
iLLM-TSC
This repository contains the code for the paper“iLLM-TSC: Integration reinforcement learning and large language model for traffic signal control policy improvement”
Stars: 54
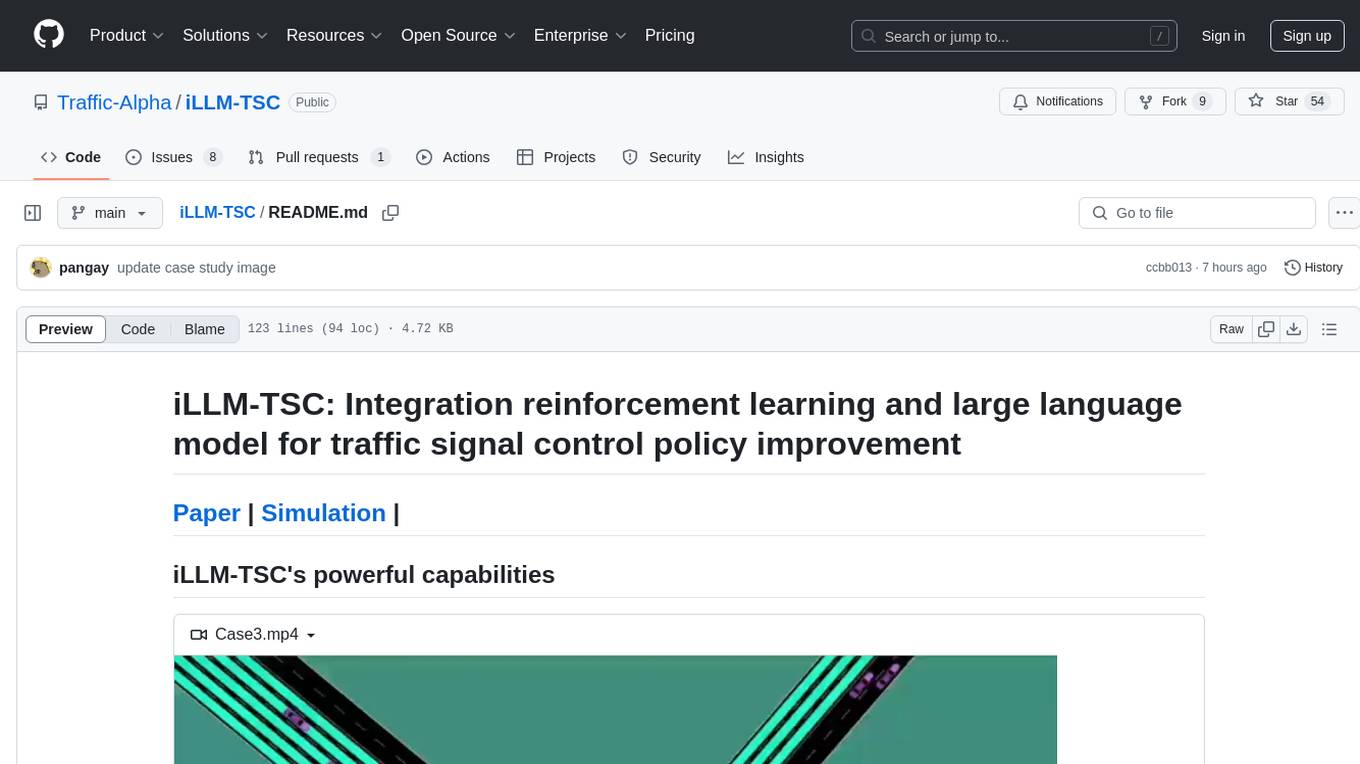
iLLM-TSC is a framework that integrates reinforcement learning and large language models for traffic signal control policy improvement. It refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions. The framework includes cases where the large language model provides explanations and recommendations for RL agent actions, such as prioritizing emergency vehicles at intersections. Users can install and run the framework locally to train RL models and evaluate the combined RL+LLM approach.
README:
iLLM-TSC: Integration reinforcement learning and large language model for traffic signal control policy improvement
Paper | Simulation |
https://github.com/Traffic-Alpha/TSC-HARLA/assets/75999557/92d6ff7f-cc5b-42ba-9feb-046022e70ad9
We propose a framework that utilizes LLM to support RL models. This framework refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions.
- Case1: LLM think that the action taken by the RL Agent was unreasonable and gave a reasonable explanation and recommended actions.
- Case 2: LLM considers that the movement made by the RL Agent is not the movement with the highest current mean occupancy but it is reasonable, after which LLM gives an explanation and recommendation.
- Case 3: An ambulance needs to pass through the intersection, but the RL Agent does not take into account that the ambulance needs to be prioritized. LLM modifies the RL Agent’s action to prioritize the ambulance to pass through the intersection.
Install TransSimHub
The simulation environment we used is TransSimHub, which is based on SUMO and can be used for TSC, V2X and UAM simulation. More information is available via docs.
You can install TransSimHub by cloning the GitHub repository. Follow these steps:
git clone https://github.com/Traffic-Alpha/TransSimHub.git
cd TransSimHub
pip install -e .After the installation is complete, you can use the following Python command to check if TransSimHub is installed and view its version:
import tshub
print(tshub.__version__)You can install HARLA by cloning the GitHub repository. Follow these steps:
git clone https://github.com/Traffic-Alpha/iLLM-TSC
cd iLLM-TSC
pip install -r requirements.txtAfter completing the above Install steps, you can use this program locally.
The first thing you need to do is train a RL model. You can do it with the following code:
cd iLLM-TSC
python sb3_ppo.pyThe training results are shown in the figure, and model weight has been uploaded in models.
The effect of the RL model can be tested with the following code:
python eval_rl_agent.pyBefore you can use LLM, you need to have your own KEY and fill it in the utils/config.yaml.
OPENAI_PROXY:
OPENAI_API_KEY:The entire framework can be used with the following code.
python rl_llm_tsc.pyEvaluation Rule: To make fair evaluation and comparison among different models, make sure you use the same LLM evaluation model (we use GPT4) for all the models you want to evaluate. Using a different scoring model or API updating might lead to different results.
All assets and code in this repository are under the Apache 2.0 license unless specified otherwise. The language data is under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Other datasets (including nuScenes) inherit their own distribution licenses. Please consider citing our project if it helps your research.
@article{pang2024illm,
title={iLLM-TSC: Integration reinforcement learning and large language model for traffic signal control policy improvement},
author={Pang, Aoyu and Wang, Maonan and Pun, Man-On and Chen, Chung Shue and Xiong, Xi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.06025},
year={2024}
}@article{wang2024llm,
title={LLM-Assisted Light: Leveraging Large Language Model Capabilities for Human-Mimetic Traffic Signal Control in Complex Urban Environments},
author={Wang, Maonan and Pang, Aoyu and Kan, Yuheng and Pun, Man-On and Chen, Chung Shue and Huang, Bo},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.08337},
year={2024}
}iLLM-TSC just explores the combination of RL and LLM, more work will be updated in TSC-LLM, welcome to star!
- Yufei Teng: Thanks for editing the video.
- Thank you to everyone who pays attention to our work. Hope our work can help you.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for iLLM-TSC
Similar Open Source Tools

iLLM-TSC
iLLM-TSC is a framework that integrates reinforcement learning and large language models for traffic signal control policy improvement. It refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions. The framework includes cases where the large language model provides explanations and recommendations for RL agent actions, such as prioritizing emergency vehicles at intersections. Users can install and run the framework locally to train RL models and evaluate the combined RL+LLM approach.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.
ModernBERT
ModernBERT is a repository focused on modernizing BERT through architecture changes and scaling. It introduces FlexBERT, a modular approach to encoder building blocks, and heavily relies on .yaml configuration files to build models. The codebase builds upon MosaicBERT and incorporates Flash Attention 2. The repository is used for pre-training and GLUE evaluations, with a focus on reproducibility and documentation. It provides a collaboration between Answer.AI, LightOn, and friends.
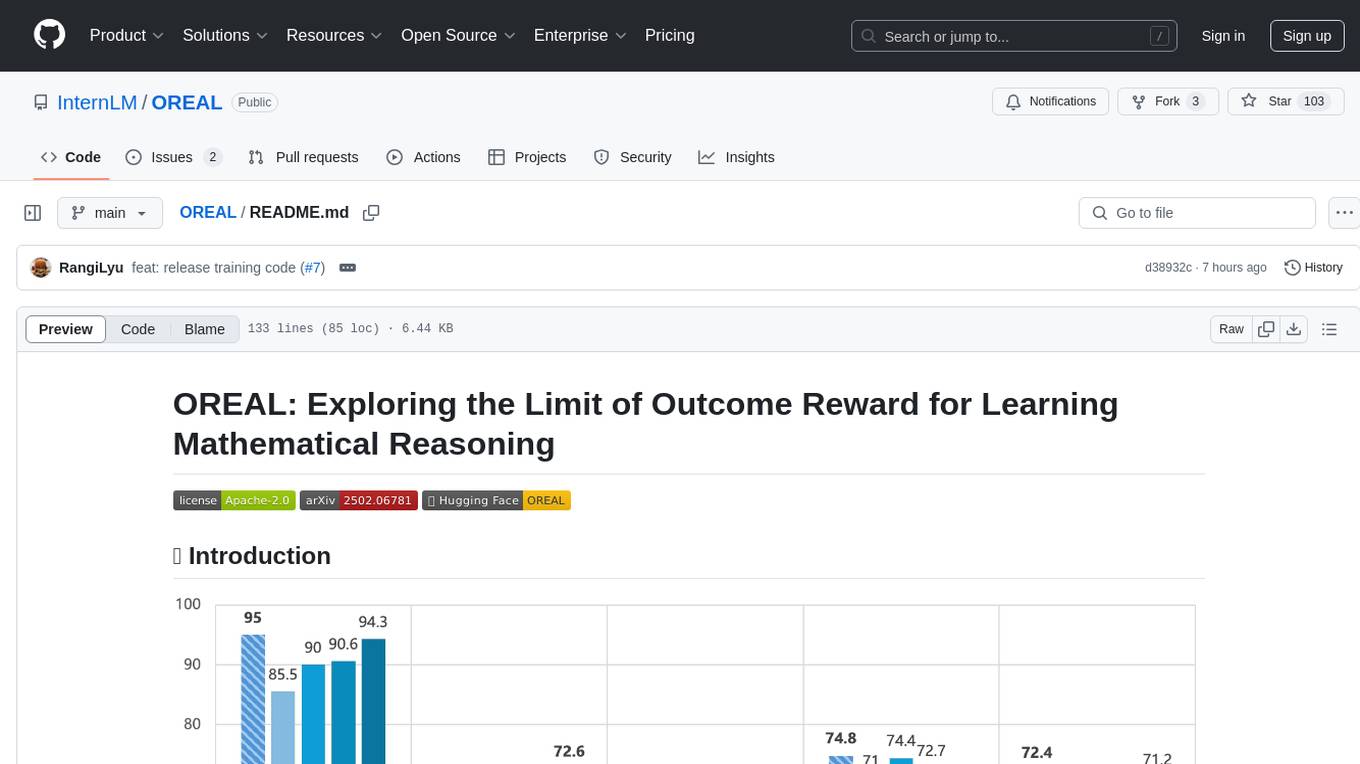
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
R1-Searcher
R1-searcher is a tool designed to incentivize the search capability in large reasoning models (LRMs) via reinforcement learning. It enables LRMs to invoke web search and obtain external information during the reasoning process by utilizing a two-stage outcome-supervision reinforcement learning approach. The tool does not require instruction fine-tuning for cold start and is compatible with existing Base LLMs or Chat LLMs. It includes training code, inference code, model checkpoints, and a detailed technical report.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.

pydantic-ai
PydanticAI is a Python agent framework designed to make it less painful to build production grade applications with Generative AI. It is built by the Pydantic Team and supports various AI models like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Ollama, Groq, and Mistral. PydanticAI seamlessly integrates with Pydantic Logfire for real-time debugging, performance monitoring, and behavior tracking of LLM-powered applications. It is type-safe, Python-centric, and offers structured responses, dependency injection system, and streamed responses. PydanticAI is in early beta, offering a Python-centric design to apply standard Python best practices in AI-driven projects.
crewAI
crewAI is a cutting-edge framework for orchestrating role-playing, autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It provides a flexible and structured approach to AI collaboration, enabling users to define agents with specific roles, goals, and tools, and assign them tasks within a customizable process. crewAI supports integration with various LLMs, including OpenAI, and offers features such as autonomous task delegation, flexible task management, and output parsing. It is open-source and welcomes contributions, with a focus on improving the library based on usage data collected through anonymous telemetry.
compl-ai
COMPL-AI is a compliance-centered evaluation framework for LLMs created by ETH Zurich, INSAIT, and LatticeFlow AI. It includes a technical interpretation of the EU AI Act and an open-source benchmarking suite. The framework offers tailored benchmarks covering various technical aspects of the EU AI Act, a public Hugging Face leaderboard, and support for multiple providers. Users can run evaluations using a custom CLI tool and contribute to expanding benchmark coverage. The framework is undergoing updates to enhance coverage over the EU AI Act principles and technical requirements, with a focus on risk management, data quality, and cybersecurity measures.
hackingBuddyGPT
hackingBuddyGPT is a framework for testing LLM-based agents for security testing. It aims to create common ground truth by creating common security testbeds and benchmarks, evaluating multiple LLMs and techniques against those, and publishing prototypes and findings as open-source/open-access reports. The initial focus is on evaluating the efficiency of LLMs for Linux privilege escalation attacks, but the framework is being expanded to evaluate the use of LLMs for web penetration-testing and web API testing. hackingBuddyGPT is released as open-source to level the playing field for blue teams against APTs that have access to more sophisticated resources.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
EdgeChains
EdgeChains is an open-source chain-of-thought engineering framework tailored for Large Language Models (LLMs)- like OpenAI GPT, LLama2, Falcon, etc. - With a focus on enterprise-grade deployability and scalability. EdgeChains is specifically designed to **orchestrate** such applications. At EdgeChains, we take a unique approach to Generative AI - we think Generative AI is a deployment and configuration management challenge rather than a UI and library design pattern challenge. We build on top of a tech that has solved this problem in a different domain - Kubernetes Config Management - and bring that to Generative AI. Edgechains is built on top of jsonnet, originally built by Google based on their experience managing a vast amount of configuration code in the Borg infrastructure.
AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
For similar tasks

iLLM-TSC
iLLM-TSC is a framework that integrates reinforcement learning and large language models for traffic signal control policy improvement. It refines RL decisions based on real-world contexts and provides reasonable actions when RL agents make erroneous decisions. The framework includes cases where the large language model provides explanations and recommendations for RL agent actions, such as prioritizing emergency vehicles at intersections. Users can install and run the framework locally to train RL models and evaluate the combined RL+LLM approach.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.




