
leaked-system-prompts
Collection of leaked system prompts
Stars: 1840
This repository contains a collection of leaked prompts for various AI systems, including Anthropic Claude, Discord Clyde, Google Gemini, Microsoft Bing Chat, OpenAI ChatGPT, and others. These prompts can be used to explore the capabilities and limitations of these AI systems and to gain insights into their inner workings.
README:
Collection of leaked prompts
- anthropic-claude_2.0_20240306.md
- anthropic-claude_2.1_20240306.md
- anthropic-claude-3-haiku_20240712.md
- anthropic-claude-3-opus_20240712.md
- anthropic-claude-3-sonnet_20240306.md
- anthropic-claude-3-sonnet_20240311.md
- anthropic-claude-3.5-sonnet_20240712.md
- anthropic-claude-3.5-sonnet_20240909.md
- anthropic-claude-3.5-sonnet_20241022.md
- anthropic-claude-3.5-sonnet_20241122.md
- anthropic-claude-3.7-sonnet_20250224.md
- anthropic-claude-api-tool-use_20250119.md
- anthropic-claude-code_20250307.md
- anthropic-claude-opus_20240306.md
- bolt.new_20241009.md
- brave-leo-ai_20240601.md
- ChatGLM4_20240821.md
- claude-artifacts_20240620.md
- codeium-windsurf-cascade_20241206.md
- codeium-windsurf-cascade-R1_20250201.md
- colab-ai_20240108.md
- colab-ai_20240511.md
- cursor-ide-agent-claude-sonnet-3.7_20250309.md
- cursor-ide-sonnet_20241224.md
- devv_20240427.md
- discord-clyde_20230420.md
- discord-clyde_20230519.md
- discord-clyde_20230715.md
- discord-clyde_20230716-1.md
- discord-clyde_20230716-2.md
- ESTsoft-alan_20230920.md
- gandalf_20230919.md
- github-copilot-chat_20230513.md
- github-copilot-chat_20240930.md
- google-gemini-1.5_20240411.md
- manus_20250309.md
- microsoft-bing-chat_20230209.md
- microsoft-copilot_20240310.md
- microsoft-copilot_20241219.md
- moonshot-kimi-chat_20241106.md
- naver-cue_20230920.md
- notion-ai_20221228.md
- openai-assistants-api_20231106.md
- openai-chatgpt_20221201.md
- openai-chatgpt-ios_20230614.md
- openai-chatgpt4-android_20240207.md
- openai-chatgpt4o_20240520.md
- openai-dall-e-3_20231007-1.md
- openai-dall-e-3_20231007-2.md
- openai-deep-research_20250204.md
- opera-aria_20230617.md
- perplexity.ai_20221208.md
- perplexity.ai_20240311.md
- perplexity.ai_20240513.md
- perplexity.ai_20240607.md
- perplexity.ai_gpt4_20240311.md
- phind_20240427.md
- remoteli-io_20230806.md
- roblox-studio-assistant_20240320.md
- snap-myai_20230430.md
- v0_20250306.md
- wrtn_20230603.md
- wrtn-gpt3.5_20240215.md
- wrtn-gpt4_20240215.md
- xAI-grok_20240307.md
- xAI-grok_20241003.md
- xAI-grok2_20241218.md
- xAI-grok2_20250111.md
- xAI-grok3_20250223.md
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for leaked-system-prompts
Similar Open Source Tools

leaked-system-prompts
This repository contains a collection of leaked prompts for various AI systems, including Anthropic Claude, Discord Clyde, Google Gemini, Microsoft Bing Chat, OpenAI ChatGPT, and others. These prompts can be used to explore the capabilities and limitations of these AI systems and to gain insights into their inner workings.
videos
The 'videos' repository contains resources related to self-media videos on platforms like Bilibili, YouTube, Xiaohongshu, and Douyin. It includes tutorials, deployment guides, and tools for various web frameworks, AI development platforms, and cloud services. The repository offers video tutorials on topics such as AI development, cloud computing, programming tools, and AI-powered applications. Users can find information on deploying AI models, utilizing AI APIs, setting up cloud servers, and enhancing video editing capabilities using AI technology.
GenshinGamePlay
GenshinGamePlay is a repository that references the gameplay framework of Genshin Impact, including combat, puzzle solving, monster AI, and storyline. It currently showcases animations for combat skills, treasure hunting puzzles, and monster AI. The repository also includes a table export tool and references various Unity frameworks and plugins for game development. The repository aims to provide resources and tools for developing gameplay mechanics similar to Genshin Impact.
AI-PhD-S25
AI-PhD-S25 is a mono-repo for the DOTE 6635 course on AI for Business Research at CUHK Business School. The course aims to provide a fundamental understanding of ML/AI concepts and methods relevant to business research, explore applications of ML/AI in business research, and discover cutting-edge AI/ML technologies. The course resources include Google CoLab for code distribution, Jupyter Notebooks, Google Sheets for group tasks, Overleaf template for lecture notes, replication projects, and access to HPC Server compute resource. The course covers topics like AI/ML in business research, deep learning basics, attention mechanisms, transformer models, LLM pretraining, posttraining, causal inference fundamentals, and more.
python-weekly
Python Trending Weekly is a curated newsletter by Python猫 that selects the most valuable articles, tutorials, open-source projects, software tools, podcasts, videos, and hot topics from over 250 English and Chinese sources. The newsletter aims to help readers improve their Python skills and increase their income from both professional and side projects. It offers paid subscription options and is available on various platforms like GitHub, WeChat, blogs, email, Telegram, and Twitter. Each issue shares a collection of articles, open-source projects, videos, and books related to Python and technology.
Building-a-Small-LLM-from-Scratch
This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide on building a small Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch using PyTorch. The author shares insights and experiences gained from working on LLM projects in the industry, aiming to help beginners understand the fundamental components of LLMs and training fine-tuning codes. The tutorial covers topics such as model structure overview, attention modules, optimization techniques, normalization layers, tokenizers, pretraining, and fine-tuning with dialogue data. It also addresses specific industry-related challenges and explores cutting-edge model concepts like DeepSeek network structure, causal attention, dynamic-to-static tensor conversion for ONNX inference, and performance optimizations for NPU chips. The series emphasizes hands-on practice with small models to enable local execution and plans to expand into multimodal language models and tensor parallel multi-card deployment.
nlp-phd-global-equality
This repository aims to promote global equality for individuals pursuing a PhD in NLP by providing resources and information on various aspects of the academic journey. It covers topics such as applying for a PhD, getting research opportunities, preparing for the job market, and succeeding in academia. The repository is actively updated and includes contributions from experts in the field.

AutoPatent
AutoPatent is a multi-agent framework designed for automatic patent generation. It challenges large language models to generate full-length patents based on initial drafts. The framework leverages planner, writer, and examiner agents along with PGTree and RRAG to craft lengthy, intricate, and high-quality patent documents. It introduces a new metric, IRR (Inverse Repetition Rate), to measure sentence repetition within patents. The tool aims to streamline the patent generation process by automating the creation of detailed and specialized patent documents.
intro_pharma_ai
This repository serves as an educational resource for pharmaceutical and chemistry students to learn the basics of Deep Learning through a collection of Jupyter Notebooks. The content covers various topics such as Introduction to Jupyter, Python, Cheminformatics & RDKit, Linear Regression, Data Science, Linear Algebra, Neural Networks, PyTorch, Convolutional Neural Networks, Transfer Learning, Recurrent Neural Networks, Autoencoders, Graph Neural Networks, and Summary. The notebooks aim to provide theoretical concepts to understand neural networks through code completion, but instructors are encouraged to supplement with their own lectures. The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
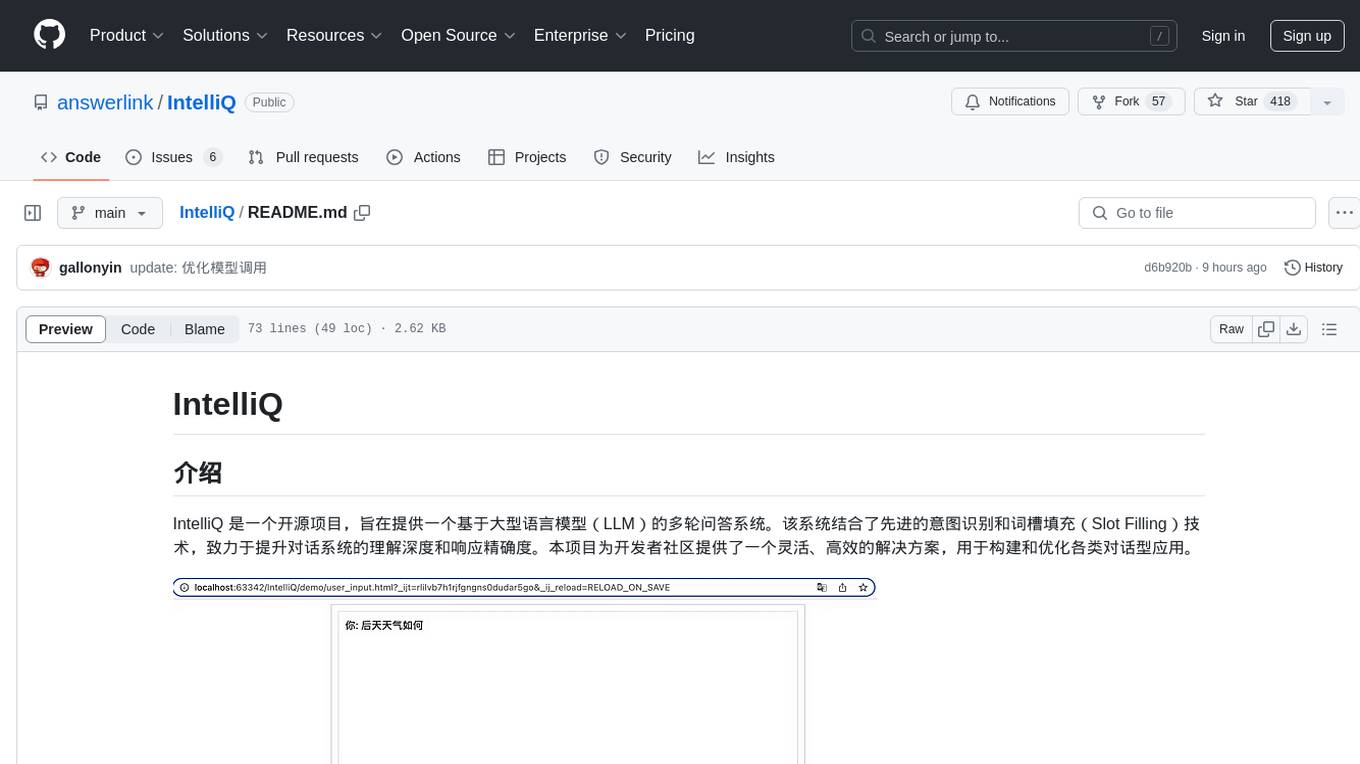
IntelliQ
IntelliQ is an open-source project aimed at providing a multi-turn question-answering system based on a large language model (LLM). The system combines advanced intent recognition and slot filling technology to enhance the depth of understanding and accuracy of responses in conversation systems. It offers a flexible and efficient solution for developers to build and optimize various conversational applications. The system features multi-turn dialogue management, intent recognition, slot filling, interface slot technology for real-time data retrieval and processing, adaptive learning for improving response accuracy and speed, and easy integration with detailed API documentation supporting multiple programming languages and platforms.
go2coding.github.io
The go2coding.github.io repository is a collection of resources for AI enthusiasts, providing information on AI products, open-source projects, AI learning websites, and AI learning frameworks. It aims to help users stay updated on industry trends, learn from community projects, access learning resources, and understand and choose AI frameworks. The repository also includes instructions for local and external deployment of the project as a static website, with details on domain registration, hosting services, uploading static web pages, configuring domain resolution, and a visual guide to the AI tool navigation website. Additionally, it offers a platform for AI knowledge exchange through a QQ group and promotes AI tools through a WeChat public account.
LLM-eval-survey
LLM-eval-survey is a collection of papers and resources related to evaluations on large language models. It includes a survey on the evaluation of large language models, covering various aspects such as natural language processing, robustness, ethics, biases, trustworthiness, social science, natural science, engineering, medical applications, agent applications, and other applications. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of different evaluation tasks and benchmarks for large language models.
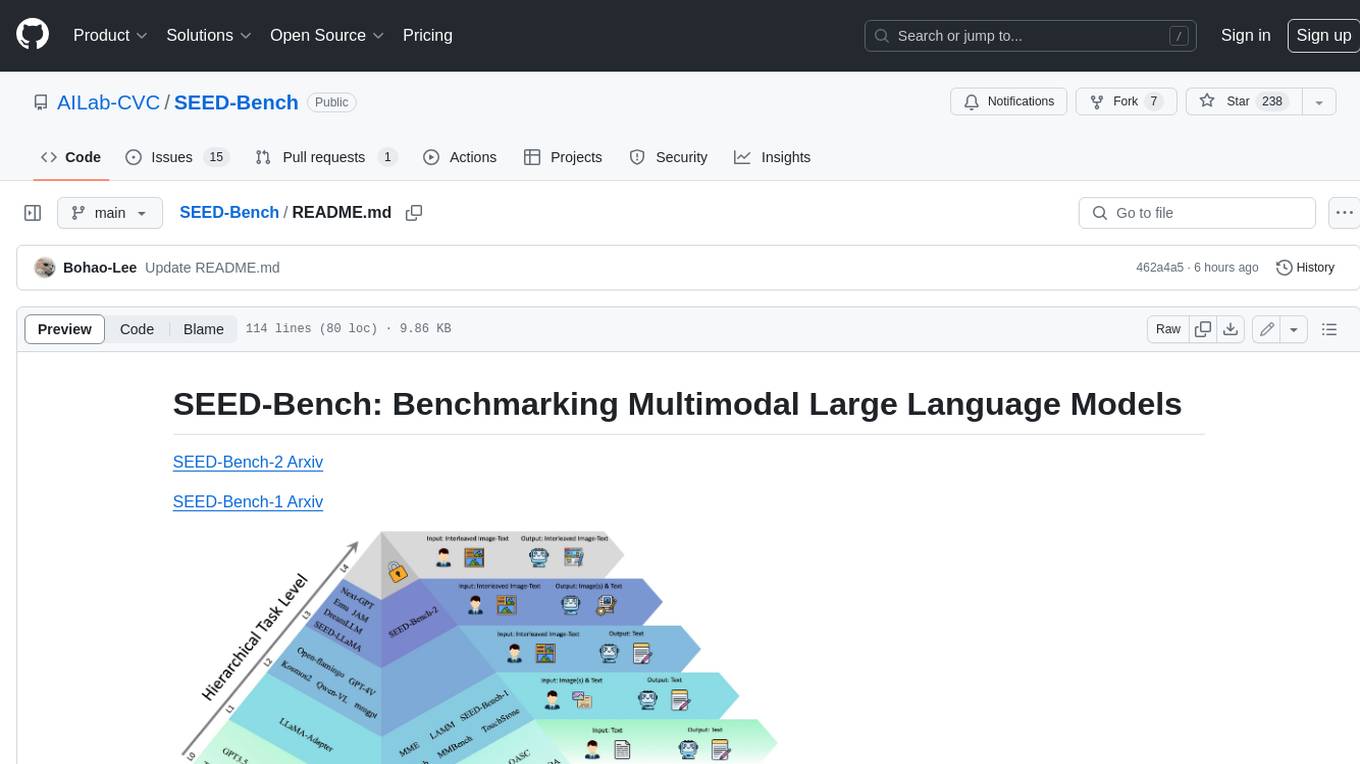
SEED-Bench
SEED-Bench is a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal large language models (LLMs) on a wide range of tasks that require both text and image understanding. It consists of two versions: SEED-Bench-1 and SEED-Bench-2. SEED-Bench-1 focuses on evaluating the spatial and temporal understanding of LLMs, while SEED-Bench-2 extends the evaluation to include text and image generation tasks. Both versions of SEED-Bench provide a diverse set of tasks that cover different aspects of multimodal understanding, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.
langchain-decoded
LangChain Decoded is an open-source framework designed to facilitate the development of applications utilizing large language models (LLMs). It can be applied to tasks such as chatbots, text summarization, data generation, code understanding, question answering, and evaluation. The framework consists of various modules like Models, Embeddings, Prompts, Indexes, Memory, Chains, Agents, and Callbacks, each explored in separate Python notebooks. Users can follow the blog post series to understand and utilize LangChain for their projects.
aws-ai-ml-workshop-kr
AWS AI/ML Workshop & example collection in Korean. The example codes in this repository are divided into 4 categories: AI services, Applied AI, SageMaker, Integration, Generative AI, and AWS Neuron. Each directory has its own Readme file. This repository also provides useful information for self-studying SageMaker.
SLAM-LLM
SLAM-LLM is a deep learning toolkit for training custom multimodal large language models (MLLM) focusing on speech, language, audio, and music processing. It provides detailed recipes for training and high-performance checkpoints for inference. The toolkit supports various tasks such as automatic speech recognition (ASR), text-to-speech (TTS), visual speech recognition (VSR), automated audio captioning (AAC), spatial audio understanding, and music caption (MC). Users can easily extend to new models and tasks, utilize mixed precision training for faster training with less GPU memory, and perform multi-GPU training with data and model parallelism. Configuration is flexible based on Hydra and dataclass, allowing different configuration methods.
For similar tasks

leaked-system-prompts
This repository contains a collection of leaked prompts for various AI systems, including Anthropic Claude, Discord Clyde, Google Gemini, Microsoft Bing Chat, OpenAI ChatGPT, and others. These prompts can be used to explore the capabilities and limitations of these AI systems and to gain insights into their inner workings.
evidently
Evidently is an open-source Python library designed for evaluating, testing, and monitoring machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) powered systems. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including working with tabular, text data, and embeddings, supporting predictive and generative systems, providing over 100 built-in metrics for data drift detection and LLM evaluation, allowing for custom metrics and tests, enabling both offline evaluations and live monitoring, and offering an open architecture for easy data export and integration with existing tools. Users can utilize Evidently for one-off evaluations using Reports or Test Suites in Python, or opt for real-time monitoring through the Dashboard service.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.