Best AI tools for< Wrap Pytorch Models >
5 - AI tool Sites
Tesla Wrap
Tesla Wrap is a free AI wrap designer and community gallery that allows users to design custom car wraps for Tesla vehicles. The platform offers an AI Wrap Editor that simplifies the design process by providing official templates, real-time previews, and export options. Users can create unique wrap concepts by describing their ideas and generating designs with AI. Tesla Wrap aims to streamline the car wrap design process, from concept to final product, ensuring consistent and professional results for Tesla owners.
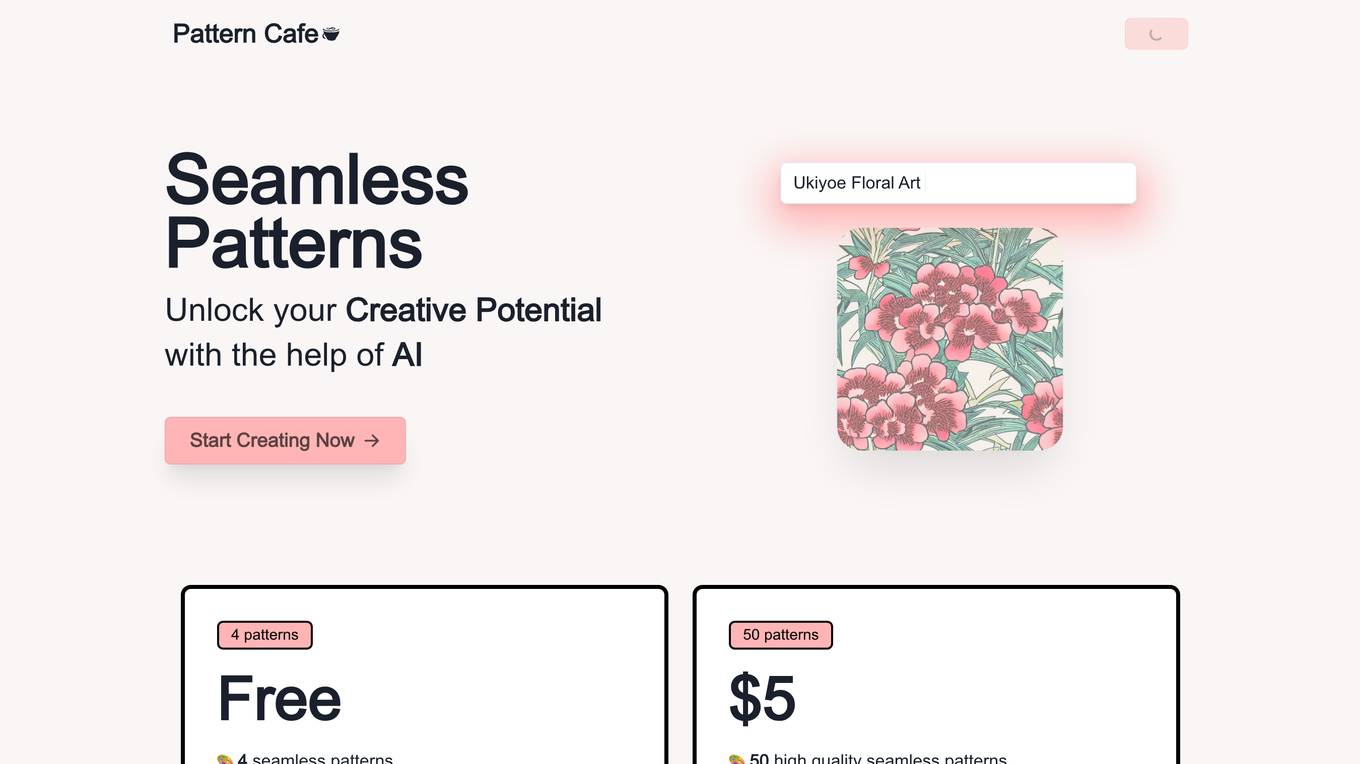
Pattern Cafe
Pattern Cafe is an AI-powered tool that helps users create unique and seamless patterns for various purposes such as fabric, gift wrap, wallpaper, and game textures. With Pattern Cafe, users can generate high-quality patterns in seconds, making it an efficient and convenient solution for designers and creatives.
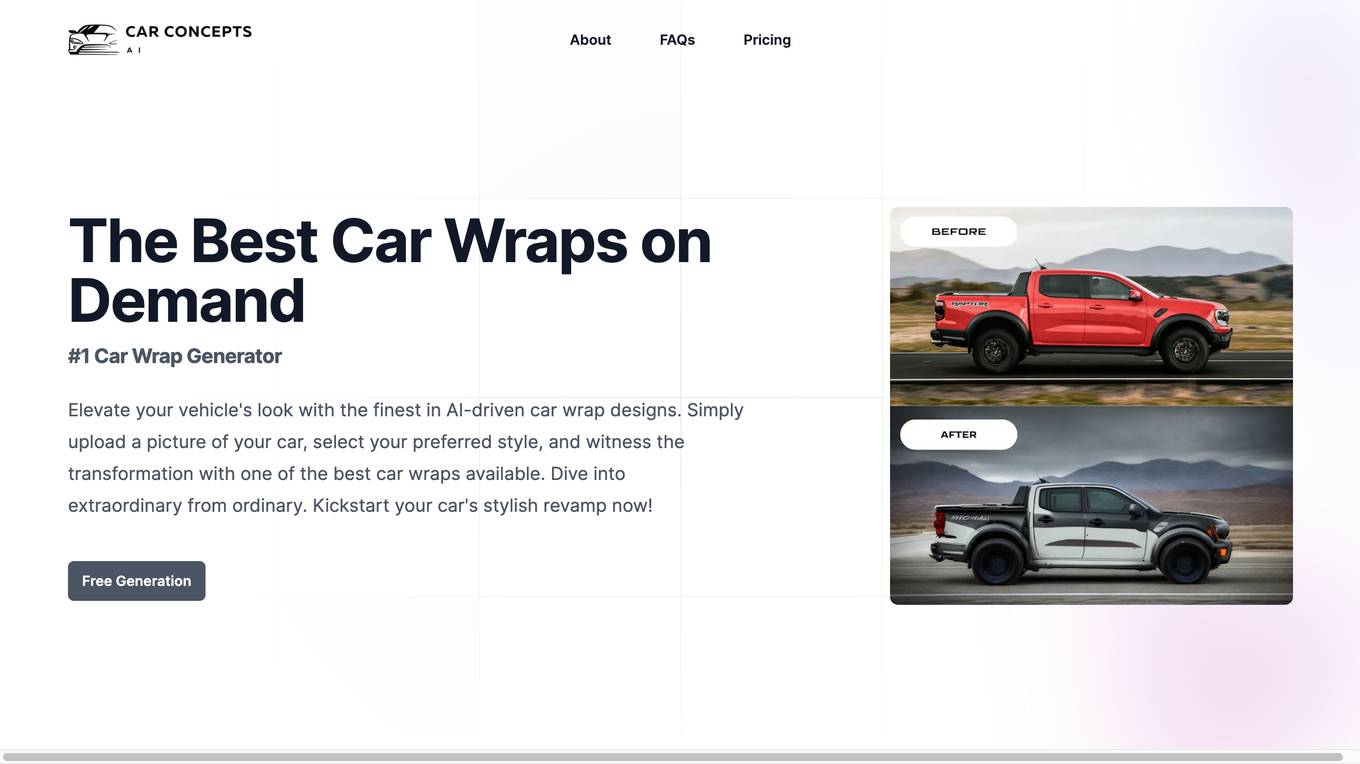
Car Concepts AI
Car Concepts AI is an innovative AI-powered tool that allows users to generate exclusive car wrap designs tailored to their vehicles. Users can upload their car images, choose a style, and let the advanced AI algorithms create stunning designs in minutes. The tool offers prompt features for customization and provides professional quality results with Basic and Advanced generation modes. Additionally, users can transform their designs into viral-ready car videos effortlessly. Car Concepts AI aims to revolutionize the automotive customization industry with cutting-edge AI technology.
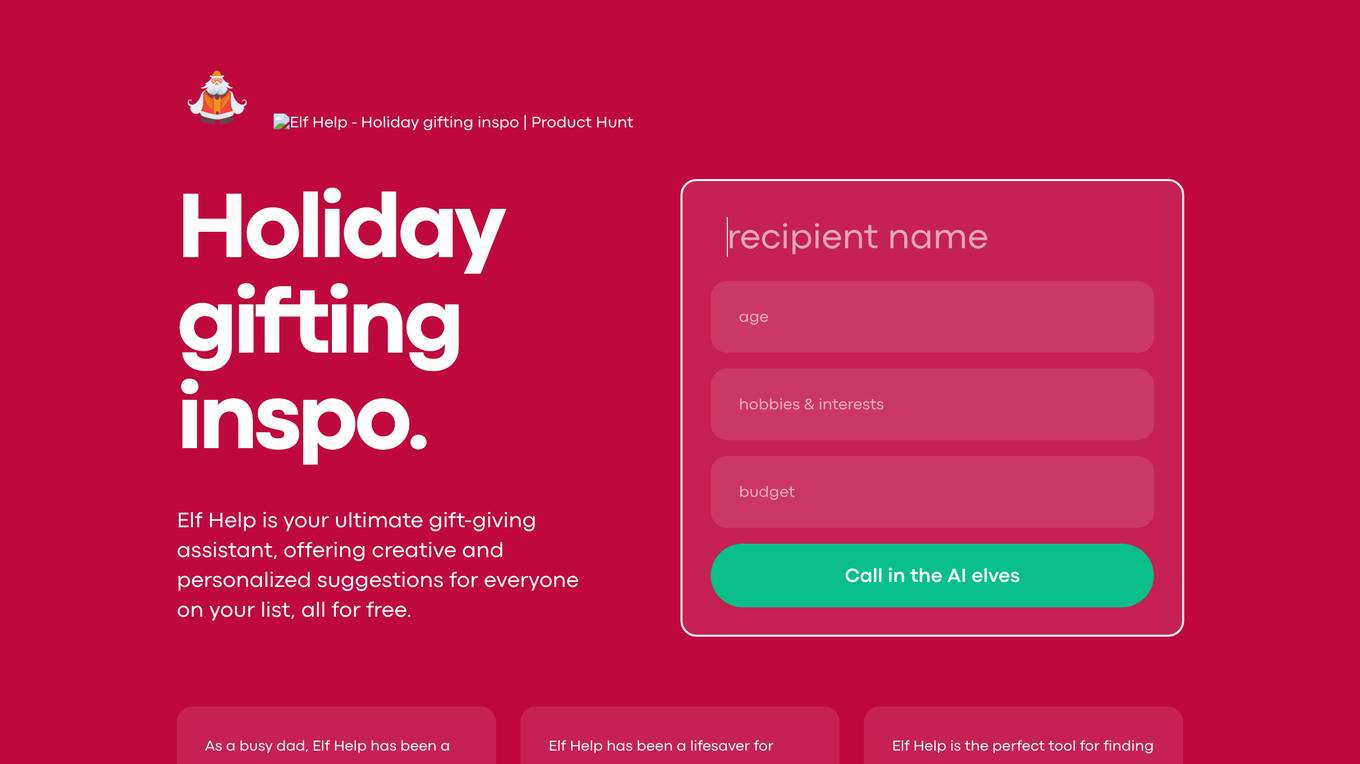
Elf Help
Elf Help is a free gift-giving assistant that offers personalized and creative suggestions for everyone on your list. It is designed to help users save time and stress during the holiday season by providing unique gift ideas. Elf Help is easy to use and convenient, making it a valuable tool for finding thoughtful gifts for even the hardest-to-shop-for people.
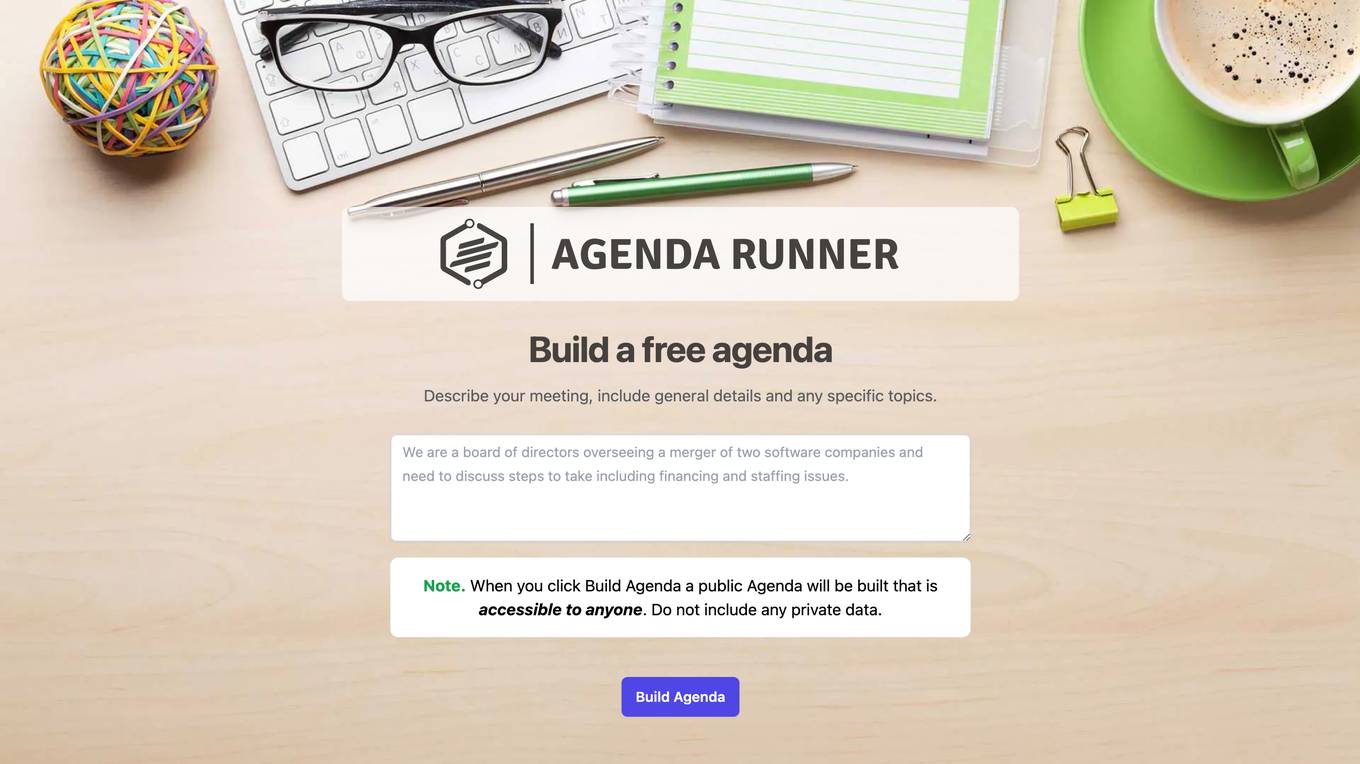
Agenda Runner
Agenda Runner is an AI-powered tool that allows users to quickly build meeting agendas for free. Users can describe their meeting, include general details, and specific topics, and with a click, a public agenda is generated. The tool focuses on enhancing meeting efficiency through improved agenda planning and execution, providing guidance on setting objectives, time management, interactive components, follow-up actions, and wrap-up procedures.
1 - Open Source AI Tools
neutone_sdk
The Neutone SDK is a tool designed for researchers to wrap their own audio models and run them in a DAW using the Neutone Plugin. It simplifies the process by allowing models to be built using PyTorch and minimal Python code, eliminating the need for extensive C++ knowledge. The SDK provides support for buffering inputs and outputs, sample rate conversion, and profiling tools for model performance testing. It also offers examples, notebooks, and a submission process for sharing models with the community.