Awesome-LLM-3D
Awesome-LLM-3D: a curated list of Multi-modal Large Language Model in 3D world Resources
Stars: 1565
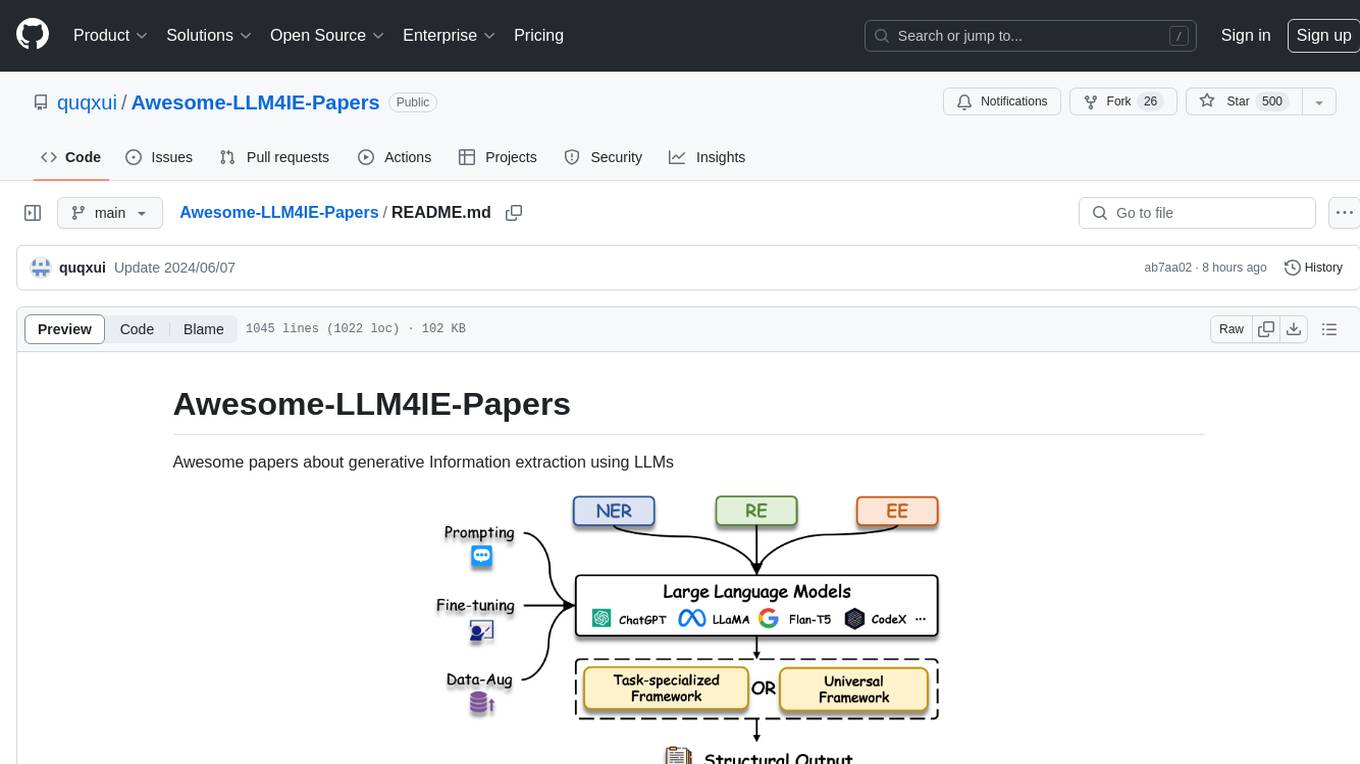
This repository is a curated list of papers related to 3D tasks empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers tasks such as 3D understanding, reasoning, generation, and embodied agents. The repository also includes other Foundation Models like CLIP and SAM to provide a comprehensive view of the area. It is actively maintained and updated to showcase the latest advances in the field. Users can find a variety of research papers and projects related to 3D tasks and LLMs in this repository.
README:
Here is a curated list of papers about 3D-Related Tasks empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs). It contains various tasks including 3D understanding, reasoning, generation, and embodied agents. Also, we include other Foundation Models (CLIP, SAM) for the whole picture of this area.
This is an active repository, you can watch for following the latest advances. If you find it useful, please kindly star ⭐ this repo and cite the paper.
- [2024-05-16] 📢 Check out the first survey paper in the 3D-LLM domain: When LLMs step into the 3D World: A Survey and Meta-Analysis of 3D Tasks via Multi-modal Large Language Models
- [2024-01-06] Runsen Xu added chronological information and Xianzheng Ma reorganized it in Z-A order for better following the latest advances.
- [2023-12-16] Xianzheng Ma and Yash Bhalgat curated this list and published the first version;
| Date | keywords | Institute (first) | Paper | Publication | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-09-08 | MSR3D | BIGAI | Multi-modal Situated Reasoning in 3D Scenes | NeurIPS '24 | project |
| 2023-5-20 | 3D-CLR | UCLA | 3D Concept Learning and Reasoning from Multi-View Images | CVPR '23 | github |
| - | Transcribe3D | TTI, Chicago | Transcribe3D: Grounding LLMs Using Transcribed Information for 3D Referential Reasoning with Self-Corrected Finetuning | CoRL '23 | github |
| Date | keywords | Institute | Paper | Publication | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-11-29 | ShapeGPT | Fudan University | ShapeGPT: 3D Shape Generation with A Unified Multi-modal Language Model | Arxiv | github |
| 2023-11-27 | MeshGPT | TUM | MeshGPT: Generating Triangle Meshes with Decoder-Only Transformers | Arxiv | project |
| 2023-10-19 | 3D-GPT | ANU | 3D-GPT: Procedural 3D Modeling with Large Language Models | Arxiv | github |
| 2023-9-21 | LLMR | MIT | LLMR: Real-time Prompting of Interactive Worlds using Large Language Models | Arxiv | - |
| 2023-9-20 | DreamLLM | MEGVII | DreamLLM: Synergistic Multimodal Comprehension and Creation | Arxiv | github |
| 2023-4-1 | ChatAvatar | Deemos Tech | DreamFace: Progressive Generation of Animatable 3D Faces under Text Guidance | ACM TOG | website |
Your contributions are always welcome!
I will keep some pull requests open if I'm not sure if they are awesome for 3D LLMs, you could vote for them by adding 👍 to them.
If you have any questions about this opinionated list, please get in touch at [email protected] or Wechat ID: mxz1997112.
If you find this repository useful, please consider citing this paper:
@misc{ma2024llmsstep3dworld,
title={When LLMs step into the 3D World: A Survey and Meta-Analysis of 3D Tasks via Multi-modal Large Language Models},
author={Xianzheng Ma and Yash Bhalgat and Brandon Smart and Shuai Chen and Xinghui Li and Jian Ding and Jindong Gu and Dave Zhenyu Chen and Songyou Peng and Jia-Wang Bian and Philip H Torr and Marc Pollefeys and Matthias Nießner and Ian D Reid and Angel X. Chang and Iro Laina and Victor Adrian Prisacariu},
year={2024},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.10255},
}
This repo is inspired by Awesome-LLM
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-LLM-3D
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-LLM-3D
This repository is a curated list of papers related to 3D tasks empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers tasks such as 3D understanding, reasoning, generation, and embodied agents. The repository also includes other Foundation Models like CLIP and SAM to provide a comprehensive view of the area. It is actively maintained and updated to showcase the latest advances in the field. Users can find a variety of research papers and projects related to 3D tasks and LLMs in this repository.
Github-Ranking-AI
This repository provides a list of the most starred and forked repositories on GitHub. It is updated automatically and includes information such as the project name, number of stars, number of forks, language, number of open issues, description, and last commit date. The repository is divided into two sections: LLM and chatGPT. The LLM section includes repositories related to large language models, while the chatGPT section includes repositories related to the chatGPT chatbot.
AudioLLM
AudioLLMs is a curated collection of research papers focusing on developing, implementing, and evaluating language models for audio data. The repository aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a comprehensive resource to explore the latest advancements in AudioLLMs. It includes models for speech interaction, speech recognition, speech translation, audio generation, and more. Additionally, it covers methodologies like multitask audioLLMs and segment-level Q-Former, as well as evaluation benchmarks like AudioBench and AIR-Bench. Adversarial attacks such as VoiceJailbreak are also discussed.
Cool-GenAI-Fashion-Papers
Cool-GenAI-Fashion-Papers is a curated list of resources related to GenAI-Fashion, including papers, workshops, companies, and products. It covers a wide range of topics such as fashion design synthesis, outfit recommendation, fashion knowledge extraction, trend analysis, and more. The repository provides valuable insights and resources for researchers, industry professionals, and enthusiasts interested in the intersection of AI and fashion.
open-llms
Open LLMs is a repository containing various Large Language Models licensed for commercial use. It includes models like T5, GPT-NeoX, UL2, Bloom, Cerebras-GPT, Pythia, Dolly, and more. These models are designed for tasks such as transfer learning, language understanding, chatbot development, code generation, and more. The repository provides information on release dates, checkpoints, papers/blogs, parameters, context length, and licenses for each model. Contributions to the repository are welcome, and it serves as a resource for exploring the capabilities of different language models.
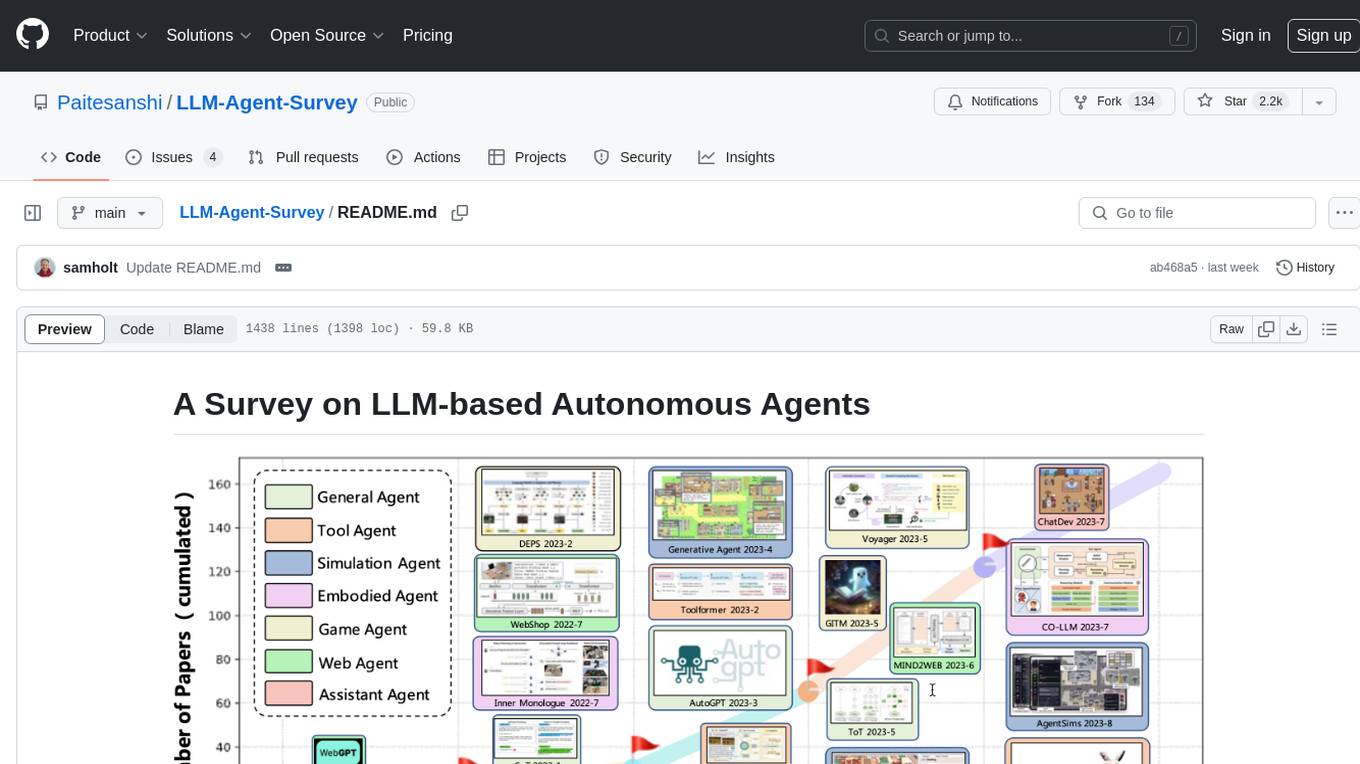
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.
Awesome-LLM-Eval
Awesome-LLM-Eval: a curated list of tools, benchmarks, demos, papers for Large Language Models (like ChatGPT, LLaMA, GLM, Baichuan, etc) Evaluation on Language capabilities, Knowledge, Reasoning, Fairness and Safety.
Awesome-Tabular-LLMs
This repository is a collection of papers on Tabular Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for processing tabular data. It includes surveys, models, and applications related to table understanding tasks such as Table Question Answering, Table-to-Text, Text-to-SQL, and more. The repository categorizes the papers based on key ideas and provides insights into the advancements in using LLMs for processing diverse tables and fulfilling various tabular tasks based on natural language instructions.
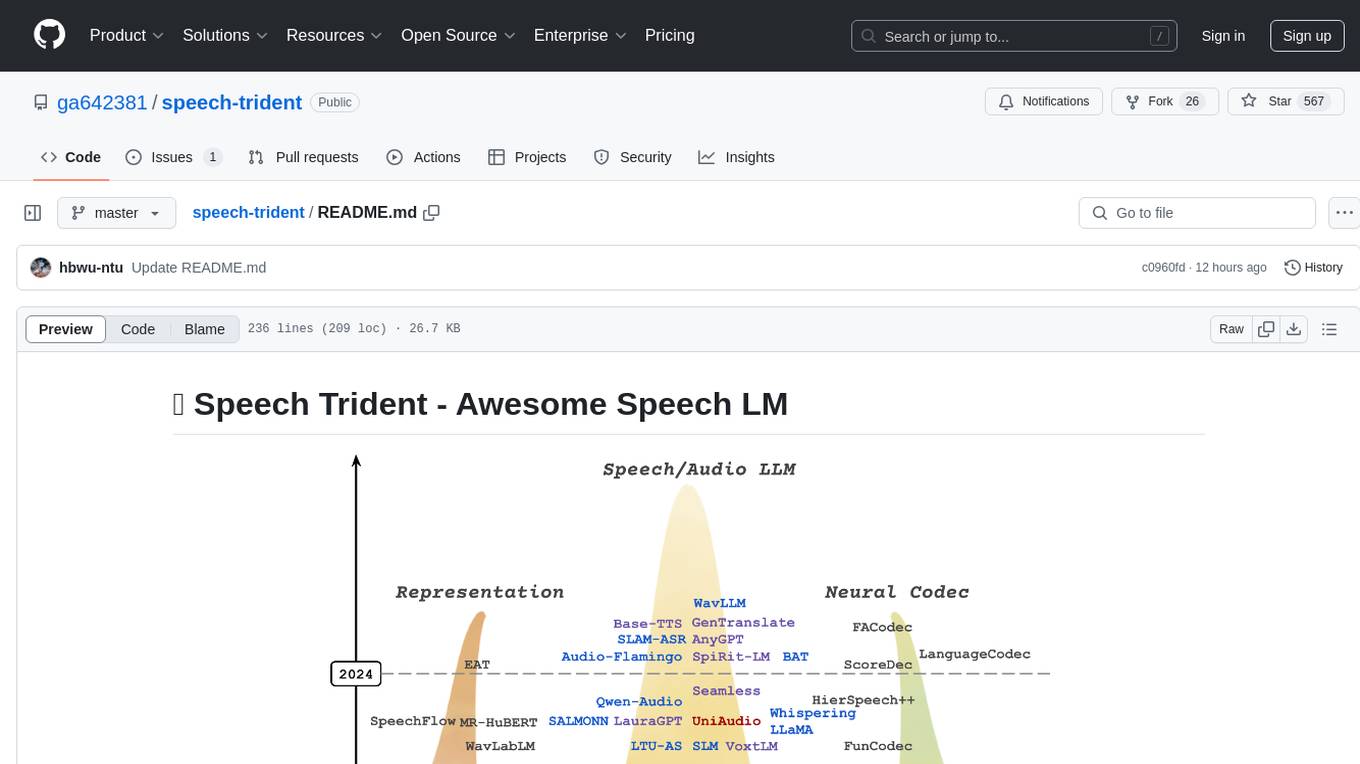
speech-trident
Speech Trident is a repository focusing on speech/audio large language models, covering representation learning, neural codec, and language models. It explores speech representation models, speech neural codec models, and speech large language models. The repository includes contributions from various researchers and provides a comprehensive list of speech/audio language models, representation models, and codec models.
LLM-PlayLab
LLM-PlayLab is a repository containing various projects related to LLM (Large Language Models) fine-tuning, generative AI, time-series forecasting, and crash courses. It includes projects for text generation, sentiment analysis, data analysis, chat assistants, image captioning, and more. The repository offers a wide range of tools and resources for exploring and implementing advanced AI techniques.
ai-game-development-tools
Here we will keep track of the AI Game Development Tools, including LLM, Agent, Code, Writer, Image, Texture, Shader, 3D Model, Animation, Video, Audio, Music, Singing Voice and Analytics. 🔥 * Tool (AI LLM) * Game (Agent) * Code * Framework * Writer * Image * Texture * Shader * 3D Model * Avatar * Animation * Video * Audio * Music * Singing Voice * Speech * Analytics * Video Tool
llm-export
llm-export is a tool for exporting llm models to onnx and mnn formats. It has features such as passing onnxruntime correctness tests, optimizing the original code to support dynamic shapes, reducing constant parts, optimizing onnx models using OnnxSlim for performance improvement, and exporting lora weights to onnx and mnn formats. Users can clone the project locally, clone the desired LLM project locally, and use LLMExporter to export the model. The tool supports various export options like exporting the entire model as one onnx model, exporting model segments as multiple models, exporting model vocabulary to a text file, exporting specific model layers like Embedding and lm_head, testing the model with queries, validating onnx model consistency with onnxruntime, converting onnx models to mnn models, and more. Users can specify export paths, skip optimization steps, and merge lora weights before exporting.

kumo-search
Kumo search is an end-to-end search engine framework that supports full-text search, inverted index, forward index, sorting, caching, hierarchical indexing, intervention system, feature collection, offline computation, storage system, and more. It runs on the EA (Elastic automic infrastructure architecture) platform, enabling engineering automation, service governance, real-time data, service degradation, and disaster recovery across multiple data centers and clusters. The framework aims to provide a ready-to-use search engine framework to help users quickly build their own search engines. Users can write business logic in Python using the AOT compiler in the project, which generates C++ code and binary dynamic libraries for rapid iteration of the search engine.
For similar tasks

Awesome-LLM-3D
This repository is a curated list of papers related to 3D tasks empowered by Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers tasks such as 3D understanding, reasoning, generation, and embodied agents. The repository also includes other Foundation Models like CLIP and SAM to provide a comprehensive view of the area. It is actively maintained and updated to showcase the latest advances in the field. Users can find a variety of research papers and projects related to 3D tasks and LLMs in this repository.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.
RLinf
RLinf is a flexible and scalable open-source infrastructure designed for post-training foundation models via reinforcement learning. It provides a robust backbone for next-generation training, supporting open-ended learning, continuous generalization, and limitless possibilities in intelligence development. The tool offers unique features like Macro-to-Micro Flow, flexible execution modes, auto-scheduling strategy, embodied agent support, and fast adaptation for mainstream VLA models. RLinf is fast with hybrid mode and automatic online scaling strategy, achieving significant throughput improvement and efficiency. It is also flexible and easy to use with multiple backend integrations, adaptive communication, and built-in support for popular RL methods. The roadmap includes system-level enhancements and application-level extensions to support various training scenarios and models. Users can get started with complete documentation, quickstart guides, key design principles, example gallery, advanced features, and guidelines for extending the framework. Contributions are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite the GitHub repository and acknowledge the broader open-source community.
ShapeLLM
ShapeLLM is the first 3D Multimodal Large Language Model designed for embodied interaction, exploring a universal 3D object understanding with 3D point clouds and languages. It supports single-view colored point cloud input and introduces a robust 3D QA benchmark, 3D MM-Vet, encompassing various variants. The model extends the powerful point encoder architecture, ReCon++, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a range of representation learning tasks. ShapeLLM can be used for tasks such as training, zero-shot understanding, visual grounding, few-shot learning, and zero-shot learning on 3D MM-Vet.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.