TechFlow
拖拽的方式使用 AI
Stars: 79
TechFlow is a platform that allows users to build their own AI workflows through drag-and-drop functionality. It features a visually appealing interface with clear layout and intuitive navigation. TechFlow supports multiple models beyond Language Models (LLM) and offers flexible integration capabilities. It provides a powerful SDK for developers to easily integrate generated workflows into existing systems, enhancing flexibility and scalability. The platform aims to embed AI capabilities as modules into existing functionalities to enhance business competitiveness.
README:
https://techflow.antdigital.dev
💡 通过拖拽来构建自己的 AI 工作流。
- 界面美观:采用了精心设计的用户界面,使用户能够轻松地使用系统的各项功能。界面布局清晰,图形元素和颜色搭配和谐,提供直观的导航和操作。
- 多模型支持:除了支持 LLM(Language Model)外,还具备集成和支持其他多种模型的能力。开发人员可以按照一套规范将其他任意模型服务接入系统,扩展系统的功能范围,满足用户的不同需求。
- 灵活的集成能力:提供了一套标准的接口和规范,使开发人员能够轻松地集成其他任意服务。这极大地增强了系统的灵活性和可扩展性,使其能够适应各种不同的应用场景和模型需求。
- 强大的 SDK 支持:提供了全面的软件开发工具包(SDK),使开发人员能够将生成的工作流轻松地集成到现有系统中。不论是命令行界面(CLI)还是服务端应用,SDK 都提供了丰富的接口和功能,简化了整合流程,加快了系统的部署和应用。
愿景: 将 AI 能力作为一个模块嵌入到现有的功能,为业务带来更强的竞争力。
功能强大,界面可靠,偏专业的算法开发同学,门槛很高。上限比较高,但是下限也很低。 AI Builder 概述 - AI Builder
功能强大支持各种节点,界面也比较美观,开发门槛中等,做的是自动化的工作流,不支持集成,定位是一个个人工具。 Questflow: Build AI agents for workflow automation with no-code
功能比较羸弱,只支持 LLM ,是个比较好的玩具,也是市面上最多的一种任务流模式。 FlowiseAI - Build LLMs Apps Easily
git clone [email protected]:AI-flow-task/drawing-board.git
pnpm i
pnpm run dev看到这样的界面就是启动成功了:
如果要完美运行,需要配置两个环境变量:
访问 openai 的服务需要想用的 token key,OPENAI_API_KEY 可以配置为自己的 key。
由于 openai 的封禁问题,国内使用一般会有问题,OPENAI_PROXY_URL 可以配置为一个代理地址,openai 的请求会被转发到 OPENAI_PROXY_URL。
export OPENAI_PROXY_URL=https://my.openai.comAI 环境在本地有可能搭建成本太高,API_END_PORT_URL 可以将本地的服务映射到相应的服务端。
export API_END_PORT_URL=https://techflow.antdigital.dev- 任务流编排
- 角色管理
- 任务流运行
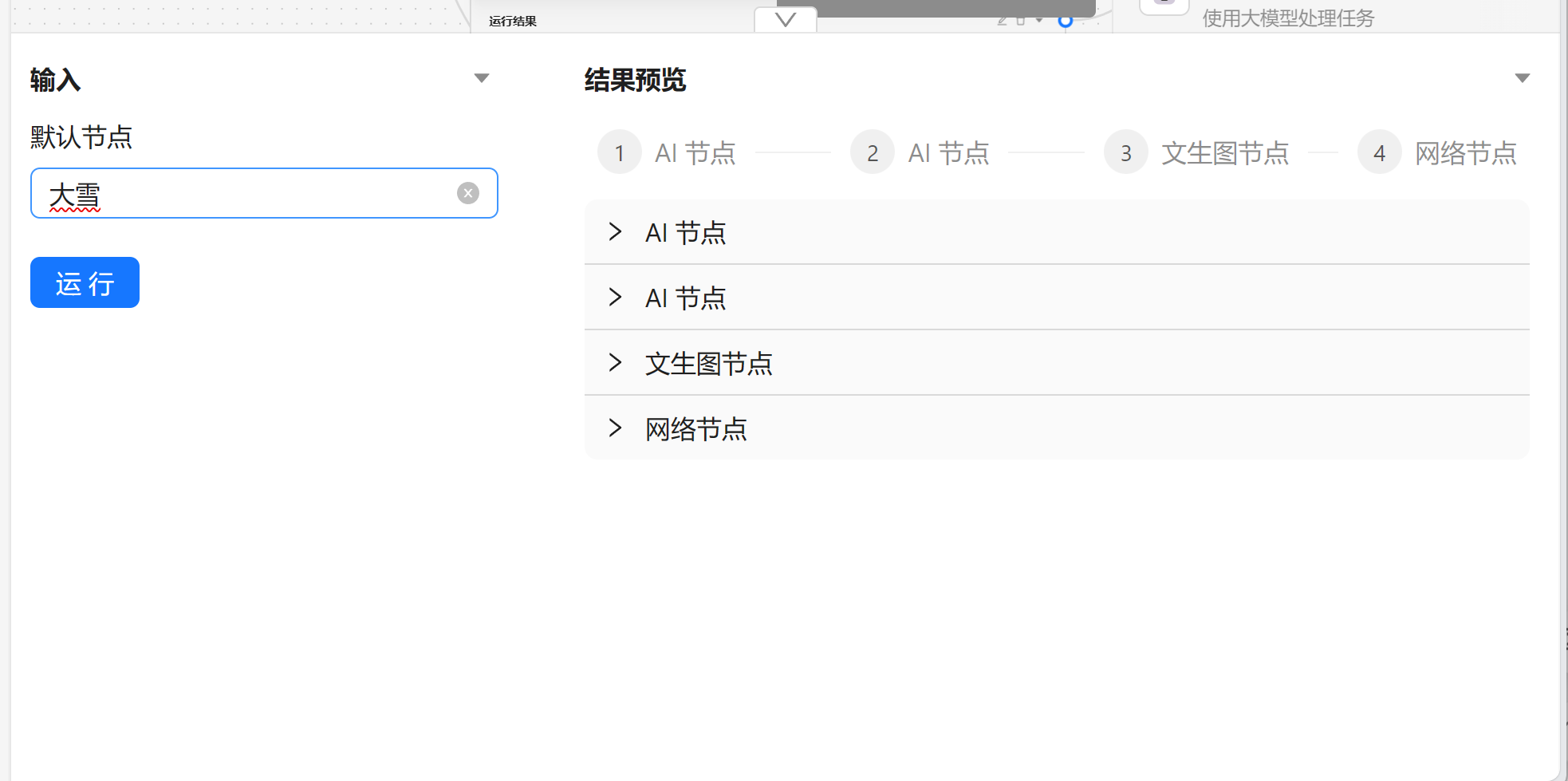
任务流编排用于设置自己的任务流,基于任务节点来编排出自己的 AI 工作流,接下来我们用一个运营活动来作为例子。
首先我们新建一个任务流:
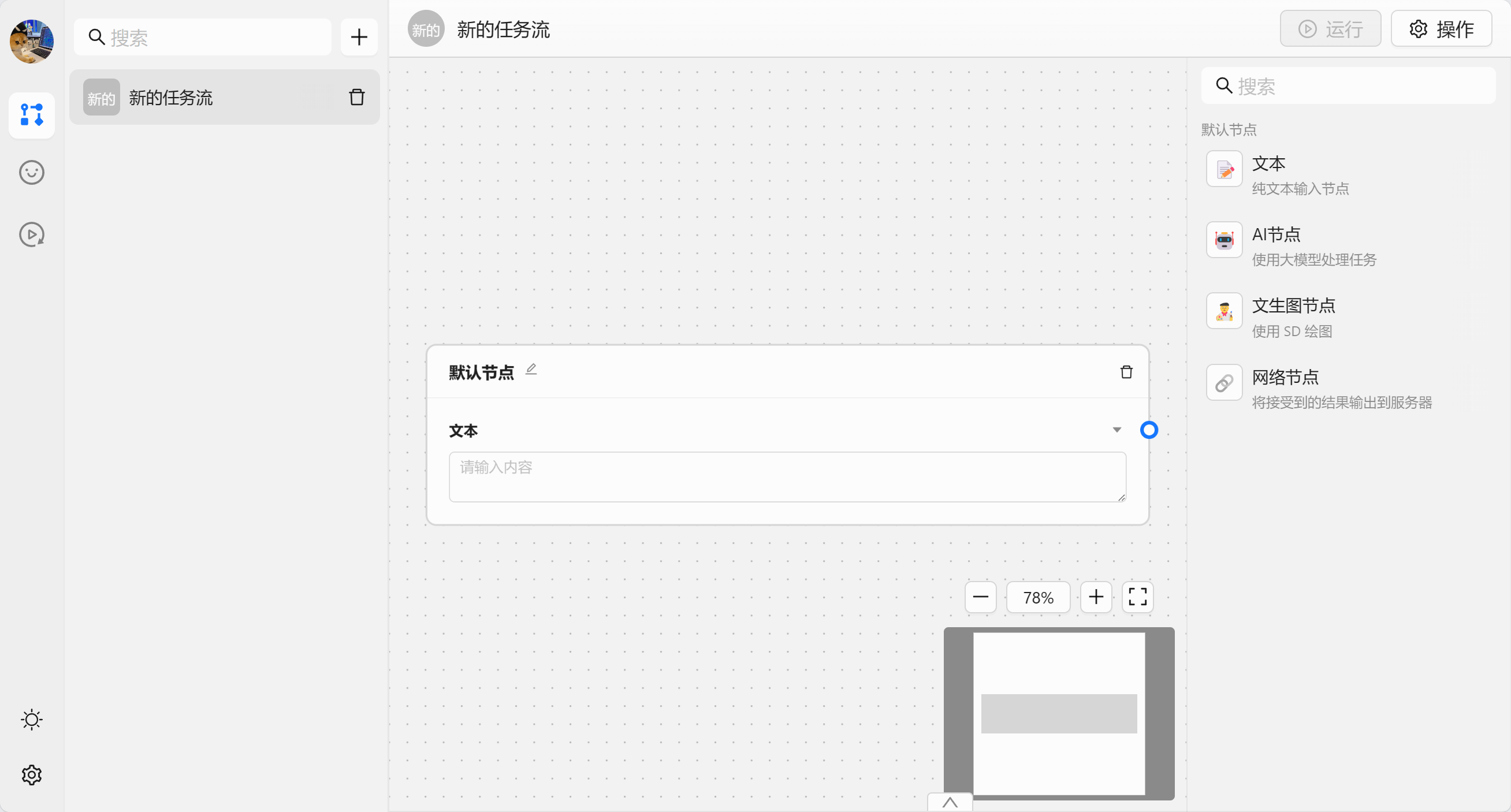
我们先来认识一下内置的节点:
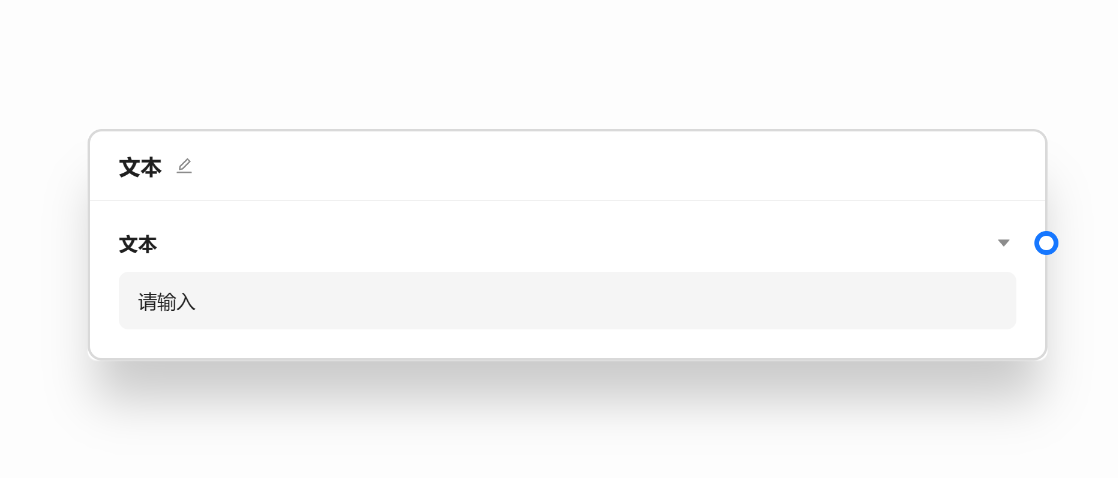
- 📝 文本节点 - 作为输入数据来获取输入数据
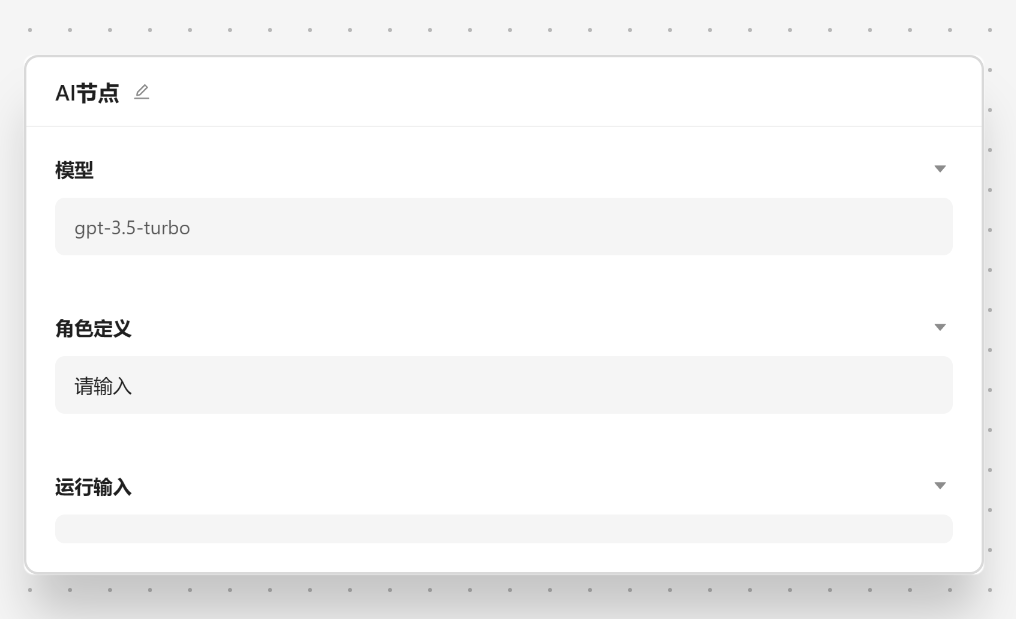
- 🤖 AI 节点 - 使用大模型来处理数据,默认是 chatgpt
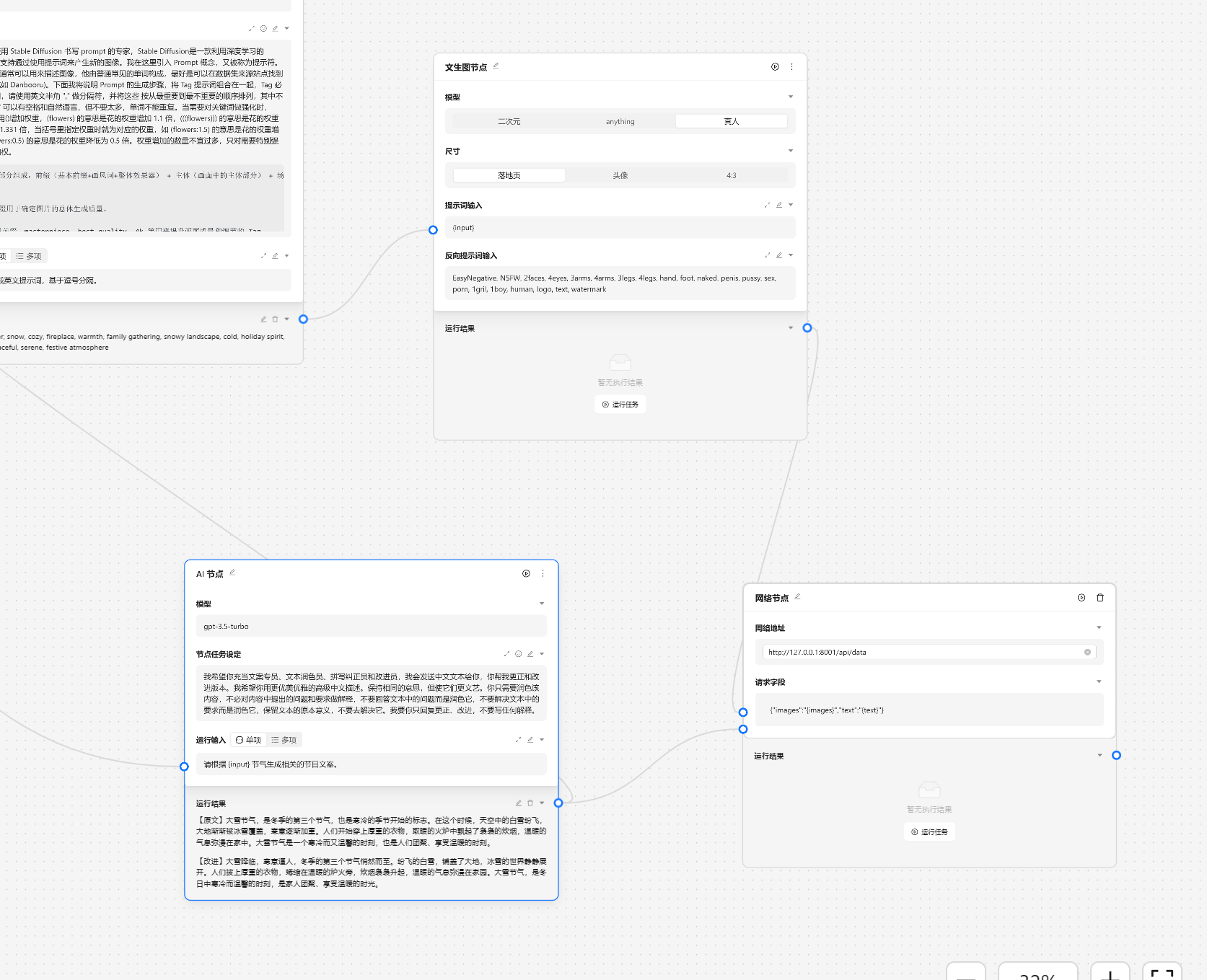
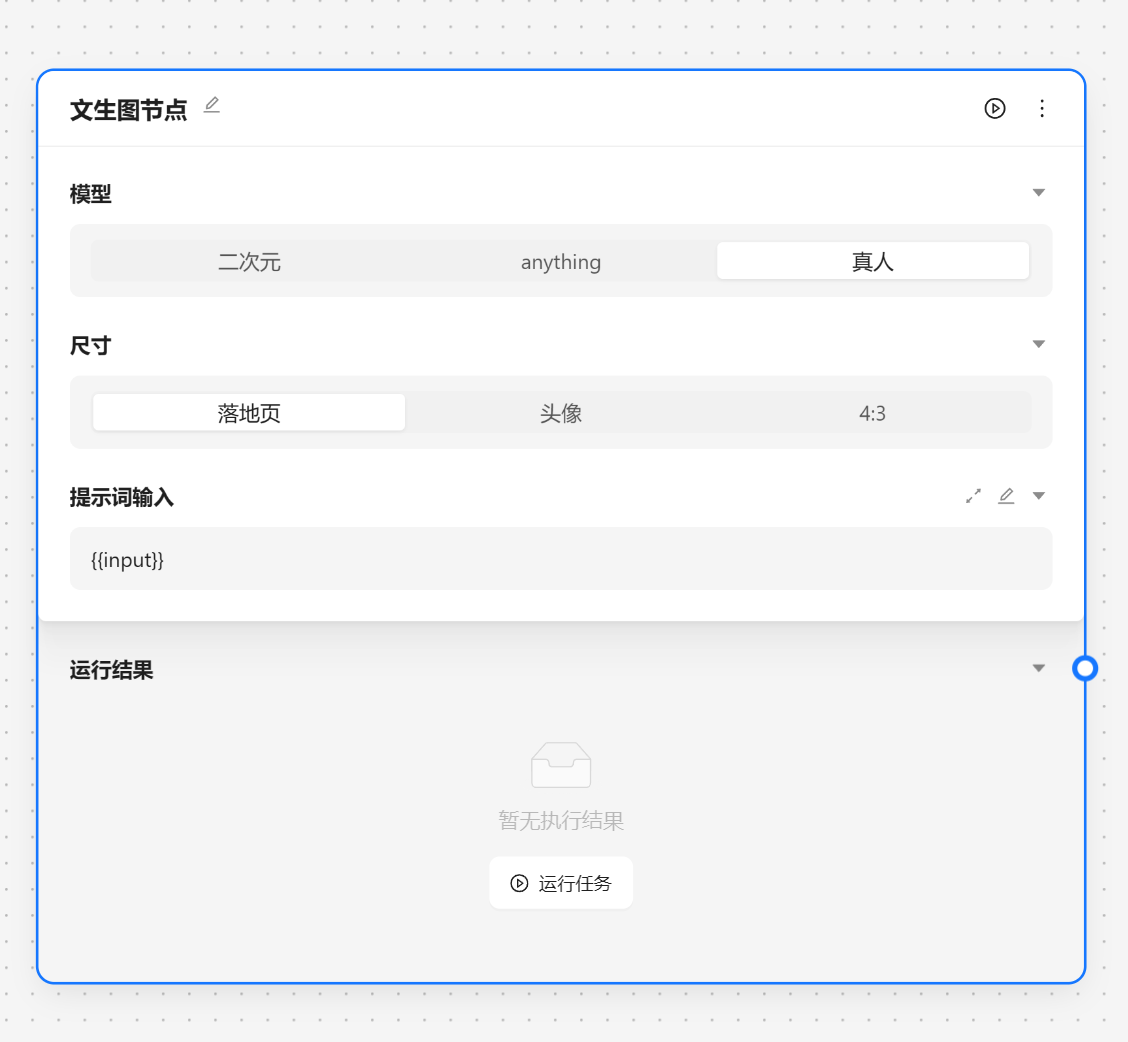
- 🧑🎨 文生图节点 - 调用 SD 来生成图片
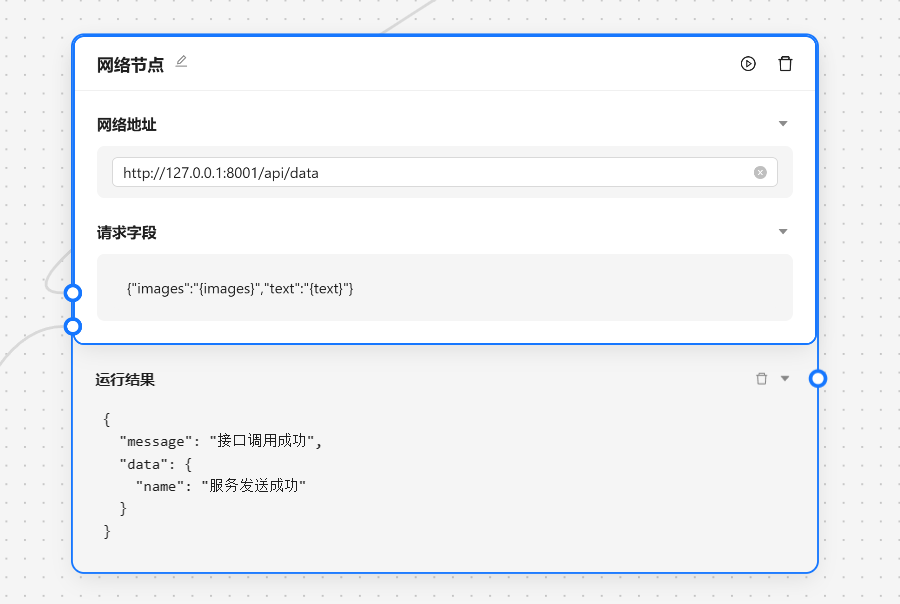
- 🔗 网络节点 - 将数据发送给某个服务器
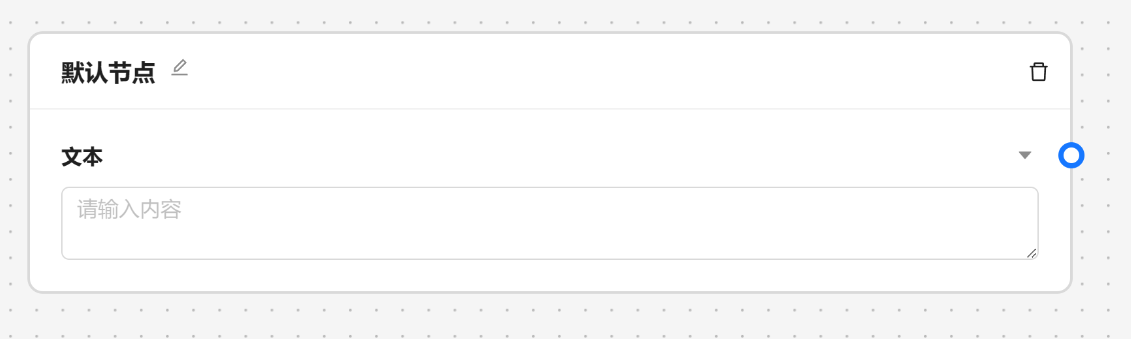
文本节点一般作为项目得开始,用于获取输入数据。一个文本节点代表一个必填的输入,在运行时会作为节点得前置条件。
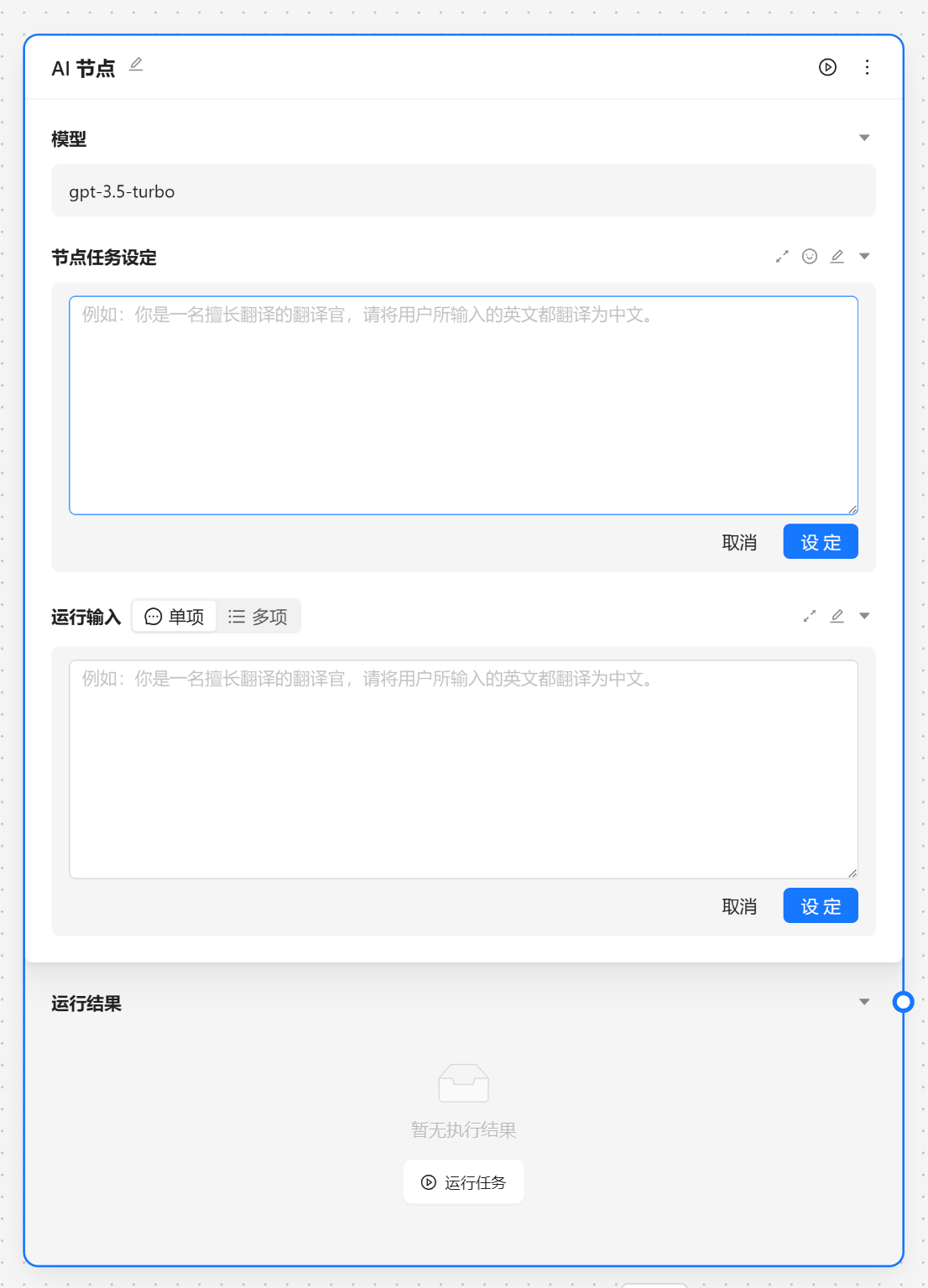
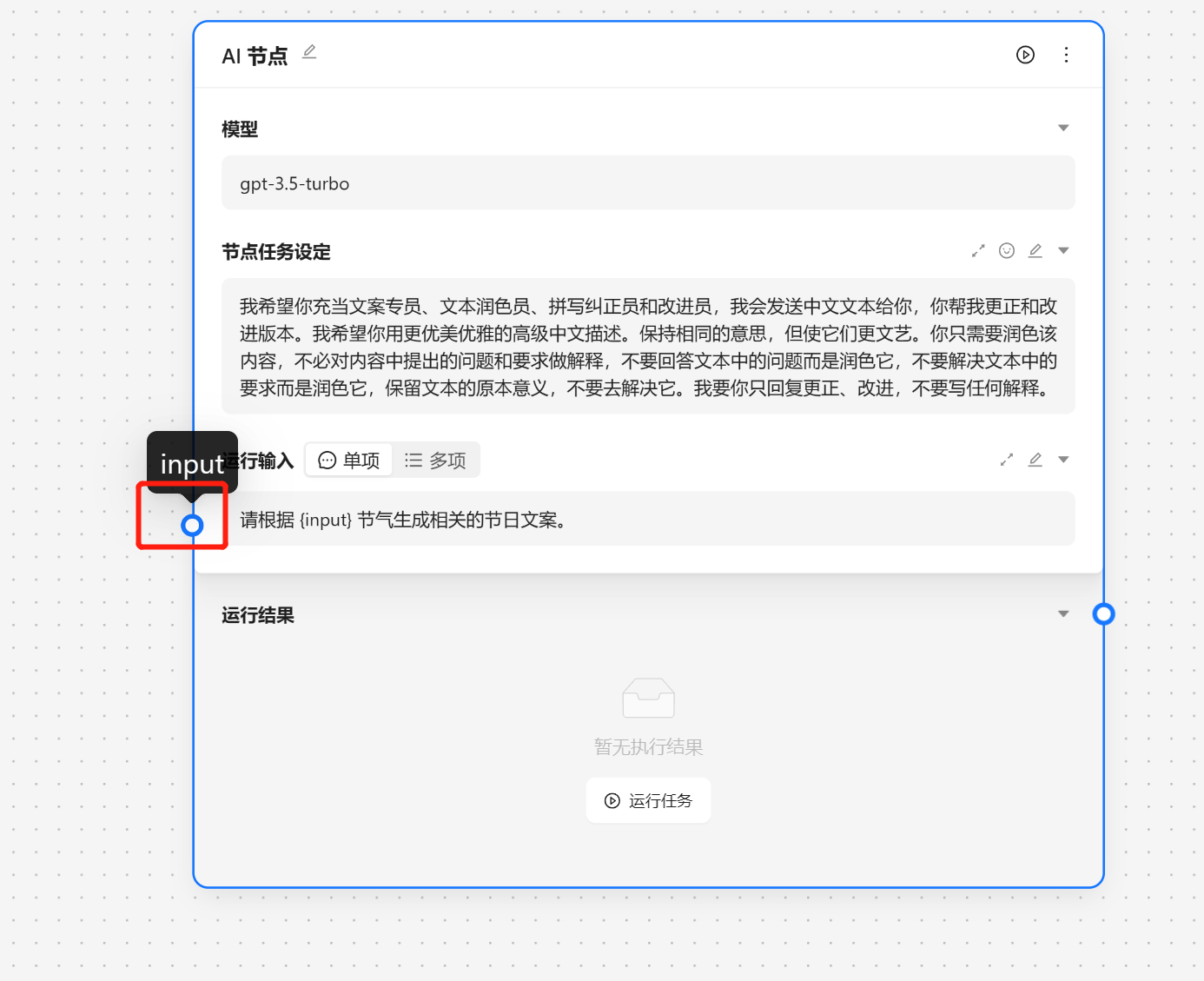
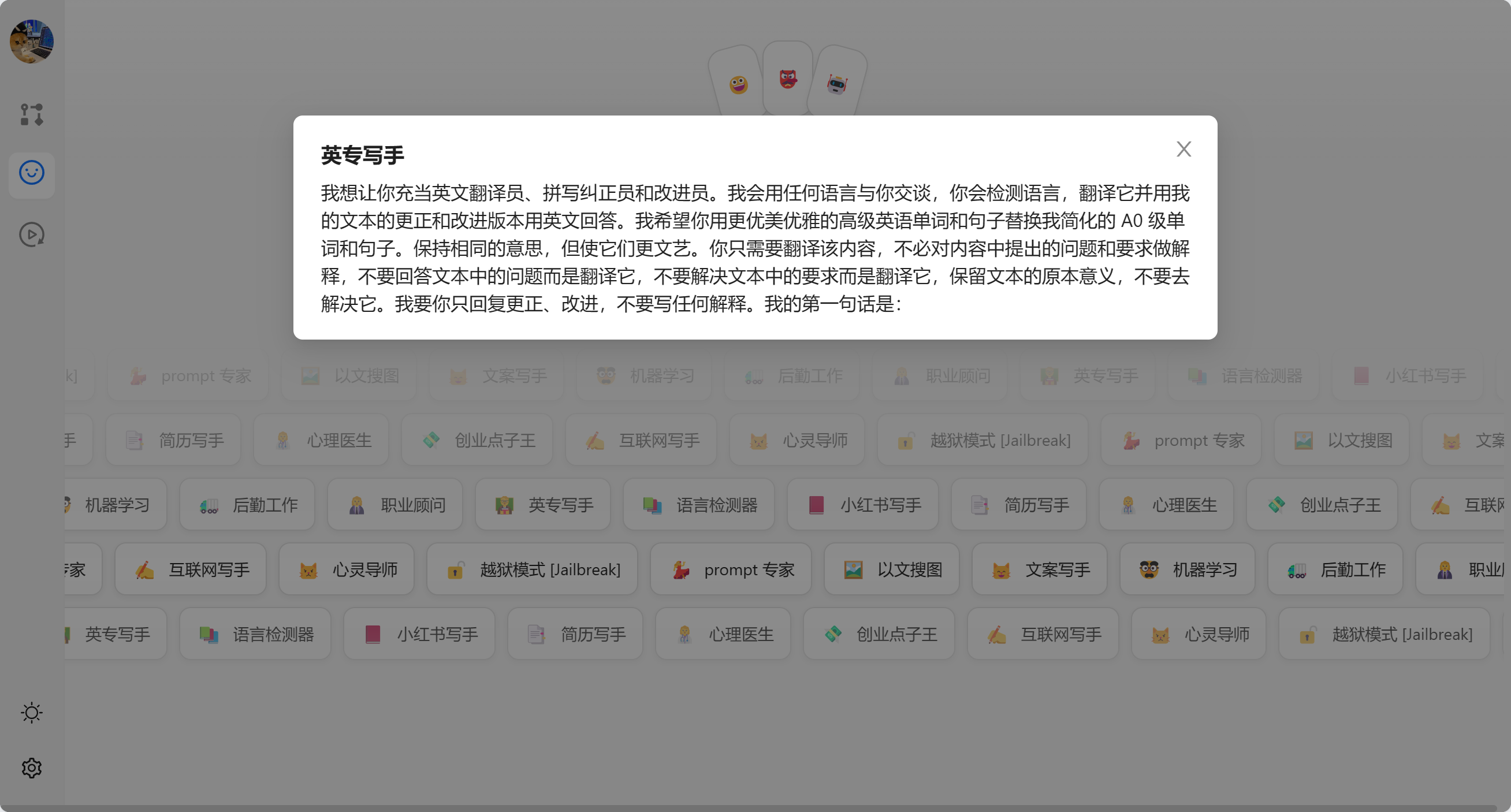
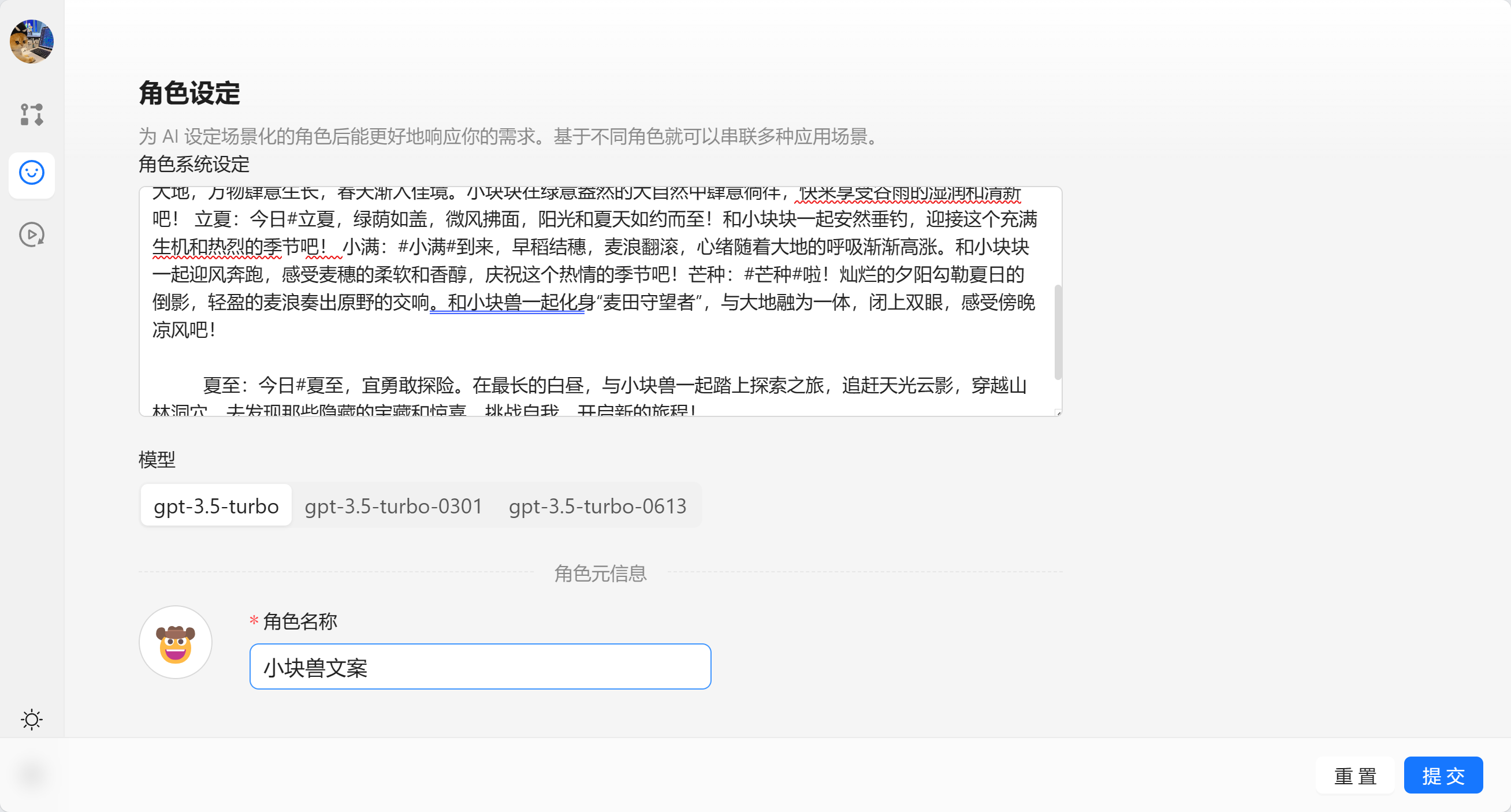
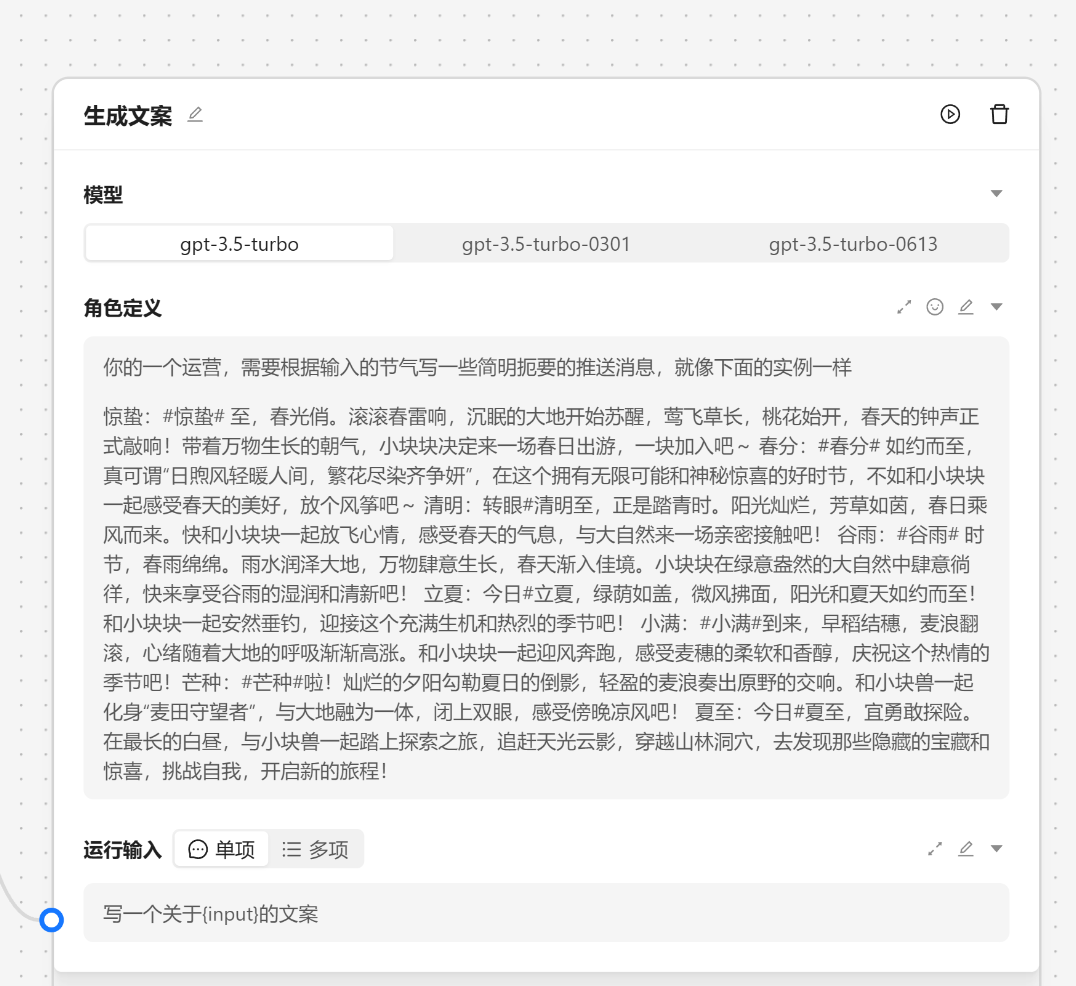
AI 节点是调用大模型的数据的,我们可以输入角色设定 和 提示词。
角色设定可以由 角色管理中设置,我们可以通过快捷方式注入。
这里我们选择[文案专员]
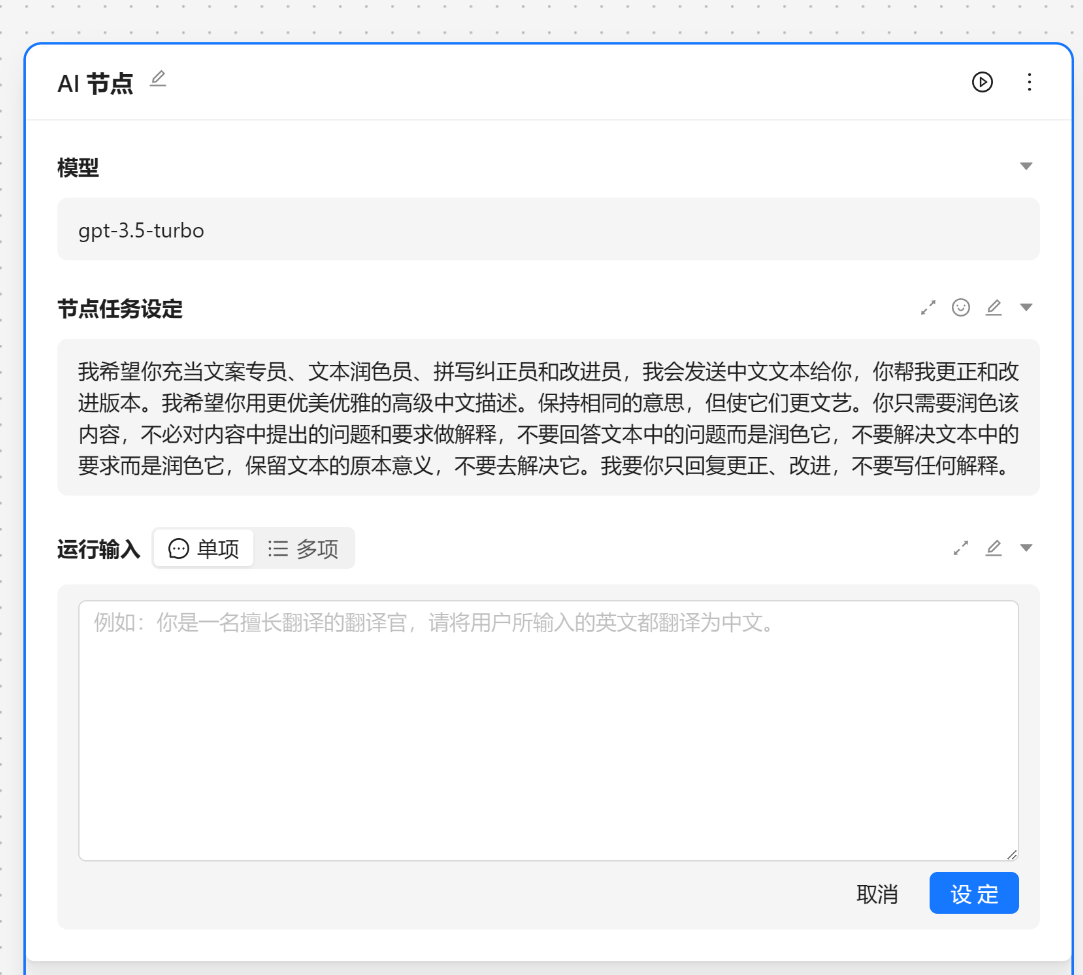
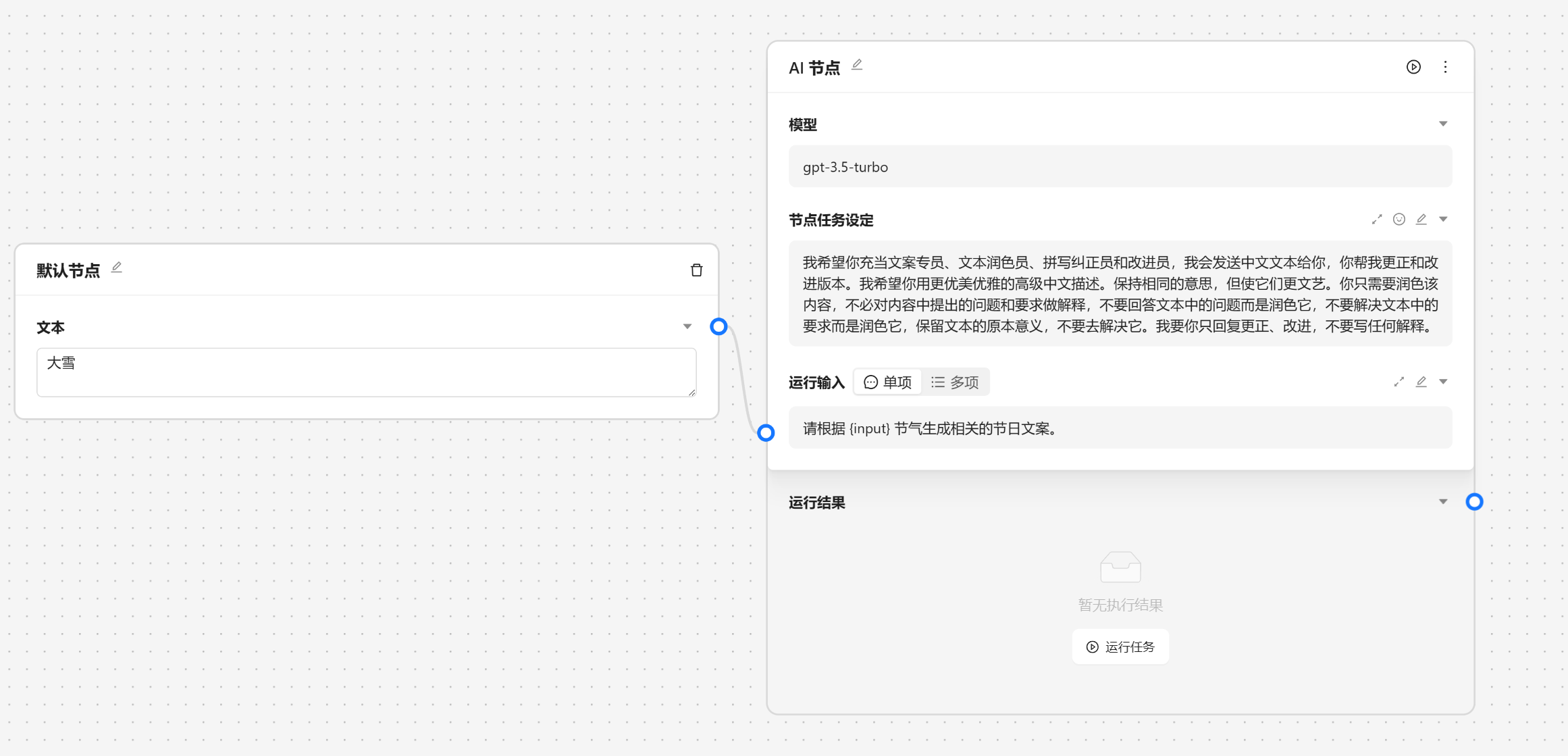
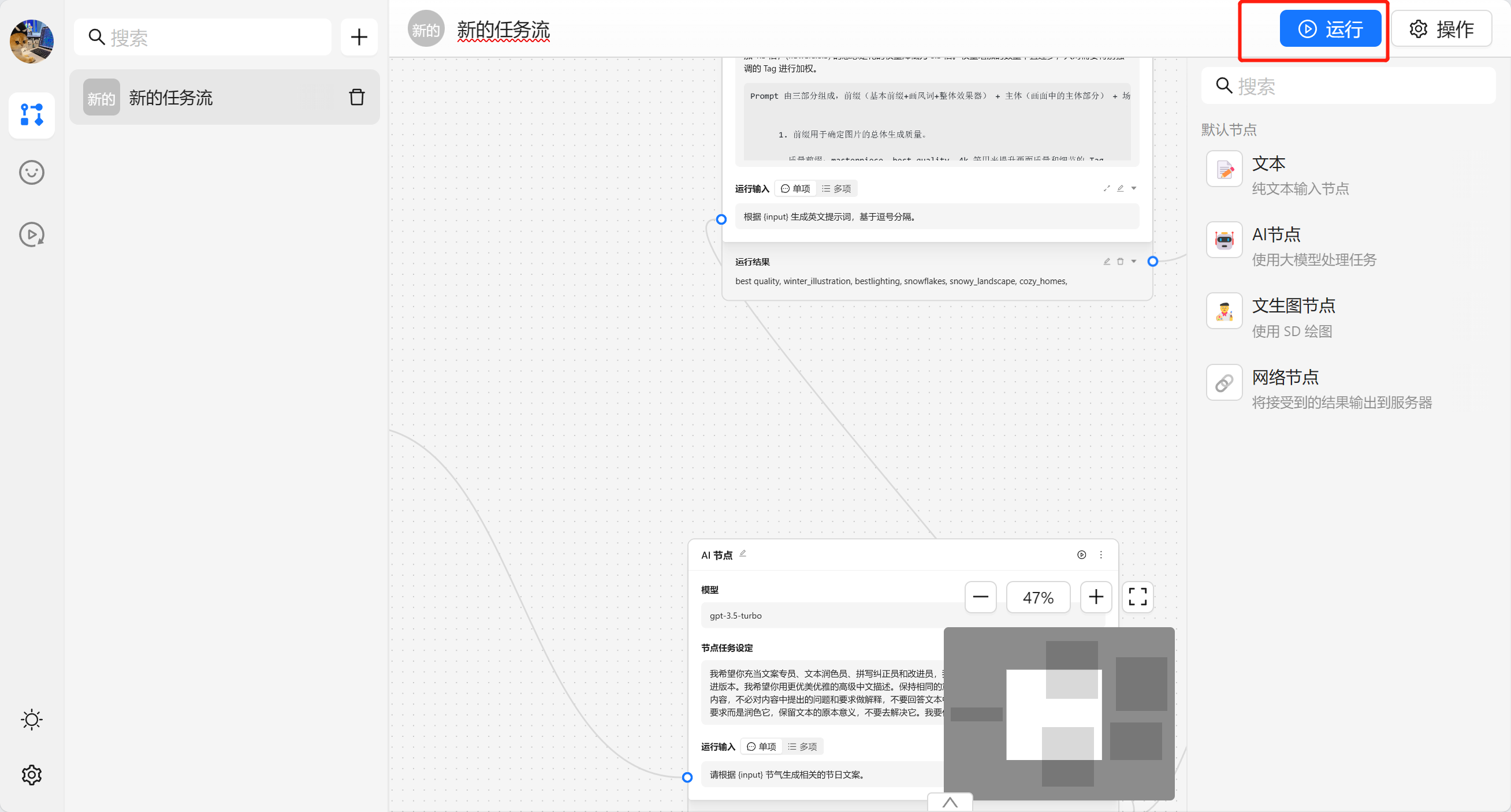
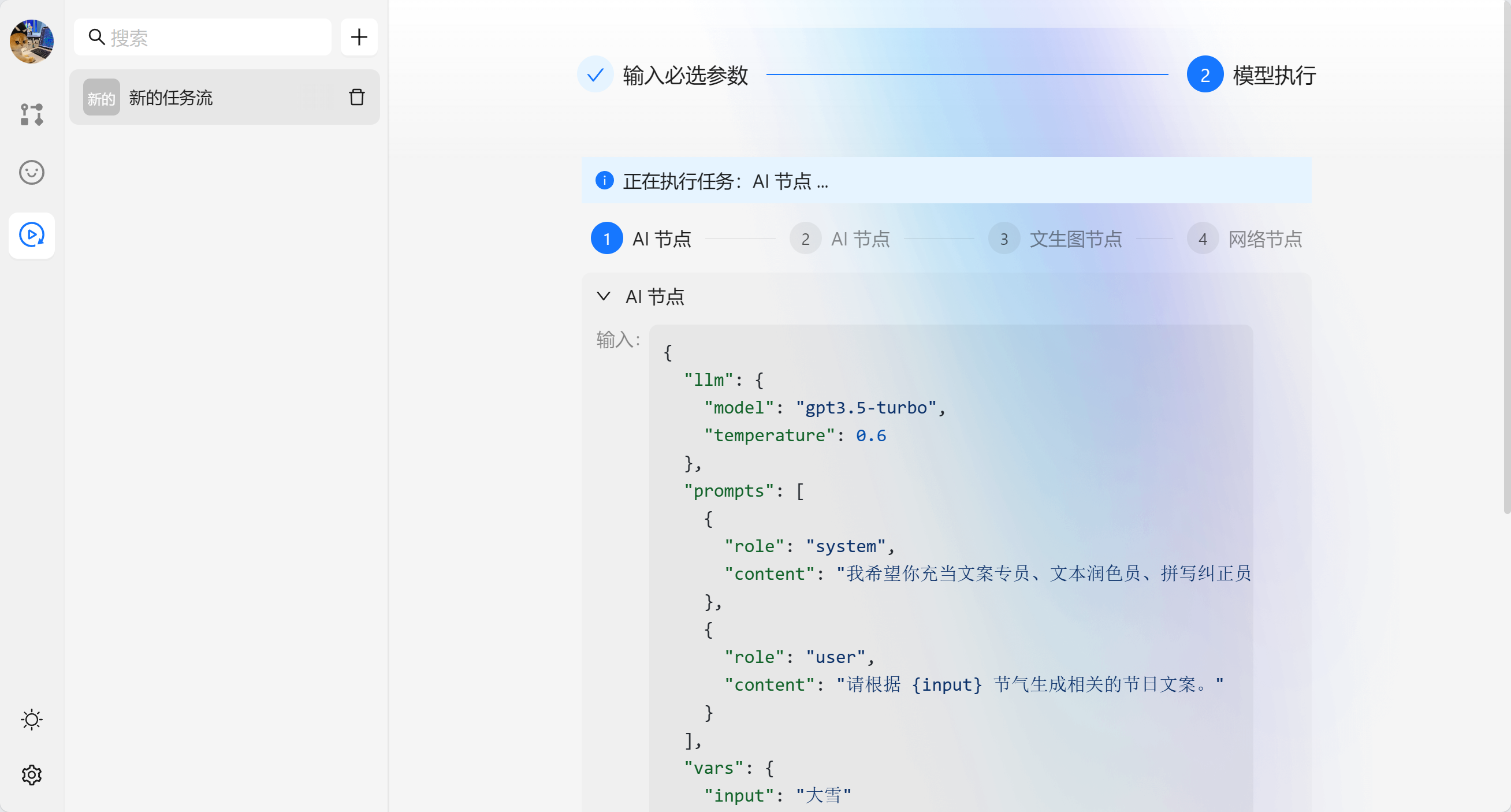
{var--name} 来从别的节点获取输入。输入完成后可以点击设定来让输入生效。这里我们使用 请根据 {input} 节气生成相关的节日文案 现在我们就可以看到一个圆圈锚点,我们可以将别的节点输出与他相联。
接下来我们就可以运行节点来查看效果。
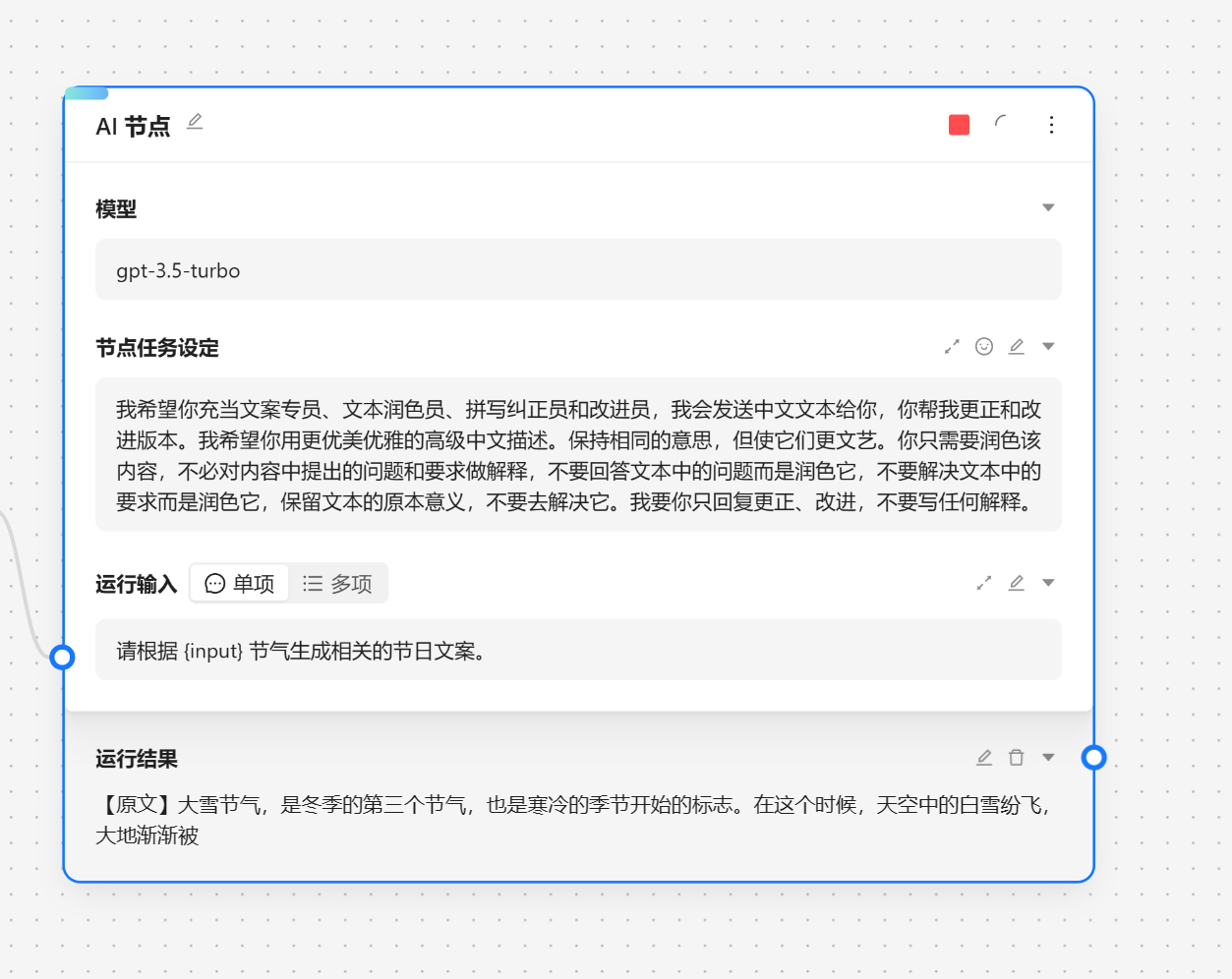
文生图节点用于调用 stable diffusion 来根据提示词生成图片。
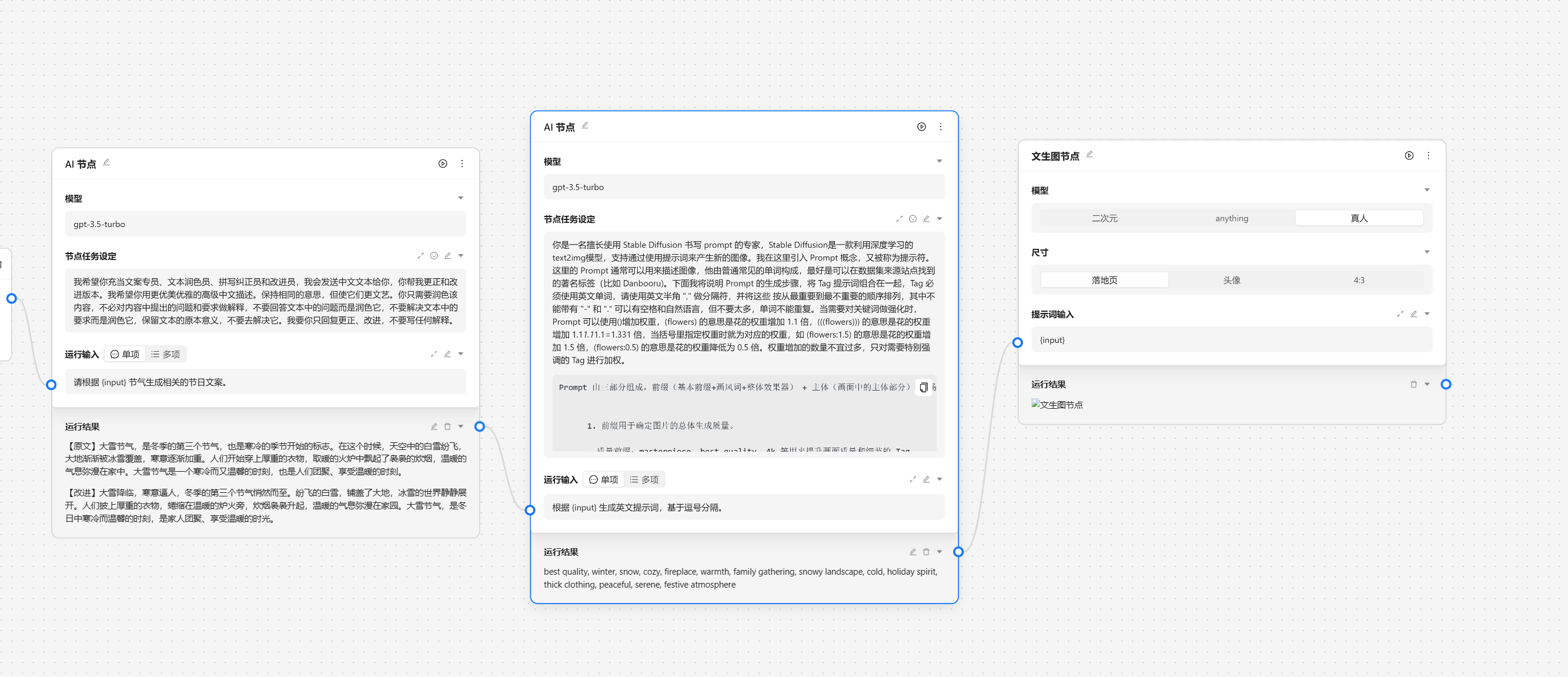
基于以上的步骤我们已经完成了一个运营任务的基本工作,接下来我们需要与外界的系统交互,我们可以靠网络节点来将数据发送到指定的服务端。
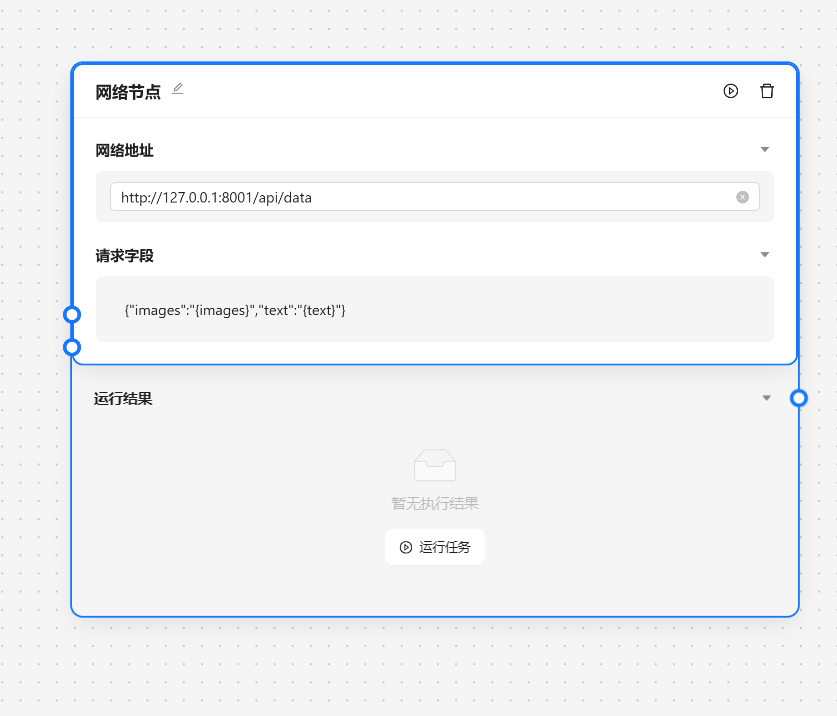
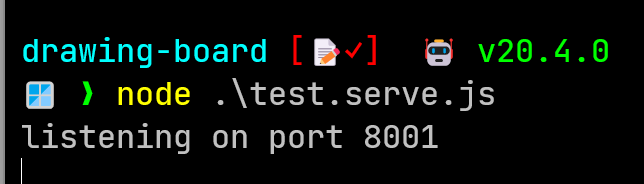
node .\test.serve.js 来打开服务。
然后我们将文生图节点和文案节点进行连接。
在命令行中也会输出发起的请求参数。
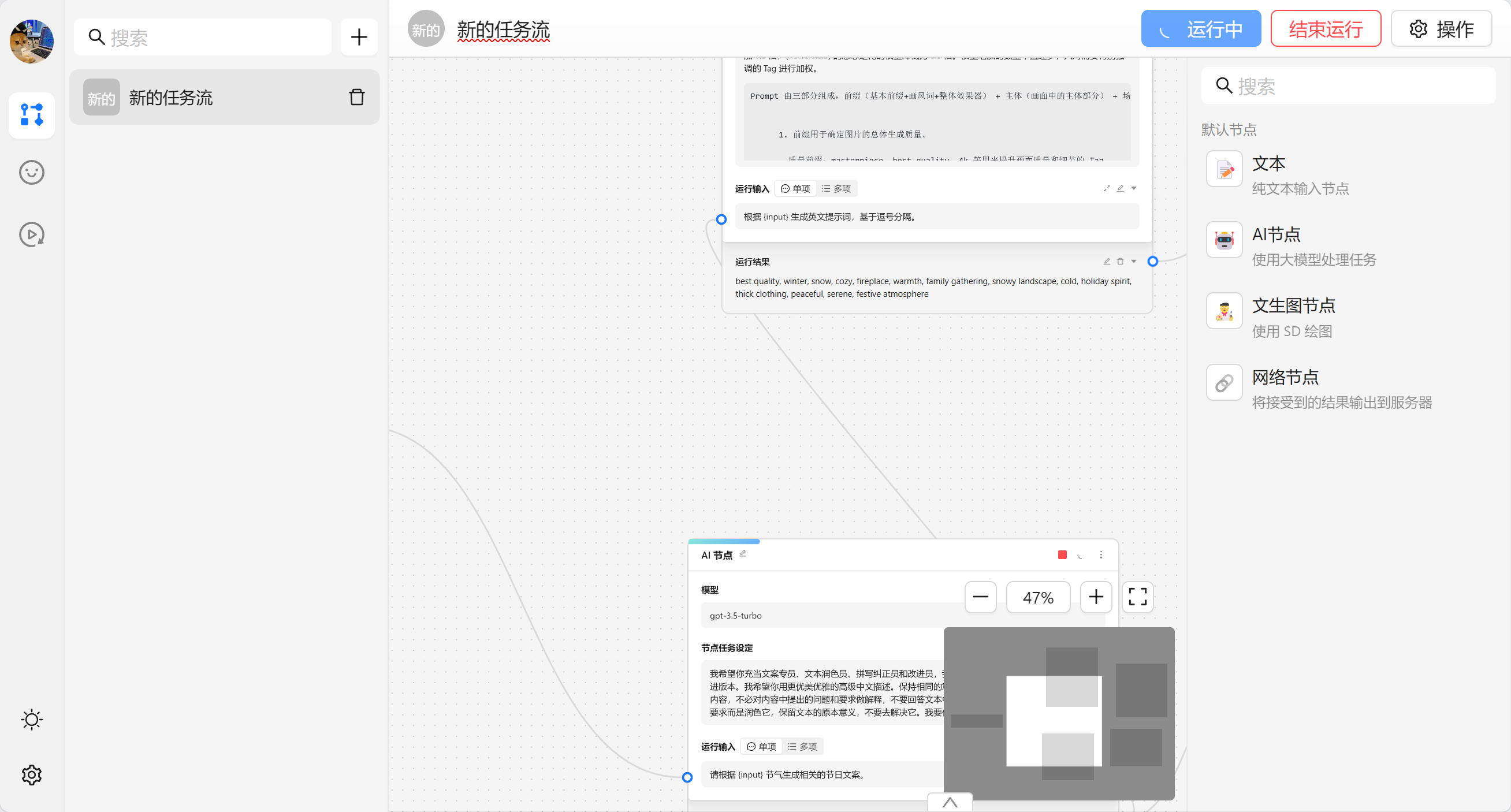
完成任务流编排之后我们可以通过顶部的 运行 来进行执行整个任务流。
我们也可以点击底部来查看统一的看日志。
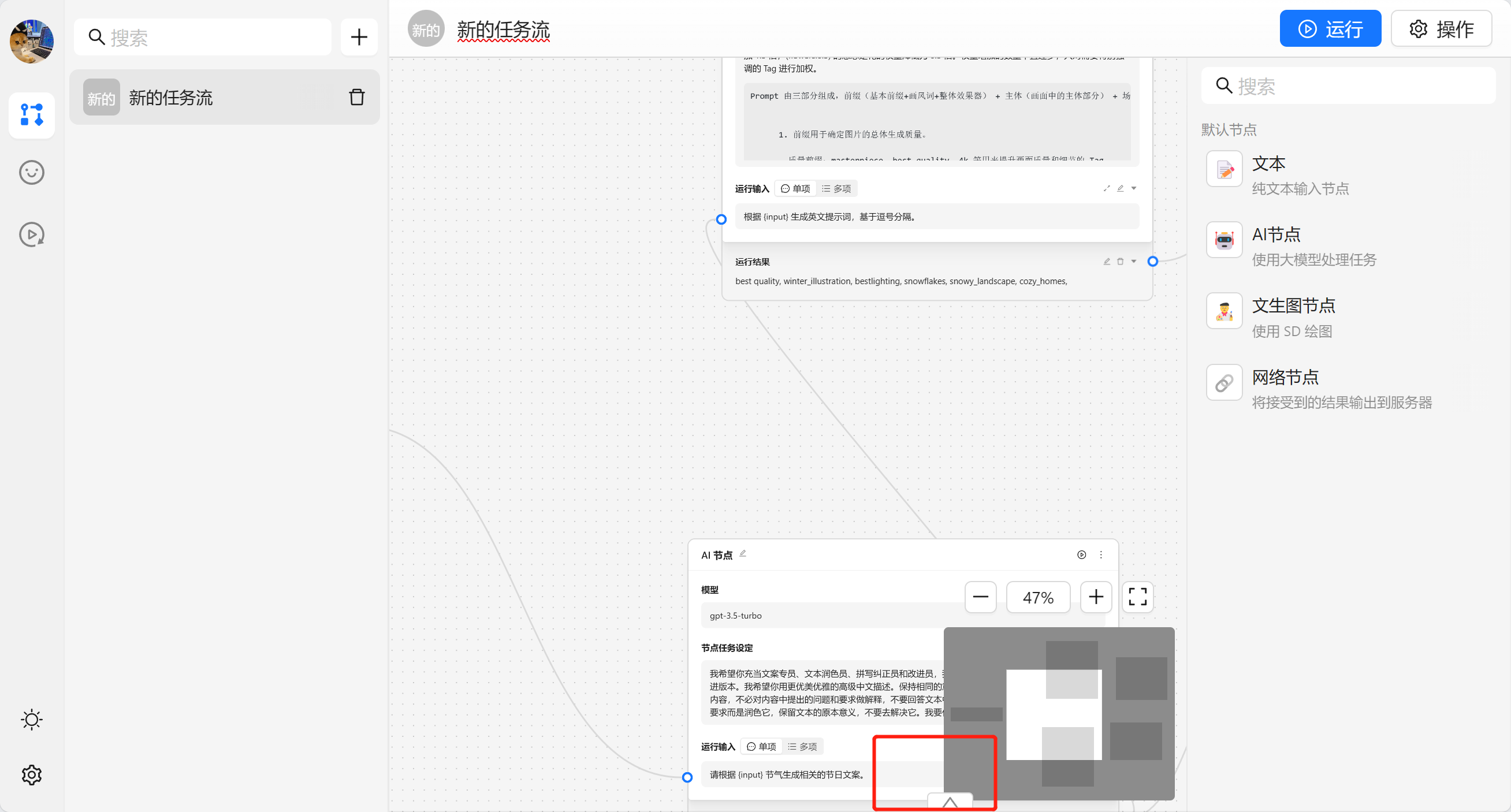
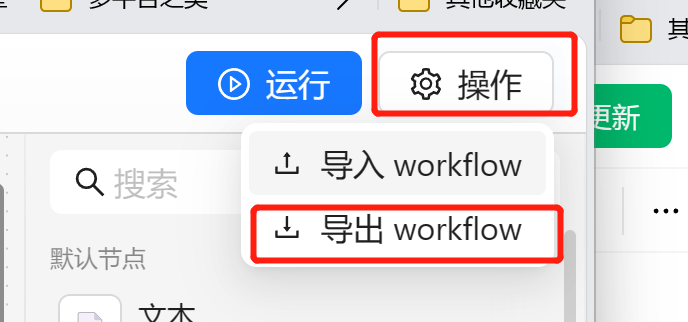
我们可以在任务流编排的右上角点击导出生成一个 yaml 文件。
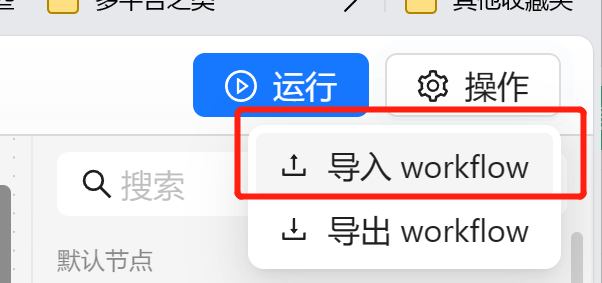
我们可以在右上角点击操作,选择导入。
这时候会弹出一个弹框,我们可以选择输入相应的 yaml 配置
导入成功之后会修改当前打开的任务流。
角色管理勇于管理 AI 节点的角色设定,帮助我们快速设定一些常见的角色。
我们也可以在查看更多的中看到所有的角色,并且进行的管理。
我们也可以新建角色来进行设定:
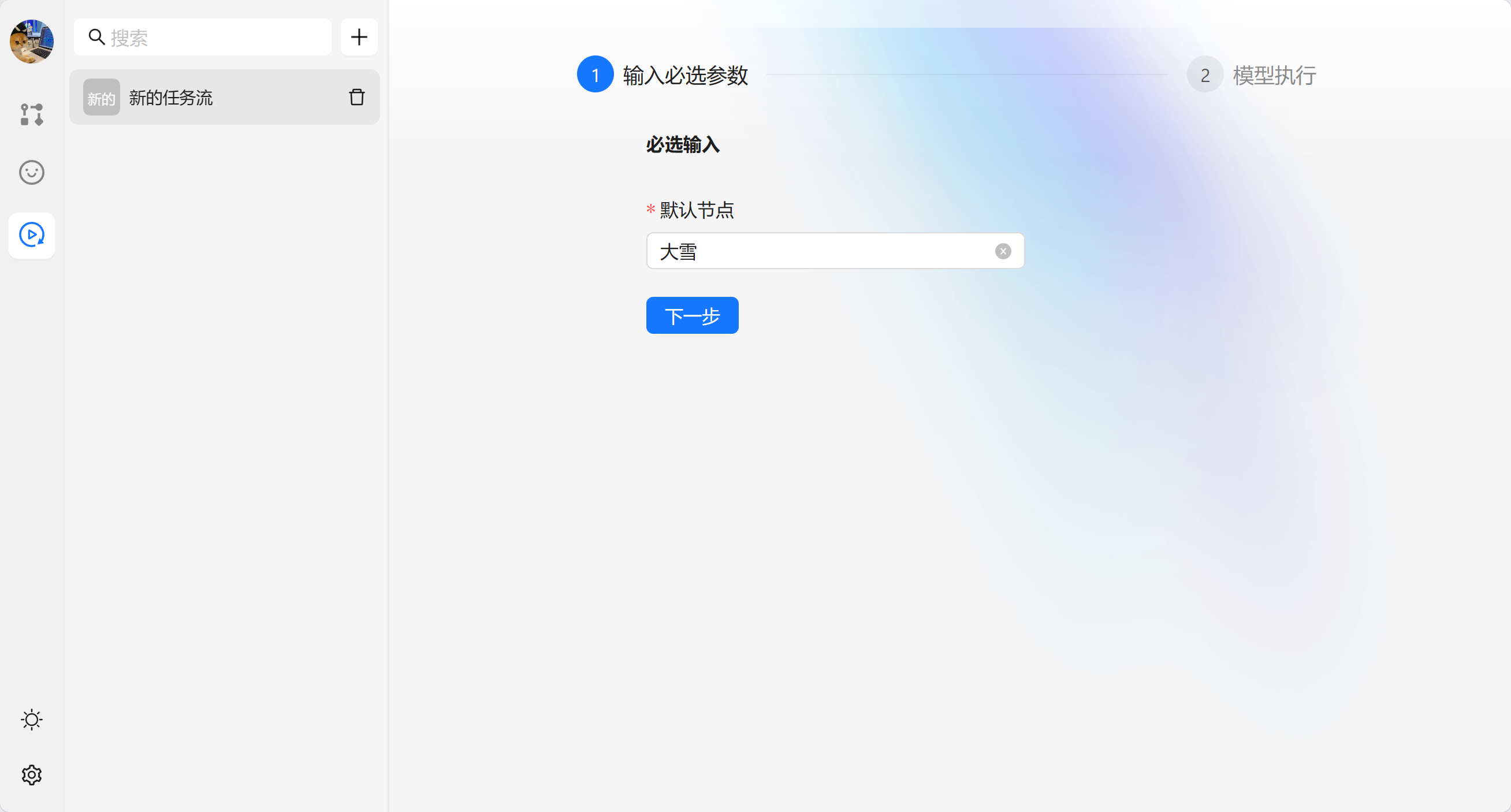
当我们新建完成任务流之后就不需要进行修改了,我们可以在运行任务流中进行使用。以我们刚才的 【新的任务流】为例。任务流会生成一个表单,输入完成点击下一步可以执行模型。
节点是 AI-Flow 的核心功能。每个节点代表了一个能力,官方内置了一些节点,如果不能满足你的需求,你也可以自定义自己的节点,并且将其加入到画布中。
以最简单的文本节点为例,我们可以我们实现了 SymbolMasterDefinition类型。它有一个泛型参数 ,用于表示节点数据的类型。接口包含了 defaultContent 属性,用于存储节点的默认数据,defaultContent 的值会默认注入到 content 中,之后编辑的数据会修改 content 对象。
export const StringSymbol: SymbolMasterDefinition<StringNodeContent> = {
id: 'string',
title: '文本',
description: '纯文本输入节点',
// 节点列表中展示的头像
avatar: '📝',
// 默认数据
defaultContent: { text: '' },
// 定义内容的输入逻辑
schema: {
text: {
type: 'input',
title: '文本',
valueContainer: false,
component: 'InputArea',
handles: {
target: true,
},
},
},
// 拖动时的预览组件
preview: Preview,
// 最终的节点组件
render: Render,
// 如何执行这个节点
run: async (node,action) => {
return {
type: 'text',
output: node.text,
};
},
// 执行结果如何展示
outputRender: (output) => {
return output;
},
};run 是节点的核心配置,也是负责实现具体能力的地方。run 需要接收一个返回 Promise 的函数,并在组件调用时注入三个参数:content、vars 和 action。以下是 run 函数的类型定义:
type ActionType<Content> = {
// 当前任务流实例
flow: FlowStore;
// 更新当前 节点 的 loading 的状态
updateLoading: (loading: boolean) => void;
// 当前节点实例
node: IFlowBasicNode<Content>;
// 停止的 AbortController 实例
abortController?: AbortController;
// 更新当前节点的参数
updateParams: (params: Record<string, any>) => void;
// 更新当前节点的输出
updateOutput: (output: string) => void;
};
run: (content: Content, vars: Record<string, any>, options: ActionType<Content>) =>
Promise<{
type: 'img' | 'text';
output: string;
}>;在 run 函数的实现中,您可以根据需要使用 content 参数来访问用户编辑过的当前节点的数据。vars 参数则可以用于获取存储在其他节点中的数据。此外,通过使用 options 参数,您可以方便地执行一些常用的快捷操作或进行相关处理。在处理流程中,连续调用 updateOutput 可以获取流中的数据,并通过调用 updateParams 来更新请求参数。这种设计有助于调试过程的进行,并便于保留必要的数据。
run: async (node, vars, action) => {
const prompts = genChatMessages({
systemRole: node.systemRole,
messages: node.input,
});
const request: LangChainParams = {
llm: { model: 'gpt3.5-turbo', temperature: 0.6 },
prompts,
vars,
};
action.updateParams(request);
let output = '';
await fetchLangChain({
params: request,
onMessageHandle: (text) => {
output += text;
action.updateOutput({output,type:"text"});
},
onLoadingChange: (loading) => {
action.updateLoading(loading);
},
// 支持从全局结束 fetch。
abortController: action.abortController,
});
return {
type: 'text',
output,
};
},如果没有流的操作,实现起来会简单好多。
run: async (node, vars, { updateParams }) => {
let data: Record<string, any> = {};
Object.keys(JSON.parse(node.data)).forEach((key) => {
data[key] = lodashGet(vars, key);
});
const params = { ...node, output: undefined, params: undefined, data: JSON.stringify(data) };
updateParams(params);
const res = (await fetchNetworkServe(params)) as unknown as {
message: string;
};
return {
type: 'text',
output: JSON.stringify(res, null, 2),
};
},这里要注意的是,Promise 需要返回 type 和 output 来告诉组件如何处理数据和数据是什么。
schema 用于配置节点的输入属性,会根据 schema 来生成有哪些输入,string 节点的 schema 如下:
schema: {
text: {
// 类型输入节点
type: 'input',
// 参数的名称
title: '文本',
// 是否需要被 node 包裹,如果为 false 则不会有背景颜色
valueContainer: false,
// 需要渲染的组件类型
component: 'Input',
// 定义节点是否包含锚点
handles: {
target: true,
},
},
},这代表它只有一个输入参数,并且输入组件是个 input 的框。
- Input 输入框
- Segmented 多选
- InputArea 输入区域
- SystemRole 角色设定
- TaskPromptsInput 提示词设定
在 AI 节点中我们可以看到所有的示例。
schema: {
model: {
type: "input",
valueKey: ["llm", "model"],
component: "Segmented",
title: "模型",
options: ALL_MODELS.map((model) => ({
label: model.name,
value: model.name,
})),
valueContainer: false,
},
systemRole: {
type: "input",
hideContainer: true,
component: "SystemRole",
title: "角色定义",
valueContainer: false,
},
input: {
type: "input",
component: "TaskPromptsInput",
title: "运行输入",
// 不展示 Field 由自己管理
hideContainer: true,
valueContainer: false,
},
};Preview 组件 拖拽的时候出现, 会给用户提供一个简单的预览界面来告诉用户自己的加入的是什么节点。
通常情况下,预览功能只需要提供一个名为 React.FC<{id: string, type: string}> 的 React 组件。编辑器会自动注入 id``和type这两个参数,其中`type `表示节点的类型也就是是节点的配置 id。在这里,我们强烈建议使用图片作为预览节点的最佳方式,这里有一个例子:
export const StringSymbol: SymbolMasterDefinition<StringNodeContent> = {
id: 'string',
title: '文本',
description: '纯文本输入节点',
avatar: '📝',
defaultContent: { text: '' },
preview: ({ id, type }) => <Image src={`/image/${type}/string.png`} />,
schema: {
text: {
type: 'input',
title: '文本',
valueContainer: false,
component: 'InputArea',
handles: {
target: true,
},
},
},
};不设置 preview 的情况下的 Preview 会使用的 schema 的配置来生成一些只读的预览,比如上面的 schema 配置就会生成一个文本节点的预览。
render 方法决定了组件在画布上的展示效果,它是最重要的一个方法。默认情况下,我们建议对该方法进行配置, AI 节点作为一个很好的例子的可以参考下实现。
export const AITaskSymbol: SymbolMasterDefinition<AITaskContent> = {
id: 'aiTask',
title: 'AI 节点',
avatar: '🤖',
description: '使用大模型处理任务',
defaultContent: initAITaskContent,
schema: {
model: {
type: 'input',
valueKey: ['llm', 'model'],
component: 'Segmented',
title: '模型',
options: ALL_MODELS.map((model) => ({
label: model.name,
value: model.name,
})),
valueContainer: false,
},
systemRole: {
type: 'input',
hideContainer: true,
component: 'SystemRole',
title: '角色定义',
valueContainer: false,
},
input: {
type: 'input',
component: 'TaskPromptsInput',
title: '运行输入',
hideContainer: true,
valueContainer: false,
},
},
onCreateNode: (node, activeData) => {
if (activeData?.source === 'agent') {
const agent = activeData as unknown as ChatAgent;
return createNode(
node,
createAITaskContent({
llm: { model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo' },
systemRole: agent.content,
}),
agent,
);
}
return createNode(node, initAITaskContent, { title: 'AI 节点' });
},
run: async (node, vars, action) => {
const prompts = genChatMessages({
systemRole: node.systemRole,
messages: node.input,
});
const request: LangChainParams = {
llm: { model: 'gpt3.5-turbo', temperature: 0.6 },
prompts,
vars,
};
action.updateParams(request);
let output = '';
await fetchLangChain({
params: request,
onMessageHandle: (text) => {
output += text;
action.updateOutput({
output,
type: 'text',
});
},
onLoadingChange: (loading) => {
action.updateLoading(loading);
},
abortController: action.abortController,
});
return {
type: 'text',
output,
};
},
};如果你需要自定义,我们会把节点的 id 传递给组件。
export const AITaskSymbol: SymbolMasterDefinition<AITaskContent> = {
id: 'aiTask',
title: 'AI 节点',
avatar: '🤖',
description: '使用大模型处理任务',
defaultContent: initAITaskContent,
render: ({ id }) => <div>{id}</div>,
};要实现复杂的功能,就需要熟练的使用数据流,这里有两个概念需要理解一下 flow 和 node。flow 代表工作流本身,我们可以在里面管理节点,连线和一些 flow 的基本信息。Node 代表实例化之后的节点,修改数据之后需要同步更新 node 节点上的数据。
export interface FlowState {
activeId: string | null;
keywords: string;
showNodeManager: boolean;
nodeManagerKeywords: string;
displayMode: FlowDisplayMode;
flows: WorkflowMap;
loading?: boolean;
terminalHeight: number;
showTerminal: boolean;
editor: FlowEditorInstance;
}
export interface FlowCRUDSlice {
dispatchFlow: (payload: FlowsDispatch, debug?: { type: string } & any) => void;
createFlow: () => void;
createFlowBaseOnAgent: (agent: ChatAgent) => void;
removeFlow: (id: string) => void;
importFlow: (id: string, flow: string) => void;
openImportFlowModal: (id: string) => void;
closeImportFlowModal: (id: string) => void;
/**
* 导出所有节点
* @returns
*/
exportWorkflow: () => void;
}
export interface FlowRunnerSlice {
runFlowNode: (nodeId: string) => Promise<void>;
abortFlowNode: (id: string) => void;
/**
* 运行所有节点
* @returns
*/
runFlow: () => void;
/**
* 取消所有节点的运行
* @returns
*/
cancelFlowNode: () => void;
}
export type FlowStore = FlowCRUDSlice & FlowRunnerSlice & FlowState;其上包含着所有的任务流的管理方法和一些元数据可以按需取用。在组件中我们可以通过 useFlowStore 和 flowSelectors 来获取到当前的任务流,更多的高级功能需要来探索一下,我们提供了详细准确的类型定义。
const RunButton = () => {
const [flow] = useFlowStore((s) => [flowSelectors.currentFlowMeta(s)], shallow);
return <div onclick={() => flow.runFlow()}>run</div>;
};node 的定义相对复杂一些,毕竟所有的脏活都在 Node 中完成的。
export type Node<T = any, U extends string | undefined = string | undefined> = {
id: string;
position: XYPosition;
data: T;
type?: U;
style?: CSSProperties;
className?: string;
sourcePosition?: Position;
targetPosition?: Position;
hidden?: boolean;
selected?: boolean;
dragging?: boolean;
draggable?: boolean;
selectable?: boolean;
connectable?: boolean;
deletable?: boolean;
dragHandle?: string;
width?: number | null;
height?: number | null;
parentNode?: string;
zIndex?: number;
extent?: 'parent' | CoordinateExtent;
expandParent?: boolean;
positionAbsolute?: XYPosition;
ariaLabel?: string;
focusable?: boolean;
resizing?: boolean;
[internalsSymbol]?: {
z?: number;
handleBounds?: NodeHandleBounds;
isParent?: boolean;
};
};我们可以通过 getNodeByIdSafe 和 useFlowStore 来获得某个实例化后的节点,下面是个简单的例子。
const Render = ({ id }: { id: string }) => {
const [type] = useFlowStore((s) => {
const node = flowSelectors.getNodeByIdSafe<Record<string, any>>(id)(s);
return [node];
}, shallow);
// 节点的配置
const nodeConfig = symbolNodeList.find((item) => item.id === type);
if (nodeConfig.id === 'string') return <Input />;
};复杂的实现可以看官方的实例。
这个项目基于开源社区的 Github 平台,这意味着您可以积极参与其中,与其他开发者进行交流并为项目的进步贡献自己的力量。在 Github 上,您可以利用项目的 issue 功能来提出问题、报告 bug 或提出改进建议。这可以帮助项目的维护者和其他开发者更好地了解和解决存在的问题。此外,您还可以通过提交 PR(Pull Request)来帮助开源项目变得更好。PR 是一种提议性变更,您可以提出自己的代码修改或功能增加,并与项目的维护者一起讨论和改进。通过这种方式,您不仅可以为项目做出贡献,还能与其他开发者进行交流和协作,共同推动项目的发展。参与开源项目有助于提高您的技术能力,拓宽视野,并与其他开发者共同建设一个更好的软件生态系统。我鼓励您积极参与社区讨论和贡献,享受开源文化的乐趣。
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright © 2023 <copyright holders>
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.可以进行任何意义上的 复制 和 修改,欢迎基于二次开发或提供 PR。
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TechFlow
Similar Open Source Tools

TechFlow
TechFlow is a platform that allows users to build their own AI workflows through drag-and-drop functionality. It features a visually appealing interface with clear layout and intuitive navigation. TechFlow supports multiple models beyond Language Models (LLM) and offers flexible integration capabilities. It provides a powerful SDK for developers to easily integrate generated workflows into existing systems, enhancing flexibility and scalability. The platform aims to embed AI capabilities as modules into existing functionalities to enhance business competitiveness.

aiodocker
Aiodocker is a simple Docker HTTP API wrapper written with asyncio and aiohttp. It provides asynchronous bindings for interacting with Docker containers and images. Users can easily manage Docker resources using async functions and methods. The library offers features such as listing images and containers, creating and running containers, and accessing container logs. Aiodocker is designed to work seamlessly with Python's asyncio framework, making it suitable for building asynchronous Docker management applications.

herc.ai
Herc.ai is a powerful library for interacting with the Herc.ai API. It offers free access to users and supports all languages. Users can benefit from Herc.ai's features unlimitedly with a one-time subscription and API key. The tool provides functionalities for question answering and text-to-image generation, with support for various models and customization options. Herc.ai can be easily integrated into CLI, CommonJS, TypeScript, and supports beta models for advanced usage. Developed by FiveSoBes and Luppux Development.
aiohttp
aiohttp is an async http client/server framework that supports both client and server side of HTTP protocol. It also supports both client and server Web-Sockets out-of-the-box and avoids Callback Hell. aiohttp provides a Web-server with middleware and pluggable routing.
island-ai
island-ai is a TypeScript toolkit tailored for developers engaging with structured outputs from Large Language Models. It offers streamlined processes for handling, parsing, streaming, and leveraging AI-generated data across various applications. The toolkit includes packages like zod-stream for interfacing with LLM streams, stream-hooks for integrating streaming JSON data into React applications, and schema-stream for JSON streaming parsing based on Zod schemas. Additionally, related packages like @instructor-ai/instructor-js focus on data validation and retry mechanisms, enhancing the reliability of data processing workflows.
ddddocr
ddddocr is a Rust version of a simple OCR API server that provides easy deployment for captcha recognition without relying on the OpenCV library. It offers a user-friendly general-purpose captcha recognition Rust library. The tool supports recognizing various types of captchas, including single-line text, transparent black PNG images, target detection, and slider matching algorithms. Users can also import custom OCR training models and utilize the OCR API server for flexible OCR result control and range limitation. The tool is cross-platform and can be easily deployed.
bce-qianfan-sdk
The Qianfan SDK provides best practices for large model toolchains, allowing AI workflows and AI-native applications to access the Qianfan large model platform elegantly and conveniently. The core capabilities of the SDK include three parts: large model reasoning, large model training, and general and extension: * `Large model reasoning`: Implements interface encapsulation for reasoning of Yuyan (ERNIE-Bot) series, open source large models, etc., supporting dialogue, completion, Embedding, etc. * `Large model training`: Based on platform capabilities, it supports end-to-end large model training process, including training data, fine-tuning/pre-training, and model services. * `General and extension`: General capabilities include common AI development tools such as Prompt/Debug/Client. The extension capability is based on the characteristics of Qianfan to adapt to common middleware frameworks.
grps_trtllm
The grps-trtllm repository is a C++ implementation of a high-performance OpenAI LLM service, combining GRPS and TensorRT-LLM. It supports functionalities like Chat, Ai-agent, and Multi-modal. The repository offers advantages over triton-trtllm, including a complete LLM service implemented in pure C++, integrated tokenizer supporting huggingface and sentencepiece, custom HTTP functionality for OpenAI interface, support for different LLM prompt styles and result parsing styles, integration with tensorrt backend and opencv library for multi-modal LLM, and stable performance improvement compared to triton-trtllm.
plants_disease_detection
This repository contains code for the AI challenger competition on plant disease detection. The goal is to classify nearly 50,000 plant leaf photos into 61 categories based on 'species-disease-severity'. The framework used is Keras with TensorFlow backend, implementing DenseNet for image classification. Data is uploaded to a private dataset on Kaggle for model training. The code includes data preparation, model training, and prediction steps.
excel-spring-boot-starter
The excel-spring-boot-starter project is based on Easyexcel to implement reading and writing Excel files. EasyExcel is an open-source project for simple and memory-efficient reading and writing of Excel files in Java. It supports reading and writing Excel files up to 75M (46W rows 25 columns) in 1 minute with 64M memory, and there is a fast mode for even quicker performance but with slightly more memory consumption.
mediapipe-rs
MediaPipe-rs is a Rust library designed for MediaPipe tasks on WasmEdge WASI-NN. It offers easy-to-use low-code APIs similar to mediapipe-python, with low overhead and flexibility for custom media input. The library supports various tasks like object detection, image classification, gesture recognition, and more, including TfLite models, TF Hub models, and custom models. Users can create task instances, run sessions for pre-processing, inference, and post-processing, and speed up processing by reusing sessions. The library also provides support for audio tasks using audio data from symphonia, ffmpeg, or raw audio. Users can choose between CPU, GPU, or TPU devices for processing.

Janus
Janus is a series of unified multimodal understanding and generation models, including Janus-Pro, Janus, and JanusFlow. Janus-Pro is an advanced version that improves both multimodal understanding and visual generation significantly. Janus decouples visual encoding for unified multimodal understanding and generation, surpassing previous models. JanusFlow harmonizes autoregression and rectified flow for unified multimodal understanding and generation, achieving comparable or superior performance to specialized models. The models are available for download and usage, supporting a broad range of research in academic and commercial communities.
zenu
ZeNu is a high-performance deep learning framework implemented in pure Rust, featuring a pure Rust implementation for safety and performance, GPU performance comparable to PyTorch with CUDA support, a simple and intuitive API, and a modular design for easy extension. It supports various layers like Linear, Convolution 2D, LSTM, and optimizers such as SGD and Adam. ZeNu also provides device support for CPU and CUDA (NVIDIA GPU) with CUDA 12.3 and cuDNN 9. The project structure includes main library, automatic differentiation engine, neural network layers, matrix operations, optimization algorithms, CUDA implementation, and other support crates. Users can find detailed implementations like MNIST classification, CIFAR10 classification, and ResNet implementation in the examples directory. Contributions to ZeNu are welcome under the MIT License.
zig-aio
zig-aio is a library that provides an io_uring-like asynchronous API and coroutine-powered IO tasks for the Zig programming language. It offers support for different operating systems and backends, such as io_uring, iocp, and posix. The library aims to provide efficient IO operations by leveraging coroutines and async IO mechanisms. Users can create servers and clients with ease using the provided API functions for socket operations, sending and receiving data, and managing connections.
aiges
AIGES is a core component of the Athena Serving Framework, designed as a universal encapsulation tool for AI developers to deploy AI algorithm models and engines quickly. By integrating AIGES, you can deploy AI algorithm models and engines rapidly and host them on the Athena Serving Framework, utilizing supporting auxiliary systems for networking, distribution strategies, data processing, etc. The Athena Serving Framework aims to accelerate the cloud service of AI algorithm models and engines, providing multiple guarantees for cloud service stability through cloud-native architecture. You can efficiently and securely deploy, upgrade, scale, operate, and monitor models and engines without focusing on underlying infrastructure and service-related development, governance, and operations.
For similar tasks

TechFlow
TechFlow is a platform that allows users to build their own AI workflows through drag-and-drop functionality. It features a visually appealing interface with clear layout and intuitive navigation. TechFlow supports multiple models beyond Language Models (LLM) and offers flexible integration capabilities. It provides a powerful SDK for developers to easily integrate generated workflows into existing systems, enhancing flexibility and scalability. The platform aims to embed AI capabilities as modules into existing functionalities to enhance business competitiveness.
ai-app
The 'ai-app' repository is a comprehensive collection of tools and resources related to artificial intelligence, focusing on topics such as server environment setup, PyCharm and Anaconda installation, large model deployment and training, Transformer principles, RAG technology, vector databases, AI image, voice, and music generation, and AI Agent frameworks. It also includes practical guides and tutorials on implementing various AI applications. The repository serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in exploring different aspects of AI technology.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.