
quantalogic
Quantalogic ReAct Agent - Coding Agent Framework - Gives a ⭐️ if you like the project
Stars: 256
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
README:
QuantaLogic is a ReAct (Reasoning & Action) framework for building advanced AI agents.
It seamlessly integrates large language models (LLMs) with a robust tool system, enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction.
The cli version include coding capabilities comparable to Aider.
We created QuantaLogic because we saw a significant gap between the advanced AI models developed by companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, DeepSeek and their practical implementation in everyday business processes.
Our mission is to bridge this gap, making the power of generative AI accessible and actionable for businesses of all sizes.
- ReAct Framework: Advanced implementation combining LLM reasoning with concrete actions
-
Universal LLM Support: Integration with OpenAI, Anthropic, LM Studio, Bedrock, Ollama, DeepSeek V3, DeepSeek R1, via LiteLLM. Example usage:
quantalogic --model-name deepseek/deepseek-reasonerorquantalogic --model-name openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-r1 - Secure Tool System: Docker-based code execution and file manipulation tools
- Real-time Monitoring: Web interface with SSE-based event visualization
- Memory Management: Intelligent context handling and optimization
- Enterprise Ready: Comprehensive logging, error handling, and validation system
Usage: quantalogic [OPTIONS] COMMAND i[ARGS]...
Environment Variables: Set OPENAI_API_KEY, ANTHROPIC_API_KEY, and DEEPSEEK_API_KEY for API integration.
Options:
-
--model-name TEXT: Specify the model (litellm format, e.g., "openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-chat") -
--log [info|debug|warning]: Set logging level -
--mode [code|basic|interpreter|full|code-basic|search|search-full]: Agent mode -
--vision-model-name TEXT: Specify vision model (litellm format) -
--max-tokens-working-memory INTEGER: Maximum tokens in working memory (default: 4000) -
--max-iterations INTEGER: Maximum task iterations (default: 30) -
--compact-every-n-iteration INTEGER: Compact memory every N iterations (default: 5) -
--no-stream: Disable streaming output (default: enabled) -
--help: Show help message
Commands:
-
task: Execute a task with the QuantaLogic AI Assistant-
--file PATH: Path to task file -
--model-name TEXT: Specify model -
--verbose: Enable verbose output -
--mode: Select agent capabilities -
--log: Set logging level -
--vision-model-name: Specify vision model -
--max-iterations: Maximum task iterations -
--max-tokens-working-memory: Memory limit -
--compact-every-n-iteration: Memory optimization -
--no-stream: Disable streaming
-
-
list-models: List available models with optional filtering.-
--search TEXT: Filter models by name or description. -
--help: Show help message.
Example:
quantalogic list-models --search qwen
Output:
Model Name Description ------------------- ------------------------------------------------------- dashscope/qwen-max Alibaba's Qwen-Max model optimized for maximum performance dashscope/qwen-plus Alibaba's Qwen-Plus model offering balanced performance -
See our Release Notes for detailed version history and changes.
| Model Name | API Key Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| openai/gpt-4o-mini | OPENAI_API_KEY | OpenAI's compact version of GPT-4, optimized for efficiency and cost-effectiveness while maintaining strong performance. |
| openai/gpt-4o | OPENAI_API_KEY | OpenAI's flagship model offering state-of-the-art performance across various tasks with enhanced reasoning capabilities. |
| anthropic/claude-3.5-sonnet | ANTHROPIC_API_KEY | Claude 3.5 Sonnet model from Anthropic, balancing performance and speed with strong reasoning capabilities. |
| deepseek/deepseek-chat | DEEPSEEK_API_KEY | DeepSeek's conversational model optimized for chat-based interactions and general-purpose tasks. |
| deepseek/deepseek-reasoner | DEEPSEEK_API_KEY | DeepSeek's specialized model for complex reasoning tasks and problem-solving. |
| openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-r1 | OPENROUTER_API_KEY | DeepSeek R1 model available through OpenRouter, optimized for research and development tasks. |
| openrouter/openai/gpt-4o | OPENROUTER_API_KEY | OpenAI's GPT-4o model accessible through OpenRouter platform. |
| openrouter/mistralai/mistral-large-2411 | OPENROUTER_API_KEY | Mistral's large model optimized for complex reasoning tasks, available through OpenRouter with enhanced multilingual capabilities. |
| mistral/mistral-large-2407 | MISTRAL_API_KEY | Mistral's high-performance model designed for enterprise-grade applications, offering advanced reasoning and multilingual support. |
| nvidia/deepseek-ai/deepseek-r1 | NVIDIA_API_KEY | NVIDIA's DeepSeek R1 model optimized for high-performance AI tasks and advanced reasoning capabilities. |
| gemini/gemini-2.0-flash | GEMINI_API_KEY | Google's Gemini Flash 2.0 model offering a balance of speed and performance for various tasks. |
| openrouter/google/gemini-2.0-flash-001 | OPENROUTER_API_KEY | Google's Gemini Flash 2.0 model offering a balance of speed and performance for various tasks through the OpenRouter platform. |
| ovh/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B | OVH_API_KEY | DeepSeek's R1 model optimized for research and development tasks hosted on OVH in France. |
| lm_studio/mistral-small-24b-instruct-2501 | LM_STUDIO_API_KEY | LM Studio's Mistral Small model optimized for local inference with advanced reasoning capabilities. |
| dashscope/qwen-max | DASHSCOPE_API_KEY | Alibaba's Qwen-Max model optimized for maximum performance and extensive reasoning capabilities. |
| dashscope/qwen-plus | DASHSCOPE_API_KEY | Alibaba's Qwen-Plus model offering balanced performance and cost-efficiency for a variety of tasks. |
| dashscope/qwen-turbo | DASHSCOPE_API_KEY | Alibaba's Qwen-Turbo model designed for fast and efficient responses, ideal for high-throughput scenarios. |
To configure the environment API key for Quantalogic using LiteLLM, set the required environment variable for your chosen provider and any optional variables like OPENAI_API_BASE or OPENROUTER_REFERRER. Use a .env file or a secrets manager to securely store these keys, and load them in your code using python-dotenv. For advanced configurations, refer to the LiteLLM documentation.
To use LM Studio with the Mistral model locally, set the following environment variables:
export LM_STUDIO_API_BASE="http://localhost:1234/v1"
export LM_STUDIO_API_KEY="your-api-key-here"Replace http://localhost:1234/v1 with your LM Studio server URL and your-api-key-here with your actual API key.
- Python 3.12+
- Docker (optional for code execution tools)
# Basic installation
pip install quantalogicgit clone https://github.com/quantalogic/quantalogic.git
cd quantalogic
python -m venv .venv
source ./venv/bin/activate
poetry installpipx install quantalogic
- code: Coding-focused agent with basic capabilities
- basic: General-purpose agent without coding tools
- interpreter: Interactive code execution agent
- full: Full-featured agent with all capabilities
- code-basic: Coding agent with basic reasoning
- search: Web search agent with Wikipedia, DuckDuckGo and SERPApi integration
Tasks can be provided:
- Directly via
taskparameter - Through a file using --file parameter
- Interactively via standard input
Using a task file:
quantalogic task --file tasks/example.md --verboseSelecting agent mode:
quantalogic --mode interpreter task "Explain quantum computing"Interactive mode:
quantalogicfrom quantalogic import Agent
# Initialize agent with default configuration
agent = Agent(model_name="deepseek/deepseek-chat")
# Execute a task
result = agent.solve_task(
"Create a Python function that calculates the Fibonacci sequence"
)
print(result)import os
from quantalogic import Agent
# Verify that DEEPSEEK_API_KEY is set
if not os.environ.get("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"):
raise ValueError("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY environment variable is not set")
# Initialize the AI agent with default configuration
agent = Agent(model_name="deepseek/deepseek-chat")
# Execute a sample task
result = agent.solve_task("Create a Python function that calculates the Fibonacci sequence")
print(result)Watch how QuantaLogic can generate complete tutorials from simple prompts:
Example prompt: 04-write-a-tutorial.md
Here are some practical examples to help you get started:
| Example | Description | File |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Agent | A basic example of an agent implementation. | examples/01-simple-agent.py |
| Agent with Event Monitoring | An example of an agent with event monitoring capabilities. | examples/02-agent-with-event-monitoring.py |
| Agent with Interpreter | An example of an agent that includes an interpreter. | examples/03-agent-with-interpreter.py |
| Agent Summary Task | An example of an agent performing a summary task. | examples/04-agent-summary-task.py |
| Code Example | A general code example. | examples/05-code.py |
| Code Screen Example | An example demonstrating code execution with screen output. | examples/06-code-screen.py |
| Write Tutorial | An example of generating a tutorial using the agent. | examples/07-write-tutorial.py |
| PRD Writer | An example of generating a Product Requirements Document (PRD). | examples/08-prd-writer.py |
| SQL Query | An example of executing SQL queries using the agent. | examples/09-sql-query.py |
| Finance Agent | An example of a finance-focused agent. | examples/10-finance-agent.py |
| Textual Agent Interface | An example of a textual user interface for the agent. | examples/11-textual-agent-interface.py |
The core agent implements the ReActparadigm, combining:
- Language model reasoning
- Tool execution capabilities
- Memory management
- Event handling
- Task validation
from quantalogic import Agent
from quantalogic.tools import PythonTool, ReadFileTool
# Create agent with specific tools
agent = Agent(
model_name="openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-chat",
tools=[
PythonTool(),
ReadFileTool()
]
)The ReAct (Reasoning & Action) framework represents a significant advancement in the development of intelligent agents capable of autonomously reasoning through tasks and taking appropriate actions.
QuantaLogic implements this framework, allowing integration with large language models (LLMs) to construct sophisticated agents that can tackle complex problems through natural language interaction.
A ReAct agent utilizes the synergy of reasoning and action. It not only processes natural language inputs but also executes actions in response to these inputs, utilizing various available tools. This functionality is particularly beneficial for environments where complex tasks can be decomposed into manageable subtasks.
QuantaLogic provides an effective implementation of the ReAct framework with several core components:
- Generative Model: This serves as the agent's brain, enabling it to interpret tasks and generate human-like text responses.
- Memory Management: This capability allows the agent to maintain context, keeping track of previous inputs and interactions to provide coherent responses.
- Tool Management: The agent has access to a diverse range of tools, enabling it to perform actions such as code execution, file manipulation, and API communication.
The following state diagram shows the core workflow of a QuantaLogic agent:
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> InitializeAgent
InitializeAgent --> Idle: Agent Initialized
state Idle {
[*] --> WaitForTask
WaitForTask --> SolveTask: Task Received
}
state SolveTask {
[*] --> ResetSession
ResetSession --> AddSystemPrompt
AddSystemPrompt --> PreparePrompt
PreparePrompt --> EmitTaskStartEvent
EmitTaskStartEvent --> UpdateTokens
UpdateTokens --> CompactMemoryIfNeeded
CompactMemoryIfNeeded --> GenerateResponse
GenerateResponse --> ObserveResponse
ObserveResponse --> CheckToolExecution
CheckToolExecution --> TaskComplete: Tool Executed (task_complete)
CheckToolExecution --> UpdatePrompt: Tool Not Executed
UpdatePrompt --> UpdateTokens
TaskComplete --> EmitTaskCompleteEvent
EmitTaskCompleteEvent --> [*]
}
state CompactMemoryIfNeeded {
[*] --> CheckMemoryOccupancy
CheckMemoryOccupancy --> CompactMemory: Memory Occupancy > MAX_OCCUPANCY
CheckMemoryOccupancy --> [*]: Memory Occupancy <= MAX_OCCUPANCY
CompactMemory --> [*]
}
state ObserveResponse {
[*] --> ProcessResponse
ProcessResponse --> ExecuteTool: Tool Identified
ProcessResponse --> UpdateAnswer: No Tool Identified
ExecuteTool --> UpdateAnswer
UpdateAnswer --> [*]
}
Idle --> [*]: Task Completed
SolveTask --> Idle: Task CompletedThe following sequence diagram illustrates the workflow of a ReAct agent as it processes and solves a task:
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Agent
participant ToolManager
participant Memory
User->>Agent: Submit task
Agent->>Memory: Store task details
Agent->>ToolManager: Retrieve tools
ToolManager-->>Agent: Provide available tools
Agent->>Agent: Prepare prompt for task
Agent->>Agent: Analyze input and generate response
Agent->>ToolManager: Execute required tool
ToolManager-->>Agent: Return tool execution result
Agent->>User: Present final result- User Input: The agent begins by receiving a task or question from the user, which initiates the interaction.
- Memory Management: Before tackling the task, the agent logs relevant task details into its memory, ensuring it has the necessary context for processing.
- Tool Retrieval: The agent communicates with the ToolManager to inquire about available tools that can facilitate the required actions.
- Prompt Generation: The agent constructs a prompt that outlines the task specifics, available tools, and any other pertinent context information.
- Analysis and Response Generation: The agent uses its generative model to analyze the task input and formulate a response.
- Tool Execution: If certain tools are needed for the task, the agent instructs the ToolManager to execute those tools, fetching the results for processing.
- Output to User: Finally, the agent compiles and presents the results back to the user.
The QuantaLogic framework incorporates a well-defined tool system that enhances the functionality of AI agents by enabling them to perform a variety of tasks efficiently. Each tool is designed to address specific needs that arise in the context of complex problem-solving and task execution:
-
Core Functionality: Tools such as AgentTool and LLMTool are fundamental to the agent's operation, allowing it to manage tasks and interact with large language models. The integration of these tools enables the agent to process natural language inputs and execute corresponding actions effectively. AgentTool enables the agent to delegate tasks to specialized agents, and LLMTool provides the agent to explore a specific area of a latent space using role play.
-
Code Execution: Tools like PythonTool, NodeJsTool, and ElixirTool are vital for executing code in different programming languages. This capability allows the agent to handle programming tasks directly, facilitating real-time coding assistance and code evaluation.
-
File Operations: The framework includes tools for file management, such as ReadFileTool, WriteFileTool, and ReplaceInFileTool. These tools are essential for enabling the agent to read from and write to files, as well as update file content dynamically. This functionality supports scenarios where agents need to manipulate data or configuration files as part of the task execution process.
-
Search Capabilities: Tools like RipgrepTool and SearchDefinitionNames enhance the agent's ability to search through codebases and identify relevant definitions. This is crucial when dealing with large volumes of code, allowing the agent to quickly locate information necessary for problem-solving.
-
Utility Functions: Additional tools such as DownloadHttpFileTool, ListDirectoryTool, and ExecuteBashCommandTool provide broader functionality that supports various tasks, from fetching external resources to executing system commands. These utilities expand the operational scope of agents, allowing them to perform diverse actions beyond simple text processing.
-
Documentation and Representation: Tools like MarkitdownTool facilitate the generation of documentation, ensuring that output from the agent can be formatted and presented clearly. This is particularly beneficial for creating reports or guides based on the agent's findings and actions.
By integrating these tools into its architecture, QuantaLogic allows agents to perform a wide range of tasks autonomously while ensuring that they have the necessary resources and capabilities to do so effectively. This tool system is fundamental to the agent's ability to reason and act in sophisticated ways, thereby enhancing the overall utility of the framework in complex scenarios.
For detailed documentation of all available tools, please see REFERENCE_TOOLS.md.
# Clone repository
git clone https://github.com/quantalogic/quantalogic.git
cd quantalogic
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
# Install dependencies
poetry install
# Run all tests
pytest
# With coverage
pytest --cov=quantalogic
# Run specific tests
pytest tests/unit# Format code
ruff format
# Type checking
mypy quantalogic
# Linting
ruff check quantalogic- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Write tests
- Implement changes
- Submit pull request
See CONTRIBUTING.md for detailed guidelines.
Copyright 2024 QuantaLogic Contributors
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See LICENSE for details.
Initiated with ❤️ by Raphaël MANSUY. Founder of Quantalogic.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for quantalogic
Similar Open Source Tools

quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
camel
CAMEL is an open-source library designed for the study of autonomous and communicative agents. We believe that studying these agents on a large scale offers valuable insights into their behaviors, capabilities, and potential risks. To facilitate research in this field, we implement and support various types of agents, tasks, prompts, models, and simulated environments.
evalchemy
Evalchemy is a unified and easy-to-use toolkit for evaluating language models, focusing on post-trained models. It integrates multiple existing benchmarks such as RepoBench, AlpacaEval, and ZeroEval. Key features include unified installation, parallel evaluation, simplified usage, and results management. Users can run various benchmarks with a consistent command-line interface and track results locally or integrate with a database for systematic tracking and leaderboard submission.
FuzzyAI
The FuzzyAI Fuzzer is a powerful tool for automated LLM fuzzing, designed to help developers and security researchers identify jailbreaks and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities in their LLM APIs. It supports various fuzzing techniques, provides input generation capabilities, can be easily integrated into existing workflows, and offers an extensible architecture for customization and extension. The tool includes attacks like ArtPrompt, Taxonomy-based paraphrasing, Many-shot jailbreaking, Genetic algorithm, Hallucinations, DAN (Do Anything Now), WordGame, Crescendo, ActorAttack, Back To The Past, Please, Thought Experiment, and Default. It supports models from providers like Anthropic, OpenAI, Gemini, Azure, Bedrock, AI21, and Ollama, with the ability to add support for newer models. The tool also supports various cloud APIs and datasets for testing and experimentation.
superduperdb
SuperDuperDB is a Python framework for integrating AI models, APIs, and vector search engines directly with your existing databases, including hosting of your own models, streaming inference and scalable model training/fine-tuning. Build, deploy and manage any AI application without the need for complex pipelines, infrastructure as well as specialized vector databases, and moving our data there, by integrating AI at your data's source: - Generative AI, LLMs, RAG, vector search - Standard machine learning use-cases (classification, segmentation, regression, forecasting recommendation etc.) - Custom AI use-cases involving specialized models - Even the most complex applications/workflows in which different models work together SuperDuperDB is **not** a database. Think `db = superduper(db)`: SuperDuperDB transforms your databases into an intelligent platform that allows you to leverage the full AI and Python ecosystem. A single development and deployment environment for all your AI applications in one place, fully scalable and easy to manage.
SoM-LLaVA
SoM-LLaVA is a new data source and learning paradigm for Multimodal LLMs, empowering open-source Multimodal LLMs with Set-of-Mark prompting and improved visual reasoning ability. The repository provides a new dataset that is complementary to existing training sources, enhancing multimodal LLMs with Set-of-Mark prompting and improved general capacity. By adding 30k SoM data to the visual instruction tuning stage of LLaVA, the tool achieves 1% to 6% relative improvements on all benchmarks. Users can train SoM-LLaVA via command line and utilize the implementation to annotate COCO images with SoM. Additionally, the tool can be loaded in Huggingface for further usage.

ps-fuzz
The Prompt Fuzzer is an open-source tool that helps you assess the security of your GenAI application's system prompt against various dynamic LLM-based attacks. It provides a security evaluation based on the outcome of these attack simulations, enabling you to strengthen your system prompt as needed. The Prompt Fuzzer dynamically tailors its tests to your application's unique configuration and domain. The Fuzzer also includes a Playground chat interface, giving you the chance to iteratively improve your system prompt, hardening it against a wide spectrum of generative AI attacks.
vision-parse
Vision Parse is a tool that leverages Vision Language Models to parse PDF documents into beautifully formatted markdown content. It offers smart content extraction, content formatting, multi-LLM support, PDF document support, and local model hosting using Ollama. Users can easily convert PDFs to markdown with high precision and preserve document hierarchy and styling. The tool supports multiple Vision LLM providers like OpenAI, LLama, and Gemini for accuracy and speed, making document processing efficient and effortless.
fastRAG
fastRAG is a research framework designed to build and explore efficient retrieval-augmented generative models. It incorporates state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) and Information Retrieval to empower researchers and developers with a comprehensive tool-set for advancing retrieval augmented generation. The framework is optimized for Intel hardware, customizable, and includes key features such as optimized RAG pipelines, efficient components, and RAG-efficient components like ColBERT and Fusion-in-Decoder (FiD). fastRAG supports various unique components and backends for running LLMs, making it a versatile tool for research and development in the field of retrieval-augmented generation.
spandrel
Spandrel is a library for loading and running pre-trained PyTorch models. It automatically detects the model architecture and hyperparameters from model files, and provides a unified interface for running models.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.
thinc
Thinc is a lightweight deep learning library that offers an elegant, type-checked, functional-programming API for composing models, with support for layers defined in other frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow and MXNet. You can use Thinc as an interface layer, a standalone toolkit or a flexible way to develop new models.
HuatuoGPT-o1
HuatuoGPT-o1 is a medical language model designed for advanced medical reasoning. It can identify mistakes, explore alternative strategies, and refine answers. The model leverages verifiable medical problems and a specialized medical verifier to guide complex reasoning trajectories and enhance reasoning through reinforcement learning. The repository provides access to models, data, and code for HuatuoGPT-o1, allowing users to deploy the model for medical reasoning tasks.
DaoCloud-docs
DaoCloud Enterprise 5.0 Documentation provides detailed information on using DaoCloud, a Certified Kubernetes Service Provider. The documentation covers current and legacy versions, workflow control using GitOps, and instructions for opening a PR and previewing changes locally. It also includes naming conventions, writing tips, references, and acknowledgments to contributors. Users can find guidelines on writing, contributing, and translating pages, along with using tools like MkDocs, Docker, and Poetry for managing the documentation.
onefilellm
OneFileLLM is a command-line tool that streamlines the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models (LLMs). It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources, compiling them into a single text file for quick use. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, token count reporting, and XML encapsulation of output for improved LLM performance. Users can easily access private GitHub repositories by generating a personal access token. The tool's output is encapsulated in XML tags to enhance LLM understanding and processing.
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
For similar tasks

quantalogic
QuantaLogic is a ReAct framework for building advanced AI agents that seamlessly integrates large language models with a robust tool system. It aims to bridge the gap between advanced AI models and practical implementation in business processes by enabling agents to understand, reason about, and execute complex tasks through natural language interaction. The framework includes features such as ReAct Framework, Universal LLM Support, Secure Tool System, Real-time Monitoring, Memory Management, and Enterprise Ready components.
clickclickclick
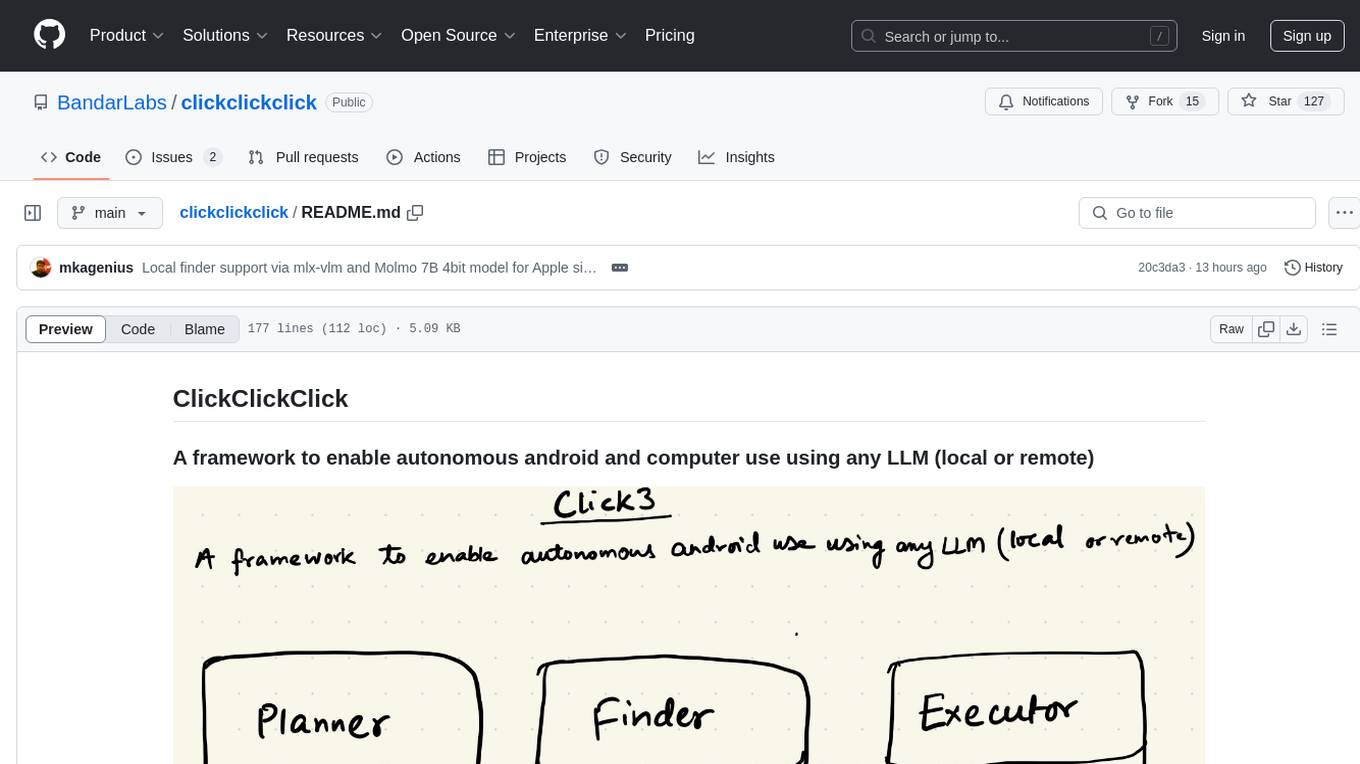
ClickClickClick is a framework designed to enable autonomous Android and computer use using various LLM models, both locally and remotely. It supports tasks such as drafting emails, opening browsers, and starting games, with current support for local models via Ollama, Gemini, and GPT 4o. The tool is highly experimental and evolving, with the best results achieved using specific model combinations. Users need prerequisites like `adb` installation and USB debugging enabled on Android phones. The tool can be installed via cloning the repository, setting up a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. It can be used as a CLI tool or script, allowing users to configure planner and finder models for different tasks. Additionally, it can be used as an API to execute tasks based on provided prompts, platform, and models.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.



