zentara Code is an AI coding assistant for VS Code that turns chat instructions into precise, auditable changes in the codebase. It is optimized for speed, safety, and correctness through parallel execution, LSP semantics, and integrated runtime debugging. It offers features like parallel subagents, integrated LSP tools, and runtime debugging for efficient code modification and analysis.
FunGen-AI-Powered-Funscript-Generator
FunGen is a Python-based tool that uses AI to generate Funscript files from VR and 2D POV videos. It enables fully automated funscript creation for individual scenes or entire folders of videos. The tool includes features like automatic system scaling support, quick installation guides for Windows, Linux, and macOS, manual installation instructions, NVIDIA GPU setup, AMD GPU acceleration, YOLO model download, GUI settings, GitHub token setup, command-line usage, modular systems for funscript filtering and motion tracking, performance and parallel processing tips, and more. The project is still in early development stages and is not intended for commercial use.
AutoDocs
AutoDocs by Sita is a tool designed to automate documentation for any repository. It parses the repository using tree-sitter and SCIP, constructs a code dependency graph, and generates repository-wide, dependency-aware documentation and summaries. It provides a FastAPI backend for ingestion/search and a Next.js web UI for chat and exploration. Additionally, it includes an MCP server for deep search capabilities. The tool aims to simplify the process of generating accurate and high-signal documentation for codebases.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
LocalAIVoiceChat
LocalAIVoiceChat is an experimental alpha software that enables real-time voice chat with a customizable AI personality and voice on your PC. It integrates Zephyr 7B language model with speech-to-text and text-to-speech libraries. The tool is designed for users interested in state-of-the-art voice solutions and provides an early version of a local real-time chatbot.
middleware
Middleware is an open-source engineering management tool that helps engineering leaders measure and analyze team effectiveness using DORA metrics. It integrates with CI/CD tools, automates DORA metric collection and analysis, visualizes key performance indicators, provides customizable reports and dashboards, and integrates with project management platforms. Users can set up Middleware using Docker or manually, generate encryption keys, set up backend and web servers, and access the application to view DORA metrics. The tool calculates DORA metrics using GitHub data, including Deployment Frequency, Lead Time for Changes, Mean Time to Restore, and Change Failure Rate. Middleware aims to provide DORA metrics to users based on their Git data, simplifying the process of tracking software delivery performance and operational efficiency.
codepair
CodePair is an open-source real-time collaborative markdown editor with AI intelligence, allowing users to collaboratively edit documents, share documents with external parties, and utilize AI intelligence within the editor. It is built using React, NestJS, and LangChain. The repository contains frontend and backend code, with detailed instructions for setting up and running each part. Users can choose between Frontend Development Only Mode or Full Stack Development Mode based on their needs. CodePair also integrates GitHub OAuth for Social Login feature. Contributors are welcome to submit patches and follow the contribution workflow.
manifold
Manifold is a powerful platform for workflow automation using AI models. It supports text generation, image generation, and retrieval-augmented generation, integrating seamlessly with popular AI endpoints. Additionally, Manifold provides robust semantic search capabilities using PGVector combined with the SEFII engine. It is under active development and not production-ready.
For similar tasks
NewEraAI-Papers
The NewEraAI-Papers repository provides links to collections of influential and interesting research papers from top AI conferences, along with open-source code to promote reproducibility and provide detailed implementation insights beyond the scope of the article. Users can stay up to date with the latest advances in AI research by exploring this repository. Contributions to improve the completeness of the list are welcomed, and users can create pull requests, open issues, or contact the repository owner via email to enhance the repository further.
Awesome_Mamba
Awesome Mamba is a curated collection of groundbreaking research papers and articles on Mamba Architecture, a pioneering framework in deep learning known for its selective state spaces and efficiency in processing complex data structures. The repository offers a comprehensive exploration of Mamba architecture through categorized research papers covering various domains like visual recognition, speech processing, remote sensing, video processing, activity recognition, image enhancement, medical imaging, reinforcement learning, natural language processing, 3D recognition, multi-modal understanding, time series analysis, graph neural networks, point cloud analysis, and tabular data handling.
OnAIR
The On-board Artificial Intelligence Research (OnAIR) Platform is a framework that enables AI algorithms written in Python to interact with NASA's cFS. It is intended to explore research concepts in autonomous operations in a simulated environment. The platform provides tools for generating environments, handling telemetry data through Redis, running unit tests, and contributing to the repository. Users can set up a conda environment, configure telemetry and Redis examples, run simulations, and conduct unit tests to ensure the functionality of their AI algorithms. The platform also includes guidelines for licensing, copyright, and contributions to the repository.
model-catalog
model-catalog is a repository containing standardized JSON descriptors for Large Language Model (LLM) model files. Each model is described in a JSON file with details about the model, authors, additional resources, available model files, and providers. The format captures factors like model size, architecture, file format, and quantization format. A Github action merges individual JSON files from the `models/` directory into a `catalog.json` file, which is validated using a JSON schema. Contributors can help by adding new model JSON files following the contribution process.

22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
The 'Object Oriented Programming in Java' repository provides notes and code examples organized into units to help users understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step. It includes theoretical notes, practical Java examples, setup files for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ IDEA, instructions on setting up Java, running Java programs from the command line, and loading projects in VS Code or IntelliJ IDEA. Users can contribute by opening issues or submitting pull requests. The repository is intended for educational purposes, allowing forking and modification for personal study or classroom use.
support-genAI-book
This repository serves as a support page for the book 'Deciphering Generative AI from Original Papers' released by Gijutsu-Hyohron Co., Ltd. It includes answers to exercises and errata from the book. The exercises are provided in chapter-specific .md files in the 'exercises' directory. Please note that there may be some rendering issues with GitHub's math rendering, and the answers are just examples for reference. Contributions to this repository can be made by following the guidelines in CONTRIBUTING.md.
For similar jobs
OpenCatEsp32
OpenCat code running on BiBoard, a high-performance ESP32 quadruped robot development board. The board is mainly designed for developers and engineers working on multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) Multi-legged robots with up to 12 servos.
Awesome-CS-Books
Awesome CS Books is a curated list of books on computer science and technology. The books are organized by topic, including programming languages, software engineering, computer networks, operating systems, databases, data structures and algorithms, big data, architecture, and interviews. The books are available in PDF format and can be downloaded for free. The repository also includes links to free online courses and other resources.
AIT
AIT is a repository focused on Algorithmic Information Theory, specifically utilizing Binary Lambda Calculus. It provides resources and tools for studying and implementing algorithms based on information theory principles. The repository aims to explore the relationship between algorithms and information theory through the lens of Binary Lambda Calculus, offering insights into computational complexity and data compression techniques.
eleeye
ElephantEye is a free Chinese Chess program that follows the GNU Lesser General Public Licence. It is designed for chess enthusiasts and programmers to use freely. The program works as a XiangQi engine for XQWizard with strong AI capabilities. ElephantEye supports UCCI 3.0 protocol and offers various parameter settings for users to customize their experience. The program uses brute-force chess algorithms and static position evaluation techniques to search for optimal moves. ElephantEye has participated in computer chess competitions and has been tested on various online chess platforms. The source code of ElephantEye is available on SourceForge for developers to explore and improve.

22AIE111-Object-Oriented-Programming-in-Java-S2-2025
The 'Object Oriented Programming in Java' repository provides notes and code examples organized into units to help users understand and practice Java concepts step-by-step. It includes theoretical notes, practical Java examples, setup files for Visual Studio Code and IntelliJ IDEA, instructions on setting up Java, running Java programs from the command line, and loading projects in VS Code or IntelliJ IDEA. Users can contribute by opening issues or submitting pull requests. The repository is intended for educational purposes, allowing forking and modification for personal study or classroom use.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

openinference
OpenInference is a set of conventions and plugins that complement OpenTelemetry to enable tracing of AI applications. It provides a way to capture and analyze the performance and behavior of AI models, including their interactions with other components of the application. OpenInference is designed to be language-agnostic and can be used with any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend. It includes a set of instrumentations for popular machine learning SDKs and frameworks, making it easy to add tracing to your AI applications.