
zenu
A Deep Learning Framework Written in Rust
Stars: 56
ZeNu is a high-performance deep learning framework implemented in pure Rust, featuring a pure Rust implementation for safety and performance, GPU performance comparable to PyTorch with CUDA support, a simple and intuitive API, and a modular design for easy extension. It supports various layers like Linear, Convolution 2D, LSTM, and optimizers such as SGD and Adam. ZeNu also provides device support for CPU and CUDA (NVIDIA GPU) with CUDA 12.3 and cuDNN 9. The project structure includes main library, automatic differentiation engine, neural network layers, matrix operations, optimization algorithms, CUDA implementation, and other support crates. Users can find detailed implementations like MNIST classification, CIFAR10 classification, and ResNet implementation in the examples directory. Contributions to ZeNu are welcome under the MIT License.
README:
ZeNu is a high-performance deep learning framework implemented in pure Rust. It features an intuitive API and high extensibility.
- 🦀 Pure Rust implementation: Maximizes safety and performance
- ⚡ GPU performance: Comparable to PyTorch (supports CUDA 12.3 + cuDNN 9)
- 🔧 Simple and intuitive API
- 📦 Modular design: Easy to extend
Add the following to your Cargo.toml:
[dependencies]
zenu = "0.1"
# To enable CUDA support:
[dependencies.zenu]
version = "0.1"
features = ["nvidia"]- Linear
- Convolution 2D
- Batch Normalization 2D
- LSTM
- RNN
- GRU
- MaxPool 2D
- Dropout
- SGD
- Adam
- AdamW
- CPU
- CUDA (NVIDIA GPU)
- CUDA 12.3
- cuDNN 9
zenu/
├── zenu # Main library
├── zenu-autograd # Automatic differentiation engine
├── zenu-layer # Neural network layers
├── zenu-matrix # Matrix operations
├── zenu-optimizer # Optimization algorithms
├── zenu-cuda # CUDA implementation
└── Other support crates
Check the examples/ directory for detailed implementations:
- MNIST classification
- CIFAR10 classification
- ResNet implementation
Here is a simple example of defining and training a model using ZeNu:
use zenu::{
dataset::{train_val_split, DataLoader, Dataset},
mnist::minist_dataset,
update_parameters, Model,
};
use zenu_autograd::{
creator::from_vec::from_vec,
functions::{activation::sigmoid::sigmoid, loss::cross_entropy::cross_entropy},
Variable,
};
use zenu_layer::{layers::linear::Linear, Layer};
use zenu_optimizer::sgd::SGD;
struct SingleLayerModel {
linear: Linear<f32>,
}
impl SingleLayerModel {
fn new() -> Self {
let mut linear = Linear::new(784, 10);
linear.init_parameters(None);
Self { linear }
}
}
impl Model<f32> for SingleLayerModel {
fn predict(&self, inputs: &[Variable<f32>]) -> Variable<f32> {
let x = &inputs[0];
let x = self.linear.call(x.clone());
sigmoid(x)
}
}
fn main() {
let (train, test) = minist_dataset().unwrap();
let (train, val) = train_val_split(&train, 0.8, true);
let test_dataloader = DataLoader::new(MnistDataset { data: test }, 1);
let sgd = SGD::new(0.01);
let model = SingleLayerModel::new();
for epoch in 0..10 {
let mut train_dataloader = DataLoader::new(
MnistDataset {
data: train.clone(),
},
16,
);
let val_dataloader = DataLoader::new(MnistDataset { data: val.clone() }, 16);
train_dataloader.shuffle();
let mut epoch_loss_train: f32 = 0.;
let mut num_iter_train = 0;
for batch in train_dataloader {
let input = batch[0].clone();
let target = batch[1].clone();
let y_pred = model.predict(&[input]);
let loss = cross_entropy(y_pred, target);
update_parameters(loss.clone(), &sgd);
epoch_loss_train += loss.get_data().index_item([]);
num_iter_train += 1;
}
let mut epoch_loss_val = 0.;
let mut num_iter_val = 0;
for batch in val_dataloader {
let input = batch[0].clone();
let target = batch[1].clone();
let y_pred = model.predict(&[input]);
let loss = cross_entropy(y_pred, target);
epoch_loss_val += loss.get_data().index_item([]);
num_iter_val += 1;
}
println!(
"Epoch: {}, Train Loss: {}, Val Loss: {}",
epoch,
epoch_loss_train / num_iter_train as f32,
epoch_loss_val / num_iter_val as f32
);
}
let mut test_loss = 0.;
let mut num_iter_test = 0;
let mut correct = 0;
let mut total = 0;
for batch in test_dataloader {
let input = batch[0].clone();
let target = batch[1].clone();
let y_pred = model.predict(&[input]);
let loss = cross_entropy(y_pred.clone(), target.clone());
test_loss += loss.get_data().index_item([]);
num_iter_test += 1;
let y_pred = y_pred.get_data();
let max_idx = y_pred.to_view().max_idx()[0];
let target = target.get_data();
let target = target.to_view().max_idx()[0];
if max_idx == target {
correct += 1;
}
total += 1;
}
println!("Accuracy: {}", correct as f32 / total as f32);
println!("Test Loss: {}", test_loss / num_iter_test as f32);
}Contributions to ZeNu are welcome! If you find any issues or have suggestions for improvements, please open an issue or submit a pull request on the GitHub repository.
ZeNu is licensed under the MIT License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for zenu
Similar Open Source Tools

zenu
ZeNu is a high-performance deep learning framework implemented in pure Rust, featuring a pure Rust implementation for safety and performance, GPU performance comparable to PyTorch with CUDA support, a simple and intuitive API, and a modular design for easy extension. It supports various layers like Linear, Convolution 2D, LSTM, and optimizers such as SGD and Adam. ZeNu also provides device support for CPU and CUDA (NVIDIA GPU) with CUDA 12.3 and cuDNN 9. The project structure includes main library, automatic differentiation engine, neural network layers, matrix operations, optimization algorithms, CUDA implementation, and other support crates. Users can find detailed implementations like MNIST classification, CIFAR10 classification, and ResNet implementation in the examples directory. Contributions to ZeNu are welcome under the MIT License.
zig-aio
zig-aio is a library that provides an io_uring-like asynchronous API and coroutine-powered IO tasks for the Zig programming language. It offers support for different operating systems and backends, such as io_uring, iocp, and posix. The library aims to provide efficient IO operations by leveraging coroutines and async IO mechanisms. Users can create servers and clients with ease using the provided API functions for socket operations, sending and receiving data, and managing connections.

Janus
Janus is a series of unified multimodal understanding and generation models, including Janus-Pro, Janus, and JanusFlow. Janus-Pro is an advanced version that improves both multimodal understanding and visual generation significantly. Janus decouples visual encoding for unified multimodal understanding and generation, surpassing previous models. JanusFlow harmonizes autoregression and rectified flow for unified multimodal understanding and generation, achieving comparable or superior performance to specialized models. The models are available for download and usage, supporting a broad range of research in academic and commercial communities.
prajna
Prajna is an open-source programming language specifically developed for building more modular, automated, and intelligent artificial intelligence infrastructure. It aims to cater to various stages of AI research, training, and deployment by providing easy access to CPU, GPU, and various TPUs for AI computing. Prajna features just-in-time compilation, GPU/heterogeneous programming support, tensor computing, syntax improvements, and user-friendly interactions through main functions, Repl, and Jupyter, making it suitable for algorithm development and deployment in various scenarios.
island-ai
island-ai is a TypeScript toolkit tailored for developers engaging with structured outputs from Large Language Models. It offers streamlined processes for handling, parsing, streaming, and leveraging AI-generated data across various applications. The toolkit includes packages like zod-stream for interfacing with LLM streams, stream-hooks for integrating streaming JSON data into React applications, and schema-stream for JSON streaming parsing based on Zod schemas. Additionally, related packages like @instructor-ai/instructor-js focus on data validation and retry mechanisms, enhancing the reliability of data processing workflows.
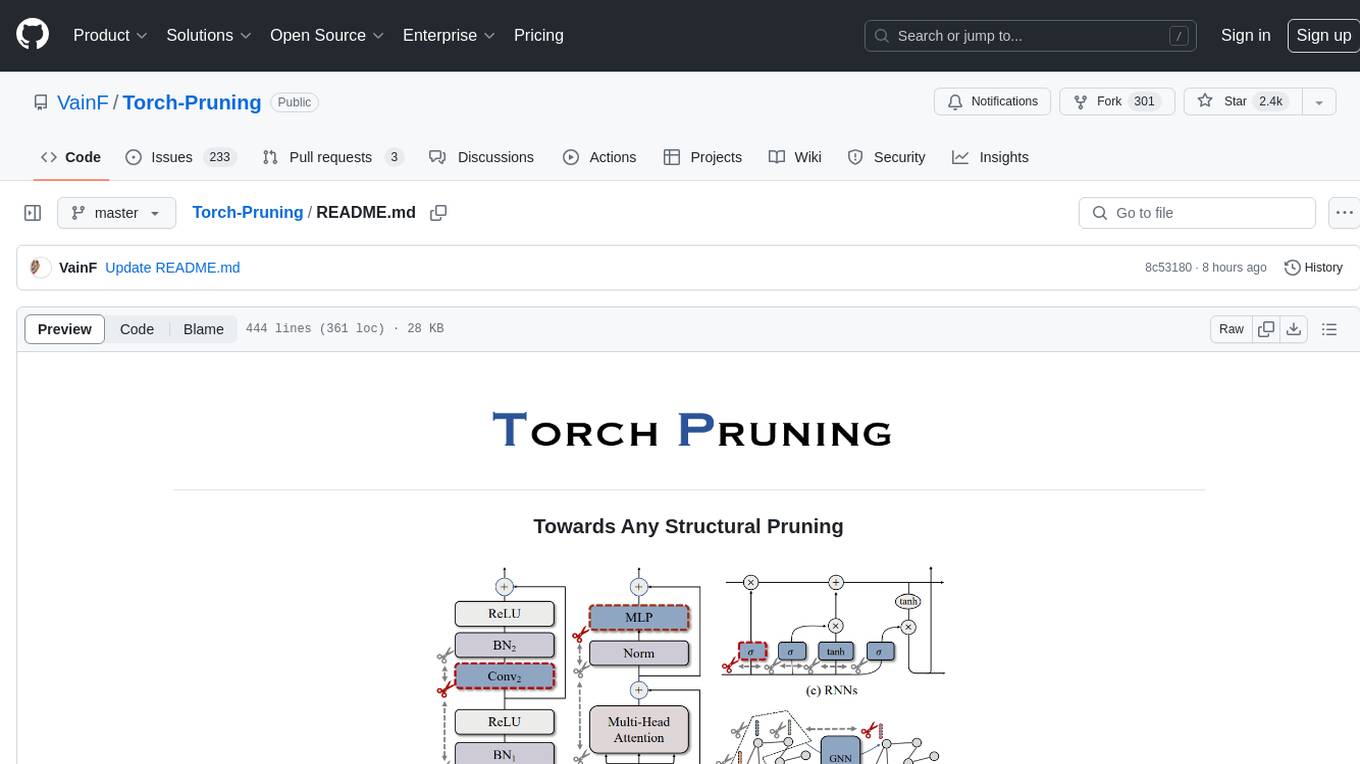
Torch-Pruning
Torch-Pruning (TP) is a library for structural pruning that enables pruning for a wide range of deep neural networks. It uses an algorithm called DepGraph to physically remove parameters. The library supports pruning off-the-shelf models from various frameworks and provides benchmarks for reproducing results. It offers high-level pruners, dependency graph for automatic pruning, low-level pruning functions, and supports various importance criteria and modules. Torch-Pruning is compatible with both PyTorch 1.x and 2.x versions.
agents-flex
Agents-Flex is a LLM Application Framework like LangChain base on Java. It provides a set of tools and components for building LLM applications, including LLM Visit, Prompt and Prompt Template Loader, Function Calling Definer, Invoker and Running, Memory, Embedding, Vector Storage, Resource Loaders, Document, Splitter, Loader, Parser, LLMs Chain, and Agents Chain.
aiscript
AiScript is a lightweight scripting language that runs on JavaScript. It supports arrays, objects, and functions as first-class citizens, and is easy to write without the need for semicolons or commas. AiScript runs in a secure sandbox environment, preventing infinite loops from freezing the host. It also allows for easy provision of variables and functions from the host.

qianfan-starter
WenXin-Starter is a spring-boot-starter for Baidu's 'WenXin Workshop' large model, facilitating quick integration of Baidu's AI capabilities. It provides complete integration with WenXin Workshop's official API documentation, supports WenShengTu, built-in conversation memory, and supports conversation streaming. It also supports QPS control for individual models and queuing mechanism, with upcoming plugin support.
netsaur
Netsaur is a powerful machine learning library for Deno, offering a lightweight and easy-to-use neural network solution. It is blazingly fast and efficient, providing a simple API for creating and training neural networks. Netsaur can run on both CPU and GPU, making it suitable for serverless environments. With Netsaur, users can quickly build and deploy machine learning models for various applications with minimal dependencies. This library is perfect for both beginners and experienced machine learning practitioners.
orch
orch is a library for building language model powered applications and agents for the Rust programming language. It can be used for tasks such as text generation, streaming text generation, structured data generation, and embedding generation. The library provides functionalities for executing various language model tasks and can be integrated into different applications and contexts. It offers flexibility for developers to create language model-powered features and applications in Rust.
wenxin-starter
WenXin-Starter is a spring-boot-starter for Baidu's "Wenxin Qianfan WENXINWORKSHOP" large model, which can help you quickly access Baidu's AI capabilities. It fully integrates the official API documentation of Wenxin Qianfan. Supports text-to-image generation, built-in dialogue memory, and supports streaming return of dialogue. Supports QPS control of a single model and supports queuing mechanism. Plugins will be added soon.
langchain-rust
LangChain Rust is a library for building applications with Large Language Models (LLMs) through composability. It provides a set of tools and components that can be used to create conversational agents, document loaders, and other applications that leverage LLMs. LangChain Rust supports a variety of LLMs, including OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Ollama, and Anthropic Claude. It also supports a variety of embeddings, vector stores, and document loaders. LangChain Rust is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a great choice for developers who want to build applications with LLMs.
matmulfreellm
MatMul-Free LM is a language model architecture that eliminates the need for Matrix Multiplication (MatMul) operations. This repository provides an implementation of MatMul-Free LM that is compatible with the 🤗 Transformers library. It evaluates how the scaling law fits to different parameter models and compares the efficiency of the architecture in leveraging additional compute to improve performance. The repo includes pre-trained models, model implementations compatible with 🤗 Transformers library, and generation examples for text using the 🤗 text generation APIs.
For similar tasks

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.
InternVL
InternVL scales up the ViT to _**6B parameters**_ and aligns it with LLM. It is a vision-language foundation model that can perform various tasks, including: **Visual Perception** - Linear-Probe Image Classification - Semantic Segmentation - Zero-Shot Image Classification - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image Classification - Zero-Shot Video Classification **Cross-Modal Retrieval** - English Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Chinese Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval - Multilingual Zero-Shot Image-Text Retrieval on XTD **Multimodal Dialogue** - Zero-Shot Image Captioning - Multimodal Benchmarks with Frozen LLM - Multimodal Benchmarks with Trainable LLM - Tiny LVLM InternVL has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on a variety of benchmarks. For example, on the MMMU image classification benchmark, InternVL achieves a top-1 accuracy of 51.6%, which is higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. On the DocVQA question answering benchmark, InternVL achieves a score of 82.2%, which is also higher than GPT-4V and Gemini Pro. InternVL is open-sourced and available on Hugging Face. It can be used for a variety of applications, including image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, image captioning, and question answering.

clarifai-python
The Clarifai Python SDK offers a comprehensive set of tools to integrate Clarifai's AI platform to leverage computer vision capabilities like classification , detection ,segementation and natural language capabilities like classification , summarisation , generation , Q&A ,etc into your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can leverage cutting-edge artificial intelligence to unlock valuable insights from visual and textual content.
X-AnyLabeling
X-AnyLabeling is a robust annotation tool that seamlessly incorporates an AI inference engine alongside an array of sophisticated features. Tailored for practical applications, it is committed to delivering comprehensive, industrial-grade solutions for image data engineers. This tool excels in swiftly and automatically executing annotations across diverse and intricate tasks.
ailia-models
The collection of pre-trained, state-of-the-art AI models. ailia SDK is a self-contained, cross-platform, high-speed inference SDK for AI. The ailia SDK provides a consistent C++ API across Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, Jetson, and Raspberry Pi platforms. It also supports Unity (C#), Python, Rust, Flutter(Dart) and JNI for efficient AI implementation. The ailia SDK makes extensive use of the GPU through Vulkan and Metal to enable accelerated computing. # Supported models 323 models as of April 8th, 2024

edenai-apis
Eden AI aims to simplify the use and deployment of AI technologies by providing a unique API that connects to all the best AI engines. With the rise of **AI as a Service** , a lot of companies provide off-the-shelf trained models that you can access directly through an API. These companies are either the tech giants (Google, Microsoft , Amazon) or other smaller, more specialized companies, and there are hundreds of them. Some of the most known are : DeepL (translation), OpenAI (text and image analysis), AssemblyAI (speech analysis). There are **hundreds of companies** doing that. We're regrouping the best ones **in one place** !
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.
open-ai
Open AI is a powerful tool for artificial intelligence research and development. It provides a wide range of machine learning models and algorithms, making it easier for developers to create innovative AI applications. With Open AI, users can explore cutting-edge technologies such as natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation to support users in building and deploying AI solutions. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, Open AI offers the tools and resources you need to accelerate your AI projects and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence.
For similar jobs
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
joliGEN
JoliGEN is an integrated framework for training custom generative AI image-to-image models. It implements GAN, Diffusion, and Consistency models for various image translation tasks, including domain and style adaptation with conservation of semantics. The tool is designed for real-world applications such as Controlled Image Generation, Augmented Reality, Dataset Smart Augmentation, and Synthetic to Real transforms. JoliGEN allows for fast and stable training with a REST API server for simplified deployment. It offers a wide range of options and parameters with detailed documentation available for models, dataset formats, and data augmentation.
ai-edge-torch
AI Edge Torch is a Python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format for on-device applications on Android, iOS, and IoT devices. It offers broad CPU coverage with initial GPU and NPU support, closely integrating with PyTorch and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators. The library includes a PyTorch converter for model conversion and a Generative API for authoring mobile-optimized PyTorch Transformer models, enabling easy deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on mobile devices.
awesome-RK3588
RK3588 is a flagship 8K SoC chip by Rockchip, integrating Cortex-A76 and Cortex-A55 cores with NEON coprocessor for 8K video codec. This repository curates resources for developing with RK3588, including official resources, RKNN models, projects, development boards, documentation, tools, and sample code.

cl-waffe2
cl-waffe2 is an experimental deep learning framework in Common Lisp, providing fast, systematic, and customizable matrix operations, reverse mode tape-based Automatic Differentiation, and neural network model building and training features accelerated by a JIT Compiler. It offers abstraction layers, extensibility, inlining, graph-level optimization, visualization, debugging, systematic nodes, and symbolic differentiation. Users can easily write extensions and optimize their networks without overheads. The framework is designed to eliminate barriers between users and developers, allowing for easy customization and extension.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
depthai
This repository contains a demo application for DepthAI, a tool that can load different networks, create pipelines, record video, and more. It provides documentation for installation and usage, including running programs through Docker. Users can explore DepthAI features via command line arguments or a clickable QT interface. Supported models include various AI models for tasks like face detection, human pose estimation, and object detection. The tool collects anonymous usage statistics by default, which can be disabled. Users can report issues to the development team for support and troubleshooting.

