
TTS-WebUI
A single Gradio + React WebUI with extensions for ACE-Step, Kimi Audio, Piper TTS, GPT-SoVITS, CosyVoice, XTTSv2, DIA, Kokoro, OpenVoice, ParlerTTS, Stable Audio, MMS, StyleTTS2, MAGNet, AudioGen, MusicGen, Tortoise, RVC, Vocos, Demucs, SeamlessM4T, and Bark!
Stars: 2533
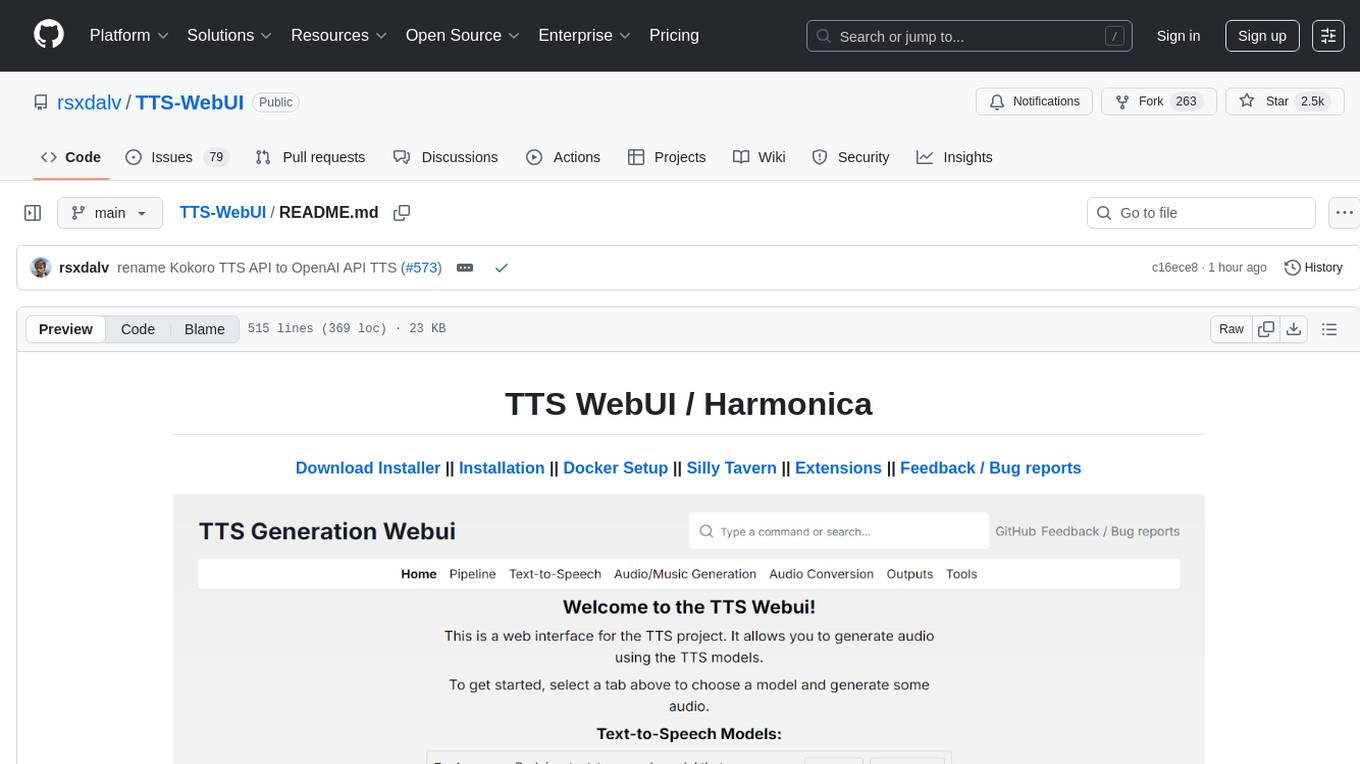
TTS WebUI is a comprehensive tool for text-to-speech synthesis, audio/music generation, and audio conversion. It offers a user-friendly interface for various AI projects related to voice and audio processing. The tool provides a range of models and extensions for different tasks, along with integrations like Silly Tavern and OpenWebUI. With support for Docker setup and compatibility with Linux and Windows, TTS WebUI aims to facilitate creative and responsible use of AI technologies in a user-friendly manner.
README:
Download Installer || Installation || Docker Setup || Silly Tavern || Extensions || Feedback / Bug reports
 |
 |
 |
|---|
.png) |
.png) |
.png) |
|---|
.png) |
.png) |
.png) |
|---|
September:
- OpenAI API now supports Whisper transcriptions
- Removed PyTorch Nightly option
- Fix Google Colab installation (Python 3.12 not supported)
- Add Kitten TTS Mini extension
- Add PyRNNoise extension
- Upgrade React UI's Chatterbox interface
August:
- Fix model downloader when no token is used, thanks Nusantara.
- Improve Chatterbox speed
- Add VibeVoice (Early Access) extension
- Add docker compose volumes to persist data #529, thanks FranckKe.
- [react-ui] Prepend voices/chatterbox to voice file selection in ap test page #542, thanks rohan-sircar.
- Add new tutorials
- Add more robust gradio launching
- Simplify installation instructions
- Improve chatterbox speed.
June 26:
- Fix React UI file size limit of 4MB, now 50MB. Thanks https://github.com/SuperFurias ! (#446)
June 20:
- Upgrade Chatterbox to enable compilation for 2-4x speedup.
- Fix React UI build errors.
- Add 'auto start' option to OpenAI-API.
June 10:
- Patch eslint warnings during build.
- Fix extension_cuda_toolkit definition.
June 9:
- Add CUDA Toolkit extension.
- Hotfix for PyTorch 2.7.0 nightly.
- Update Docker to 2.7.0
June 8:
- Fix decorators for generation.
- Refactor server.py code.
- Hotfix for docker, thanks https://github.com/chrislawso for reporting.
June 7:
- Chatterbox upgrade for streaming.
June 6:
- Update DIA Extension for Float16 support.
- Improve decorators for streaming usage.
June 4:
- Attempt dockerfile fix.
- Add interactivity to model unloading button, improve Gradio random seed UI.
- Add sample voices.
June 1:
- Add presets API.
- Add API Preset config to React UI.
May 31:
- Improve React UI Audio player.
- Fix ROCm installation version.
May 30:
- Make OpenAI API extension installed by default (extension_kokoro_tts_api).
- Add Favicon.
- Fix OpenVoice v2 extension.
- Improve UI layout for StyleTTS2, MahaTTS, Vall-E-X, Parler TTS
May 29:
- Add Chatterbox extension.
- Add Kokoro TTS to React UI.
- Fix React Build, thanks noaht8um!
May 28:
- Restore gr.Tabs to the old style for easier stacking of many tabs.
- Integrate custom IconButton.
- Fix Gradio's output tab display
- Add tutorial section
May 27:
- Include gradio==5.5.0 in each installation of extensions. While this might cause some extensions to fail to install, it should prevent extensions from breaking the UI. Please report extensions that fail to install. Thanks to cwlowden for debugging this issue.
- Make XTTS-RVC-UI an unrecommended extension.
May 26:
- Add fixes for decorators to work with non-'text' inputs.
- Clean up .env generator and remove the Bark environment variables from settings.
- Add Audio book extension definitions for future use (extensions not available yet).
- Fix SeamlessM4T Audio to Audio tab.
- Update ACE-Step extension.
- Improve Kokoro TTS API.
May 14:
- Prepare for Python 3.11 and 3.12 support.
May 12:
- Fix deepspeed for Windows. Thank you for the reports!
- Improve decorator extensions for future API.
- Improve Kokoro TTS API for OpenAI compatibility, now usable with SillyTavern.
- Add setup.py for future pip installs. Sync versions.json with setup.py and package.json.
- Remove deprecated requirements_* files.
- Removed Windows deepspeed until it no longer requires NVCC, thank you https://github.com/lcmiracle for extensive debugging and testing.
May 10:
- Fix missing directory bug causing extensions to fail to load. Thanks Discord/Comstock for discovery of the bug.
- Add ACE-Step to React UI.
- Add emoji to Gradio UI categories for simplicity.
- Add enhanced logging for every update and app startup, allowing for easier debugging once issues happen.
- Show gr.Info when models are being loaded or unloaded.
- Allow users to use React UI together with Gradio auth by specifying GRADIO_AUTH="username:pass" environment variable.
May 7:
May 6:
- Add Kimi Audio 7B Instruct extension
- Fix React-Gradio file proxy missing slash
- Add Kokoro TTS API extension
Apr 25:
- Add OpenVoice V2 extension
Apr 24:
- Add OpenVoice V1 extension
Apr 23:
- Deprecate requirements_* files using direct extension installation instead.
- Add proxy for gradio files in React UI.
- Added DIA extension.
Apr 22:
- Allow newer versions of pip
- Remove PyTorch's +cpu for Apple M Series Chip
- Installer fixes - fix CUDA repair, CRLF, warn about GCC, terminate if pip fails.
Apr 20:
- Fix install/uninstall in extension manager
- Add Kokoro TTS extension
Apr 18:
- Fix extension manager startup
- Convert most models to extensions, install the classic ones by default
- Attempt to fix linux installer
- Add 'recommended' flag for extensions
Apr 17:
- Create extension manager
- Warn Windows users if conda is installed
- upgrade dockerfile to PyTorch 2.6.0
Apr 12:
- Upgrade to PyTorch 2.6.0 Cuda 12.4, switch to pip for pytorch install
- Add compatibility layer for older models
- Fix StyleTTS2 missing nlkt downloader
- Reorder TTS tabs
- Allow disabled extensions to be configured in config.json
- Remove PyTorch CPU via pip option, redundant
- Move all core conda packages to init_mamba scripts.
- Upgrade the installer to include a web-based UI
- Add conda storage optimizer extension
- Hotfix: New init_app bug that caused the installer to freeze
Apr 11:
- Add AP BWE upscaling extension
Apr 02:
- Fix pydantic (#465, #468)
- Add --no-react --no-database advanced flags
- Add a fix to avoid directory errors on the very first React UI build (#466)
Mar 21:
- Add CosyVoice extension [Unstable] and GPT-SoVITS [Alpha] extension
Mar 20:
- Add executable macOS script for double-click launching
- Add unstable CosyVoice extension
Mar 18:
- Remove old rvc files
- Fix missing torchfcpe dependency for RVC
Mar 17:
- Upgrade Google Colab to PyTorch 2.6.0, add Conda to downgrade Python to 3.10
- No longer abort when the automatic update fails to fetch the new code (Improving offline support #457)
- Upgrade Tortoise to v3.0.1 for transformers 4.49.0 #454
- Prevent running in Windows/System32 folder #459
Feb 15:
- Fix Stable Audio to match the new version
Feb 14:
- Pin accelerate>=0.33.0 project wide
- Add basic Seamless M4T quantization code
Feb 13:
- Fix Stable Audio and Seamless M4T incompatibility
- Make Seamless M4T automatically use CUDA if available, otherwise CPU
Feb 10:
- Improve installation instructions in README
Click to expand
See the 2024 Changelog for a detailed list of changes in 2024.
Click to expand
See the 2023 Changelog for a detailed list of changes in 2023.
Extensions are available to install from the webui itself, or using React UI. They can also be installed using the extension manager. Internally, extensions are just python packages that are installed using pip. Multiple extensions can be installed at the same time, but there might be compatibility issues between them. After installing or updating an extension, you need to restart the app to load it.
Updates need to be done manually by using the mini-control panel:
-
Update OpenAI TTS API extension to latest version
-
Start the API and test it with Python Requests
(OpenAI client might not be installed thus the Test with Python OpenAI client might fail)
-
Once you can see the audio generates successfully, go to Silly Tavern, and add a new TTS API Default provider endpoint:
http://localhost:7778/v1/audio/speech
-
Test it out!
- Install https://github.com/rsxdalv/text-to-tts-webui extension in text-generation-webui
- Start the API and test it with Python Requests
- Configure using the panel:

- Enable OpenAI API extension in TTS WebUI
- Start the API and test it with Python Requests
- Once you can see the audio generates successfully, go to OpenWebUI, and add a new TTS API
Default provider endpoint:
http://localhost:7778/v1/audio/speech - Test it out!

Using the instructions above, you can install an OpenAI compatible API, and use it with Silly Tavern or other OpenAI compatible clients.
Current base installation size is around 10.7 GB. Each model will require 2-8 GB of space in addition.
- Download the latest version and extract it.
- Run start_tts_webui.bat or start_tts_webui.sh to start the server. It will ask you to select the GPU/Chip you are using. Once everything has installed, it will start the Gradio server at http://localhost:7770 and the React UI at http://localhost:3000.
- Output log will be available in the installer_scripts/output.log file.
- Note: The start script sets up a conda environment and a python virtual environment. Thus you don't need to make a venv before that, and in fact, launching from another venv might break this script.
For detailed manual installation instructions, please refer to the Manual Installation Guide.
tts-webui can also be ran inside of a Docker container. Using CUDA inside of docker requires (NVIDIA Container Toolkit)[https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/latest/install-guide.html]. To get started, pull the image from GitHub Container Registry:
docker pull ghcr.io/rsxdalv/tts-webui:main
Once the image has been pulled it can be started with Docker Compose: The ports are 7770 (env:TTS_PORT) for the Gradio backend and 3000 (env:UI_PORT) for the React front end.
docker compose up -d
The container will take some time to generate the first output while models are downloaded in the background. The status of this download can be verified by checking the container logs:
docker logs tts-webui
If you wish to build your own docker container, you can use the included Dockerfile:
docker build -t tts-webui .
Please note that the docker-compose needs to be edited to use the image you just built.
Audiocraft is currently only compatible with Linux and Windows. MacOS support still has not arrived, although it might be possible to install manually.
Due to the python package manager (pip) limitations, torch can get reinstalled several times. This is a wide ranging issue of pip and torch.
These messages:
---- requires ----, but you have ---- which is incompatible.
Are completely normal. It's both a limitation of pip and because this Web UI combines a lot of different AI projects together. Since the projects are not always compatible with each other, they will complain about the other projects being installed. This is normal and expected. And in the end, despite the warnings/errors the projects will work together. It's not clear if this situation will ever be resolvable, but that is the hope.
https://github.com/rsxdalv/tts-webui/discussions/186#discussioncomment-7291274
This project utilizes the following open source libraries:
-
suno-ai/bark - MIT License
- Description: Inference code for Bark model.
- Repository: suno/bark
-
tortoise-tts - Apache-2.0 License
- Description: A flexible text-to-speech synthesis library for various platforms.
- Repository: neonbjb/tortoise-tts
-
ffmpeg - LGPL License
- Description: A complete and cross-platform solution for video and audio processing.
- Repository: FFmpeg
- Use: Encoding Vorbis Ogg files
-
ffmpeg-python - Apache 2.0 License
- Description: Python bindings for FFmpeg library for handling multimedia files.
- Repository: kkroening/ffmpeg-python
-
audiocraft - MIT License
- Description: A library for audio generation and MusicGen.
- Repository: facebookresearch/audiocraft
-
vocos - MIT License
- Description: An improved decoder for encodec samples
- Repository: charactr-platform/vocos
-
RVC - MIT License
- Description: An easy-to-use Voice Conversion framework based on VITS.
- Repository: RVC-Project/Retrieval-based-Voice-Conversion-WebUI
This technology is intended for enablement and creativity, not for harm.
By engaging with this AI model, you acknowledge and agree to abide by these guidelines, employing the AI model in a responsible, ethical, and legal manner.
- Non-Malicious Intent: Do not use this AI model for malicious, harmful, or unlawful activities. It should only be used for lawful and ethical purposes that promote positive engagement, knowledge sharing, and constructive conversations.
- No Impersonation: Do not use this AI model to impersonate or misrepresent yourself as someone else, including individuals, organizations, or entities. It should not be used to deceive, defraud, or manipulate others.
- No Fraudulent Activities: This AI model must not be used for fraudulent purposes, such as financial scams, phishing attempts, or any form of deceitful practices aimed at acquiring sensitive information, monetary gain, or unauthorized access to systems.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure that your use of this AI model complies with applicable laws, regulations, and policies regarding AI usage, data protection, privacy, intellectual property, and any other relevant legal obligations in your jurisdiction.
- Acknowledgement: By engaging with this AI model, you acknowledge and agree to abide by these guidelines, using the AI model in a responsible, ethical, and legal manner.
The codebase is licensed under MIT. However, it's important to note that when installing the dependencies, you will also be subject to their respective licenses. Although most of these licenses are permissive, there may be some that are not. Therefore, it's essential to understand that the permissive license only applies to the codebase itself, not the entire project.
That being said, the goal is to maintain MIT compatibility throughout the project. If you come across a dependency that is not compatible with the MIT license, please feel free to open an issue and bring it to our attention.
Known non-permissive dependencies:
| Library | License | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| encodec | CC BY-NC 4.0 | Newer versions are MIT, but need to be installed manually |
| diffq | CC BY-NC 4.0 | Optional in the future, not necessary to run, can be uninstalled, should be updated with demucs |
| lameenc | GPL License | Future versions will make it LGPL, but need to be installed manually |
| unidecode | GPL License | Not mission critical, can be replaced with another library, issue: https://github.com/neonbjb/tortoise-tts/issues/494 |
Model weights have different licenses, please pay attention to the license of the model you are using.
Most notably:
- Bark: MIT
- Tortoise: Unknown (Apache-2.0 according to repo, but no license file in HuggingFace)
- MusicGen: CC BY-NC 4.0
- AudioGen: CC BY-NC 4.0
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TTS-WebUI
Similar Open Source Tools

TTS-WebUI
TTS WebUI is a comprehensive tool for text-to-speech synthesis, audio/music generation, and audio conversion. It offers a user-friendly interface for various AI projects related to voice and audio processing. The tool provides a range of models and extensions for different tasks, along with integrations like Silly Tavern and OpenWebUI. With support for Docker setup and compatibility with Linux and Windows, TTS WebUI aims to facilitate creative and responsible use of AI technologies in a user-friendly manner.
Open-Interface
Open Interface is a self-driving software that automates computer tasks by sending user requests to a language model backend (e.g., GPT-4V) and simulating keyboard and mouse inputs to execute the steps. It course-corrects by sending current screenshots to the language models. The tool supports MacOS, Linux, and Windows, and requires setting up the OpenAI API key for access to GPT-4V. It can automate tasks like creating meal plans, setting up custom language model backends, and more. Open Interface is currently not efficient in accurate spatial reasoning, tracking itself in tabular contexts, and navigating complex GUI-rich applications. Future improvements aim to enhance the tool's capabilities with better models trained on video walkthroughs. The tool is cost-effective, with user requests priced between $0.05 - $0.20, and offers features like interrupting the app and primary display visibility in multi-monitor setups.
MaxKB
MaxKB is a knowledge base Q&A system based on the LLM large language model. MaxKB = Max Knowledge Base, which aims to become the most powerful brain of the enterprise.

anx-reader
Anx Reader is a meticulously designed e-book reader tailored for book enthusiasts. It boasts powerful AI functionalities and supports various e-book formats, enhancing the reading experience. With a modern interface, the tool aims to provide a seamless and enjoyable reading journey. It offers rich format support, seamless sync across devices, smart AI assistance, personalized reading experiences, professional reading analytics, a powerful note system, practical tools, and cross-platform support. The tool is continuously evolving with features like UI adaptation for tablets, page-turning animation, TTS voice reading, reading fonts, translation, and more in the pipeline.
palico-ai
Palico AI is a tech stack designed for rapid iteration of LLM applications. It allows users to preview changes instantly, improve performance through experiments, debug issues with logs and tracing, deploy applications behind a REST API, and manage applications with a UI control panel. Users have complete flexibility in building their applications with Palico, integrating with various tools and libraries. The tool enables users to swap models, prompts, and logic easily using AppConfig. It also facilitates performance improvement through experiments and provides options for deploying applications to cloud providers or using managed hosting. Contributions to the project are welcomed, with easy ways to get involved by picking issues labeled as 'good first issue'.
lemonade
Lemonade is a tool that helps users run local Large Language Models (LLMs) with high performance by configuring state-of-the-art inference engines for their Neural Processing Units (NPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). It is used by startups, research teams, and large companies to run LLMs efficiently. Lemonade provides a high-level Python API for direct integration of LLMs into Python applications and a CLI for mixing and matching LLMs with various features like prompting templates, accuracy testing, performance benchmarking, and memory profiling. The tool supports both GGUF and ONNX models and allows importing custom models from Hugging Face using the Model Manager. Lemonade is designed to be easy to use and switch between different configurations at runtime, making it a versatile tool for running LLMs locally.
computer
Cua is a tool for creating and running high-performance macOS and Linux VMs on Apple Silicon, with built-in support for AI agents. It provides libraries like Lume for running VMs with near-native performance, Computer for interacting with sandboxes, and Agent for running agentic workflows. Users can refer to the documentation for onboarding and explore demos showcasing the tool's capabilities. Additionally, accessory libraries like Core, PyLume, Computer Server, and SOM offer additional functionality. Contributions to Cua are welcome, and the tool is open-sourced under the MIT License.
cocoindex
CocoIndex is the world's first open-source engine that supports both custom transformation logic and incremental updates specialized for data indexing. Users declare the transformation, CocoIndex creates & maintains an index, and keeps the derived index up to date based on source update, with minimal computation and changes. It provides a Python library for data indexing with features like text embedding, code embedding, PDF parsing, and more. The tool is designed to simplify the process of indexing data for semantic search and structured information extraction.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.
cognee
Cognee is an open-source framework designed for creating self-improving deterministic outputs for Large Language Models (LLMs) using graphs, LLMs, and vector retrieval. It provides a platform for AI engineers to enhance their models and generate more accurate results. Users can leverage Cognee to add new information, utilize LLMs for knowledge creation, and query the system for relevant knowledge. The tool supports various LLM providers and offers flexibility in adding different data types, such as text files or directories. Cognee aims to streamline the process of working with LLMs and improving AI models for better performance and efficiency.
big-AGI
big-AGI is an AI suite designed for professionals seeking function, form, simplicity, and speed. It offers best-in-class Chats, Beams, and Calls with AI personas, visualizations, coding, drawing, side-by-side chatting, and more, all wrapped in a polished UX. The tool is powered by the latest models from 12 vendors and open-source servers, providing users with advanced AI capabilities and a seamless user experience. With continuous updates and enhancements, big-AGI aims to stay ahead of the curve in the AI landscape, catering to the needs of both developers and AI enthusiasts.

openrl
OpenRL is an open-source general reinforcement learning research framework that supports training for various tasks such as single-agent, multi-agent, offline RL, self-play, and natural language. Developed based on PyTorch, the goal of OpenRL is to provide a simple-to-use, flexible, efficient and sustainable platform for the reinforcement learning research community. It supports a universal interface for all tasks/environments, single-agent and multi-agent tasks, offline RL training with expert dataset, self-play training, reinforcement learning training for natural language tasks, DeepSpeed, Arena for evaluation, importing models and datasets from Hugging Face, user-defined environments, models, and datasets, gymnasium environments, callbacks, visualization tools, unit testing, and code coverage testing. It also supports various algorithms like PPO, DQN, SAC, and environments like Gymnasium, MuJoCo, Atari, and more.

deepchat
DeepChat is a versatile chat tool that supports multiple model cloud services and local model deployment. It offers multi-channel chat concurrency support, platform compatibility, complete Markdown rendering, and easy usability with a comprehensive guide. The tool aims to enhance chat experiences by leveraging various AI models and ensuring efficient conversation management.

postiz-app
Postiz is an ultimate AI social media scheduling tool that offers everything you need to manage your social media posts, build an audience, capture leads, and grow your business. It allows you to schedule posts with AI features, measure work with analytics, collaborate with team members, and invite others to comment and schedule posts. The tech stack includes NX (Monorepo), NextJS (React), NestJS, Prisma, Redis, and Resend for email notifications.
autoflow
AutoFlow is an open source graph rag based knowledge base tool built on top of TiDB Vector and LlamaIndex and DSPy. It features a Perplexity-style Conversational Search page and an Embeddable JavaScript Snippet for easy integration into websites. The tool allows for comprehensive coverage and streamlined search processes through sitemap URL scraping.

axolotl
Axolotl is a lightweight and efficient tool for managing and analyzing large datasets. It provides a user-friendly interface for data manipulation, visualization, and statistical analysis. With Axolotl, users can easily import, clean, and explore data to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. The tool supports various data formats and offers a wide range of functions for data processing and modeling. Whether you are a data scientist, researcher, or business analyst, Axolotl can help streamline your data workflows and enhance your data analysis capabilities.
For similar tasks

nodejs-whisper
Node.js bindings for OpenAI's Whisper model that automatically converts audio to WAV format with a 16000 Hz frequency to support the whisper model. It outputs transcripts to various formats, is optimized for CPU including Apple Silicon ARM, provides timestamp precision to single word, allows splitting on word rather than token, translation from source language to English, and conversion of audio format to WAV for whisper model support.

TTS-WebUI
TTS WebUI is a comprehensive tool for text-to-speech synthesis, audio/music generation, and audio conversion. It offers a user-friendly interface for various AI projects related to voice and audio processing. The tool provides a range of models and extensions for different tasks, along with integrations like Silly Tavern and OpenWebUI. With support for Docker setup and compatibility with Linux and Windows, TTS WebUI aims to facilitate creative and responsible use of AI technologies in a user-friendly manner.
Awesome-AITools
This repo collects AI-related utilities. ## All Categories * All Categories * ChatGPT and other closed-source LLMs * AI Search engine * Open Source LLMs * GPT/LLMs Applications * LLM training platform * Applications that integrate multiple LLMs * AI Agent * Writing * Programming Development * Translation * AI Conversation or AI Voice Conversation * Image Creation * Speech Recognition * Text To Speech * Voice Processing * AI generated music or sound effects * Speech translation * Video Creation * Video Content Summary * OCR(Optical Character Recognition)
NSMusicS
NSMusicS is a local music software that is expected to support multiple platforms with AI capabilities and multimodal features. The goal of NSMusicS is to integrate various functions (such as artificial intelligence, streaming, music library management, cross platform, etc.), which can be understood as similar to Navidrome but with more features than Navidrome. It wants to become a plugin integrated application that can almost have all music functions.
biniou
biniou is a self-hosted webui for various GenAI (generative artificial intelligence) tasks. It allows users to generate multimedia content using AI models and chatbots on their own computer, even without a dedicated GPU. The tool can work offline once deployed and required models are downloaded. It offers a wide range of features for text, image, audio, video, and 3D object generation and modification. Users can easily manage the tool through a control panel within the webui, with support for various operating systems and CUDA optimization. biniou is powered by Huggingface and Gradio, providing a cross-platform solution for AI content generation.
generative-ai-js
Generative AI JS is a JavaScript library that provides tools for creating generative art and music using artificial intelligence techniques. It allows users to generate unique and creative content by leveraging machine learning models. The library includes functions for generating images, music, and text based on user input and preferences. With Generative AI JS, users can explore the intersection of art and technology, experiment with different creative processes, and create dynamic and interactive content for various applications.
pictureChange
The 'pictureChange' repository is a plugin that supports image processing using Baidu AI, stable diffusion webui, and suno music composition AI. It also allows for file summarization and image summarization using AI. The plugin supports various stable diffusion models, administrator control over group chat features, concurrent control, and custom templates for image and text generation. It can be deployed on WeChat enterprise accounts, personal accounts, and public accounts.
Generative-AI-Indepth-Basic-to-Advance
Generative AI Indepth Basic to Advance is a repository focused on providing tutorials and resources related to generative artificial intelligence. The repository covers a wide range of topics from basic concepts to advanced techniques in the field of generative AI. Users can find detailed explanations, code examples, and practical demonstrations to help them understand and implement generative AI algorithms. The goal of this repository is to help beginners get started with generative AI and to provide valuable insights for more experienced practitioners.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.






