
feeds.fun
News reader with tags, scoring, and AI
Stars: 260
Feeds Fun is a self-hosted news reader tool that automatically assigns tags to news entries. Users can create rules to score news based on tags, filter and sort news as needed, and track read news. The tool offers multi/single-user support, feeds management, and various features for personalized news consumption. Users can access the tool's backend as the ffun package on PyPI and the frontend as the feeds-fun package on NPM. Feeds Fun requires setting up OpenAI or Gemini API keys for full tag generation capabilities. The tool uses tag processors to detect tags for news entries, with options for simple and complex processors. Feeds Fun primarily relies on LLM tag processors from OpenAI and Google for tag generation.
README:
News reader with tags & AI. Self-hosted, if it is your way.
- Reader automatically assigns tags to news.
- You create rules to score news by tags.
- Filter and sort news how you want ⇒ read only what you need.
Site: feeds.fun with curated collections of feeds that are tagged for free.
Blog: blog.feeds.fun
Roadmap: long-term plans
- Multi-/single-user.
- Feeds management.
- Automatic tag assignment for every news entry.
- Rules to score news by tags.
- Filter news: exclude news by tags, show only news with tags.
- Sort news by score, date, etc.
- Track news you've read already.
- A lot of other features are comming.
I've subscribed to a lot of news feeds and want to read only the most interesting & important from them.
I did not find an open-source solution that suited my needs => decided to create my own.
The last stable version is always available at https://feeds.fun/
It is free and should be stable: no database resets, minimal downtime, etc.
Just do not forget to set up your OpenAI or Gemini API key to access the full power of tags generation.
Check instructions in the docs/examples/single-user directory.
Instructions for docker-based installation:
Also:
- Backend is accessible as ffun package on PyPI.
- Frontend is accessible as feeds-fun package on NPM.
- Use the same versions for front and back.
Alternatively, you can install from tags in this repo.
All configs can be redefined via environment variables or .env file in the working directory.
You can print actual backend config values with:
ffun print-configs
The output is not as pretty and ready for copying as it should be, but I'll improve it later.
All actual frontend configs can be found here.
Format of environment variables:
- For backend:
FFUN_<component>_<option>orFFUN_<component>_<option>__<suboption>. - For frontend:
VITE_FFUN_<component>_<option>orVITE_FFUN_<component>_<option>__<suboption>— must be set on build time!
For example:
FFUN_AUTH_MODE="supertokens"
FFUN_LIBRARIAN_OPENAI_GENERAL_PROCESSOR__ENABLED="True"
Feeds Fun uses different tag processors to detect tags for news entries. Some of them are simple, like set domain as tag, some of them are more complex, like use LLM to detect all possible tags.
Processors are configured via a separate configuration file.
You can find an example of configuration in the code.
To pass your own configuration, set FFUN_LIBRARIAN_TAG_PROCESSORS_CONFIG to the path to your configuration file.
To configure LLM processors, you may be interested in configuring models. You can find an example of it in the code. It mostly the slice of info from the official OpenAI/Google documentation.
To pass your own configuration, set FFUN_LLMS_FRAMEWORK_MODELS_CONFIG to the path to your configuration file.
Currently implemented processors:
-
domain— extracts domain and subdomains from URL and saves them as tags. -
native_tags— saves tags that are received with the feed entry. -
llm_general— asks ChatGPT/GeminiGPT to detect tags. Currently, it is the most powerful processor. Must-have if you want to use Feed Fun in full power. -
upper_case_title— detects news with uppercase titles and marks them withupper-case-titletag.
LLM tag processors are the primary source of tags for Feeds Fun.
Currently, we support two API providers: OpenAI (ChatGPT) and Google (Gemini). In the future, there will be more, including self-hosted.
By default, LLM processors will skip feeds from default collections and use user API keys to process their news.
You can set the API key for collections in the processor's config.
DANGER!!! You can set the "general API key" in the processor's config; in this case, the processor will use it to process ALL news. It may be convenient if you self-host the service and fully control who has access to it.
You can set custom URLs as entry points for OpenAi and Gemini API by setting nthe ext environment variables:
FFUN_OPENAI_API_ENTRY_POINT="<your url>"
FFUN_GOOGLE_GEMINI_API_ENTRY_POINT="<your url>"
That will allow you to use any compatible API provider.
Tag processors produce what we call "raw tags". They are relevant to the text, but may lack consistency. It is especially true for LLM-generated tags. It makes it difficult to use them in rules and filters.
Thus, we have a chain of tag normalizers that receive raw tags and produce normalized tags.
For example:
- We remove articles
the,a,anfrom the tags, and tags likebook-review,a-book-review,the-book-reviewwill become a single tagbook-review. - We also split tags by various parts like
-vs-, sogoogle-vs-microsoftwill become two tags:googleandmicrosoft.
Tags normalization is a complex topic, and it is in active development, so we really appreciate your feedback.
Normalizers are configured via a separate configuration file.
You can find an example of configuration in the code.
To pass your own configuration, set FFUN_TAGS_NORMALIZERS_CONFIG to the path to your configuration file.
Currently implemented processors:
-
part_blacklist— removes blacklisted parts from tags:a-book,the-book⇒book. -
part_replacer— replaces parts in tags:e-mail⇒email. -
splitter— splits tags by specified parts:google-vs-microsoft⇒google,microsoft.
pip install ffun
# run DB migrations
ffun migrate
# run API server
uvicorn ffun.application.application:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 --workers 1
# run workers
ffun workers --librarian --loader
The minimal configuration for the backend:
# DB connection parameters have default values,
# but it is better to redefine them
FFUN_POSTGRESQL__HOST=...
FFUN_POSTGRESQL__USER=...
FFUN_POSTGRESQL__PASSWORD=...
FFUN_POSTGRESQL__DATABASE=...
FFUN_ENVIRONMENT="prod"
# Required for API server.
FFUN_ENABLE_API="True"
# Set if you want multi-user setup.
FFUN_ENABLE_SUPERTOKENS="True"
FFUN_API_PORT="443"
FFUN_APP_DOMAIN=...
FFUN_APP_PORT="443"
FFUN_AUTH_MODE: "supertokens"
FFUN_AUTH_SUPERTOKENS__COOKIE_SECURE="True"
FFUN_AUTH_SUPERTOKENS__API_KEY=...
FFUN_AUTH_SUPERTOKENS__CONNECTION_URI=...
# Has default value for development environment.
# I strongly recommend to redefine it because of potential security issues.
FFUN_USER_SETTINGS_SECRET_KEY=...
If you want to periodically clean your database from old entries, add the call ffun cleaner clean to your cron tasks. It is recommended.
More details see in the architecture section.
If you find this approach too strange, just use tags frontend-<version>.
npm init -y
npm install feeds-fun
npm install --prefix ./node_modules/feeds-fun
# Set environment variables before next step!!!
# Build static content.
npm run build-only --prefix ./node_modules/feeds-fun
cp -r ./node_modules/feeds-fun/dist ./wherever-you-place-static-content
The minimal configuration for the frontend:
VITE_FFUN_AUTH_MODE="supertokens" # or "single_user"
VITE_FFUN_APP_DOMAIN=...
VITE_FFUN_APP_PORT=...
ASGI application, which you run with uvicorn (in the example) provides only HTTP API to access the data and change user-related properties.
All actual work is done by workers, which you run with ffun workers command.
Simply loads & parses feeds.
Can use HTTP proxies, see configuration options
Analyse feeds' entries and assign tags to them.
All logic is split between tag processors. Each processor implements a single approach to produce tags that can be enabled/disabled via configuration.
git clone [email protected]:Tiendil/feeds.fun.git
cd ./feeds.fun
Build some docker images
./bin/build-local-containers.sh
Start the API server and frontend:
docker compose up -d
The site will be accessible at http://localhost:5173/
Start workers:
./bin/backend-utils.sh poetry run ffun workers --librarian --loader
List all backend utils:
./bin/backend-utils.sh poetry run ffun --help
Apply migrations:
./bin/backend-utils.sh poetry run ffun migrate
Create new migration:
./bin/backend-utils.sh poetry run yoyo new --message "what you want to do" ./ffun/<component>/migrations/
Pay attention. There are different directories layouts in the repository and in the docker containers => paths for migrations should be with only a single ffun directory.
You should always keep versions of the backend and frontend in sync.
Open CHANGELOG and look at which versions require DB migrations. You should upgrade to the first of them, run migrations and only after that upgrade to the next version.
Algorithm:
- Stop services.
- Install the next version.
- Run
ffun migrate. - Start services. You can skip this step if you plan to upgrade to the next version immediately.
Also, pay attention to breaking changes and notes in the CHANGELOG.
To profile a cli command, run py-spy record -o profile.svg -- python ./ffun/cli/application.py <command name>
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for feeds.fun
Similar Open Source Tools

feeds.fun
Feeds Fun is a self-hosted news reader tool that automatically assigns tags to news entries. Users can create rules to score news based on tags, filter and sort news as needed, and track read news. The tool offers multi/single-user support, feeds management, and various features for personalized news consumption. Users can access the tool's backend as the ffun package on PyPI and the frontend as the feeds-fun package on NPM. Feeds Fun requires setting up OpenAI or Gemini API keys for full tag generation capabilities. The tool uses tag processors to detect tags for news entries, with options for simple and complex processors. Feeds Fun primarily relies on LLM tag processors from OpenAI and Google for tag generation.
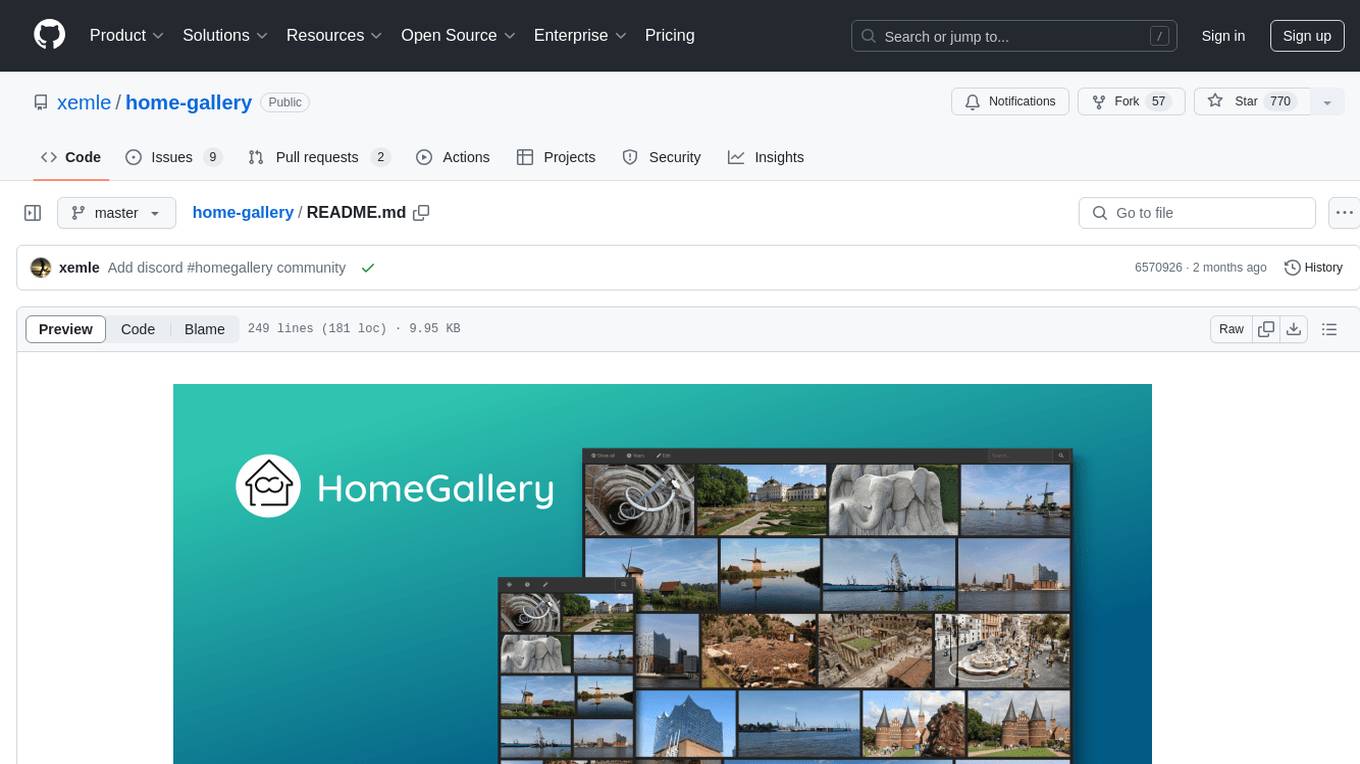
home-gallery
Home-Gallery.org is a self-hosted open-source web gallery for browsing personal photos and videos with tagging, mobile-friendly interface, and AI-powered image and face discovery. It aims to provide a fast user experience on mobile phones and help users browse and rediscover memories from their media archive. The tool allows users to serve their local data without relying on cloud services, view photos and videos from mobile phones, and manage images from multiple media source directories. Features include endless photo stream, video transcoding, reverse image lookup, face detection, GEO location reverse lookups, tagging, and more. The tool runs on NodeJS and supports various platforms like Linux, Mac, and Windows.
Pixelle-MCP
Pixelle-MCP is a multi-channel publishing tool designed to streamline the process of publishing content across various social media platforms. It allows users to create, schedule, and publish posts simultaneously on platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. With a user-friendly interface and advanced scheduling features, Pixelle-MCP helps users save time and effort in managing their social media presence. The tool also provides analytics and insights to track the performance of posts and optimize content strategy. Whether you are a social media manager, content creator, or digital marketer, Pixelle-MCP is a valuable tool to enhance your online presence and engage with your audience effectively.
mdream
Mdream is a lightweight and user-friendly markdown editor designed for developers and writers. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for creating and editing markdown files with real-time preview. The tool offers syntax highlighting, markdown formatting options, and the ability to export files in various formats. Mdream aims to streamline the writing process and enhance productivity for individuals working with markdown documents.
langfuse-docs
Langfuse Docs is a repository for langfuse.com, built on Nextra. It provides guidelines for contributing to the documentation using GitHub Codespaces and local development setup. The repository includes Python cookbooks in Jupyter notebooks format, which are converted to markdown for rendering on the site. It also covers media management for images, videos, and gifs. The stack includes Nextra, Next.js, shadcn/ui, and Tailwind CSS. Additionally, there is a bundle analysis feature to analyze the production build bundle size using @next/bundle-analyzer.
nvim-aider
Nvim-aider is a plugin for Neovim that provides additional functionality and key mappings to enhance the user's editing experience. It offers features such as code navigation, quick access to commonly used commands, and improved text manipulation tools. With Nvim-aider, users can streamline their workflow and increase productivity while working with Neovim.
OllamaSharp
OllamaSharp is a .NET binding for the Ollama API, providing an intuitive API client to interact with Ollama. It offers support for all Ollama API endpoints, real-time streaming, progress reporting, and an API console for remote management. Users can easily set up the client, list models, pull models with progress feedback, stream completions, and build interactive chats. The project includes a demo console for exploring and managing the Ollama host.
vivaria
Vivaria is a web application tool designed for running evaluations and conducting agent elicitation research. Users can interact with Vivaria using a web UI and a command-line interface. It allows users to start task environments based on METR Task Standard definitions, run AI agents, perform agent elicitation research, view API requests and responses, add tags and comments to runs, store results in a PostgreSQL database, sync data to Airtable, test prompts against LLMs, and authenticate using Auth0.

foundry-samples
The 'foundry-samples' repository serves as the main directory for official Azure AI Foundry documentation sample code and examples. It contains notebooks and code snippets for various developer tasks, offering both end-to-end examples and smaller snippets. The repository is open source, encouraging contributions and providing guidance on how to contribute.
trubrics-sdk
Trubrics-sdk is a software development kit designed to facilitate the integration of analytics features into applications. It provides a set of tools and functionalities that enable developers to easily incorporate analytics capabilities, such as data collection, analysis, and reporting, into their software products. The SDK streamlines the process of implementing analytics solutions, allowing developers to focus on building and enhancing their applications' functionality and user experience. By leveraging trubrics-sdk, developers can quickly and efficiently integrate robust analytics features, gaining valuable insights into user behavior and application performance.

PotPlayer_ChatGPT_Translate
PotPlayer_ChatGPT_Translate is a GitHub repository that provides a script to integrate ChatGPT with PotPlayer for real-time translation of chat messages during video playback. The script utilizes the power of ChatGPT's natural language processing capabilities to translate chat messages in various languages, enhancing the viewing experience for users who consume video content with subtitles or chat interactions. By seamlessly integrating ChatGPT with PotPlayer, this tool offers a convenient solution for users to enjoy multilingual content without the need for manual translation efforts. The repository includes detailed instructions on how to set up and use the script, making it accessible for both novice and experienced users interested in leveraging AI-powered translation services within the PotPlayer environment.
duckduckgo-ai-chat
This repository contains a chatbot tool powered by AI technology. The chatbot is designed to interact with users in a conversational manner, providing information and assistance on various topics. Users can engage with the chatbot to ask questions, seek recommendations, or simply have a casual conversation. The AI technology behind the chatbot enables it to understand natural language inputs and provide relevant responses, making the interaction more intuitive and engaging. The tool is versatile and can be customized for different use cases, such as customer support, information retrieval, or entertainment purposes. Overall, the chatbot offers a user-friendly and interactive experience, leveraging AI to enhance communication and engagement.
ollama4j
Ollama4j is a Java library that serves as a wrapper or binding for the Ollama server. It allows users to communicate with the Ollama server and manage models for various deployment scenarios. The library provides APIs for interacting with Ollama, generating fake data, testing UI interactions, translating messages, and building web UIs. Users can easily integrate Ollama4j into their Java projects to leverage the functionalities offered by the Ollama server.
lite.koboldai.net
KoboldAI Lite is a standalone Web UI that serves as a text editor designed for use with generative LLMs. It is compatible with KoboldAI United and KoboldAI Client, bundled with KoboldCPP, and integrates with the AI Horde for text and image generation. The UI offers multiple modes for different writing styles, supports various file formats, includes premade scenarios, and allows easy sharing of stories. Users can enjoy features such as memory, undo/redo, text-to-speech, and a range of samplers and configurations. The tool is mobile-friendly and can be used directly from a browser without any setup or installation.
Website-Crawler
Website-Crawler is a tool designed to extract data from websites in an automated manner. It allows users to scrape information such as text, images, links, and more from web pages. The tool provides functionalities to navigate through websites, handle different types of content, and store extracted data for further analysis. Website-Crawler is useful for tasks like web scraping, data collection, content aggregation, and competitive analysis. It can be customized to extract specific data elements based on user requirements, making it a versatile tool for various web data extraction needs.
promptl
Promptl is a versatile command-line tool designed to streamline the process of creating and managing prompts for user input in various programming projects. It offers a simple and efficient way to prompt users for information, validate their input, and handle different scenarios based on their responses. With Promptl, developers can easily integrate interactive prompts into their scripts, applications, and automation workflows, enhancing user experience and improving overall usability. The tool provides a range of customization options and features, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases across different programming languages and environments.
For similar tasks

feeds.fun
Feeds Fun is a self-hosted news reader tool that automatically assigns tags to news entries. Users can create rules to score news based on tags, filter and sort news as needed, and track read news. The tool offers multi/single-user support, feeds management, and various features for personalized news consumption. Users can access the tool's backend as the ffun package on PyPI and the frontend as the feeds-fun package on NPM. Feeds Fun requires setting up OpenAI or Gemini API keys for full tag generation capabilities. The tool uses tag processors to detect tags for news entries, with options for simple and complex processors. Feeds Fun primarily relies on LLM tag processors from OpenAI and Google for tag generation.
rss-can
RSS Can is a tool designed to simplify and improve RSS feed management. It supports various systems and architectures, including Linux and macOS. Users can download the binary from the GitHub release page or use the Docker image for easy deployment. The tool provides CLI parameters and environment variables for customization. It offers features such as memory and Redis cache services, web service configuration, and rule directory settings. The project aims to support RSS pipeline flow, NLP tasks, integration with open-source software rules, and tools like a quick RSS rules generator.
For similar jobs
book
Podwise is an AI knowledge management app designed specifically for podcast listeners. With the Podwise platform, you only need to follow your favorite podcasts, such as "Hardcore Hackers". When a program is released, Podwise will use AI to transcribe, extract, summarize, and analyze the podcast content, helping you to break down the hard-core podcast knowledge. At the same time, it is connected to platforms such as Notion, Obsidian, Logseq, and Readwise, embedded in your knowledge management workflow, and integrated with content from other channels including news, newsletters, and blogs, helping you to improve your second brain 🧠.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.
Scrapegraph-ai
ScrapeGraphAI is a Python library that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) and direct graph logic to create web scraping pipelines for websites, documents, and XML files. It allows users to extract specific information from web pages by providing a prompt describing the desired data. ScrapeGraphAI supports various LLMs, including Ollama, OpenAI, Gemini, and Docker, enabling users to choose the most suitable model for their needs. The library provides a user-friendly interface through its `SmartScraper` class, which simplifies the process of building and executing scraping pipelines. ScrapeGraphAI is open-source and available on GitHub, with extensive documentation and examples to guide users. It is particularly useful for researchers and data scientists who need to extract structured data from web pages for analysis and exploration.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.

auto-news
Auto-News is an automatic news aggregator tool that utilizes Large Language Models (LLM) to pull information from various sources such as Tweets, RSS feeds, YouTube videos, web articles, Reddit, and journal notes. The tool aims to help users efficiently read and filter content based on personal interests, providing a unified reading experience and organizing information effectively. It features feed aggregation with summarization, transcript generation for videos and articles, noise reduction, task organization, and deep dive topic exploration. The tool supports multiple LLM backends, offers weekly top-k aggregations, and can be deployed on Linux/MacOS using docker-compose or Kubernetes.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
Agently-Daily-News-Collector
Agently Daily News Collector is an open-source project showcasing a workflow powered by the Agent ly AI application development framework. It allows users to generate news collections on various topics by inputting the field topic. The AI agents automatically perform the necessary tasks to generate a high-quality news collection saved in a markdown file. Users can edit settings in the YAML file, install Python and required packages, input their topic idea, and wait for the news collection to be generated. The process involves tasks like outlining, searching, summarizing, and preparing column data. The project dependencies include Agently AI Development Framework, duckduckgo-search, BeautifulSoup4, and PyYAM.
