
JetStream
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for LLM inference on XLA devices, starting with TPUs (and GPUs in future -- PRs welcome).
Stars: 290
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for Large Language Model (LLM) inference on XLA devices, specifically TPUs. It provides reference engine implementations for Jax and Pytorch models, along with documentation for online inference, serving Gemma using TPUs on GKE, benchmarking, observability, profiling, and standalone local setup. Users can easily set up a local server, run tests, and test core modules. JetStream aims to enhance the performance of LLM inference on XLA devices.
README:
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for LLM inference on XLA devices, starting with TPUs (and GPUs in future -- PRs welcome).
Currently, there are two reference engine implementations available -- one for Jax models and another for Pytorch models.
- Git: https://github.com/google/maxtext
- README: https://github.com/google/JetStream/blob/main/docs/online-inference-with-maxtext-engine.md
- Git: https://github.com/google/jetstream-pytorch
- README: https://github.com/google/jetstream-pytorch/blob/main/README.md
- Online Inference with MaxText on v5e Cloud TPU VM [README]
- Online Inference with Pytorch on v5e Cloud TPU VM [README]
- Serve Gemma using TPUs on GKE with JetStream
- Benchmark JetStream Server
- Observability in JetStream Server
- Profiling in JetStream Server
- JetStream Standalone Local Setup
make install-deps
Use the following commands to run a server locally:
# Start a server
python -m jetstream.core.implementations.mock.server
# Test local mock server
python -m jetstream.tools.requester
# Load test local mock server
python -m jetstream.tools.load_tester
# Test JetStream core orchestrator
python -m unittest -v jetstream.tests.core.test_orchestrator
# Test JetStream core server library
python -m unittest -v jetstream.tests.core.test_server
# Test mock JetStream engine implementation
python -m unittest -v jetstream.tests.engine.test_mock_engine
# Test mock JetStream token utils
python -m unittest -v jetstream.tests.engine.test_token_utils
python -m unittest -v jetstream.tests.engine.test_utils
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for JetStream
Similar Open Source Tools

JetStream
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for Large Language Model (LLM) inference on XLA devices, specifically TPUs. It provides reference engine implementations for Jax and Pytorch models, along with documentation for online inference, serving Gemma using TPUs on GKE, benchmarking, observability, profiling, and standalone local setup. Users can easily set up a local server, run tests, and test core modules. JetStream aims to enhance the performance of LLM inference on XLA devices.
JetStream
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for LLM inference on XLA devices, starting with TPUs (and GPUs in future -- PRs welcome). It is designed to provide high performance and scalability for large language models, enabling efficient inference on cloud-based TPUs. JetStream leverages XLA to optimize the execution of LLM models, resulting in faster and more efficient inference. Additionally, JetStream supports quantization techniques to further enhance performance and reduce memory consumption. By utilizing JetStream, developers can deploy and run LLM models on TPUs with ease, achieving optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
moling
MoLing is a computer-use and browser-use MCP Server that implements system interaction through operating system APIs, enabling file system operations such as reading, writing, merging, statistics, and aggregation, as well as the ability to execute system commands. It is a dependency-free local office automation assistant. Requiring no installation of any dependencies, MoLing can be run directly and is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. This eliminates the hassle of dealing with environment conflicts involving Node.js, Python, Docker, and other development environments. Command-line operations are dangerous and should be used with caution. MoLing supports features like file system operations, command-line terminal execution, browser control powered by 'github.com/chromedp/chromedp', and future plans for personal PC data organization, document writing assistance, schedule planning, and life assistant features. MoLing has been tested on macOS but may have issues on other operating systems.
SiLLM
SiLLM is a toolkit that simplifies the process of training and running Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple Silicon by leveraging the MLX framework. It provides features such as LLM loading, LoRA training, DPO training, a web app for a seamless chat experience, an API server with OpenAI compatible chat endpoints, and command-line interface (CLI) scripts for chat, server, LoRA fine-tuning, DPO fine-tuning, conversion, and quantization.
bagofwords
Bag of words is an open-source AI platform that helps data teams deploy and manage chat-with-your-data agents in a controlled, reliable, and self-learning environment. It enables users to create charts, tables, and dashboards by chatting with their data, capture AI decisions and user feedback, automatically improve AI quality, integrate with various data sources and APIs, and ensure governance and integrations. The platform supports self-hosting in VPC via VMs, Docker/Compose, or Kubernetes, and offers additional integrations for AI Analyst in Slack, Excel, Google Sheets, and more. Users can start in minutes and scale to org-wide analytics.
java-sdk
The MCP Java SDK is a set of projects that provide Java SDK integration for the Model Context Protocol. It enables Java applications to interact with AI models and tools through a standardized interface, supporting both synchronous and asynchronous communication patterns.
brain4j
Brain4J is a lightweight, performant, and open-source machine learning framework for Java. Designed with portability and speed in mind, it is optimized for high performance and ideal for those looking to implement machine learning solutions in pure Java. The framework provides tools and functionalities to facilitate the development of machine learning models within Java applications, offering ease of use and efficiency.
ai-optimizer
The Oracle AI Optimizer and Toolkit provides a streamlined environment for developers and data scientists to explore Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities. It integrates Oracle Database 23ai AI VectorSearch and SelectAI to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) through RAG.
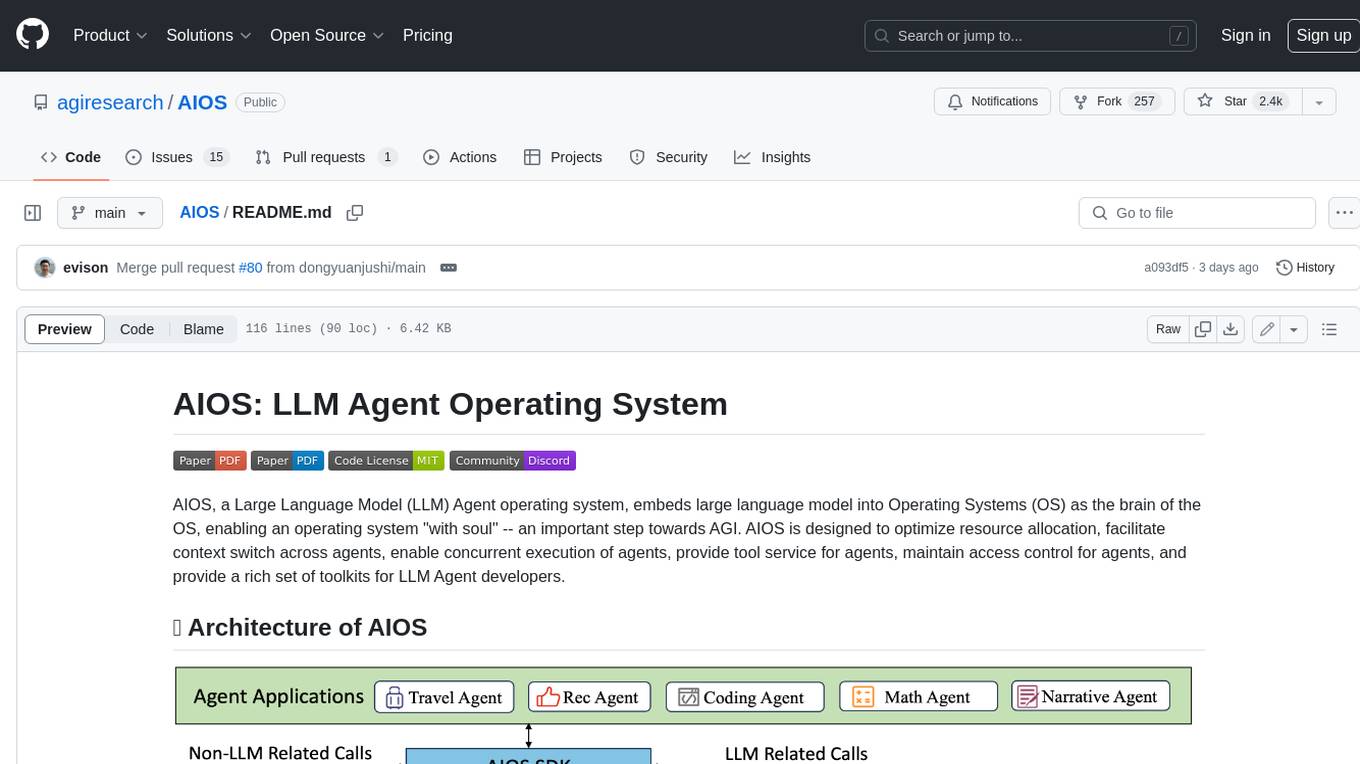
AIOS
AIOS, a Large Language Model (LLM) Agent operating system, embeds large language model into Operating Systems (OS) as the brain of the OS, enabling an operating system "with soul" -- an important step towards AGI. AIOS is designed to optimize resource allocation, facilitate context switch across agents, enable concurrent execution of agents, provide tool service for agents, maintain access control for agents, and provide a rich set of toolkits for LLM Agent developers.
flock
Flock is a workflow-based low-code platform that enables rapid development of chatbots, RAG applications, and coordination of multi-agent teams. It offers a flexible, low-code solution for orchestrating collaborative agents, supporting various node types for specific tasks, such as input processing, text generation, knowledge retrieval, tool execution, intent recognition, answer generation, and more. Flock integrates LangChain and LangGraph to provide offline operation capabilities and supports future nodes like Conditional Branch, File Upload, and Parameter Extraction for creating complex workflows. Inspired by StreetLamb, Lobe-chat, Dify, and fastgpt projects, Flock introduces new features and directions while leveraging open-source models and multi-tenancy support.
StratosphereLinuxIPS
Slips is a powerful endpoint behavioral intrusion prevention and detection system that uses machine learning to detect malicious behaviors in network traffic. It can work with network traffic in real-time, PCAP files, and network flows from tools like Suricata, Zeek/Bro, and Argus. Slips threat detection is based on machine learning models, threat intelligence feeds, and expert heuristics. It gathers evidence of malicious behavior and triggers alerts when enough evidence is accumulated. The tool is Python-based and supported on Linux and MacOS, with blocking features only on Linux. Slips relies on Zeek network analysis framework and Redis for interprocess communication. It offers a graphical user interface for easy monitoring and analysis.
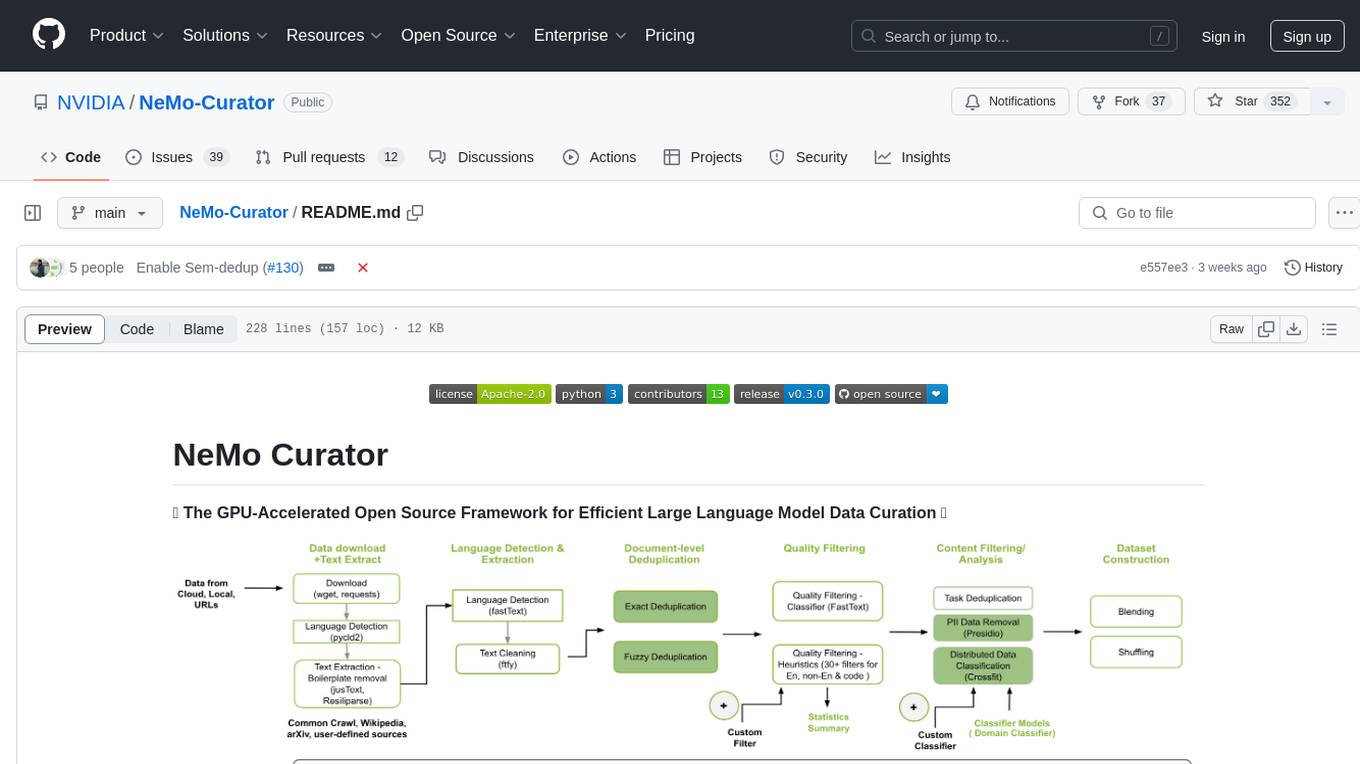
NeMo-Curator
NeMo Curator is a GPU-accelerated open-source framework designed for efficient large language model data curation. It provides scalable dataset preparation for tasks like foundation model pretraining, domain-adaptive pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning. The library leverages GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS to accelerate data curation, offering customizable and modular interfaces for pipeline expansion and model convergence. Key features include data download, text extraction, quality filtering, deduplication, downstream-task decontamination, distributed data classification, and PII redaction. NeMo Curator is suitable for curating high-quality datasets for large language model training.

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.

xpander.ai
xpander.ai is a Backend-as-a-Service for autonomous agents that abstracts the ops layer, allowing AI engineers to focus on behavior and outcomes. It provides managed agent hosting with version control and CI/CD, a fully managed PostgreSQL memory layer, and a library of 2,000+ functions. The platform features an AI native triggering system that processes inputs from various sources and delivers unified messages to agents. With support for any agent framework or SDK, including Agno and OpenAI, xpander.ai enables users to build intelligent, production-ready AI agents without dealing with infrastructure complexity.
DataFlow
DataFlow is a data preparation and training system designed to parse, generate, process, and evaluate high-quality data from noisy sources, improving the performance of large language models in specific domains. It constructs diverse operators and pipelines, validated to enhance domain-oriented LLM's performance in fields like healthcare, finance, and law. DataFlow also features an intelligent DataFlow-agent capable of dynamically assembling new pipelines by recombining existing operators on demand.

aigne-framework
AIGNE Framework is a functional AI application development framework designed to simplify and accelerate the process of building modern applications. It combines functional programming features, powerful artificial intelligence capabilities, and modular design principles to help developers easily create scalable solutions. With key features like modular design, TypeScript support, multiple AI model support, flexible workflow patterns, MCP protocol integration, code execution capabilities, and Blocklet ecosystem integration, AIGNE Framework offers a comprehensive solution for developers. The framework provides various workflow patterns such as Workflow Router, Workflow Sequential, Workflow Concurrency, Workflow Handoff, Workflow Reflection, Workflow Orchestration, Workflow Code Execution, and Workflow Group Chat to address different application scenarios efficiently. It also includes built-in MCP support for running MCP servers and integrating with external MCP servers, along with packages for core functionality, agent library, CLI, and various models like OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, and Nova.
For similar tasks

JetStream
JetStream is a throughput and memory optimized engine for Large Language Model (LLM) inference on XLA devices, specifically TPUs. It provides reference engine implementations for Jax and Pytorch models, along with documentation for online inference, serving Gemma using TPUs on GKE, benchmarking, observability, profiling, and standalone local setup. Users can easily set up a local server, run tests, and test core modules. JetStream aims to enhance the performance of LLM inference on XLA devices.
commanddash
Dash AI is an open-source coding assistant for Flutter developers. It is designed to not only write code but also run and debug it, allowing it to assist beyond code completion and automate routine tasks. Dash AI is powered by Gemini, integrated with the Dart Analyzer, and specifically tailored for Flutter engineers. The vision for Dash AI is to create a single-command assistant that can automate tedious development tasks, enabling developers to focus on creativity and innovation. It aims to assist with the entire process of engineering a feature for an app, from breaking down the task into steps to generating exploratory tests and iterating on the code until the feature is complete. To achieve this vision, Dash AI is working on providing LLMs with the same access and information that human developers have, including full contextual knowledge, the latest syntax and dependencies data, and the ability to write, run, and debug code. Dash AI welcomes contributions from the community, including feature requests, issue fixes, and participation in discussions. The project is committed to building a coding assistant that empowers all Flutter developers.
ollama4j
Ollama4j is a Java library that serves as a wrapper or binding for the Ollama server. It facilitates communication with the Ollama server and provides models for deployment. The tool requires Java 11 or higher and can be installed locally or via Docker. Users can integrate Ollama4j into Maven projects by adding the specified dependency. The tool offers API specifications and supports various development tasks such as building, running unit tests, and integration tests. Releases are automated through GitHub Actions CI workflow. Areas of improvement include adhering to Java naming conventions, updating deprecated code, implementing logging, using lombok, and enhancing request body creation. Contributions to the project are encouraged, whether reporting bugs, suggesting enhancements, or contributing code.
crewAI-tools
The crewAI Tools repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents, enabling the creation of custom tools to enhance AI solutions. Tools play a crucial role in improving agent functionality. The guide explains how to equip agents with a range of tools and how to create new tools. Tools are designed to return strings for generating responses. There are two main methods for creating tools: subclassing BaseTool and using the tool decorator. Contributions to the toolset are encouraged, and the development setup includes steps for installing dependencies, activating the virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. Enhance AI agent capabilities with advanced tooling.
lightning-lab
Lightning Lab is a public template for artificial intelligence and machine learning research projects using Lightning AI's PyTorch Lightning. It provides a structured project layout with modules for command line interface, experiment utilities, Lightning Module and Trainer, data acquisition and preprocessing, model serving APIs, project configurations, training checkpoints, technical documentation, logs, notebooks for data analysis, requirements management, testing, and packaging. The template simplifies the setup of deep learning projects and offers extras for different domains like vision, text, audio, reinforcement learning, and forecasting.
Magic_Words
Magic_Words is a repository containing code for the paper 'What's the Magic Word? A Control Theory of LLM Prompting'. It implements greedy back generation and greedy coordinate gradient (GCG) to find optimal control prompts (magic words). Users can set up a virtual environment, install the package and dependencies, and run example scripts for pointwise control and optimizing prompts for datasets. The repository provides scripts for finding optimal control prompts for question-answer pairs and dataset optimization using the GCG algorithm.
grafana-llm-app
This repository contains separate packages for Grafana LLM Plugin and the @grafana/llm package for interfacing with it. The packages are tightly coupled and developed together with identical dependencies. The repository provides instructions for developing the packages, including backend and frontend development, testing, and release processes.
crewAI-tools
This repository provides a guide for setting up tools for crewAI agents to enhance functionality. It offers steps to equip agents with ready-to-use tools and create custom ones. Tools are expected to return strings for generating responses. Users can create tools by subclassing BaseTool or using the tool decorator. Contributions are welcome to enrich the toolset, and guidelines are provided for contributing. The development setup includes installing dependencies, activating virtual environment, setting up pre-commit hooks, running tests, static type checking, packaging, and local installation. The goal is to empower AI solutions through advanced tooling.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

