
blackmarlin
WIP Chess Engine
Stars: 89
Black Marlin is a UCI compliant chess engine fully written in Rust by Doruk Sekercioglu. It supports Chess960 and features a variety of search algorithms, pruning techniques, and evaluation methods. Black Marlin is designed to be efficient and accurate, and it has been shown to perform well against other top chess engines.
README:
WIP UCI Chess Engine
 |
|---|
| Logo by Alex Brunetti |
Black Marlin is a UCI compliant chess engine fully written in Rust by Doruk Sekercioglu.
Black Marlin supports Chess960 as of December 26, 2021 although no extensive testing has been done.
Make sure to have Git LFS and compile the engine with make in the root directory. This will output a BlackMarlin executable.
Black Marlin doesn't come with a built-in GUI. The recommended way of playing against the engine is to get the latest release or compile it locally and use it along with a Chess GUI that supports the UCI protocol.
The repository used for NN training is NNUE Marlin.
The above repo has been replaced by Marlinflow.
- Iterative Deepening
- Aspiration Windows
- Principal Variation Search
- Lazy SMP
- Search Evaluation Instability
- Failed Searches at Root
- Best Move consistency
Iterative Deepening is the idea of performing consecutive searches at higher depths each time.
Aspiration Windows are a way of reducing the search space by making the assumption that the resulting evaluation will be in [alpha, beta] range. If we get a score such that alpha < score < beta, we know that the resulting score from the search is exact and thus can be used. Otherwise, we execute another search with a larger window.
In Principal Variation Search (PVS), we do a search with the window [alpha - 1, alpha] for each move to see if it is worse than alpha efficiently. If so, we don't need to execute a full search on the given move.
Pruning in general is the idea of ignoring certain parts of the search tree in order to reduce the amount of time it takes to execute a search.
Reverse Futility Pruning (RFP) is the idea of returning the evaluation of the current position if it is above beta by a margin.
Null Move Pruning (NMP) is based on the assumption that, if we can reach beta by not making a move at lower depths, we will most likely be able to reach it anyway.
Late Move Pruning (LMP) is the idea that all quiet moves can be pruned after searching the first few given by the move ordering algorithm.
Futility Pruning is the idea that quiet moves don't tend to improve positions significantly, therefore we can safely prune quiet moves in positions where the current position is evaluated to be below alpha by a margin.
History Heuristic is usually a table that keeps track of which moves failed high/low in the past. This can be used to identify moves that tend to be good in the current search space.
History Based Pruning is the idea of using the history table to see which moves performed worse in the local search area and pruning accordingly.
Doing Futility Pruning at higher depths by correcting the evaluation based on static exchange evaluation (SEE).
Late Move Reductions (LMR) are a way of proving if a move is lower than alpha quickly. This is done by searching moves that are expected to underperform at a lower depth.
History Based Reductions are the idea of adjusting LMR reductions based on the history score of a move. This is done for both quiet and noisy (non-quiet) moves as history is kept separately for both.
Black Marlin additionally reduces less in principal variation nodes and nodes that improve the static evaluation of a position compared to its parent.
Usually the search algortihm is optimized by pruning or reducing where moves aren't promising. However, it can also be done by executing a deeper search on promising moves.
We don't want to miss three-fold repetition lines or forcing sequences, so we extend moves that give a check.
If a move is better than all other moves by a margin, we can extend the search on this move. Candidate singular moves are usually decided based on the transposition table.
If a move isn't singular and the singular move is above beta, we know that there is more than one move that beats beta. We can thus fail soft and return the singular move beta.
This idea is inspired by Koivisto however the implementation is slightly different. At lower depths, Black Marlin doesn't search to prove singularity but rather uses the static evaluation directly. Since static evaluation isn't a reliable estimate, Black Marlin doesn't apply multi cut pruning if low depth singular extensions are done.
In order to maximize the efficiency of alpha beta search, we optimally want to try the best moves first.
The Transposition Table (TT) gives us the move we have found to be the best in case we have visited the position previously. TT moves are one of the most crucial ways of improving move ordering.
We can evaluate each move by using SEE and put winning captures first in move ordering. Although moves aren't ordered by SEE but rather by their capture history scores and the value of the piece the move is capturing. This both provides more performance over pure SEE and benefits from the adaptive nature of history.
Killer Heuristic is the idea of using quiet moves that produced a beta cutoff in sibling nodes. This is based on the assumption that a move doesn't change the position a lot and we can benefit from moves that worked in very similar positions.
Black Marlin keeps a table of the last best quiet response to each move. These moves are later used in quiet move ordering.
We can order quiet moves based on their history scores in order to search quiets that historically performed better than others first.
Bad Captures are moves that most likely make the position worse. They are usually put last as they rarely improve the position. Similar to winning captures, bad captures are also sorted by capture history.
There isn't really a reason to promote to a piece other than the queen in most positions. All promotions other than queen promotions are put to the very last of the move ordering list.
Lazy SMP stands for Lazy Symmetric Multi Processing. The idea behind Lazy SMP is to execute the search function on N many threads and share the hash table. This allows for faster filling of the hash table, resulting in a faster and wider search.
In order to prevent data races and data corruption, we can use the "XOR Trick". Instead of saving the hash of the position directlly, we XOR it with the related entry. When we access the table later on, we can revert the hash back with the corresponding entry. This ensures a different hash will be produced in case the entry was corrupted.
Prior to NNUE, most engines used a hand crafted evaluation function. Hand crafted evaluation (HCE) included hand picked features such as material, pawn structure, piece squares and similar. These values quickly get overwhelming to tune, in order to solve this problem, most engines employ a strategy called "Texel Tuning". The idea behind Texel Tuning is to optimize the evaluation function in such a way that it'll reflect the result of the game the best. Once we obtain a loss function, we can use metaheuristics such as genetic algorithms or gradient based algorithms such as AdaGrad to tune the hand crafted evaluation function.
A Machine Learned model that has information on all the board is naturally expected to perform better than hand picked features.
There are many distinct ways of training a neural network for chess however the one that is employed the most is using the evaluation score from a low depth search. This results in evaluations that see more into the future and produce neural networks more capable than HCE functions.
Data is usually generated by self-play where the engine plays against itself at a fixed depth/node count. This enables us to also keep track of win draw loss (WDL) information to be later used in training.
In order keep the weights low and make the neural network more aware of evaluations close to 0, the evaluation score is usually scaled and passed through sigmoid. Usually using a formula along the lines of sigmoid(eval * SCALE). We can also add a WDL term to our train set in order to make the networ more aware of how winnable positions are. This can be done by taking the weighted average of WDL and evaluation.
Neural Networks are the state of the art machine learning models. Although they have one problem: they are usually very slow in execution. Efficietly Updatable Neural Networks (NNUE) solves this problem by doing incremental updates.
Alpha-Beta Search has one feature that allows us to efficiently update our neural networks. Since a depth first search is employed, a series of moves are played one after the other only causing slight changes in the actual input. It is possible to take advantage of this and only calculate what has changed in the network than propogate forward completely.
Skipped connections are the idea of connecting a layer to a layer other than the next. This increases learning speed and the strength of the resulting model.
A Neural Network might have sub networks that it picks from based on a condition. This enables the network to better distinguish between different types of positions, usually decided by game phase(mid game, end game). Buckets cause almost no slow down in the resulting neural network while increasing the representative power of the model.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for blackmarlin
Similar Open Source Tools

blackmarlin
Black Marlin is a UCI compliant chess engine fully written in Rust by Doruk Sekercioglu. It supports Chess960 and features a variety of search algorithms, pruning techniques, and evaluation methods. Black Marlin is designed to be efficient and accurate, and it has been shown to perform well against other top chess engines.
Winter
Winter is a UCI chess engine that has competed at top invite-only computer chess events. It is the top-rated chess engine from Switzerland and has a level of play that is super human but below the state of the art reached by large, distributed, and resource-intensive open-source projects like Stockfish and Leela Chess Zero. Winter has relied on many machine learning algorithms and techniques over the course of its development, including certain clustering methods not used in any other chess programs, such as Gaussian Mixture Models and Soft K-Means. As of Winter 0.6.2, the evaluation function relies on a small neural network for more precise evaluations.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.
LLocalSearch
LLocalSearch is a completely locally running search aggregator using LLM Agents. The user can ask a question and the system will use a chain of LLMs to find the answer. The user can see the progress of the agents and the final answer. No OpenAI or Google API keys are needed.

qlora-pipe
qlora-pipe is a pipeline parallel training script designed for efficiently training large language models that cannot fit on one GPU. It supports QLoRA, LoRA, and full fine-tuning, with efficient model loading and the ability to load any dataset that Axolotl can handle. The script allows for raw text training, resuming training from a checkpoint, logging metrics to Tensorboard, specifying a separate evaluation dataset, training on multiple datasets simultaneously, and supports various models like Llama, Mistral, Mixtral, Qwen-1.5, and Cohere (Command R). It handles pipeline- and data-parallelism using Deepspeed, enabling users to set the number of GPUs, pipeline stages, and gradient accumulation steps for optimal utilization.
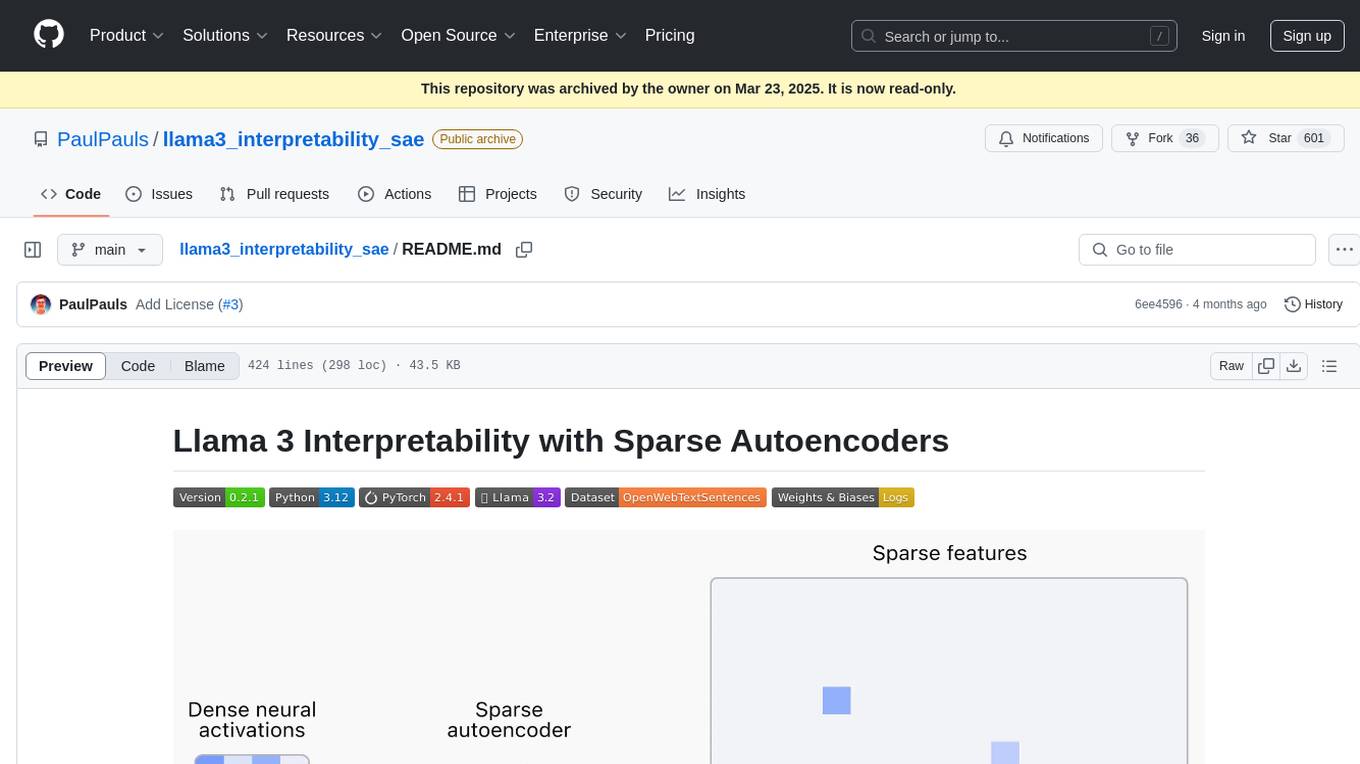
llama3_interpretability_sae
This project focuses on implementing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for mechanistic interpretability in Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama 3.2-3B. The SAEs aim to untangle superimposed representations in LLMs into separate, interpretable features for each neuron activation. The project provides an end-to-end pipeline for capturing training data, training the SAEs, analyzing learned features, and verifying results experimentally. It includes comprehensive logging, visualization, and checkpointing of SAE training, interpretability analysis tools, and a pure PyTorch implementation of Llama 3.1/3.2 chat and text completion. The project is designed for scalability, efficiency, and maintainability.
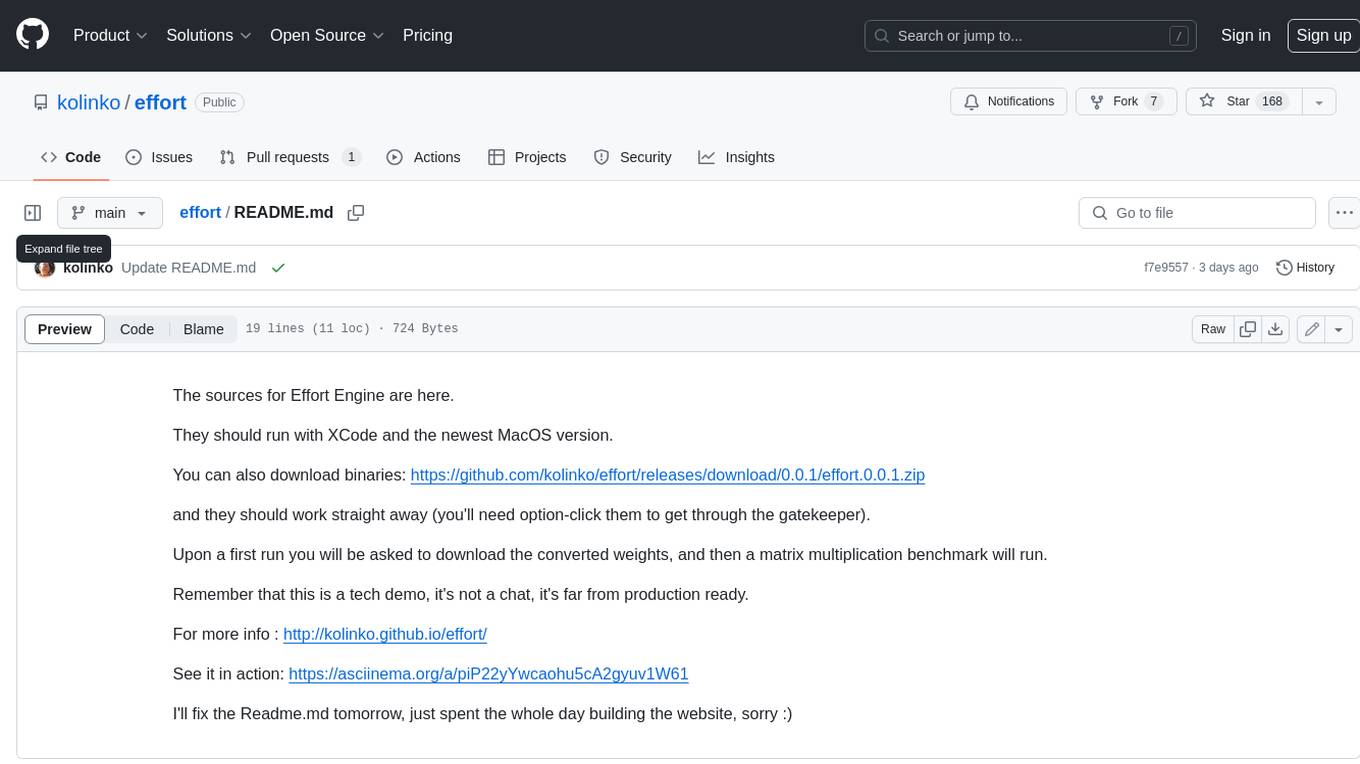
effort
Effort is an example implementation of the bucketMul algorithm, which allows for real-time adjustment of the number of calculations performed during inference of an LLM model. At 50% effort, it performs as fast as regular matrix multiplications on Apple Silicon chips; at 25% effort, it is twice as fast while still retaining most of the quality. Additionally, users have the option to skip loading the least important weights.
aiohomekit
aiohomekit is a Python library that implements the HomeKit protocol for controlling HomeKit accessories using asyncio. It is primarily used with Home Assistant, targeting the same versions of Python and following their code standards. The library is still under development and does not offer API guarantees yet. It aims to match the behavior of real HAP controllers, even when not strictly specified, and works around issues like JSON formatting, boolean encoding, header sensitivity, and TCP packet splitting. aiohomekit is primarily tested with Phillips Hue and Eve Extend bridges via Home Assistant, but is known to work with many more devices. It does not support BLE accessories and is intended for client-side use only.
raft
RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning) is a method for creating conversational agents that realistically emulate specific human targets. It involves a dual-phase process of fine-tuning and retrieval-based augmentation to generate nuanced and personalized dialogue. The tool is designed to combine interview transcripts with memories from past writings to enhance language model responses. RAFT has the potential to advance the field of personalized, context-sensitive conversational agents.
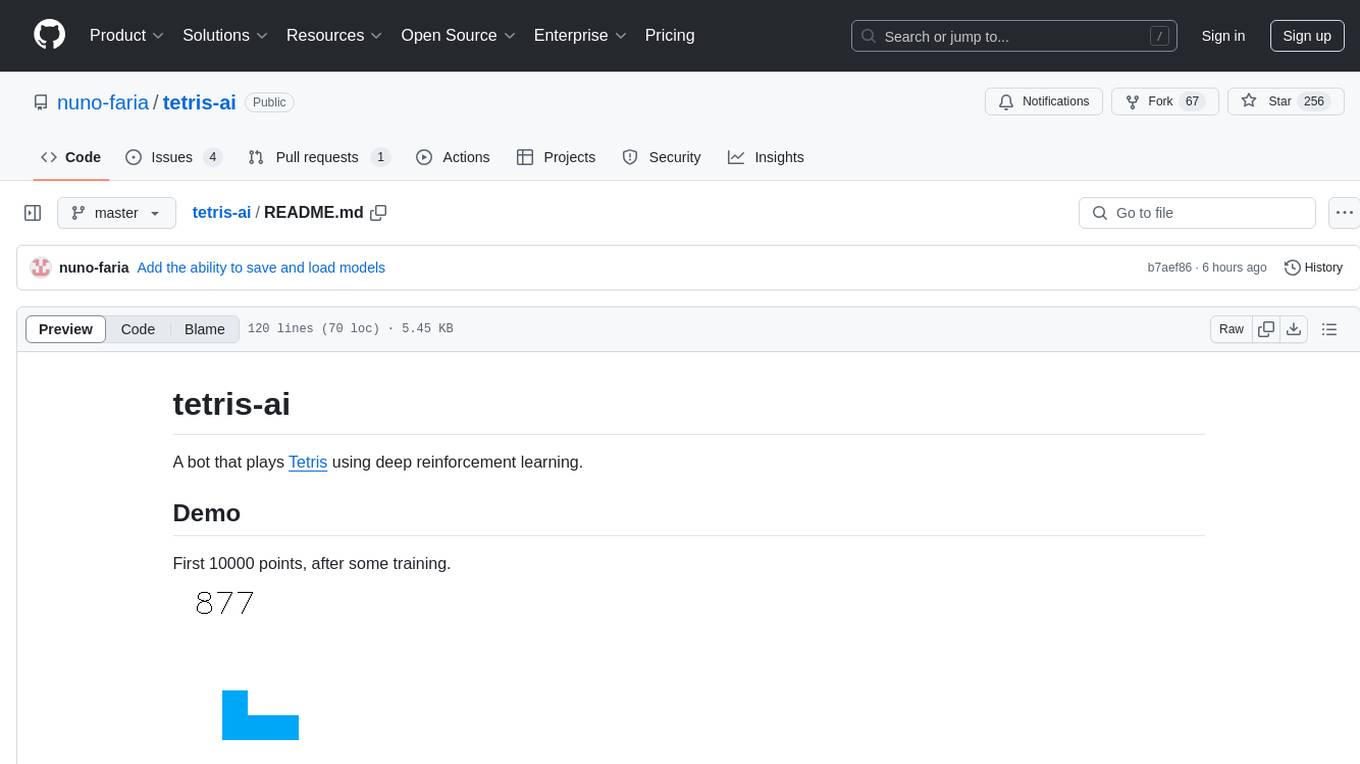
tetris-ai
A bot that plays Tetris using deep reinforcement learning. The agent learns to play by training itself with a neural network and Q Learning algorithm. It explores different 'paths' to achieve higher scores and makes decisions based on predicted scores for possible moves. The game state includes attributes like lines cleared, holes, bumpiness, and total height. The agent is implemented in Python using Keras framework with a deep neural network structure. Training involves a replay queue, random sampling, and optimization techniques. Results show the agent's progress in achieving higher scores over episodes.
gpdb
Greenplum Database (GPDB) is an advanced, fully featured, open source data warehouse, based on PostgreSQL. It provides powerful and rapid analytics on petabyte scale data volumes. Uniquely geared toward big data analytics, Greenplum Database is powered by the world’s most advanced cost-based query optimizer delivering high analytical query performance on large data volumes.
prompt-tuning-playbook
The LLM Prompt Tuning Playbook is a comprehensive guide for improving the performance of post-trained Language Models (LLMs) through effective prompting strategies. It covers topics such as pre-training vs. post-training, considerations for prompting, a rudimentary style guide for prompts, and a procedure for iterating on new system instructions. The playbook emphasizes the importance of clear, concise, and explicit instructions to guide LLMs in generating desired outputs. It also highlights the iterative nature of prompt development and the need for systematic evaluation of model responses.
SciMLBenchmarks.jl
SciMLBenchmarks.jl holds webpages, pdfs, and notebooks showing the benchmarks for the SciML Scientific Machine Learning Software ecosystem, including: * Benchmarks of equation solver implementations * Speed and robustness comparisons of methods for parameter estimation / inverse problems * Training universal differential equations (and subsets like neural ODEs) * Training of physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) * Surrogate comparisons, including radial basis functions, neural operators (DeepONets, Fourier Neural Operators), and more The SciML Bench suite is made to be a comprehensive open source benchmark from the ground up, covering the methods of computational science and scientific computing all the way to AI for science.
modelbench
ModelBench is a tool for running safety benchmarks against AI models and generating detailed reports. It is part of the MLCommons project and is designed as a proof of concept to aggregate measures, relate them to specific harms, create benchmarks, and produce reports. The tool requires LlamaGuard for evaluating responses and a TogetherAI account for running benchmarks. Users can install ModelBench from GitHub or PyPI, run tests using Poetry, and create benchmarks by providing necessary API keys. The tool generates static HTML pages displaying benchmark scores and allows users to dump raw scores and manage cache for faster runs. ModelBench is aimed at enabling users to test their own models and create tests and benchmarks.
textcoder
Textcoder is a proof-of-concept tool for steganographically encoding secret messages into ordinary text using arithmetic coding based on a statistical model derived from an LLM. It encrypts the secret message to produce a pseudorandom bit stream, which is then decompressed to generate text that appears randomly sampled from the LLM while encoding the secret message in specific token choices.
HybridAGI
HybridAGI is the first Programmable LLM-based Autonomous Agent that lets you program its behavior using a **graph-based prompt programming** approach. This state-of-the-art feature allows the AGI to efficiently use any tool while controlling the long-term behavior of the agent. Become the _first Prompt Programmers in history_ ; be a part of the AI revolution one node at a time! **Disclaimer: We are currently in the process of upgrading the codebase to integrate DSPy**
For similar tasks

Winter
Winter is a UCI chess engine that has competed at top invite-only computer chess events. It is the top-rated chess engine from Switzerland and has a level of play that is super human but below the state of the art reached by large, distributed, and resource-intensive open-source projects like Stockfish and Leela Chess Zero. Winter has relied on many machine learning algorithms and techniques over the course of its development, including certain clustering methods not used in any other chess programs, such as Gaussian Mixture Models and Soft K-Means. As of Winter 0.6.2, the evaluation function relies on a small neural network for more precise evaluations.

blackmarlin
Black Marlin is a UCI compliant chess engine fully written in Rust by Doruk Sekercioglu. It supports Chess960 and features a variety of search algorithms, pruning techniques, and evaluation methods. Black Marlin is designed to be efficient and accurate, and it has been shown to perform well against other top chess engines.
CameraChessWeb
Camera Chess Web is a tool that allows you to use your phone camera to replace chess eBoards. With Camera Chess Web, you can broadcast your game to Lichess, play a game on Lichess, or digitize a chess game from a video or live stream. Camera Chess Web is free to download on Google Play.
For similar jobs

Winter
Winter is a UCI chess engine that has competed at top invite-only computer chess events. It is the top-rated chess engine from Switzerland and has a level of play that is super human but below the state of the art reached by large, distributed, and resource-intensive open-source projects like Stockfish and Leela Chess Zero. Winter has relied on many machine learning algorithms and techniques over the course of its development, including certain clustering methods not used in any other chess programs, such as Gaussian Mixture Models and Soft K-Means. As of Winter 0.6.2, the evaluation function relies on a small neural network for more precise evaluations.

blackmarlin
Black Marlin is a UCI compliant chess engine fully written in Rust by Doruk Sekercioglu. It supports Chess960 and features a variety of search algorithms, pruning techniques, and evaluation methods. Black Marlin is designed to be efficient and accurate, and it has been shown to perform well against other top chess engines.