
spiceai
A portable accelerated SQL query, search, and LLM-inference engine, written in Rust, for data-grounded AI apps and agents.
Stars: 2587

Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.
README:
📄 Docs | ⚡️ Quickstart | 🧑🍳 Cookbook
Spice is a SQL query, search, and LLM-inference engine, written in Rust, for data apps and agents.
Spice provides four industry standard APIs in a lightweight, portable runtime (single binary/container):
-
SQL Query & Search: HTTP, Arrow Flight, Arrow Flight SQL, ODBC, JDBC, and ADBC APIs;
vector_searchandtext_searchUDTFs. - OpenAI-Compatible APIs: HTTP APIs for OpenAI SDK compatibility, local model serving (CUDA/Metal accelerated), and hosted model gateway.
- Iceberg Catalog REST APIs: A unified Iceberg REST Catalog API.
- MCP HTTP+SSE APIs: Integration with external tools via Model Context Protocol (MCP) using HTTP and Server-Sent Events (SSE).
🎯 Goal: Developers can focus on building data apps and AI agents confidently, knowing they are grounded in data.
Spice is primarily used for:
- Data Federation: SQL query across any database, data warehouse, or data lake. Learn More.
- Data Materialization and Acceleration: Materialize, accelerate, and cache database queries. Read the MaterializedView interview - Building a CDN for Databases
- Enterprise Search: Keyword, vector, and full-text search with Tantivy-powered BM25 and vector similarity search for structured and unstructured data.
- AI apps and agents: An AI-database powering retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and intelligent agents. Learn More.
If you want to build with DataFusion or using DuckDB, Spice provides a simple, flexible, and production-ready engine you can just use.
📣 Read the Spice.ai 1.0-stable announcement.
Spice is built-on industry leading technologies including Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB.
🎥 Watch the CMU Databases Accelerating Data and AI with Spice.ai Open-Source
🎥 Watch How to Query Data using Spice, OpenAI, and MCP
🎥 Watch How to search with Amazon S3 Vectors
Spice simplifies building data-driven AI applications and agents by making it fast and easy to query, federate, and accelerate data from one or more sources using SQL, while grounding AI in real-time, reliable data. Co-locate datasets with apps and AI models to power AI feedback loops, enable RAG and search, and deliver fast, low-latency data-query and AI-inference with full control over cost and performance.
-
AI-Native Runtime: Spice combines data query and AI inference in a single engine, for data-grounded AI and accurate AI.
-
Application-Focused: Designed to run distributed at the application and agent level, often as a 1:1 or 1:N mapping between app and Spice instance, unlike traditional data systems built for many apps on one centralized database. It’s common to spin up multiple Spice instances—even one per tenant or customer.
-
Dual-Engine Acceleration: Supports both OLAP (Arrow/DuckDB) and OLTP (SQLite/PostgreSQL) engines at the dataset level, providing flexible performance across analytical and transactional workloads.
-
Disaggregated Storage: Separation of compute from disaggregated storage, co-locating local, materialized working sets of data with applications, dashboards, or ML pipelines while accessing source data in its original storage.
-
Edge to Cloud Native: Deploy as a standalone instance, Kubernetes sidecar, microservice, or cluster—across edge/POP, on-prem, and public clouds. Chain multiple Spice instances for tier-optimized, distributed deployments.
| Feature | Spice | Trino / Presto | Dremio | ClickHouse | Materialize |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use-Case | Data & AI apps/agents | Big data analytics | Interactive analytics | Real-time analytics | Real-time analytics |
| Primary deployment model | Sidecar | Cluster | Cluster | Cluster | Cluster |
| Federated Query Support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ― | ― |
| Acceleration/Materialization | ✅ (Arrow, SQLite, DuckDB, PostgreSQL) | Intermediate storage | Reflections (Iceberg) | Materialized views | ✅ (Real-time views) |
| Catalog Support | ✅ (Iceberg, Unity Catalog, AWS Glue) | ✅ | ✅ | ― | ― |
| Query Result Caching | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Limited |
| Multi-Modal Acceleration | ✅ (OLAP + OLTP) | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Change Data Capture (CDC) | ✅ (Debezium) | ― | ― | ― | ✅ (Debezium) |
| Feature | Spice | LangChain | LlamaIndex | AgentOps.ai | Ollama |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use-Case | Data & AI apps | Agentic workflows | RAG apps | Agent operations | LLM apps |
| Programming Language | Any language (HTTP interface) | JavaScript, Python | Python | Python | Any language (HTTP interface) |
| Unified Data + AI Runtime | ✅ | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Federated Data Query | ✅ | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Accelerated Data Access | ✅ | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Tools/Functions | ✅ (MCP HTTP+SSE) | ✅ | ✅ | Limited | Limited |
| LLM Memory | ✅ | ✅ | ― | ✅ | ― |
| Evaluations (Evals) | ✅ | Limited | ― | Limited | ― |
| Search | ✅ (Keyword, Vector, & Full-Text-Search) | ✅ | ✅ | Limited | Limited |
| Caching | ✅ (Query and results caching) | Limited | ― | ― | ― |
| Embeddings | ✅ (Built-in & pluggable models/DBs) | ✅ | ✅ | Limited | ― |
✅ = Fully supported ❌ = Not supported Limited = Partial or restricted support
- OpenAI-compatible API: Connect to hosted models (OpenAI, Anthropic, xAI) or deploy locally (Llama, NVIDIA NIM). AI Gateway Recipe
- Federated Data Access: Query using SQL and NSQL (text-to-SQL) across databases, data warehouses, and data lakes with advanced query push-down for fast retrieval across disparate data sources. Federated SQL Query Recipe
-
Search and RAG: Search and retrieve context with accelerated embeddings for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) workflows, including full-text search (FTS) via Tantivy-powered BM25 scoring and vector similarity search (VSS) integrated into SQL queries. Use SQL functions like
vector_searchfor semantic search andtext_searchfor keyword-based search. Supports multi-column vector search with reciprocal rank fusion for aggregated results. Amazon S3 Vectors Cookbook Recipe - LLM Memory and Observability: Store and retrieve history and context for AI agents while gaining deep visibility into data flows, model performance, and traces. LLM Memory Recipe | Observability & Monitoring Features Documentation
- Data Acceleration: Co-locate materialized datasets in Arrow, SQLite, and DuckDB with applications for sub-second query. DuckDB Data Accelerator Recipe
- Resiliency and Local Dataset Replication: Maintain application availability with local replicas of critical datasets. Local Dataset Replication Recipe
- Responsive Dashboards: Enable fast, real-time analytics by accelerating data for frontends and BI tools. Sales BI Dashboard Demo
- Simplified Legacy Migration: Use a single endpoint to unify legacy systems with modern infrastructure, including federated SQL querying across multiple sources. Federated SQL Query Recipe
-
Unified Search with Vector Similarity: Perform efficient vector similarity search across structured and unstructured data sources, now with native support for Amazon S3 Vectors for petabyte-scale vector storage and querying. The Spice runtime manages the vector lifecycle: ingesting data from disparate sources, embedding it using models like Amazon Titan Embeddings or Cohere Embeddings via AWS Bedrock, or MiniLM L6 from HuggingFace, and storing in S3 Vector buckets. Supports distance metrics like cosine similarity, Euclidean distance, or dot product. Example SQL:
SELECT * FROM vector_search(my_table, 'search query', 10) WHERE condition ORDER BY score;. Amazon S3 Vectors Cookbook Recipe - Semantic Knowledge Layer: Define a semantic context model to enrich data for AI. Semantic Model Feature Documentation
- Text-to-SQL: Convert natural language queries into SQL using built-in NSQL and sampling tools for accurate query. Text-to-SQL Recipe
- Model and Data Evaluations: Assess model performance and data quality with integrated evaluation tools. Language Model Evaluations Recipe
-
Is Spice a cache? No specifically; you can think of Spice data acceleration as an active cache, materialization, or data prefetcher. A cache would fetch data on a cache-miss while Spice prefetches and materializes filtered data on an interval, trigger, or as data changes using CDC. In addition to acceleration Spice supports results caching.
-
Is Spice a CDN for databases? Yes, a common use-case for Spice is as a CDN for different data sources. Using CDN concepts, Spice enables you to ship (load) a working set of your database (or data lake, or data warehouse) where it's most frequently accessed, like from a data-intensive application or for AI context.
https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/assets/80174/7735ee94-3f4a-4983-a98e-fe766e79e03a
See more demos on YouTube.
| Name | Description | Status | Protocol/Format |
|---|---|---|---|
databricks (mode: delta_lake) |
Databricks | Stable | S3/Delta Lake |
delta_lake |
Delta Lake | Stable | Delta Lake |
dremio |
Dremio | Stable | Arrow Flight |
duckdb |
DuckDB | Stable | Embedded |
file |
File | Stable | Parquet, CSV |
github |
GitHub | Stable | GitHub API |
postgres |
PostgreSQL | Stable | |
s3 |
S3 | Stable | Parquet, CSV |
mysql |
MySQL | Stable | |
spice.ai |
Spice.ai | Stable | Arrow Flight |
graphql |
GraphQL | Release Candidate | JSON |
databricks (mode: spark_connect) |
Databricks | Beta | Spark Connect |
flightsql |
FlightSQL | Beta | Arrow Flight SQL |
iceberg |
Apache Iceberg | Beta | Parquet |
mssql |
Microsoft SQL Server | Beta | Tabular Data Stream (TDS) |
odbc |
ODBC | Beta | ODBC |
snowflake |
Snowflake | Beta | Arrow |
spark |
Spark | Beta | Spark Connect |
oracle |
Oracle | Alpha | Oracle ODPI-C |
abfs |
Azure BlobFS | Alpha | Parquet, CSV |
clickhouse |
Clickhouse | Alpha | |
debezium |
Debezium CDC | Alpha | Kafka + JSON |
kafka |
Kafka | Alpha | Kafka + JSON |
dynamodb |
Amazon DynamoDB | Alpha | |
ftp, sftp
|
FTP/SFTP | Alpha | Parquet, CSV |
glue |
AWS Glue | Alpha | Iceberg, Parquet, CSV |
http, https
|
HTTP(s) | Alpha | Parquet, CSV |
imap |
IMAP | Alpha | IMAP Emails |
localpod |
Local dataset replication | Alpha | |
sharepoint |
Microsoft SharePoint | Alpha | Unstructured UTF-8 documents |
mongodb |
MongoDB | Coming Soon | |
elasticsearch |
ElasticSearch | Roadmap |
| Name | Description | Status | Engine Modes |
|---|---|---|---|
arrow |
In-Memory Arrow Records | Stable | memory |
duckdb |
Embedded DuckDB | Stable |
memory, file
|
postgres |
Attached PostgreSQL | Release Candidate | N/A |
sqlite |
Embedded SQLite | Release Candidate |
memory, file
|
| Name | Description | Status | ML Format(s) | LLM Format(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
openai |
OpenAI (or compatible) LLM endpoint | Release Candidate | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
file |
Local filesystem | Release Candidate | ONNX | GGUF, GGML, SafeTensor |
huggingface |
Models hosted on HuggingFace | Release Candidate | ONNX | GGUF, GGML, SafeTensor |
spice.ai |
Models hosted on the Spice.ai Cloud Platform | ONNX | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint | |
azure |
Azure OpenAI | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint | |
anthropic |
Models hosted on Anthropic | Alpha | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
xai |
Models hosted on xAI | Alpha | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
| Name | Description | Status | ML Format(s) | LLM Format(s)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
openai |
OpenAI (or compatible) LLM endpoint | Release Candidate | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
file |
Local filesystem | Release Candidate | ONNX | GGUF, GGML, SafeTensor |
huggingface |
Models hosted on HuggingFace | Release Candidate | ONNX | GGUF, GGML, SafeTensor |
azure |
Azure OpenAI | Alpha | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
bedrock |
AWS Bedrock (e.g., Titan, Cohere) | Alpha | - | OpenAI-compatible HTTP endpoint |
| Name | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
s3_vectors |
Amazon S3 Vectors for petabyte-scale vector storage and querying | Alpha |
pgvector |
PostgreSQL with pgvector extension | Alpha |
duckdb_vector |
DuckDB with vector extension for efficient vector storage and search | Alpha |
sqlite_vec |
SQLite with sqlite-vec extension for lightweight vector operations | Alpha |
Catalog Connectors connect to external catalog providers and make their tables available for federated SQL query in Spice. Configuring accelerations for tables in external catalogs is not supported. The schema hierarchy of the external catalog is preserved in Spice.
| Name | Description | Status | Protocol/Format |
|---|---|---|---|
spice.ai |
Spice.ai Cloud Platform | Stable | Arrow Flight |
unity_catalog |
Unity Catalog | Stable | Delta Lake |
databricks |
Databricks | Beta | Spark Connect, S3/Delta Lake |
iceberg |
Apache Iceberg | Beta | Parquet |
glue |
AWS Glue | Alpha | CSV, Parquet, Iceberg |
https://github.com/spiceai/spiceai/assets/88671039/85cf9a69-46e7-412e-8b68-22617dcbd4e0
Install the Spice CLI:
On macOS, Linux, and WSL:
curl https://install.spiceai.org | /bin/bashOr using brew:
brew install spiceai/spiceai/spiceOn Windows using PowerShell:
iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://install.spiceai.org/Install.ps1"))Step 1. Initialize a new Spice app with the spice init command:
spice init spice_qsA spicepod.yaml file is created in the spice_qs directory. Change to that directory:
cd spice_qsStep 2. Start the Spice runtime:
spice runExample output will be shown as follows:
2025/01/20 11:26:10 INFO Spice.ai runtime starting...
2025-01-20T19:26:10.679068Z INFO runtime::init::dataset: No datasets were configured. If this is unexpected, check the Spicepod configuration.
2025-01-20T19:26:10.679716Z INFO runtime::flight: Spice Runtime Flight listening on 127.0.0.1:50051
2025-01-20T19:26:10.679786Z INFO runtime::metrics_server: Spice Runtime Metrics listening on 127.0.0.1:9090
2025-01-20T19:26:10.680140Z INFO runtime::http: Spice Runtime HTTP listening on 127.0.0.1:8090
2025-01-20T19:26:10.682080Z INFO runtime::opentelemetry: Spice Runtime OpenTelemetry listening on 127.0.0.1:50052
2025-01-20T19:26:10.879126Z INFO runtime::init::results_cache: Initialized results cache; max size: 128.00 MiB, item ttl: 1sThe runtime is now started and ready for queries.
Step 3. In a new terminal window, add the spiceai/quickstart Spicepod. A Spicepod is a package of configuration defining datasets and ML models.
spice add spiceai/quickstartThe spicepod.yaml file will be updated with the spiceai/quickstart dependency.
version: v1
kind: Spicepod
name: spice_qs
dependencies:
- spiceai/quickstartThe spiceai/quickstart Spicepod will add a taxi_trips data table to the runtime which is now available to query by SQL.
2025-01-20T19:26:30.011633Z INFO runtime::init::dataset: Dataset taxi_trips registered (s3://spiceai-demo-datasets/taxi_trips/2024/), acceleration (arrow), results cache enabled.
2025-01-20T19:26:30.013002Z INFO runtime::accelerated_table::refresh_task: Loading data for dataset taxi_trips
2025-01-20T19:26:40.312839Z INFO runtime::accelerated_table::refresh_task: Loaded 2,964,624 rows (399.41 MiB) for dataset taxi_trips in 10s 299msStep 4. Start the Spice SQL REPL:
spice sqlThe SQL REPL inferface will be shown:
Welcome to the Spice.ai SQL REPL! Type 'help' for help.
show tables; -- list available tables
sql>Enter show tables; to display the available tables for query:
sql> show tables;
+---------------+--------------+---------------+------------+
| table_catalog | table_schema | table_name | table_type |
+---------------+--------------+---------------+------------+
| spice | public | taxi_trips | BASE TABLE |
| spice | runtime | query_history | BASE TABLE |
| spice | runtime | metrics | BASE TABLE |
+---------------+--------------+---------------+------------+
Time: 0.022671708 seconds. 3 rows.Enter a query to display the longest taxi trips:
SELECT trip_distance, total_amount FROM taxi_trips ORDER BY trip_distance DESC LIMIT 10;Output:
+---------------+--------------+
| trip_distance | total_amount |
+---------------+--------------+
| 312722.3 | 22.15 |
| 97793.92 | 36.31 |
| 82015.45 | 21.56 |
| 72975.97 | 20.04 |
| 71752.26 | 49.57 |
| 59282.45 | 33.52 |
| 59076.43 | 23.17 |
| 58298.51 | 18.63 |
| 51619.36 | 24.2 |
| 44018.64 | 52.43 |
+---------------+--------------+
Time: 0.045150667 seconds. 10 rows.Using the Docker image locally:
docker pull spiceai/spiceaiIn a Dockerfile:
from spiceai/spiceai:latestUsing Helm:
helm repo add spiceai https://helm.spiceai.org
helm install spiceai spiceai/spiceaiThe Spice.ai Cookbook is a collection of recipes and examples for using Spice. Find it at https://github.com/spiceai/cookbook.
Access ready-to-use Spicepods and datasets hosted on the Spice.ai Cloud Platform using the Spice runtime. A list of public Spicepods is available on Spicerack: https://spicerack.org/.
To use public datasets, create a free account on Spice.ai:
-
Visit spice.ai and click Try for Free.
-
After creating an account, create an app to generate an API key.
Once set up, you can access ready-to-use Spicepods including datasets. For this demonstration, use the taxi_trips dataset from the Spice.ai Quickstart.
Step 1. Initialize a new project.
# Initialize a new Spice app
spice init spice_app
# Change to app directory
cd spice_appStep 2. Log in and authenticate from the command line using the spice login command. A pop up browser window will prompt you to authenticate:
spice loginStep 3. Start the runtime:
# Start the runtime
spice runStep 4. Configure the dataset:
In a new terminal window, configure a new dataset using the spice dataset configure command:
spice dataset configureEnter a dataset name that will be used to reference the dataset in queries. This name does not need to match the name in the dataset source.
dataset name: (spice_app) taxi_tripsEnter the description of the dataset:
description: Taxi trips datasetEnter the location of the dataset:
from: spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_tripsSelect y when prompted whether to accelerate the data:
Locally accelerate (y/n)? yYou should see the following output from your runtime terminal:
2024-12-16T05:12:45.803694Z INFO runtime::init::dataset: Dataset taxi_trips registered (spice.ai/spiceai/quickstart/datasets/taxi_trips), acceleration (arrow, 10s refresh), results cache enabled.
2024-12-16T05:12:45.805494Z INFO runtime::accelerated_table::refresh_task: Loading data for dataset taxi_trips
2024-12-16T05:13:24.218345Z INFO runtime::accelerated_table::refresh_task: Loaded 2,964,624 rows (8.41 GiB) for dataset taxi_trips in 38s 412ms.Step 5. In a new terminal window, use the Spice SQL REPL to query the dataset
spice sqlSELECT tpep_pickup_datetime, passenger_count, trip_distance from taxi_trips LIMIT 10;The output displays the results of the query along with the query execution time:
+----------------------+-----------------+---------------+
| tpep_pickup_datetime | passenger_count | trip_distance |
+----------------------+-----------------+---------------+
| 2024-01-11T12:55:12 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2024-01-11T12:55:12 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 2024-01-11T12:04:56 | 1 | 0.63 |
| 2024-01-11T12:18:31 | 1 | 1.38 |
| 2024-01-11T12:39:26 | 1 | 1.01 |
| 2024-01-11T12:18:58 | 1 | 5.13 |
| 2024-01-11T12:43:13 | 1 | 2.9 |
| 2024-01-11T12:05:41 | 1 | 1.36 |
| 2024-01-11T12:20:41 | 1 | 1.11 |
| 2024-01-11T12:37:25 | 1 | 2.04 |
+----------------------+-----------------+---------------+
Time: 0.00538925 seconds. 10 rows.You can experiment with the time it takes to generate queries when using non-accelerated datasets. You can change the acceleration setting from true to false in the datasets.yaml file.
Comprehensive documentation is available at spiceai.org/docs.
Over 45 quickstarts and samples available in the Spice Cookbook.
Spice.ai is designed to be extensible with extension points documented at EXTENSIBILITY.md. Build custom Data Connectors, Data Accelerators, Catalog Connectors, Secret Stores, Models, or Embeddings.
🚀 See the Roadmap for upcoming features.
We greatly appreciate and value your support! You can help Spice in a number of ways:
- Build an app with Spice.ai and send us feedback and suggestions at [email protected] or on Discord, X, or LinkedIn.
- File an issue if you see something not quite working correctly.
- Join our team (We’re hiring!)
- Contribute code or documentation to the project (see CONTRIBUTING.md).
- Follow our blog at spiceai.org/blog
⭐️ star this repo! Thank you for your support! 🙏
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for spiceai
Similar Open Source Tools

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.
redb-open
reDB Node is a distributed, policy-driven data mesh platform that enables True Data Portability across various databases, warehouses, clouds, and environments. It unifies data access, data mobility, and schema transformation into one open platform. Built for developers, architects, and AI systems, reDB addresses the challenges of fragmented data ecosystems in modern enterprises by providing multi-database interoperability, automated schema versioning, zero-downtime migration, real-time developer data environments with obfuscation, quantum-resistant encryption, and policy-based access control. The project aims to build a foundation for future-proof data infrastructure.
AIaW
AIaW is a next-generation LLM client with full functionality, lightweight, and extensible. It supports various basic functions such as streaming transfer, image uploading, and latex formulas. The tool is cross-platform with a responsive interface design. It supports multiple service providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Users can modify questions, regenerate in a forked manner, and visualize conversations in a tree structure. Additionally, it offers features like file parsing, video parsing, plugin system, assistant market, local storage with real-time cloud sync, and customizable interface themes. Users can create multiple workspaces, use dynamic prompt word variables, extend plugins, and benefit from detailed design elements like real-time content preview, optimized code pasting, and support for various file types.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.

lmnr
Laminar is an all-in-one open-source platform designed for engineering AI products. It allows users to trace, evaluate, label, and analyze LLM data efficiently. The platform offers features such as automatic tracing of common AI frameworks and SDKs, local and online evaluations, simple UI for data labeling, dataset management, and scalability with gRPC communication. Laminar is built with a modern open-source stack including RabbitMQ, Postgres, Clickhouse, and Qdrant for semantic similarity search. It provides fast and beautiful dashboards for traces, evaluations, and labels, making it a comprehensive tool for AI product development.
mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
tools
Strands Agents Tools is a community-driven project that provides a powerful set of tools for your agents to use. It bridges the gap between large language models and practical applications by offering ready-to-use tools for file operations, system execution, API interactions, mathematical operations, and more. The tools cover a wide range of functionalities including file operations, shell integration, memory storage, web infrastructure, HTTP client, Slack client, Python execution, mathematical tools, AWS integration, image and video processing, audio output, environment management, task scheduling, advanced reasoning, swarm intelligence, dynamic MCP client, parallel tool execution, browser automation, diagram creation, RSS feed management, and computer automation.

pointer
Pointer is a lightweight and efficient tool for analyzing and visualizing data structures in C and C++ programs. It provides a user-friendly interface to track memory allocations, pointer references, and data structures, helping developers to identify memory leaks, pointer errors, and optimize memory usage. With Pointer, users can easily navigate through complex data structures, visualize memory layouts, and debug pointer-related issues in their codebase. The tool offers interactive features such as memory snapshots, pointer tracking, and memory visualization, making it a valuable asset for C and C++ developers working on memory-intensive applications.
jadx-mcp-server
JADX-MCP-SERVER is a standalone Python server that interacts with JADX-AI-MCP Plugin to analyze Android APKs using LLMs like Claude. It enables live communication with decompiled Android app context, uncovering vulnerabilities, parsing manifests, and facilitating reverse engineering effortlessly. The tool combines JADX-AI-MCP and JADX MCP SERVER to provide real-time reverse engineering support with LLMs, offering features like quick analysis, vulnerability detection, AI code modification, static analysis, and reverse engineering helpers. It supports various MCP tools for fetching class information, text, methods, fields, smali code, AndroidManifest.xml content, strings.xml file, resource files, and more. Tested on Claude Desktop, it aims to support other LLMs in the future, enhancing Android reverse engineering and APK modification tools connectivity for easier reverse engineering purely from vibes.

hyper-mcp
hyper-mcp is a fast and secure MCP server that enables adding AI capabilities to applications through WebAssembly plugins. It supports writing plugins in various languages, distributing them via standard OCI registries, and running them in resource-constrained environments. The tool offers sandboxing with WASM for limiting access, cross-platform compatibility, and deployment flexibility. Security features include sandboxed plugins, memory-safe execution, secure plugin distribution, and fine-grained access control. Users can configure the tool for global or project-specific use, start the server with different transport options, and utilize available plugins for tasks like time calculations, QR code generation, hash generation, IP retrieval, and webpage fetching.
SQLBot
SQLBot is a versatile tool for executing SQL queries and managing databases. It provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with databases, allowing users to easily query, insert, update, and delete data. SQLBot supports various database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite, making it a valuable tool for developers, data analysts, and database administrators. With SQLBot, users can streamline their database management tasks and improve their productivity by quickly accessing and manipulating data without the need for complex SQL commands.
paiml-mcp-agent-toolkit
PAIML MCP Agent Toolkit (PMAT) is a zero-configuration AI context generation system with extreme quality enforcement and Toyota Way standards. It allows users to analyze any codebase instantly through CLI, MCP, or HTTP interfaces. The toolkit provides features such as technical debt analysis, advanced monitoring, metrics aggregation, performance profiling, bottleneck detection, alert system, multi-format export, storage flexibility, and more. It also offers AI-powered intelligence for smart recommendations, polyglot analysis, repository showcase, and integration points. PMAT enforces quality standards like complexity ≤20, zero SATD comments, test coverage >80%, no lint warnings, and synchronized documentation with commits. The toolkit follows Toyota Way development principles for iterative improvement, direct AST traversal, automated quality gates, and zero SATD policy.
koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building and running AI agents entirely in idiomatic Kotlin. It allows users to create agents that interact with tools, handle complex workflows, and communicate with users. Key features include pure Kotlin implementation, MCP integration, embedding capabilities, custom tool creation, ready-to-use components, intelligent history compression, powerful streaming API, persistent agent memory, comprehensive tracing, flexible graph workflows, modular feature system, scalable architecture, and multiplatform support.

gonzo
Gonzo is a powerful, real-time log analysis terminal UI tool inspired by k9s. It allows users to analyze log streams with beautiful charts, AI-powered insights, and advanced filtering directly from the terminal. The tool provides features like live streaming log processing, OTLP support, interactive dashboard with real-time charts, advanced filtering options including regex support, and AI-powered insights such as pattern detection, anomaly analysis, and root cause suggestions. Users can also configure AI models from providers like OpenAI, LM Studio, and Ollama for intelligent log analysis. Gonzo is built with Bubble Tea, Lipgloss, Cobra, Viper, and OpenTelemetry, following a clean architecture with separate modules for TUI, log analysis, frequency tracking, OTLP handling, and AI integration.
holmesgpt
HolmesGPT is an open-source DevOps assistant powered by OpenAI or any tool-calling LLM of your choice. It helps in troubleshooting Kubernetes, incident response, ticket management, automated investigation, and runbook automation in plain English. The tool connects to existing observability data, is compliance-friendly, provides transparent results, supports extensible data sources, runbook automation, and integrates with existing workflows. Users can install HolmesGPT using Brew, prebuilt Docker container, Python Poetry, or Docker. The tool requires an API key for functioning and supports OpenAI, Azure AI, and self-hosted LLMs.
emqx
EMQX is a highly scalable and reliable MQTT platform designed for IoT data infrastructure. It supports various protocols like MQTT 5.0, 3.1.1, and 3.1, as well as MQTT-SN, CoAP, LwM2M, and MQTT over QUIC. EMQX allows connecting millions of IoT devices, processing messages in real time, and integrating with backend data systems. It is suitable for applications in AI, IoT, IIoT, connected vehicles, smart cities, and more. The tool offers features like massive scalability, powerful rule engine, flow designer, AI processing, robust security, observability, management, extensibility, and a unified experience with the Business Source License (BSL) 1.1.
For similar tasks

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.
Pathway-AI-Bootcamp
Welcome to the μLearn x Pathway Initiative, an exciting adventure into the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI)! This comprehensive course, developed in collaboration with Pathway, will empower you with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the fascinating world of AI, with a special focus on Large Language Models (LLMs).
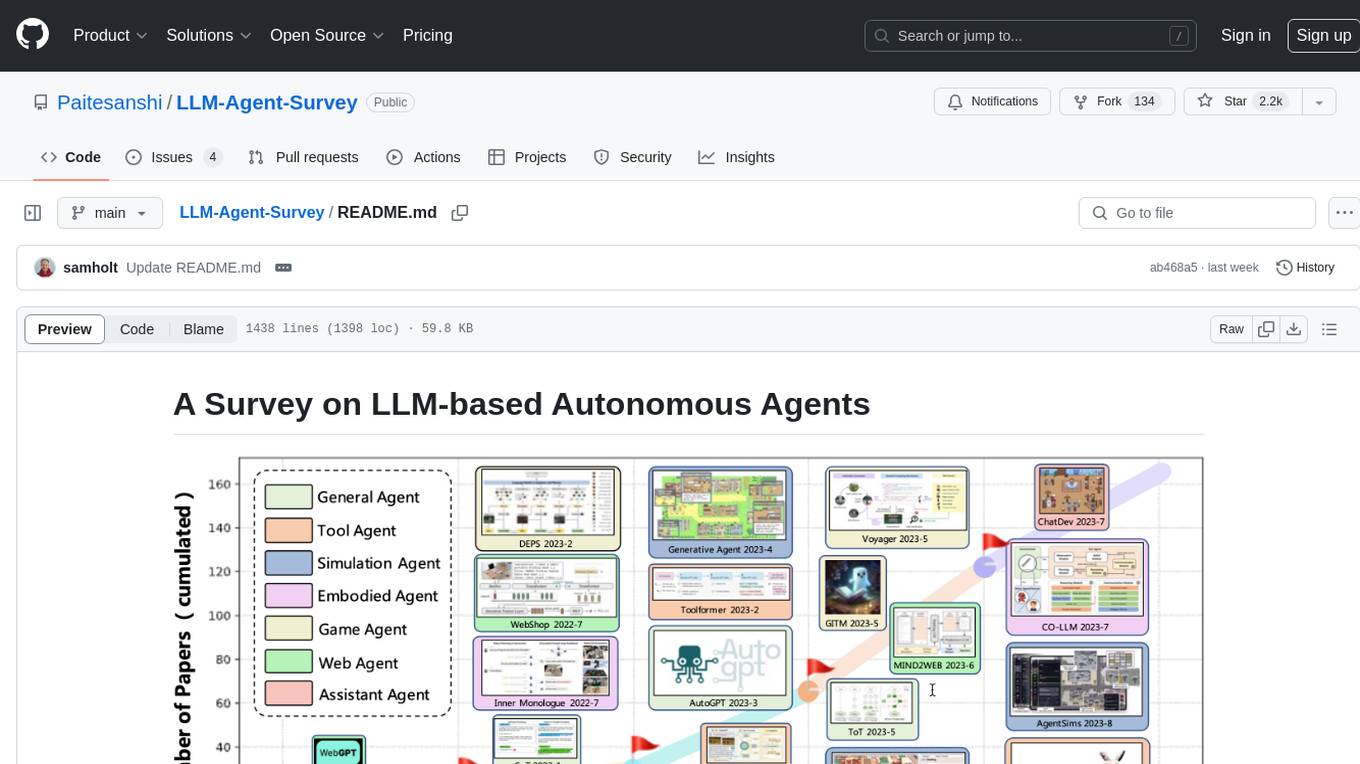
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.

genkit
Firebase Genkit (beta) is a framework with powerful tooling to help app developers build, test, deploy, and monitor AI-powered features with confidence. Genkit is cloud optimized and code-centric, integrating with many services that have free tiers to get started. It provides unified API for generation, context-aware AI features, evaluation of AI workflow, extensibility with plugins, easy deployment to Firebase or Google Cloud, observability and monitoring with OpenTelemetry, and a developer UI for prototyping and testing AI features locally. Genkit works seamlessly with Firebase or Google Cloud projects through official plugins and templates.
vector-cookbook
The Vector Cookbook is a collection of recipes and sample application starter kits for building AI applications with LLMs using PostgreSQL and Timescale Vector. Timescale Vector enhances PostgreSQL for AI applications by enabling the storage of vector, relational, and time-series data with faster search, higher recall, and more efficient time-based filtering. The repository includes resources, sample applications like TSV Time Machine, and guides for creating, storing, and querying OpenAI embeddings with PostgreSQL and pgvector. Users can learn about Timescale Vector, explore performance benchmarks, and access Python client libraries and tutorials.
cogai
The W3C Cognitive AI Community Group focuses on advancing Cognitive AI through collaboration on defining use cases, open source implementations, and application areas. The group aims to demonstrate the potential of Cognitive AI in various domains such as customer services, healthcare, cybersecurity, online learning, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, and web search. They work on formal specifications for chunk data and rules, plausible knowledge notation, and neural networks for human-like AI. The group positions Cognitive AI as a combination of symbolic and statistical approaches inspired by human thought processes. They address research challenges including mimicry, emotional intelligence, natural language processing, and common sense reasoning. The long-term goal is to develop cognitive agents that are knowledgeable, creative, collaborative, empathic, and multilingual, capable of continual learning and self-awareness.
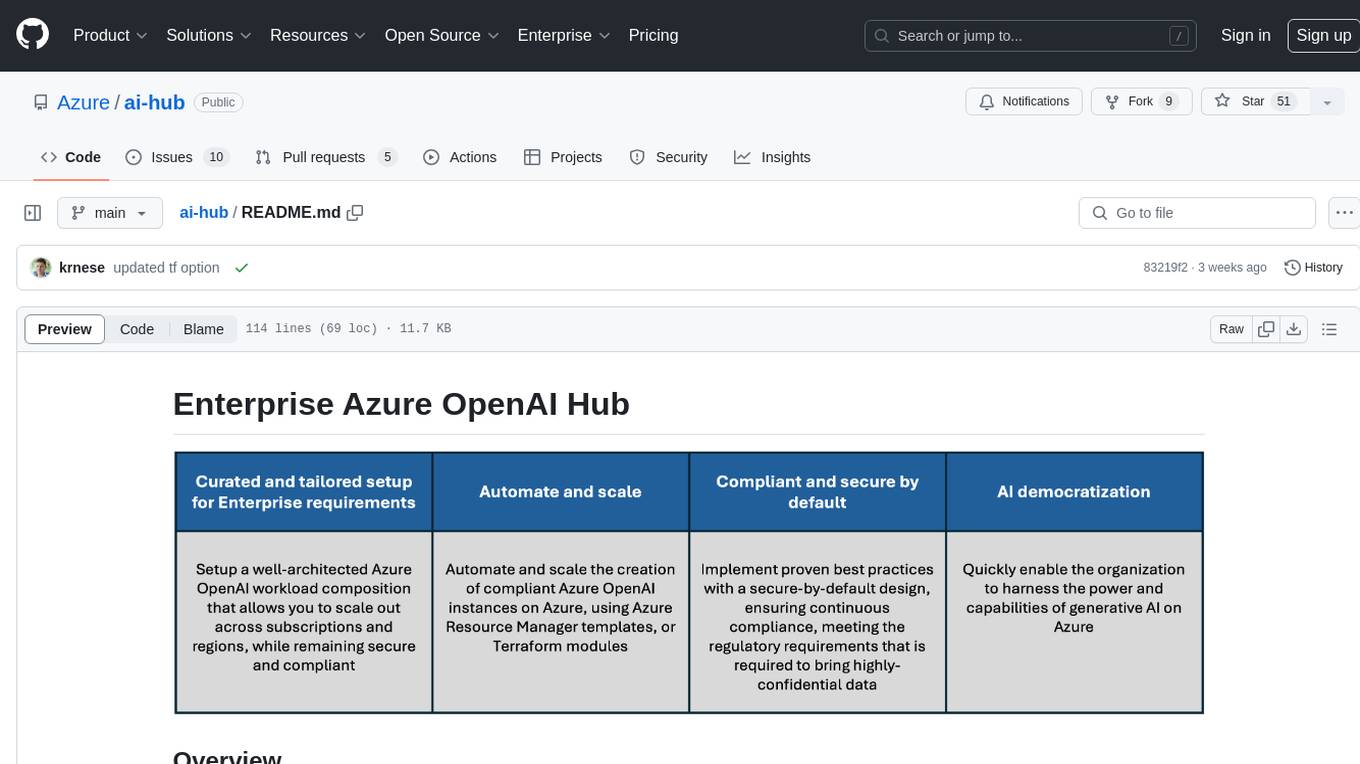
ai-hub
The Enterprise Azure OpenAI Hub is a comprehensive repository designed to guide users through the world of Generative AI on the Azure platform. It offers a structured learning experience to accelerate the transition from concept to production in an Enterprise context. The hub empowers users to explore various use cases with Azure services, ensuring security and compliance. It provides real-world examples and playbooks for practical insights into solving complex problems and developing cutting-edge AI solutions. The repository also serves as a library of proven patterns, aligning with industry standards and promoting best practices for secure and compliant AI development.
earth2studio
Earth2Studio is a Python-based package designed to enable users to quickly get started with AI weather and climate models. It provides access to pre-trained models, diagnostic tools, data sources, IO utilities, perturbation methods, and sample workflows for building custom weather prediction workflows. The package aims to empower users to explore AI-driven meteorology through modular components and seamless integration with other Nvidia packages like Modulus.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.







)
