
WebDreamer
"Is Your LLM Secretly a World Model of the Internet? Model-Based Planning for Web Agents"
Stars: 82
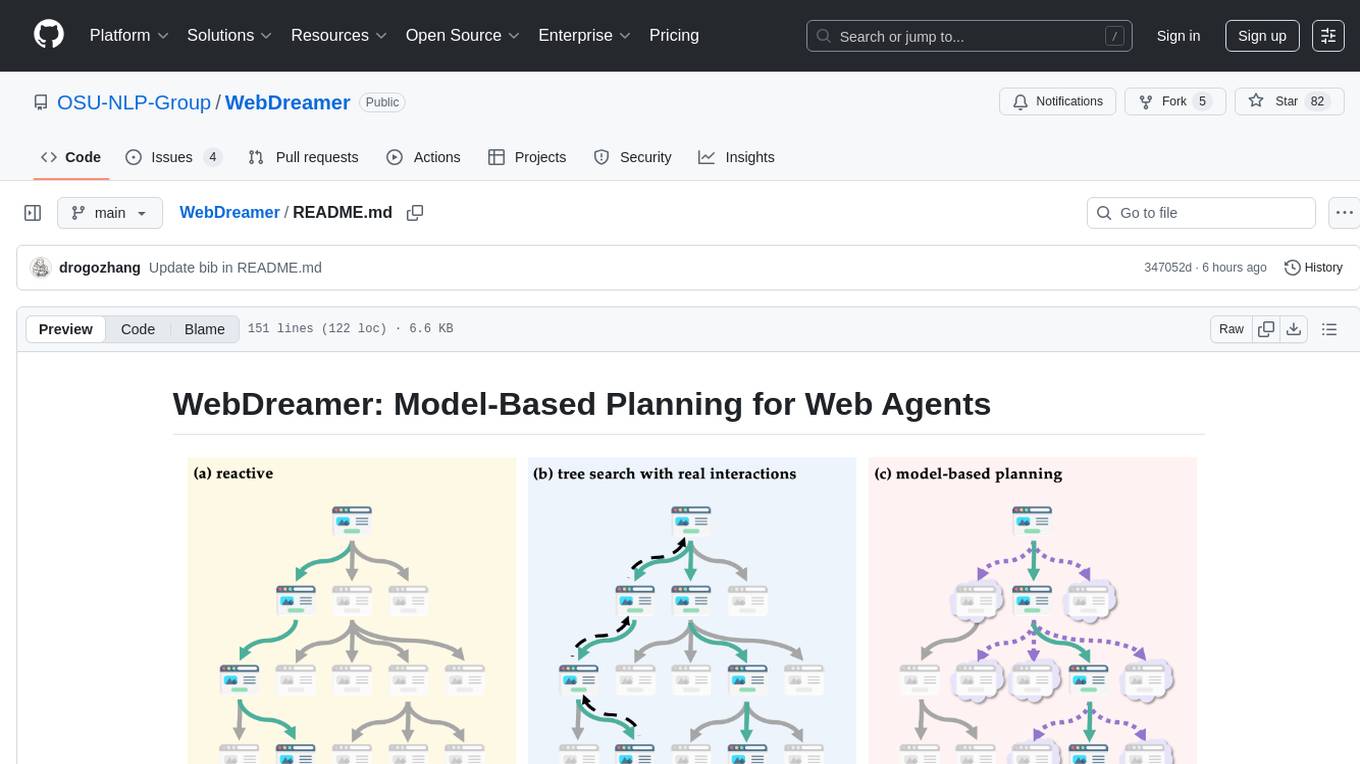
WebDreamer is a model-based planning tool for web agents that uses large language models (LLMs) as a world model of the internet to predict outcomes of actions on websites. It employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, offering greater safety and flexibility compared to traditional tree search methods. The tool provides modules for world model prediction, simulation scoring, and controller actions, enabling users to interact with web pages and achieve specific goals through simulated actions.
README:
- [x] Release world model training data
- [x] Release checkpoints
This repo contains the code for our paper Is Your LLM Secretly a World Model of the Internet? Model-Based Planning for Web Agents.
Our paper tackles the critical question: “How to scale inference-time compute for language agents?” The solution lies in using LLMs as a world model of the internet to predict the outcomes of actions on websites. Our method, WebDreamer, employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, surpassing reactive baselines while offering greater safety and flexibility compared to tree search methods. All resources (including training data and resulting models) are available at HF Collection.
| Benchmark | Method | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| VisualWebArena | GPT-4o + Reactive | 17.6% |
| GPT-4o + Tree Search | 26.2% | |
| GPT-4o + WebDreamer | 23.6% (↑34.1%) | |
| Online-Mind2Web | GPT-4o + Reactive | 26.0% |
| GPT-4o + WebDreamer | 37.0% (↑42.3%) | |
| Mind2Web-live | GPT-4o + Reactive | 20.2% |
| GPT-4o + WebDreamer | 25.0% (↑23.8%) |
Compared to the reactive baselines, WebDreamer significantly improves performance by 34.1%, 42.3%, and 23.8% on VisualWebArena, Online-Mind2Web, and Mind2Web-live, respectively.
WebDreamer effectively explores the search space through simulations, which largely reduces the reliance on real-world interactions while maintaining robust performance.
main: Different modules of WebDreamer that can be played with independently.
vwa: Code to reproduce our experiments on VisualWebArena. 🚧
mind2web-live: Code to reproduce our experiments on Mind2Web-live. 🚧
The world model module predicts webpage changes in multiple format (change description, a11y tree, html).
world_model = WebWorldModel(OpenAI(api_key=os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]))
screenshot_path = "demo_data/shopping_0.png"
screenshot = encode_image(screenshot_path)
screenshot = "data:image/jpeg;base64," + screenshot
action_description = "type 'red blanket' in the search bar and click search"
task = "Buy the least expensive red blanket (in any size) from 'Blankets & Throws' category."
imagination = world_model.multiple_step_change_prediction(screenshot, screenshot_path, task,
action_description,
format='accessibility', k=3)- screenshot_path: Path to the screenshot of the webpage.
- task: Description of the goal to achieve on the webpage.
- action_description: Initial action to perform.
- format: Desired output format for webpage state changes:
- 'change' for textual descriptions.
- 'accessibility' for an accessibility tree structure.
- 'html' for HTML structure of the predicted page.
- k: Number of imagination steps to simulate.
screenshot_path = "demo_data/shopping_0.png"
screenshots = [Image.open(screenshot_path)]
actions = ["None"]
action_description_list = [
"type 'red blanket' in the search bar",
"click the element Home & Kitchen",
"type 'kobe' in the search bar",
"type 'the ohio state university' in the search bar"
]
task = "Buy the least expensive red blanket (in any size)"
scores, simulations = evaluate_simulation(
screenshots,
actions,
task,
"https://www.amazon.com",
action_description_list,
num_of_sim=3,
num_workers=50,
n=10,
steps=2
)- screenshots: List of PIL.Image screenshots representing webpage states.
- actions: List of actions performed by the agent.
- task: Description of the goal to achieve on the webpage.
- url: The current webpage URL.
- action_description_list: List of action descriptions to evaluate.
- num_of_sim: Number of simulations per action.
- steps: Number of imagination steps per simulation.
- num_workers: Number of parallel workers for simulations.
screenshot_path = "demo_data/shopping_0.png"
screenshots = [Image.open(screenshot_path)]
actions = ["None"] # previous actions so far
action_description = "type 'red skirt' in the search bar"
task = "Buy the least expensive red skirt (in any size) on Amazon."
action_description_list = [
"type 'red skirt' in the search bar",
"click the element Women Clothes",
"type 'kobe' in the search bar",
"type 'the ohio state university' in the search bar"
]
random.shuffle(action_description_list)
selected_actions = select_actions(screenshots, actions, task, "https://www.amazon.com", action_description_list)
# Map selected indices back to action descriptions
selected_actions = [action_description_list[int(i)] for i in selected_actions]- screenshots: List of PIL.Image screenshots representing webpage states.
- actions: List of previously executed actions.
- task: Description of the goal to achieve on the webpage.
- url: The current webpage URL.
- action_description_list: List of action descriptions to evaluate.
We released Dreamer-7B and its VWA in-domain continue trained variants (https://huggingface.co/osunlp/Dreamer-7B). Please note that current Dreamer-7B only supports image (w/ or w/o SoM) observation space.
@article{Gu2024WebDreamer,
author = {Yu Gu and Kai Zhang and Yuting Ning and Boyuan Zheng and Boyu Gou and Tianci Xue and Cheng Chang and Sanjari Srivastava and Yanan Xie and Peng Qi and Huan Sun and Yu Su},
title = {Is Your LLM Secretly a World Model of the Internet? Model-Based Planning for Web Agents},
journal = {Transactions on Machine Learning Research},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for WebDreamer
Similar Open Source Tools

WebDreamer
WebDreamer is a model-based planning tool for web agents that uses large language models (LLMs) as a world model of the internet to predict outcomes of actions on websites. It employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, offering greater safety and flexibility compared to traditional tree search methods. The tool provides modules for world model prediction, simulation scoring, and controller actions, enabling users to interact with web pages and achieve specific goals through simulated actions.

CodeGeeX4
CodeGeeX4-ALL-9B is an open-source multilingual code generation model based on GLM-4-9B, offering enhanced code generation capabilities. It supports functions like code completion, code interpreter, web search, function call, and repository-level code Q&A. The model has competitive performance on benchmarks like BigCodeBench and NaturalCodeBench, outperforming larger models in terms of speed and performance.
SynapseML
SynapseML (previously known as MMLSpark) is an open-source library that simplifies the creation of massively scalable machine learning (ML) pipelines. It provides simple, composable, and distributed APIs for various machine learning tasks such as text analytics, vision, anomaly detection, and more. Built on Apache Spark, SynapseML allows seamless integration of models into existing workflows. It supports training and evaluation on single-node, multi-node, and resizable clusters, enabling scalability without resource wastage. Compatible with Python, R, Scala, Java, and .NET, SynapseML abstracts over different data sources for easy experimentation. Requires Scala 2.12, Spark 3.4+, and Python 3.8+.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.
ai-chunking
AI Chunking is a powerful Python library for semantic document chunking and enrichment using AI. It provides intelligent document chunking capabilities with various strategies to split text while preserving semantic meaning, particularly useful for processing markdown documentation. The library offers multiple chunking strategies such as Recursive Text Splitting, Section-based Semantic Chunking, and Base Chunking. Users can configure chunk sizes, overlap, and support various text formats. The tool is easy to extend with custom chunking strategies, making it versatile for different document processing needs.
PhoGPT
PhoGPT is an open-source 4B-parameter generative model series for Vietnamese, including the base pre-trained monolingual model PhoGPT-4B and its chat variant, PhoGPT-4B-Chat. PhoGPT-4B is pre-trained from scratch on a Vietnamese corpus of 102B tokens, with an 8192 context length and a vocabulary of 20K token types. PhoGPT-4B-Chat is fine-tuned on instructional prompts and conversations, demonstrating superior performance. Users can run the model with inference engines like vLLM and Text Generation Inference, and fine-tune it using llm-foundry. However, PhoGPT has limitations in reasoning, coding, and mathematics tasks, and may generate harmful or biased responses.
CrackSQL
CrackSQL is a powerful SQL dialect translation tool that integrates rule-based strategies with large language models (LLMs) for high accuracy. It enables seamless conversion between dialects (e.g., PostgreSQL → MySQL) with flexible access through Python API, command line, and web interface. The tool supports extensive dialect compatibility, precision & advanced processing, and versatile access & integration. It offers three modes for dialect translation and demonstrates high translation accuracy over collected benchmarks. Users can deploy CrackSQL using PyPI package installation or source code installation methods. The tool can be extended to support additional syntax, new dialects, and improve translation efficiency. The project is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community.
effective_llm_alignment
This is a super customizable, concise, user-friendly, and efficient toolkit for training and aligning LLMs. It provides support for various methods such as SFT, Distillation, DPO, ORPO, CPO, SimPO, SMPO, Non-pair Reward Modeling, Special prompts basket format, Rejection Sampling, Scoring using RM, Effective FAISS Map-Reduce Deduplication, LLM scoring using RM, NER, CLIP, Classification, and STS. The toolkit offers key libraries like PyTorch, Transformers, TRL, Accelerate, FSDP, DeepSpeed, and tools for result logging with wandb or clearml. It allows mixing datasets, generation and logging in wandb/clearml, vLLM batched generation, and aligns models using the SMPO method.
notte
Notte is a web browser designed specifically for LLM agents, providing a language-first web navigation experience without the need for DOM/HTML parsing. It transforms websites into structured, navigable maps described in natural language, enabling users to interact with the web using natural language commands. By simplifying browser complexity, Notte allows LLM policies to focus on conversational reasoning and planning, reducing token usage, costs, and latency. The tool supports various language model providers and offers a reinforcement learning style action space and controls for full navigation control.
GraphRAG-SDK
Build fast and accurate GenAI applications with GraphRAG SDK, a specialized toolkit for building Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) systems. It integrates knowledge graphs, ontology management, and state-of-the-art LLMs to deliver accurate, efficient, and customizable RAG workflows. The SDK simplifies the development process by automating ontology creation, knowledge graph agent creation, and query handling, enabling users to interact and query their knowledge graphs effectively. It supports multi-agent systems and orchestrates agents specialized in different domains. The SDK is optimized for FalkorDB, ensuring high performance and scalability for large-scale applications. By leveraging knowledge graphs, it enables semantic relationships and ontology-driven queries that go beyond standard vector similarity, enhancing retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
MarkLLM
MarkLLM is an open-source toolkit designed for watermarking technologies within large language models (LLMs). It simplifies access, understanding, and assessment of watermarking technologies, supporting various algorithms, visualization tools, and evaluation modules. The toolkit aids researchers and the community in ensuring the authenticity and origin of machine-generated text.
lionagi
LionAGI is a powerful intelligent workflow automation framework that introduces advanced ML models into any existing workflows and data infrastructure. It can interact with almost any model, run interactions in parallel for most models, produce structured pydantic outputs with flexible usage, automate workflow via graph based agents, use advanced prompting techniques, and more. LionAGI aims to provide a centralized agent-managed framework for "ML-powered tools coordination" and to dramatically lower the barrier of entries for creating use-case/domain specific tools. It is designed to be asynchronous only and requires Python 3.10 or higher.
curator
Bespoke Curator is an open-source tool for data curation and structured data extraction. It provides a Python library for generating synthetic data at scale, with features like programmability, performance optimization, caching, and integration with HuggingFace Datasets. The tool includes a Curator Viewer for dataset visualization and offers a rich set of functionalities for creating and refining data generation strategies.

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
sophia
Sophia is an open-source TypeScript platform designed for autonomous AI agents and LLM based workflows. It aims to automate processes, review code, assist with refactorings, and support various integrations. The platform offers features like advanced autonomous agents, reasoning/planning inspired by Google's Self-Discover paper, memory and function call history, adaptive iterative planning, and more. Sophia supports multiple LLMs/services, CLI and web interface, human-in-the-loop interactions, flexible deployment options, observability with OpenTelemetry tracing, and specific agents for code editing, software engineering, and code review. It provides a flexible platform for the TypeScript community to expand and support various use cases and integrations.
For similar tasks

WebDreamer
WebDreamer is a model-based planning tool for web agents that uses large language models (LLMs) as a world model of the internet to predict outcomes of actions on websites. It employs LLM-based simulation for speculative planning on the web, offering greater safety and flexibility compared to traditional tree search methods. The tool provides modules for world model prediction, simulation scoring, and controller actions, enabling users to interact with web pages and achieve specific goals through simulated actions.
AutoNode
AutoNode is a self-operating computer system designed to automate web interactions and data extraction processes. It leverages advanced technologies like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), YOLO (You Only Look Once) models for object detection, and a custom site-graph to navigate and interact with web pages programmatically. Users can define objectives, create site-graphs, and utilize AutoNode via API to automate tasks on websites. The tool also supports training custom YOLO models for object detection and OCR for text recognition on web pages. AutoNode can be used for tasks such as extracting product details, automating web interactions, and more.
playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.